无机材料学报 ›› 2022, Vol. 37 ›› Issue (3): 255-266.DOI: 10.15541/jim20210608 CSTR: 32189.14.10.15541/jim20210608
刘海方1,2( ), 苏海军1,2(
), 苏海军1,2( ), 申仲琳1, 姜浩1, 赵迪1, 刘园1, 张军1, 刘林1, 傅恒志1
), 申仲琳1, 姜浩1, 赵迪1, 刘园1, 张军1, 刘林1, 傅恒志1
收稿日期:2021-10-02
修回日期:2021-11-05
出版日期:2022-03-20
网络出版日期:2021-12-24
通讯作者:
苏海军, 教授. E-mail: shjnpu@nwpu.edu.cn
作者简介:刘海方(1987-), 男, 博士研究生. E-mail: liuhaifang@mail.nwpu.edu.cn
基金资助:
LIU Haifang1,2( ), SU Haijun1,2(
), SU Haijun1,2( ), SHEN Zhonglin1, JIANG Hao1, ZHAO Di1, LIU Yuan1, ZHANG Jun1, LIU Lin1, FU Hengzhi1
), SHEN Zhonglin1, JIANG Hao1, ZHAO Di1, LIU Yuan1, ZHANG Jun1, LIU Lin1, FU Hengzhi1
Received:2021-10-02
Revised:2021-11-05
Published:2022-03-20
Online:2021-12-24
Contact:
SU Haijun, professor. E-mail: shjnpu@nwpu.edu.cn
About author:LIU Haifang (1987-), male, PhD candidate. E-mail: liuhaifang@mail.nwpu.edu.cn
Supported by:摘要:
超高温氧化物共晶陶瓷具有优异的高温强度、高温蠕变性能、高温结构稳定性以及良好的高温抗氧化和抗腐蚀性能, 成为1400 ℃以上高温氧化环境下长期服役的新型候选超高温结构材料之一, 在新一代航空航天高端装备热结构部件中具有重要的应用前景。基于熔体生长技术, 以选择性激光熔化和激光定性能量沉积为代表的激光增材制造技术具有一步快速近净成形大尺寸、复杂形状构件的独特优势, 近年来已发展成为制备高性能氧化物共晶陶瓷最具潜力的前沿技术。本文从工作原理、成形特点、技术分类等方面概述了基于熔体生长的两种典型激光增材制造技术, 综述了激光增材制造技术在超高温氧化物共晶陶瓷制备领域的研究现状和特点优势, 重点介绍了选择性激光熔化和激光定向能量沉积超高温氧化物共晶陶瓷在激光成形工艺、凝固缺陷控制、凝固组织演化、力学性能等方面的研究进展。最后, 指出了实现氧化物共晶陶瓷激光增材制造工程化应用亟需突破的关键瓶颈, 并对该领域未来的重点发展方向进行了展望。
中图分类号:
刘海方, 苏海军, 申仲琳, 姜浩, 赵迪, 刘园, 张军, 刘林, 傅恒志. 激光增材制造超高温氧化物共晶陶瓷研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(3): 255-266.
LIU Haifang, SU Haijun, SHEN Zhonglin, JIANG Hao, ZHAO Di, LIU Yuan, ZHANG Jun, LIU Lin, FU Hengzhi. Research Progress on Ultrahigh Temperature Oxide Eutectic Ceramics by Laser Additive Manufacturing[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(3): 255-266.
