无机材料学报 ›› 2019, Vol. 34 ›› Issue (11): 1133-1144.DOI: 10.15541/jim20180591 CSTR: 32189.14.10.15541/jim20180591
• 综述 • 下一篇
收稿日期:2018-12-17
修回日期:2019-03-25
出版日期:2019-11-20
网络出版日期:2019-05-29
作者简介:佟 威(1990-), 男, 博士研究生. E-mail: tomson90@126.com
基金资助:Received:2018-12-17
Revised:2019-03-25
Published:2019-11-20
Online:2019-05-29
Supported by:摘要:
受自然界荷叶 “出淤泥而不染”的启发, 超疏水现象引起了研究者广泛的关注, 并成功制备了人工超疏水表面。本文对典型的仿生超疏水材料进行梳理, 并针对近期研究成果进行了综述, 对超疏水涂层的诸多制备方法作了优缺点总结和评述, 概述了超疏水涂层在自清洁、防覆冰、耐腐蚀和油水分离领域的应用研究现状, 尤其对超疏水防覆冰的机理及实现方式作了总结分析, 剖析了现阶段超疏水研究过程中面临的挑战, 展望了未来的发展趋势, 希望为超疏水涂层在工程领域的应用研究提供参考。
中图分类号:
佟威, 熊党生. 仿生超疏水表面的发展及其应用研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2019, 34(11): 1133-1144.
TONG Wei, XIONG Dang-Sheng. Bioinspired Superhydrophobic Materials: Progress and Functional Application[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2019, 34(11): 1133-1144.
| Year | Bioinspired materials | Multiple functionalities for applications | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1997 | Lotus leaf | Superhydrophobicity, self-cleaning | [8-9] |
| 2000 | Gecko foot-hair Spider silk | Superhydrophobicity, high adhesion Water collection | [10] [23] |
| 2001 | Desert beetle | Superhydrophobicity/superhydrophilicity | [11] |
| 2002 | Rice leaf Cactus stems | Superhydrophobicity, anisotropic wetting Fog collection, gradient wetting | [2] [24] |
| 2004 | Water strider leg Cicada wing | Superhydrophobicity, fluid friction reduction Superhydrophobicity, antireflection | [12] [13] |
| 2006 | Nepenthes pitcher plant | Slippery, underwater omniphobicity | [31-34] |
| 2007 | Butterfly wing Mosquito eye | Anisotropic wetting, structural coloration Antireflection, antifogging | [14] [15] |
| 2008 | Red rose petal | Superhydrophobicity, high or low adhesion | [16] |
| 2009 | Fish scale | Superhydrophilicity/underwater superoleophobicity | [17] |
| 2010 | Salvinia leaf Shark skin | Superhydrophobicity, high adhesion Fluid drag reduction | [18-19] [26-27] |
| 2011 | Poplar leaf hair Springtail cuticle | Superhydrophobicity, antireflection Superamphiphobicity | [20] [28] |
| 2012 | Clam shell | Superhydrophilicity/underwater superoleophobicity | [21] |
| 2016 | Penguin feather Skimmer beak | Icephobicity Drag reduction | [22] [29] |
| 2018 | Sarracenia trichome Earthworms | Water harvesting and transport Self-replenishing lubrication, friction reduction, antifouling | [25] [30] |
表1 仿生材料的功能性应用
Table 1 Multiple functionalities of bioinspired materials
| Year | Bioinspired materials | Multiple functionalities for applications | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1997 | Lotus leaf | Superhydrophobicity, self-cleaning | [8-9] |
| 2000 | Gecko foot-hair Spider silk | Superhydrophobicity, high adhesion Water collection | [10] [23] |
| 2001 | Desert beetle | Superhydrophobicity/superhydrophilicity | [11] |
| 2002 | Rice leaf Cactus stems | Superhydrophobicity, anisotropic wetting Fog collection, gradient wetting | [2] [24] |
| 2004 | Water strider leg Cicada wing | Superhydrophobicity, fluid friction reduction Superhydrophobicity, antireflection | [12] [13] |
| 2006 | Nepenthes pitcher plant | Slippery, underwater omniphobicity | [31-34] |
| 2007 | Butterfly wing Mosquito eye | Anisotropic wetting, structural coloration Antireflection, antifogging | [14] [15] |
| 2008 | Red rose petal | Superhydrophobicity, high or low adhesion | [16] |
| 2009 | Fish scale | Superhydrophilicity/underwater superoleophobicity | [17] |
| 2010 | Salvinia leaf Shark skin | Superhydrophobicity, high adhesion Fluid drag reduction | [18-19] [26-27] |
| 2011 | Poplar leaf hair Springtail cuticle | Superhydrophobicity, antireflection Superamphiphobicity | [20] [28] |
| 2012 | Clam shell | Superhydrophilicity/underwater superoleophobicity | [21] |
| 2016 | Penguin feather Skimmer beak | Icephobicity Drag reduction | [22] [29] |
| 2018 | Sarracenia trichome Earthworms | Water harvesting and transport Self-replenishing lubrication, friction reduction, antifouling | [25] [30] |
| Preparation | Advantages and Disadvantages | Mechanical durability | Wetting behaviors | Ref. | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sandpaper | Loading | Anti-wear situation | Before wear/(°) | After wear/(°) | |||
| Etching methods | Time-saving, low cost, but poor mechanical durability | 400# | 100 g | 200 cm | 161 | 156 | [42] |
| 240# | 200 g | 100 cm | 162 | 154 | [44] | ||
| Oscillating sand test Sand erosion test | 120 min | 170 | 155 | [41] | |||
| 9 kg | 161 | 158 | [43] | ||||
| Electrochemical methods | Fast, easily tuned, good mechanical durability, but high energy-consumption, needed complex operations | 1000# | 1.3 kPa | 500 cm | 160 | 148 | [49] |
| 1000# | 1.3 kPa | 500 cm | 167 | 137 | [51] | ||
| 400# | 2 kPa | 1200 cm | 155 | 143 | [52] | ||
| 800# | 3 kPa | 200 cm | 162 | 142 | [53] | ||
| 1000# | 3 kPa | 200 cm | 160 | 156 | [54] | ||
| 400# | 100 g | 500 cm | 165 | >150 | [58] | ||
| Chemical and physical deposition | Appplicable to different substrates, excellent mechanical durability, but time-consuming, limited to small areas | 1000# | 5 kPa | 1010 cm | 152 | 149 | [62] |
| 800# | 53 g | 400 cm | 157 | 152 | [63] | ||
| 320# | 300 g | 1460 cm | 178 | 140 | [64] | ||
| 1200# | 100 g | 320 cm | 152 | 150 | [65] | ||
| 240# | 100 g | 400 cm | 168 | 156 | [66] | ||
| 200# | 200 g | 965 cm | 166 | 153 | [67] | ||
| 2000# | 9.8 kPa | 6000 cm | 164 | 150 | [68] | ||
| 1000# | 100 g | 400 cm | 158 | 151 | [69] | ||
| 1500# | 200 g | 500 cm | 153 | 150 | [70] | ||
| Any other methods | - | 1000# | 50 g | 1200 cm | 172 | 150 | [74] |
| - | 400 g | 500 cm | 158 | 150 | [76] | ||
表2 采用不同制备方法制得超疏水表面的优缺点
Table 2 Advantages and disadvantages with regard to superhydrophobic surface by different preparations