| Technology | Scanning control | Molten pool size/mm | Energy density /(W·cm-2) | Building rate /(cm3·min-1) | Manufacturing precision | Preferred applications |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SLM | Scanner | <0.2 | 106-107 | ~1.3 | High | Net-shaping small- and medium-sized components |
| LDED | Laser nozzle | >3 | ~105 | 11.5 | Low | Preparing large-scale components |
表1 SLM与LDED技术特点对比[28]
Table 1 Comparison of the SLM and LDED technologies[28]
| Technology | Scanning control | Molten pool size/mm | Energy density /(W·cm-2) | Building rate /(cm3·min-1) | Manufacturing precision | Preferred applications |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SLM | Scanner | <0.2 | 106-107 | ~1.3 | High | Net-shaping small- and medium-sized components |
| LDED | Laser nozzle | >3 | ~105 | 11.5 | Low | Preparing large-scale components |
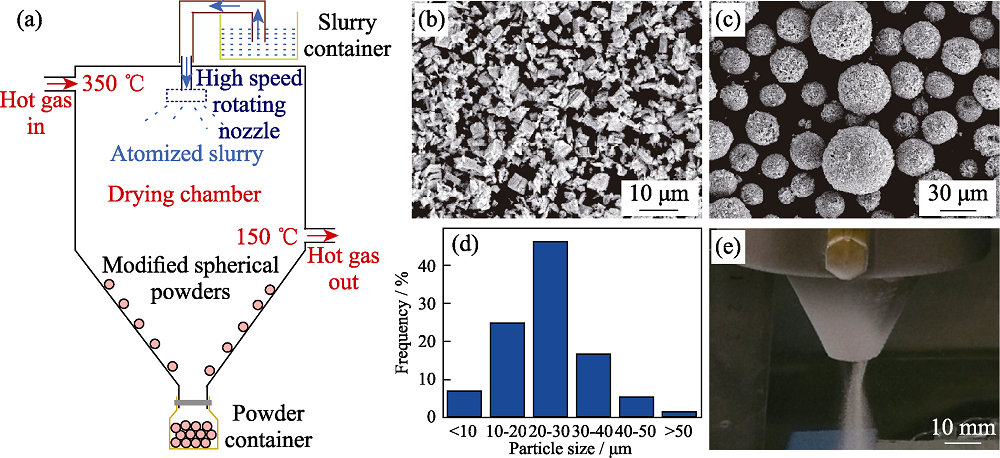
图3 球形陶瓷粉末制备工艺及其特性[68]
Fig. 3 Preparation technology and characteristics of spherical ceramic powders[68] (a) Schematic diagram of centrifugal spray drying method; (b) Morphology of the initial ceramic powders; (c) Morphology of the modified ceramic powders; (d) Particle size distribution of the modified ceramic powders; (e) Powder feeding test
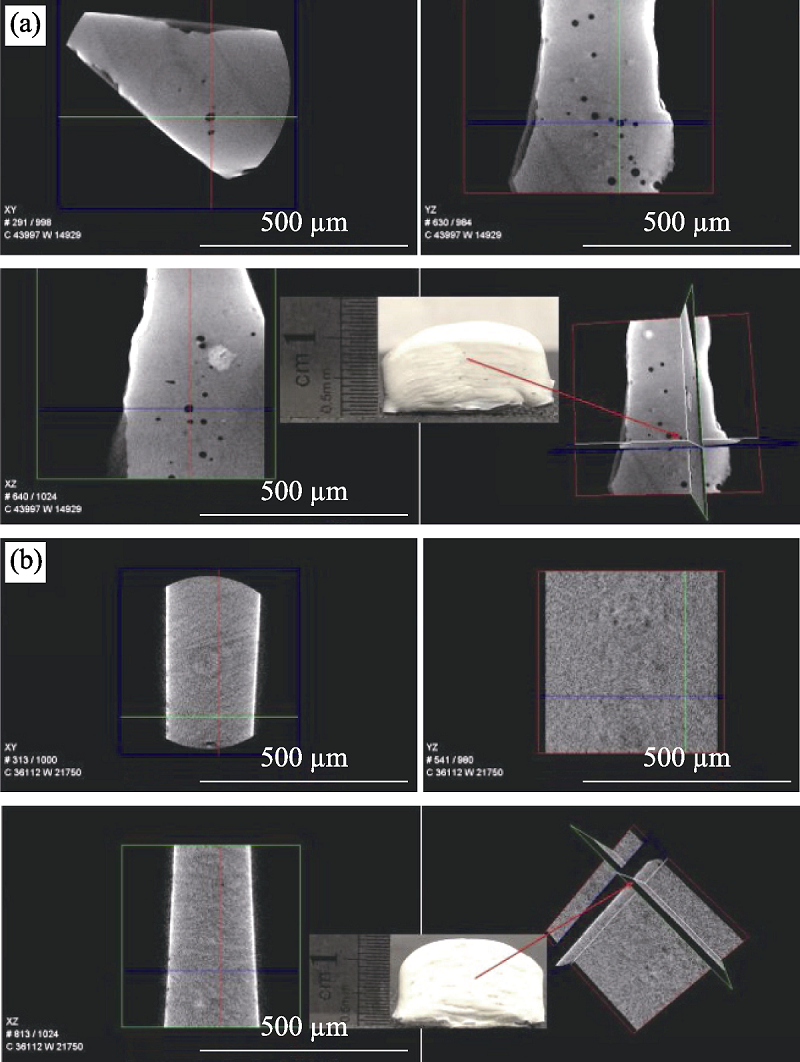
图5 超声振动对气孔的影响[43]
Fig. 5 Effect of assisted ultrasonic on porosity[43] (a) Sample sections before ultrasonic addition; (b) Sample sections after ultrasonic addition

图6 不同成形环境下制备的Al2O3/GAP/ZrO2共晶陶瓷试样