| Preparation | Advantages and Disadvantages | Mechanical durability | Wetting behaviors | Ref. | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sandpaper | Loading | Anti-wear situation | Before wear/(°) | After wear/(°) | |||
| Etching methods | Time-saving, low cost, but poor mechanical durability | 400# | 100 g | 200 cm | 161 | 156 | [42] |
| 240# | 200 g | 100 cm | 162 | 154 | [44] | ||
| Oscillating sand test Sand erosion test | 120 min | 170 | 155 | [41] | |||
| 9 kg | 161 | 158 | [43] | ||||
| Electrochemical methods | Fast, easily tuned, good mechanical durability, but high energy-consumption, needed complex operations | 1000# | 1.3 kPa | 500 cm | 160 | 148 | [49] |
| 1000# | 1.3 kPa | 500 cm | 167 | 137 | [51] | ||
| 400# | 2 kPa | 1200 cm | 155 | 143 | [52] | ||
| 800# | 3 kPa | 200 cm | 162 | 142 | [53] | ||
| 1000# | 3 kPa | 200 cm | 160 | 156 | [54] | ||
| 400# | 100 g | 500 cm | 165 | >150 | [58] | ||
| Chemical and physical deposition | Appplicable to different substrates, excellent mechanical durability, but time-consuming, limited to small areas | 1000# | 5 kPa | 1010 cm | 152 | 149 | [62] |
| 800# | 53 g | 400 cm | 157 | 152 | [63] | ||
| 320# | 300 g | 1460 cm | 178 | 140 | [64] | ||
| 1200# | 100 g | 320 cm | 152 | 150 | [65] | ||
| 240# | 100 g | 400 cm | 168 | 156 | [66] | ||
| 200# | 200 g | 965 cm | 166 | 153 | [67] | ||
| 2000# | 9.8 kPa | 6000 cm | 164 | 150 | [68] | ||
| 1000# | 100 g | 400 cm | 158 | 151 | [69] | ||
| 1500# | 200 g | 500 cm | 153 | 150 | [70] | ||
| Any other methods | - | 1000# | 50 g | 1200 cm | 172 | 150 | [74] |
| - | 400 g | 500 cm | 158 | 150 | [76] | ||
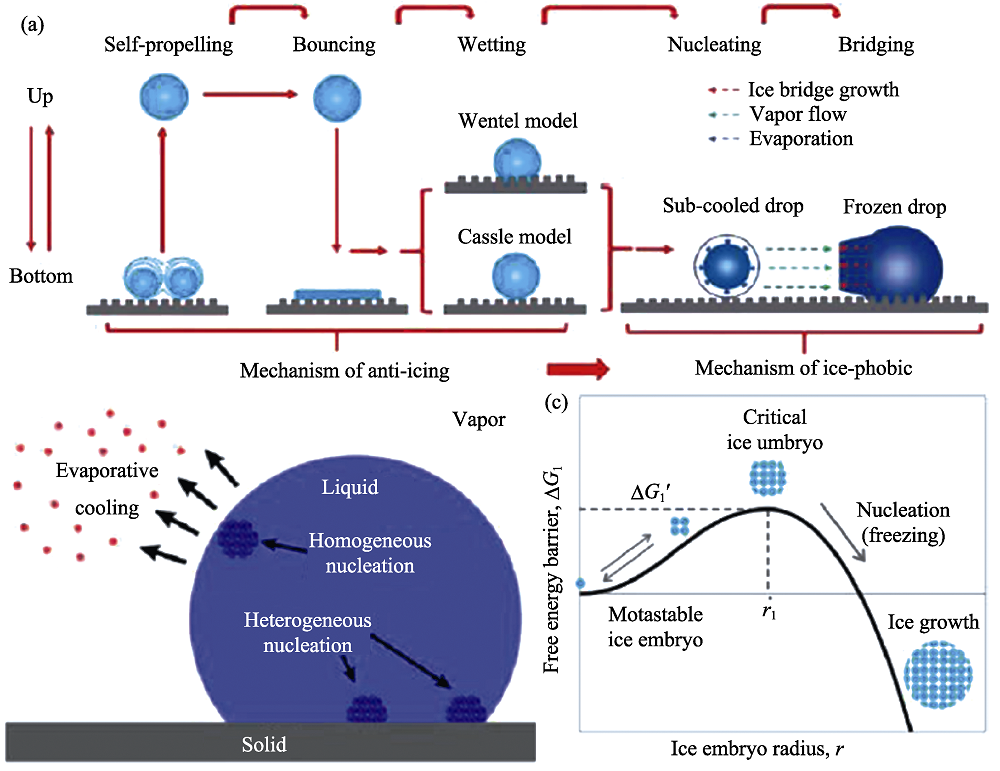
图3 防-疏冰机理和小液滴形核结冰过程[85,86]
Fig. 3 (a) Mechanisms of anti-icing and ice-phobic surface[85]; (b) Schematic diagram showing the regions within a water droplet where homogeneous and heterogeneous ice nucleation occurs; (c) Gibbs free energy barrier during freezing process against the ice embryo radius (Below critical size the ice embryo is metastable and above critical size the ice embryo is stable to initiate the freezing process)[86]
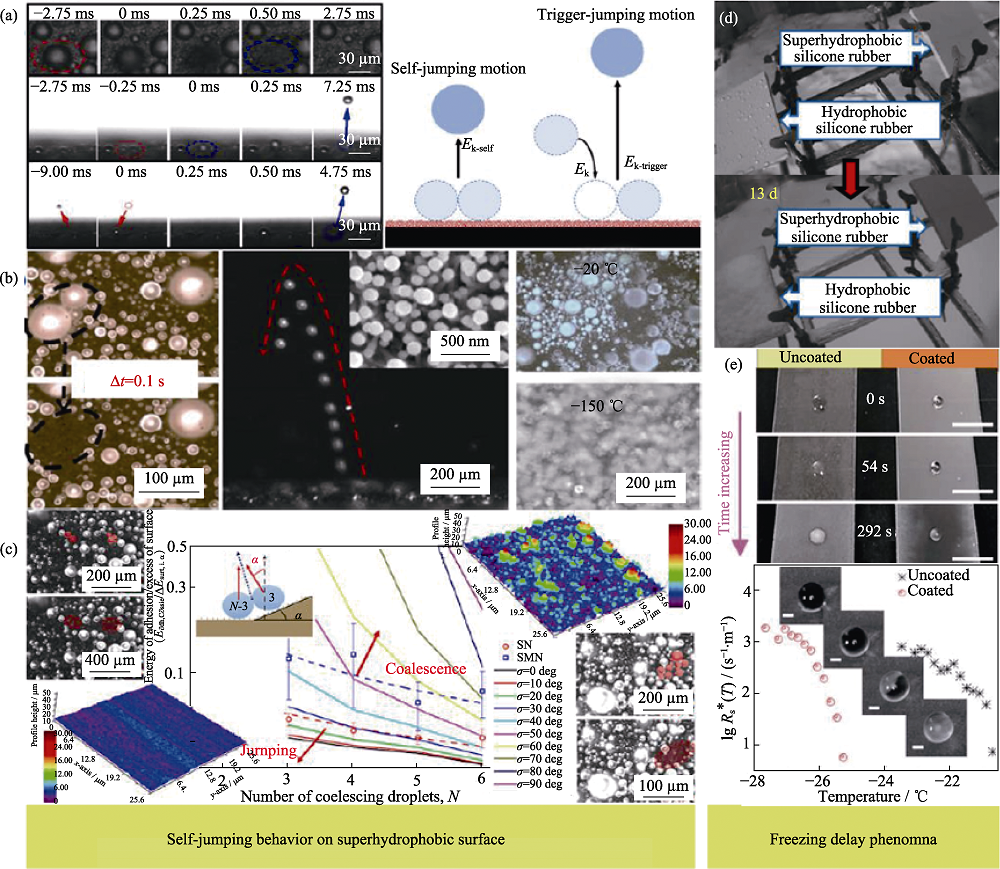
图5 (a~c)冷凝液滴的自跳动行为[94,95,96]和(d, e)延迟结冰现象[98,99]
Fig. 5 (a-c) Self-jumping behavior of over-cooled droplets on superhydrophobic surface[94,95,96] and (d, e) freezing delay phenomena[98,99].
| Superhydrophobic surfaces (Ref.) | [101] | [102] | [103] | [104] | [105] | [106] | [107] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ice adhesion strength | 35.7 kPa | 201 kPa | 100 kPa | 64.7 kPa | 25 N | 113 kPa | 26.3 kPa |
| Contact angles/(°) | 164 | 154.3 | 164 | 157 | 161 | 153 | 155.3 |
| Sliding angles/(°) | 1.5 | 4.1 | 2 | - | 6.5 | 14.3 | 2 |
表3 超疏水表面的抗结冰粘附力
Table 3 Superhydrophobic surface against ice adhesion
| Superhydrophobic surfaces (Ref.) | [101] | [102] | [103] | [104] | [105] | [106] | [107] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ice adhesion strength | 35.7 kPa | 201 kPa | 100 kPa | 64.7 kPa | 25 N | 113 kPa | 26.3 kPa |
| Contact angles/(°) | 164 | 154.3 | 164 | 157 | 161 | 153 | 155.3 |
| Sliding angles/(°) | 1.5 | 4.1 | 2 | - | 6.5 | 14.3 | 2 |
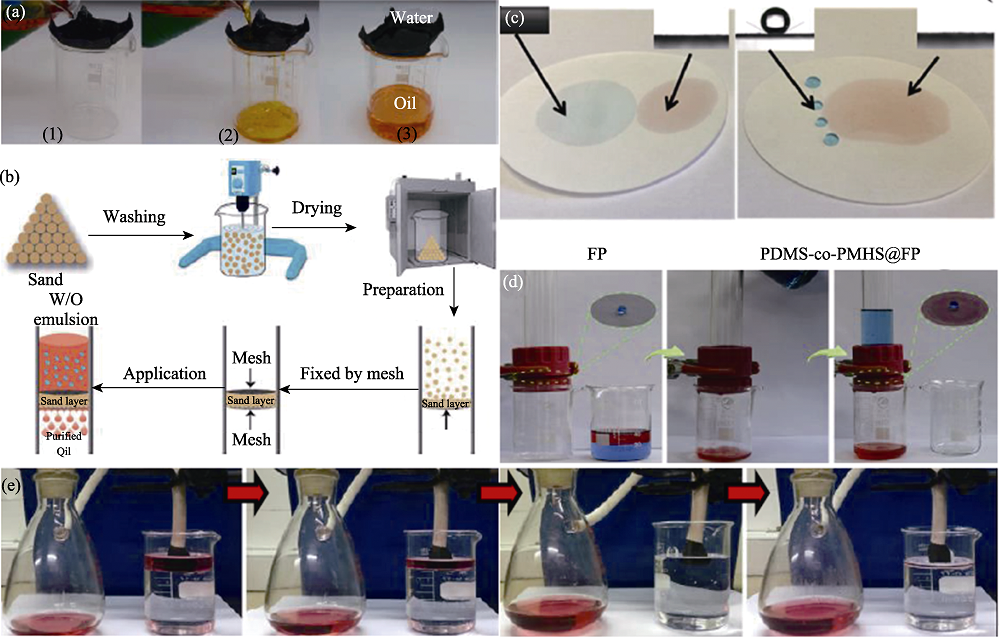
图8 超疏水/超亲油性油水分离[114,115,116,117,118]
Fig. 8 Oil/water separation based on metal[114], sand[115], paper[116], fiber[117], and sponge[118] via superhydrophobic and lipophilic properties
| [1] | 江雷, 冯琳 . 仿生智能纳米界面材料. 北京: 化学工业出版社, 2007: 1-48. |
| [2] | LIN F, LI S, LI Y , et al. Super-hydrophobic surfaces: from natural to artificial. Adv. Mater., 2002,14(24):1857-1860. |
| [3] | YOUNG T . An essay on the cohesion of fliuds. Philos. Trans. R. S. London, 1805,95:65-87. |
| [4] | WENZEL R N . Resistance of solid surfaces to wetting by water. Ind. Eng. Chem, 1936,28(8):988-994. |
| [5] | CASSIE A, BAXTER S . Wettability of porous surfaces. Trans. Faraday Soc., 1944,40:546-551. |
| [6] | SI Y, DONG Z, JIANG L . Bioinspired designs of superhydrophobic and superhydrophilic materials. ACS Cent. Sci., 2018,4(9):1102-1112. |
| [7] | SUN Y, GUO Z . Recent advances of bioinspired functional materials with special wettability: from nature and beyond nature. Nanoscale Horiz., 2019,4:52-76. |
| [8] | BARTHLOTT W, NEINHUIS C . Purity of the sacred lotus, or escape from contamination in biological surfaces. Planta, 1997,202(1):1-8. |
| [9] | NEINHUIS C, BARTHLOTT W . Characterization and distribution of water-repellent, self-cleaning plant surfaces. Ann. Bot., 1997,79(6):667-677. |
| [10] | AUTUMN K, LIANG Y A, HSIEH S T , et al. Adhesive force of a single gecko foot-hair. Nature, 2000,405(6787):681-685. |
| [11] | PARKER A R, LAWRENCE C R . Water capture by a desert beetle. Nature, 2001,414(6859):33-34. |
| [12] | GAO X, JIANG L . Biophysics: water-repellent legs of water striders. Nature, 2004,432(7013):36. |
| [13] | LEE W, JIN M K, YOO W C , et al. Nanostructuring of a polymeric substrate with well-defined nanometer-scale topography and tailored surface wettability. Langmuir, 2004,20(18):7665-7669. |
| [14] | ZHENG Y, GAO X, JIANG L . Directional adhesion of superhydrophobic butterfly wings. Soft Matter, 2007,3(2):178-182. |
| [15] | GAO X, YAN X, YAO X , et al. The dry-style antifogging properties of mosquito compound eyes and artificial analogues prepared by soft lithography. Adv. Mater., 2007,19(17):2213-2217. |
| [16] | FENG L, ZHANG Y, XI J , et al. Petal effect: a superhydrophobic state with high adhesive force. Langmuir, 2008,24(8):4114-4119. |
| [17] | LIU M, WANG S, WEI Z , et al. Bioinspired design of a superoleophobic and low adhesive water/solid interface. Adv. Mater., 2009,21(6):665-669. |
| [18] | KOCH K, BHUSHAN B, BARTHLOTT W . Multifunctional surface structures of plants: an inspiration for biomimetics. Prog. Mater. Sci., 2009,54(2):137-178. |
| [19] | BARTHLOTT W, SCHIMMEL T, WIERSCH S , et al. The salvinia paradox: superhydrophobic surfaces with hydrophilic pins for air retention under. Adv. Mater., 2010,22(21):2325-2328. |