Fig. 6 Al2O3/GAP/ZrO2 eutectic ceramics prepared at different environments (a) Atmospheric atmosphere; (b) Ar atmosphere with oxygen content >200 μg/L; (c) Ar atmosphere with oxygen content <50 μg/L
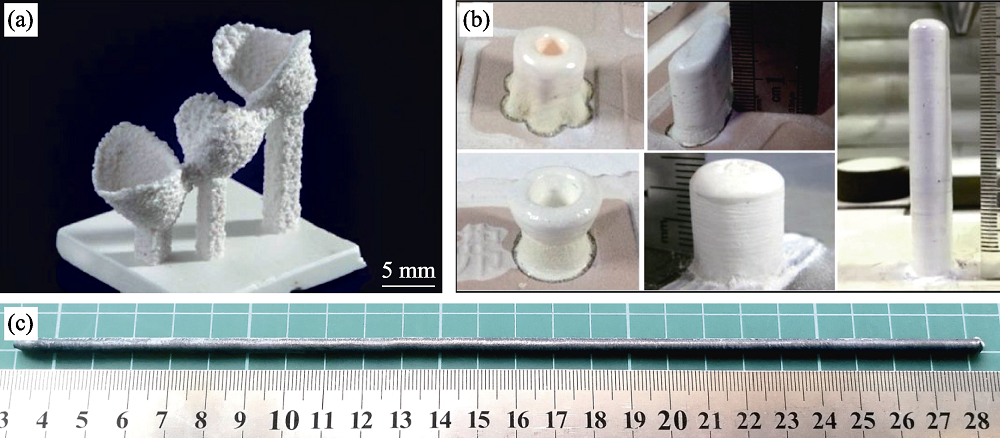
图7 采用激光增材制造技术制备的氧化物共晶陶瓷试样
Fig. 7 Oxide eutectic ceramics prepared by laser additive manufacturing (a) SLM-processed Al2O3/ZrO2 eutectic ceramic with shape of framework for a dental restoration[30]; (b) LDED-processed Al2O3/ZrO2 eutectic ceramics with various shapes[43]; (c) LDED-processed Al2O3/GAP/ZrO2 eutectic ceramic rod[70]
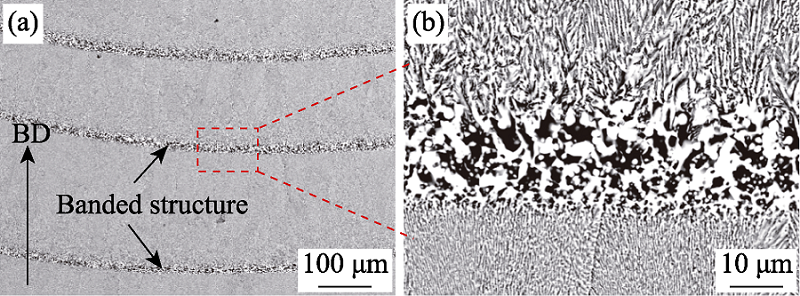
图8 激光增材制造氧化物共晶陶瓷沿堆积方向的微观组织特征[68]
Fig. 8 Microstructure characteristics of the LAM-processed oxide eutectic ceramic along the building direction[68] (a) Periodic banded structure; (b) Magnified image of the banded structure
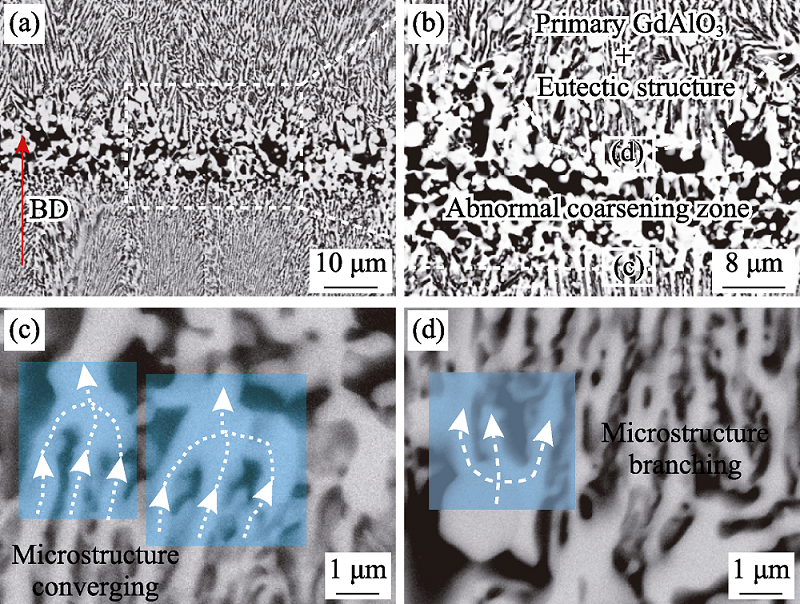
图9 LDED制备的Al2O3/GAP/ZrO2共晶陶瓷带状区附近的凝固组织特征[68]
Fig. 9 Microstructure characteristics in vicinity of the banded structure of the LDED-processed Al2O3/GAP/ZrO2 eutectic ceramic[68] (a) Banded structure; (b) Microstructure characteristic of the banded structure; (c) Microstructure at the lower boundary of the banded structure; (d) Microstructure at the upper boundary of the banded structure
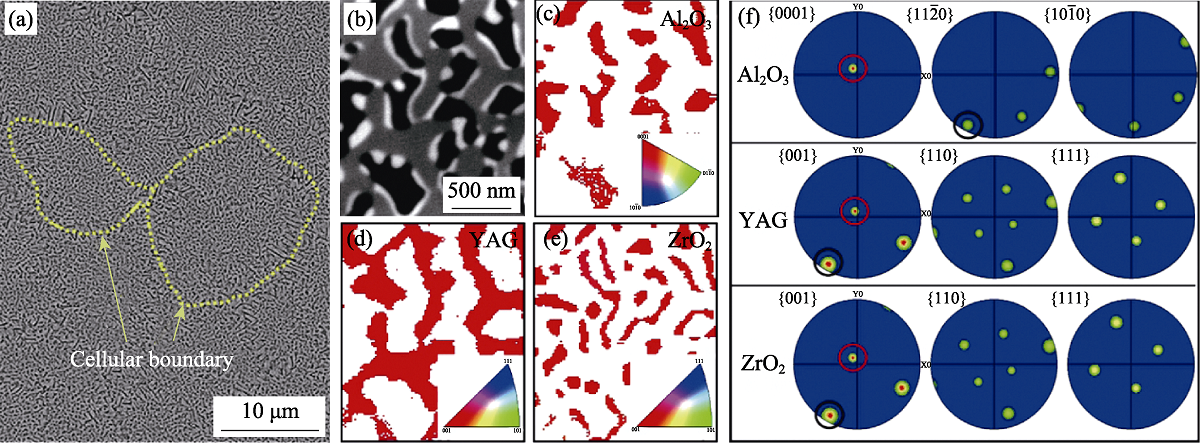
图10 LDED制备的Al2O3/YAG/ZrO2共晶陶瓷沉积层内的凝固组织特征[47]
Fig. 10 Microstructure characteristics of the LDED-processed Al2O3/YAG/ZrO2 eutectic ceramic in a deposited layer[47] (a) Eutectic colony structure; (b) Microstructure inside the colony; (c-e) TKD (Transmission kikuchi diffraction) orientation maps of the phases of Al2O3, YAG and ZrO2, respectively; (f) Pole figures of Al2O3, YAG and ZrO2, corresponding to (c-e), respectively