| [20] | YE C, LI M, HU J , et al. Highly reflective superhydrophobic white coating inspired by poplar leaf hairs toward an effective “cool roof”. Energy Environ. Sci., 2011,4(9):3364-3367. |
| [21] | LIU X, ZHOU J, XUE Z , et al. Clam’s shell inspired high-energy inorganic coatings with underwater low adhesive superoleophobicity. Adv. Mater., 2012,24(25):3401-3405. |
| [22] | WANG S, YANG Z, GUO G , et al. Icephobicity of penguins spheniscus humboldti and an artificial replica of penguin feather with air-infused hierarchical rough structures. J. Phys. Chem. C, 2016,120(29):15923-15929. |
| [23] | ZHENG Y, BAI H, HUANG Z , et al. Directional water collection on wetted spider silk. Nature, 2010,463(7281):640-643. |
| [24] | JU J, BAI H, ZHENG Y , et al. A multi-structural and multi- functional integrated fog collection system in cactus. Nat. Commun., 2012,3(1):1247. |
| [25] | CHEN H, RAN T, GAN Y , et al. Ultrafast water harvesting and transport in hierarchical microchannels. Nat. Mater., 2018,17(10):935-942. |
| [26] | DEAN B, BHUSHAN B . Shark-skin surfaces for fluid-drag reduction in turbulent flow: a review. Phil. Trans. R. Soc. A, 2010,368(1929):4775-4806. |
| [27] | BIXLER G D, BHUSHAN B . Fluid drag reduction with shark- skin riblet inspired microstructured surfaces. Adv. Funct. Mater., 2013,23(26):4507-4528. |
| [28] | HELBIG R, NICKERL J, NEINHUIS C , et al. Smart skin patterns protect springtails. PLoS One, 2011,6(9):e25105. |
| [29] | MARTIN S, BHUSHAN B . Discovery of riblets in a bird beak (Rynchops) for low fluid drag. Phil. Trans. R. Soc. A, 2016,374(2073):20160134. |
| [30] | ZHAO H, SUN Q, DENG X , et al. Earthworm-inspired rough polymer coatings with self-replenishing lubrication for adaptive friction-reduction and antifouling surfaces. Adv. Mater., 2018,30(29):1802141. |
| [31] | GORB E V, GORB S N . Physicochernical properties of functional surfaces in pitchers of the carnivorous plant nepenthes alata blanco (Nepenthaceae). Plant Biol., 2006,8(6):841-848. |
| [32] | BOHN H F, FEDERLE W . Insect aquaplaning: nepenthes pitcher plants capture prey with the peristome, a fully wettable waterlubricated anisotropic surface. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A., 2004,101(39):14138-14143. |
| [33] | GORB E, KASTNER V, PERESSADKO A , et al. Structure and properties of the glandular surface in the digestive zone of the pitcher in the carnivorous plant nepenthes ventrata and its role in insect trapping and retention. J. Exp. Biol., 2004,207(17):2947-2963. |
| [34] | WONG T S, KANG S H, TANG S K , et al. Bioinspired self- repairing slippery surfaces with pressure-stable omniphobicity. Nature, 2011,477(7365):443-447. |
| [35] | DOU W, WU J, GU T , et al. Preparation of super-hydrophobic micro-needle CuO surface as a barrier against marine atmospheric corrosion. Corros. Sci., 2018,131:156-163. |