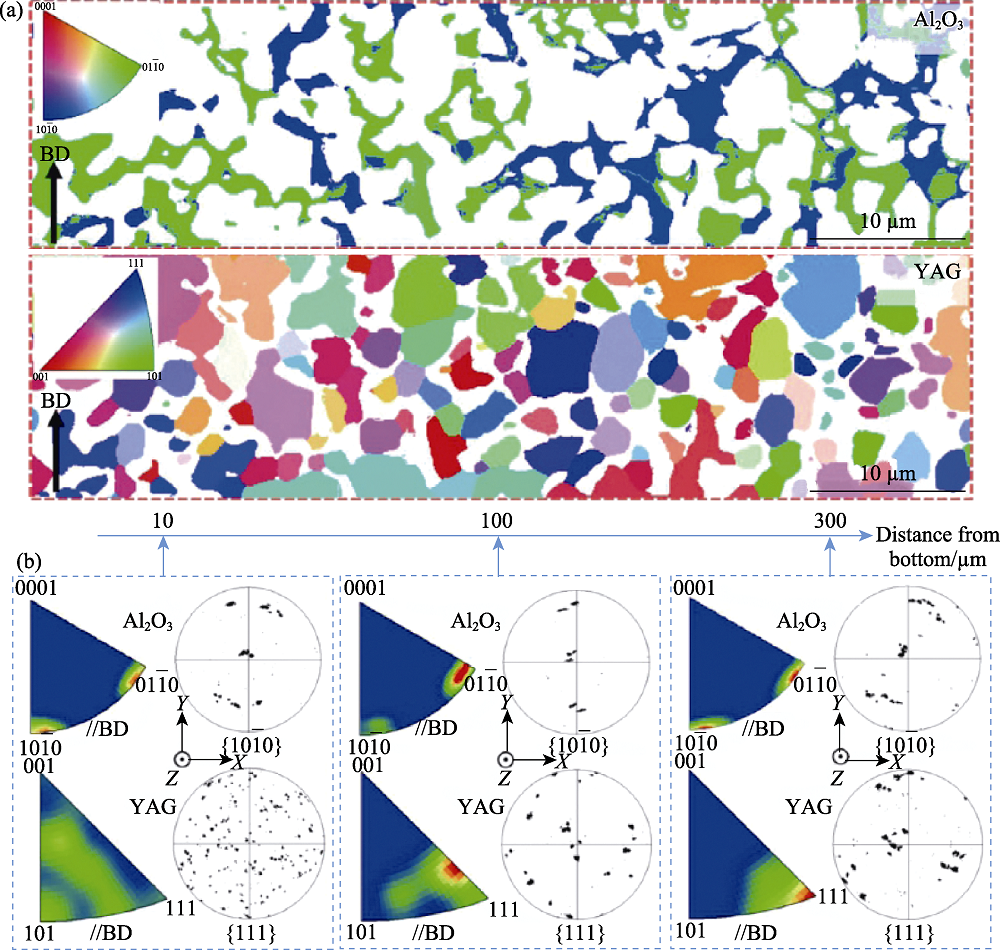
图11 LDED制备的Al2O3/YAG共晶陶瓷各相在熔池凝固过程中的生长方向演变[46]
Fig. 11 Orientation variations of eutectic phases of the LDED-processed Al2O3/YAG eutectic ceramic during solidification process[46] (a) EBSD orientation maps of Al2O3 and YAG in bottom zone of the molten pool; (b) Orientation variations of Al2O3 and YAG along the height direction of the molten pool
| Eutectic system | Hardness /GPa | Fracture toughness /(MPa·m1/2) | Preparation method |
|---|---|---|---|
| Al2O3/YAG | 21.50 | 5.86 | LDED[ |
| Al2O3/ZrO2 | 16.22 | 7.67 | LDED[ |
| Al2O3/YAG/ZrO2 | 18.90 | 3.84 | LDED[ |
| Al2O3/GAP/ZrO2 | 15.30 | 7.80 | SLM[ |
| Al2O3/YAG | 17.50 | 3.60 | DS[ |
| Al2O3/ZrO2 | 16.53 | 6.50 | DS[ |
| Al2O3/YAG/ZrO2 | 16.70 | 8.00 | DS[ |
| Al2O3/GAP/ZrO2 | 17.90 | 8.50 | DS[ |
表2 激光增材制造与定向凝固共晶陶瓷性能对比
Table 2 Mechanical property comparison of the oxide eutectic ceramics prepared by laser additive manufacturing and directional solidification (DS)
| Eutectic system | Hardness /GPa | Fracture toughness /(MPa·m1/2) | Preparation method |
|---|---|---|---|
| Al2O3/YAG | 21.50 | 5.86 | LDED[ |
| Al2O3/ZrO2 | 16.22 | 7.67 | LDED[ |
| Al2O3/YAG/ZrO2 | 18.90 | 3.84 | LDED[ |
| Al2O3/GAP/ZrO2 | 15.30 | 7.80 | SLM[ |
| Al2O3/YAG | 17.50 | 3.60 | DS[ |
| Al2O3/ZrO2 | 16.53 | 6.50 | DS[ |
| Al2O3/YAG/ZrO2 | 16.70 | 8.00 | DS[ |
| Al2O3/GAP/ZrO2 | 17.90 | 8.50 | DS[ |
| [1] |
JAMES C W, EDGAR A S. Progress in structural materials for aerospace systems. Acta Materialia, 2003, 51(19): 5775-5799.
DOI URL |
| [2] |
WAKU Y, SAKUMA T. Dislocation mechanism of deformation and strength of Al2O3-YAG single crystal composites at high temperatures above 1500 ℃. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2000, 20(10): 1453-1458.
DOI URL |
| [3] |
PASTOR J Y, MARTIN A, MOLINA-ALDAREGUIA J M, et al. Superplastic deformation of directionally solidified nanofibrillar Al2O3-Y3Al5O12-ZrO2 eutectics. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2013, 33(13/14): 2579-2586.
DOI URL |
| [4] |
OCHIAI S, UEDA T, SATO K, et al. Deformation and fracture behavior of an Al2O3/YAG composite from room temperature to 2023 K. Composites Science and Technology, 2001, 61(14): 2117-2128.
DOI URL |
| [5] |
WAKU Y, NAKAGAWA N, WAKAMOTO T, et al. A ductile ceramic eutectic composite with high strength at 1873 K. Nature, 1997, 389(6646): 49-52.
DOI URL |
| [6] |
LLORCA J, ORERA V M. Directionally solidified eutectic ceramic oxides. Progress in Materials Science, 2006, 51(6): 711-809.
DOI URL |
| [7] |
WANG X, ZHANG W, ZHONG Y J, et al. Introduction of low strain energy GdAlO3 grain boundaries into directionally solidified Al2O3/GdAlO3 eutectics. Acta Materialia, 2021, 221: 117355.
DOI URL |
| [8] | MA W D, ZHANG J, SU H J, et al. Phase growth patterns for Al2O3/GdAlO3 eutectics over wide ranges of compositions and solidification rates. Journal of Materials Science & Technology, 2021, 65: 89-98. |
| [9] | SU H J, LIU Y, REN Q, et al. Distribution control and formation mechanism of gas inclusions in directionally solidified Al2O3-Er3Al5O12-ZrO2 ternary eutectic ceramic by laser floating zone melting. Journal of Materials Science & Technology, 2021, 66: 21-27. |
| [10] |
SUN L C, ZHOU C, DU T F, et al. Directionally solidified Al2O3/Er3Al5O12 and Al2O3/Yb3Al5O12 eutectic ceramics prepared by optical floating zone melting. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(6): 652-658.
DOI URL |
| [11] |
NAKAGAWA N, OHSSUBO H, MITANI A, et al. High temperature strength and thermal stability for melt growth composite. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2005, 25(8): 1251-1257.
DOI URL |
| [12] |
NAKAGAWA N, OHSSUBO H, WAKU Y, et al. Thermal emission properties of Al2O3/Er3Al5O12 eutectic ceramics. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2005, 25(8): 1285-1291.
DOI URL |
| [13] |
OTSUKA A, WAKU Y, TANAKA R. Corrosion of a unidirectionally solidified Al2O3/YAG eutectic composite in a combustion environment. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2005, 25(8): 1269-1274.
DOI URL |
| [14] | ZHANG F Y, GAO P P, TAN H, et al. Tailoring grain morphology in Ti-6Al-3Mo through heterogeneous nucleation in directed energy deposition. Journal of Materials Science & Technology, 2021, 88: 132-142. |
| [15] | CHAKRABORTY A, TANGESTANI R, BATMAZ R, et al. In-process failure analysis of thin-wall structures made by laser powder bed fusion additive manufacturing. Journal of Materials Science & Technology, 2022, 98: 233-243. |
| [16] | KIM Y K, KIM M C, LEE K A. 1.45 GPa ultrastrong cryogenic strength with superior impact toughness in the in-situ nano oxide reinforced CrMnFeCoNi high-entropy alloy matrix nanocomposite manufactured by laser powder bed fusion. Journal of Materials Science & Technology, 2022, 97: 10-19. |
| [17] | XING L L, ZHAO C C, CHEN H, et al. Microstructure of a Ti-50wt% Ta alloy produced via laser powder bed fusion. Acta Metallurgica Sinica, 2020, 33(7): 981-990. |
| [18] | EBRAHIMNIA M, XIE Y J, CHI C T. Effect of laser power and deposition environment on the microstructure and properties of direct laser metal-deposited 12CrNi2 steel. Acta Metallurgica Sinica, 2020, 33(4): 528-538. |
| [19] | YU C F, ZHONG Y, ZHANG P, et al. Effect of build direction on fatigue performance of L-PBF 316L stainless steel. Acta Metallurgica Sinica, 2020, 33(4): 539-550. |
| [20] | WANG X, LÜ F, SHEN L D, et al. Influence of island scanning strategy on microstructures and mechanical properties of direct laser-deposited Ti-6Al-4V structures. Acta Metallurgica Sinica, 2019, 32(9): 1173-1180. |
| [21] | SHEN Z L, SU H J, LIU H F, et al. Research progress on laser additive manufacturing technology and its defect control for ultra-high temperature oxide ceramics. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica, 2021, 38(3): 668-679. |
| [22] | GU D D, ZHANG H M, CHEN H Y, et al. Laser additive manufacturing of high-performance metallic aerospace components. Chinese Journal of Lasers, 2020, 47(5): 32-55. |
| [23] | SU H J, WEI K C, GUO W, et al. New development of laser rapid forming and its application in high performance materials processing. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2013, 23(6): 1567-1574. |
| [24] |
LAKHDAR Y, TUCK C, BINNER J, et al. Additive manufacturing of advanced ceramic materials. Progress in Materials Science, 2021, 116: 100736.
DOI URL |
| [25] |
CHEN Z W, LI Z Y, LI J J, et al. 3D printing of ceramics: a review. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2019, 39(4): 661-687.