| [36] | TONG W, XIONG D, WANG N , et al. Green and timesaving fabrication of a superhydrophobic surface and its application to anti-icing, self-cleaning and oil-water separation. Surf. Coat. Technol., 2018,352:609-618. |
| [37] | WAN Y, CHEN M, LIU W , et al. The research on preparation of superhydrophobic surfaces of pure copper by hydrothermal method and its corrosion resistance. Electrochim. Acta, 2018,270:310-318. |
| [38] | KIM J, MIRZAEI A, KIM H W , et al. Realization of superhydrophobic aluminum surfaces with novel micro-terrace nano- leaf hierarchical structure. Appl. Surf. Sci., 2018,451:207-217. |
| [39] | NANDA D, SAHOO A, KUMAR A , et al. Facile approach to develop durable and reusable superhydrophobic/superoleophilic coatings for steel mesh surfaces. J. Colloid Interface Sci., 2019,535:50-57. |
| [40] | LIU Y, LI X, JIN J , et al. Anti-icing property of bio-inspired micro- structure superhydrophobic surfaces and heat transfer model. Appl. Surf. Sci., 2017,400:498-505. |
| [41] | BOINOVICH L B, MODIN E B, SAYFUTDINOVA A R , et al. Combination of functional nanoengineering and nanosecond laser texturing for design of superhydrophobic aluminum alloy with exceptional mechanical and chemical properties. ACS Nano, 2017,11(10):10113-10123. |
| [42] | MA Q, TONG Z, WANG W , et al. Fabricating robust and repairable superhydrophobic surface on carbon steel by nanosecond laser texturing for corrosion protection. Appl. Surf. Sci., 2018,455:748-757. |
| [43] | LIN Y, HAN J, CAI M , et al. Durable and robust transparent superhydrophobic glass surfaces fabricated by a femtosecond laser with exceptional water repellency and thermostability. J. Mater. Chem. A, 2018,6(19):9049-9056. |
| [44] | SONG J, WANG D, HU L , et al. Superhydrophobic surface fabricated by nanosecond laser and perhydropolysilazane. Appl. Surf. Sci., 2018,455:771-779. |
| [45] | ZHU J, HU X . A novel route for fabrication of the corrosion- resistant superhydrophobic surface by turning operation. Surf. Coat. Technol., 2017,313:294-298. |
| [46] | ZHU J . A novel fabrication of superhydrophobic surfaces on aluminum substrate. Appl. Surf. Sci., 2018,447:363-367. |
| [47] | MOKHTARI S, KARIMZADEH F, ABBASI M H , et al. Development of super-hydrophobic surface on Al 6061 by anodizing and the evaluation of its corrosion behavior. Surf. Coat. Technol., 2017,324:99-105. |
| [48] | LI S, XIANG X, MA B , et al. Facile preparation of diverse alumina surface structures by anodization and superhydrophobic surfaces with tunable water droplet adhesion. J. Alloys Compd., 2019,779:219-228. |
| [49] | LIU Q, CHEN D, KANG Z . One-step electrodeposition process to fabricate corrosion-resistant superhydrophobic surface on magnesium alloy. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2015,7(3):1859-1867. |
| [50] | TESLER A B, KIM P, KOLLE S , et al. Extremely durable biofouling-resistant metallic surfaces based on electrodeposited nanoporous tungstite films on steel. Nat. Commun., 2015,6(1):8649. |