DOI URL |
| [26] |
TAMEZ M B A, TAHA I. A review of additive manufacturing technologies and markets for thermosetting resins and their potential for carbon fiber integration. Additive Manufacturing, 2021, 37: 101748.
DOI URL |
| [27] |
SUN C, WANG Y, MCMURTREY M D, et al. Additive manufacturing for energy: a review. Applied Energy, 2021, 282: 116041.
DOI URL |
| [28] | GU D D, SHI X Y, POPRAWE R, et al. Material-structure- performance integrated laser-metal additive manufacturing. Science, 2021, 372(6545): 932-947. |
| [29] |
SU H J, ZHANG J, LIU L, et al. Rapid growth and formation mechanism of ultrafine structural oxide eutectic ceramics by laser direct forming. Applied Physics Letters, 2011, 99(22): 221913.
DOI URL |
| [30] |
WILKES J, HAGEDORN Y, MEINERS W, et al. Additive manufacturing of ZrO2-Al2O3 ceramic components by selective laser melting. Rapid Prototyping Journal, 2013, 19(1): 51-57.
DOI URL |
| [31] |
NIU F Y, WU D J, MA G Y, et al. Nanosized microstructure of Al2O3-ZrO2(Y2O3) eutectics fabricated by laser engineered net shaping. Scripta Materialia, 2015, 95: 39-41.
DOI URL |
| [32] | NIU F Y, WU D J, MA G Y, et al. Rapid fabrication of eutectic ceramic structures by laser engineered net shaping. ISEM XVIII, 2016, 42: 91-95. |
| [33] |
YAN S, WU D J, MA G Y, et al. Formation mechanism and process optimization of nano Al2O3-ZrO2 eutectic ceramic via laser engineered net shaping (LENS). Ceramics International, 2017, 43(17): 14742-14747.
DOI URL |
| [34] |
MA G Y, YAN S, NIU F Y, et al. Microstructure and mechanical properties of solid Al2O3-ZrO2 (Y2O3) eutectics prepared by laser engineered net shaping. Journal of Laser Applications, 2017, 29(2): 022305.
DOI URL |
| [35] |
YAN S, WU D J, NIU F Y, et al. Al2O3-ZrO2 eutectic ceramic via ultrasonic-assisted laser engineered net shaping. Ceramics International, 2017, 43(17): 15905-15910.
DOI URL |
| [36] |
YAN S, WU D J, MA G Y, et al. Nano-sized Al2O3-ZrO2 eutectic ceramic structures prepared by ultrasonic-assisted laser engineered net shaping. Materials Letters, 2018, 212: 8-11.
DOI URL |
| [37] |
YAN S, WU D J, NIU F Y, et al. Effect of ultrasonic power on forming quality of nano-sized Al2O3-ZrO2 eutectic ceramic via laser engineered net shaping (LENS). Ceramics International, 2018, 44(1): 1120-1126.
DOI URL |
| [38] |
WU D J, LU F, ZHAO D K, et al. Effect of doping SiC particles on cracks and pores of Al2O3-ZrO2 eutectic ceramics fabricated by directed laser deposition. Journal of Materials Science, 2019, 54(13): 9321-9330.
DOI URL |
| [39] |
WU D J, SAN J D, NIU F Y, et al. Directed laser deposition of Al2O3-ZrO2 melt-grown composite ceramics with multiple composition ratios. Journal of Materials Science, 2020, 55(16): 6794-6809.
DOI URL |
| [40] |
WU D J, SAN J D, NIU F Y, et al. Effect and mechanism of ZrO2 doping on the cracking behavior of melt-grown Al2O3 ceramics prepared by directed laser deposition. International Journal of Applied Ceramic Technology, 2020, 17(1): 227-238.
DOI URL |
| [41] |
WU D J, LIU H C, LU F, et al. Al2O3-YAG eutectic ceramic prepared by laser additive manufacturing with water-cooled substrate. Ceramics International, 2019, 45(3): 4119-4122.
DOI URL |
| [42] |
YAN S, WU D J, HUANG Y F, et al. C fiber toughening Al2O3-ZrO2 eutectic via ultrasonic-assisted directed laser deposition. Materials Letters, 2019, 235: 228-231.
DOI URL |
| [43] |
YAN S, HUANG Y F, ZHAO D K, et al. 3D printing of nano- scale Al2O3-ZrO2 eutectic ceramic: principle analysis and process optimization of pores. Additive Manufacturing, 2019, 28: 120-126.
DOI URL |
| [44] |
LI F Z, ZHANG X W, SUI C Y, et al. Microstructure and mechanical properties of Al2O3-ZrO2 ceramic deposited by laser direct material deposition. Ceramics International, 2018, 44(15): 18960-18968.
DOI URL |
| [45] |
LI F Z, LIU Z W, LI B, et al. Pore formation model for direct laser deposition of Al2O3-ZrO2 ceramic. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2022, 42(1): 207-215.
DOI URL |
| [46] |
FAN Z Q, ZHAO Y T, TAN Q Y, et al. New insights into the growth mechanism of 3D-printed Al2O3-Y3Al5O12 binary eutectic composites. Scripta Materialia, 2020, 178: 274-280.
DOI URL |
| [47] |
FAN Z Q, ZHAO Y T, TAN Q Y, et al. Nanostructured Al2O3-YAG-ZrO2 ternary eutectic components prepared by laser engineered net shaping. Acta Materialia, 2019, 170: 24-37.
DOI URL |
| [48] |
BARTLETT J L, LI X. An overview of residual stresses in metal powder bed fusion. Additive Manufacturing, 2019, 27: 131-149.