| [51] | ZHANG B, ZHAO X, LI Y , et al. Fabrication of durable anticorrosion superhydrophobic surfaces on aluminum substrates via a facile one-step electrodeposition approach. RSC Advances, 2016,6(42):35455-35465. |
| [52] | TAM J, JIAO Z, LAU J C F , , et al. Wear stability of superhydrophobic nano Ni-PTFE electrodeposits. Wear, 2017, 374-375:1-4. |
| [53] | JAIN R, PITCHUMANI R . Facile fabrication of durable copper- based superhydrophobic surfaces via electrodeposition. Langmuir, 2018,34(10):3159-3169. |
| [54] | JAIN R, PITCHUMANI R . Fabrication and characterization of zinc-based superhydrophobic coatings. Surf. Coat. Technol., 2018,337:223-231. |
| [55] | YE Y, LIU Z, LIU W , et al. Superhydrophobic oligoaniline- containing electroactive silica coating as pre-process coating for corrosion protection of carbon steel. Chem. Eng. J., 2018,348:940-951. |
| [56] | ZOU Y, WANG Y, XU S , et al. Superhydrophobic double-layer coating for efficient heat dissipation and corrosion protection. Chem. Eng. J., 2019,362:638-649. |
| [57] | ZANG D, ZHU R, ZHANG W , et al. Corrosion-resistant superhydrophobic coatings on Mg alloy surfaces inspired by lotus seedpod. Adv. Funct. Mater., 2017,27(8):1605446. |
| [58] | QING Y, HU C, YANG C , et al. Rough structure of electrodeposition as a template for an ultrarobust self-cleaning surface. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2017,9(19):16571-16580. |
| [59] | BÖKE F, GINER I, KELLER A , et al. Plasma-enhanced chemical vapor deposition (PE-CVD) yields better hydrolytical stability of biocompatible SiOx thin films on implant alumina ceramics compared to rapid thermal evaporation physical vapor deposition (PVD). ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2016,8(28):17805-17816. |
| [60] | VILARÓ I, YAGÜE J L, BORRÓS S . Superhydrophobic copper surfaces with anticorrosion properties fabricated by solventless CVD methods. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2017,9(1):1057-1065. |
| [61] | ZHANG F, SHI Z, CHEN L , et al. Porous superhydrophobic and superoleophilic surfaces prepared by template assisted chemical vapor deposition. Surf. Coat. Technol., 2017,315:385-390. |
| [62] | WU Y, JIA S, WANG S , et al. A facile and novel emulsion for efficient and convenient fabrication of durable superhydrophobic materials. Chem. Eng. J., 2017,328:186-196. |
| [63] | REN G, SONG Y, LI X , et al. A simple way to an ultra-robust superhydrophobic fabric with mechanical stability, UV durability, and UV shielding property. J. Colloid Interface Sci., 2018,522:57-62. |
| [64] | ZHONG M, ZHANG Y, LI X , et al. Facile fabrication of durable superhydrophobic silica/epoxy resin coatings with compatible transparency and stability. Surf. Coat. Technol., 2018,347:191-198. |
| [65] | YU N, XIAO X, YE Z , et al. Facile preparation of durable superhydrophobic coating with self-cleaning property. Surf. Coat. Technol., 2018,347:199-208. |