DOI URL |
| [49] |
FANG Z C, WU Z L, HUANG C G, et al. Review on residual stress in selective laser melting additive manufacturing of alloy parts. Optics and Laser Technology, 2020, 129: 106283.
DOI URL |
| [50] | ACEVEDO R, SEDLAK P, KOLMAN R, et al. Residual stress analysis of additive manufacturing of metallic parts using ultrasonic waves: state of the art review. Journal of Materials Research and Technology, 2020, 9(4): 9457-9477. |
| [51] |
CHEN W, XU L Y, HAN Y D, et al. Control of residual stress in metal additive manufacturing by low-temperature solid-state phase transformation: an experimental and numerical study. Additive Manufacturing, 2021, 42: 102016.
DOI URL |
| [52] | SONG X, FEIH S, ZHAI W, et al. Advances in additive manufacturing process simulation: residual stresses and distortion predictions in complex metallic components. Materials & Design, 2020, 193: 108779. |
| [53] |
HA K, KIM T, BAEK G Y, et al. Numerical study of the effect of progressive solidification on residual stress in single-bead-on-plate additive manufacturing. Additive Manufacturing, 2020, 34: 101245.
DOI URL |
| [54] |
ROEHLING J D, SMITH W L, ROEHLING T T, et al. Reducing residual stress by selective large-area diode surface heating during laser powder bed fusion additive manufacturing. Additive Manufacturing, 2019, 28: 228-235.
DOI URL |
| [55] |
HUANG H, MA N S, CHEN J, et al. Toward large-scale simulation of residual stress and distortion in wire and arc additive manufacturing. Additive Manufacturing, 2020, 34: 101248.
DOI URL |
| [56] |
ŞIRIN T B, KAYNAK Y. Prediction of residual stress and distortion in laser powder bed fusion additive manufacturing process of Inconel 718 alloy. Procedia CIRP, 2021, 99: 330-335.
DOI URL |
| [57] |
SUN J M, HENSEL J, KOHLER M, et al. Residual stress in wire and arc additively manufactured aluminum components. Journal of Manufacturing Processes, 2021, 65: 97-111.
DOI URL |
| [58] |
LI R S, WANG G L, ZHAO X S, et al. Effect of path strategy on residual stress and distortion in laser and cold metal transfer hybrid additive manufacturing. Additive Manufacturing, 2021, 46: 102203.
DOI URL |
| [59] | STRANTZA M, GANERIWALA R K, CLAUSEN B, et al. Effect of the scanning strategy on the formation of residual stresses in additively manufactured Ti-6Al-4V. Additive Manufacturing, 2021, 45: 102003.s |
| [60] |
NADAMMAL N, MISHUROVA T, FRITSCH T, et al. Critical role of scan strategies on the development of microstructure, texture, and residual stresses during laser powder bed fusion additive manufacturing. Additive Manufacturing, 2021, 38: 101792.
DOI URL |
| [61] | PROMOPPATUM P, UTHAISANGSUK V. Part scale estimation of residual stress development in laser powder bed fusion additive manufacturing of Inconel 718. Finite Elements in Analysis & Design, 2021, 189: 103528. |
| [62] |
LIU Q, DANLOS Y, SONG B, et al. Effect of high-temperature preheating on the selective laser melting of yttria-stabilized zirconia ceramic. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 2015, 222: 61-74.
DOI URL |
| [63] | NIU F Y, WU D J, YAN S, et al. Process optimization for suppressing cracks in laser engineered net shaping of Al2O3 ceramics. The Journal of The Minerals, Metals & Materials Society, 2017, 69(3): 557-562. |
| [64] |
ZHANG K, LIU T T, LIAO W H, et al. Influence of laser parameters on the surface morphology of slurry-based Al2O3 parts produced through selective laser melting. Rapid Prototyping Journal, 2018, 24(2): 333-341.
DOI URL |
| [65] |
HU Y B, NING F D, CONG W L, et al. Ultrasonic vibration- assisted laser engineering net shaping of ZrO2-Al2O3 bulk parts: effects on crack suppression, microstructure, and mechanical properties. Ceramics International, 2018, 44(3): 2752-2760.
DOI URL |
| [66] |
ZHENG Y, ZHANG K, LIU T T, et al. Cracks of alumina ceramics by selective laser melting. Ceramics International, 2019, 45(1): 175-184.
DOI URL |
| [67] |
LIU H F, SU H J, SHEN Z L, et al. Effect of scanning speed on the solidification process of Al2O3/GdAlO3/ZrO2 eutectic ceramics in a single track by selective laser melting. Ceramics International, 2019, 45(14): 17252-17257.
DOI URL |
| [68] |
LIU H F, SU H J, SHEN Z L, et al. One-step additive manufacturing and microstructure evolution of melt-grown Al2O3/GdAlO3/ZrO2 eutectic ceramics by laser directed energy deposition. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2021, 41(6): 3547-3558.
DOI URL |
| [69] |
LIU H F, SU H J, SHEN Z L, et al. Direct formation of Al2O3/GdAlO3/ZrO2 ternary eutectic ceramics by selective laser melting: microstructure evolutions. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2018, 38(15): 5144-5152.
DOI URL |
| [70] | LIU H F, SU H J, SHEN Z L, et al. Preparation of large-size Al2O3/GdAlO3/ZrO2 ternary eutectic ceramic rod by laser directed energy deposition and its microstructure homogenization mechanism. Journal of Materials Science & Technology, 2021, 85: 218-223. |
| [71] | TRIANTAFYLLIDIS D, LI L, STOTT F H. Mechanisms of porosity formation along the solid/liquid interface during laser melting of ceramics. Applied Surface Science, 2003, 208: 458-462. |
| [72] |
OLIETE P B, PENA J I. Study of the gas inclusions in Al2O3/Y3Al5O12 and Al2O3/Y3Al5O12/ZrO2 eutectic fibers grown by laser floating zone. Journal of Crystal Growth, 2007, 304(2): 514-519.
DOI URL |
| [73] |
REN Q, SU H J, ZHANG J, et al. Eutectic growth behavior with regular arrangement in the faceted Al2O3/Er3Al5O12 irregular eutectic system at low growth rate. Scripta Materialia, 2019, 162: 49-53.
DOI URL |
| [74] |
MA W D, ZHANG J, SU H J, et al. Theoretical prediction and experimental comparison for eutectic growth of Al2O3/GdAlO3 faceted eutectics. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2019, 39(13): 3837-3842.
DOI URL |
| [75] |
REN Q, SU H J, ZHANG J, et al. Microstructure control, competitive growth and precipitation rule in faceted Al2O3/Er3Al5O12 eutectic in situ composite ceramics prepared by laser floating zone melting. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2019, 39(5): 1900-1908.
DOI URL |
| [76] |
SU H J, REN Q, ZHANG J, et al. Microstructures and mechanical properties of directionally solidified Al2O3/GdAlO3 eutectic ceramic by laser floating zone melting with high temperature gradient. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2017, 37(4): 1617-1626.
DOI URL |
| [77] |
SU H J, ZHANG J, CUI C J, et al. Rapid solidification behaviour of Al2O3/Y3Al5O12(YAG) binary eutectic ceramic in situ composites. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2008, 479(1/2): 380-388.
DOI URL |
| [78] |
FAN G R, SU H J, ZHANG J, et al. Microstructure and cytotoxicity of Al2O3-ZrO2 eutectic bioceramics with high mechanical properties prepared by laser floating zone melting. Ceramics International, 2018, 44(15): 17978-17985.
DOI URL |
| [79] |
SU H J, ZHANG J, CUI C J, et al. Rapid solidification of Al2O3/Y3Al5O12/ZrO2 eutectic in situ composites by laser zone remelting. Journal of Crystal Growth, 2007, 307(2): 448-456.
DOI URL |
| [80] |
MAZEROLLES L, PIQUET N, TRICHET M, et al. New microstructures in ceramic materials from the melt for high temperature applications. Aerospace Science and Technology, 2008, 12(7): 499-505.
DOI URL |
| [1] | 朱文杰, 唐璐, 陆继长, 刘江平, 罗永明. 钙钛矿型氧化物催化氧化挥发性有机化合物的研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(7): 735-746. |
| [2] | 胡智超, 杨鸿宇, 杨鸿程, 孙成礼, 杨俊, 李恩竹. P-V-L键理论在微波介质陶瓷性能调控中的应用[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(6): 609-626. |
| [3] | 吴琼, 沈炳林, 张茂华, 姚方周, 邢志鹏, 王轲. 铅基织构压电陶瓷研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(6): 563-574. |
| [4] | 张碧辉, 刘小强, 陈湘明. Ruddlesden-Popper结构杂化非常规铁电体的研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(6): 587-608. |
| [5] | 吴杰, 杨帅, 王明文, 李景雷, 李纯纯, 李飞. 铅基织构压电陶瓷的发展历程、现状与挑战[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(6): 575-586. |
| [6] | 姜昆, 李乐天, 郑木鹏, 胡永明, 潘勤学, 吴超峰, 王轲. PZT陶瓷的低温烧结研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(6): 627-638. |
| [7] | 田睿智, 兰正义, 殷杰, 郝南京, 陈航榕, 马明. 基于微流控技术的纳米无机生物材料制备: 原理及其研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(4): 337-347. |
| [8] | 张继国, 吴田, 赵旭, 杨钒, 夏天, 孙士恩. 钠离子电池正极材料循环稳定性提升策略及产业化进程[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(4): 348-362. |
| [9] | 殷杰, 耿佳毅, 王康龙, 陈忠明, 刘学建, 黄政仁. SiC陶瓷的3D打印成形与致密化新进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(3): 245-255. |
| [10] | 谌广昌, 段小明, 朱金荣, 龚情, 蔡德龙, 李宇航, 杨东雷, 陈彪, 李新民, 邓旭东, 余瑾, 刘博雅, 何培刚, 贾德昌, 周玉. 直升机特定结构先进陶瓷材料研究进展与应用展望[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(3): 225-244. |
| [11] | 范晓波, 祖梅, 杨向飞, 宋策, 陈晨, 王子, 罗文华, 程海峰. 质子调控型电化学离子突触研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(3): 256-270. |
| [12] | 海热古·吐逊, 郭乐, 丁嘉仪, 周嘉琪, 张学良, 努尔尼沙·阿力甫. 上转换荧光探针辅助的光学成像技术在肿瘤显影中的应用研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(2): 145-158. |
| [13] | 孙树娟, 郑南南, 潘昊坤, 马猛, 陈俊, 黄秀兵. 单原子催化剂制备方法的研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(2): 113-127. |
| [14] | 陶桂龙, 支国伟, 罗添友, 欧阳佩东, 衣新燕, 李国强. 空腔型薄膜体声波滤波器的关键技术进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(2): 128-144. |
| [15] | 周帆, 田志林, 李斌. 热防护系统用碳化物超高温陶瓷抗烧蚀涂层研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(1): 1-16. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||