| [66] | LU Y, SATHASIVAM S, SONG J , et al. Robust self-cleaning surfaces that function when exposed to either air or oil. Science, 2015,347(6226):1132-1135. |
| [67] | WANG N, LU Y, XIONG D , et al. Designing durable and flexible superhydrophobic coating and its application in oil purification. J. Mater. Chem. A, 2016,4(11):4107-4116. |
| [68] | LI Y, LI B, ZHAO X , et al. Totally waterborne, nonfluorinated, mechanically robust, and self-healing superhydrophobic coatings for actual anti-icing. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2018,10(45):39391-39399. |
| [69] | CHEN Z, LI G, WANG L , et al. A strategy for constructing superhydrophobic multilayer coatings with self-cleaning properties and mechanical durability based on the anchoring effect of organopolysilazane. Mater. Des., 2018,141:37-47. |
| [70] | TU K, WANG X, KONG L , et al. Facile preparation of mechanically durable, self-healing and multifunctional superhydrophobic surfaces on solid wood. Mater. Des., 2018,140:30-36. |
| [71] | DENG X, MAMMEN L, BUTT H , et al. Candle soot as a template for a transparent robust superamphiphobic coating. Science, 2012,335(6064):67-69. |
| [72] | XIAO L, ZENG W, LIAO G , et al. Thermally and chemically stable candle soot superhydrophobic surface with excellent self- cleaning properties in air and oil. ACS Appl. Nano Mater., 2018,1(3):1204-1211. |
| [73] | TONG W, XIONG D, TIAN T , et al. Superhydrophobic surface on aeronautical materials via the deposition of nanoparticles and a PDMS seal. Appl. Phys. A, 2019,125(3):177. |
| [74] | DONG S, WANG Z, WANG Y , et al. Roll-to-roll manufacturing of robust superhydrophobic coating on metallic engineering materials. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2018,10(2):2174-2184. |
| [75] | WU Y, ZHAO M, GUO Z . Multifunctional superamphiphobic SiO2 coating for crude oil transportation. Chem. Eng. J., 2018,334:1584-1593. |
| [76] | PENG W, GOU X, QIN H , et al. Creation of a multifunctional superhydrophobic coating for composite insulators. Chem. Eng. J., 2018,352:774-781. |
| [77] | SU X, LI H, LAI X , et al. Vacuum-assisted layer-by-layer superhydrophobic carbon nanotube films with electrothermal and photothermal effects for deicing and controllable manipulation. J. Mater. Chem. A, 2018,6(35):16910-16919. |
| [78] | PENG C, CHEN Z, TIWARI M K . All-organic superhydrophobic coatings with mechanochemical robustness and liquid impalement resistance. Nat. Mater., 2018,17(4):355-360. |
| [79] | KIM Y S, SHANG M, KANG S , et al. Strong hydrophobic coating by conducting a new hierarchical architecture. J. Phys. Chem. C, 2018,112(8):4628-4634. |
| [80] | ZHAO S, ZHAO J, WEN M , et al. Sequentially reinforced additive coating for transparent and durable superhydrophobic glass. Langmuir, 2018,34(38):11316-11324. |
| [81] | CHEN S, SONG Y, XU F . Highly transparent and hazy cellulose nanopaper simultaneously with a self-cleaning superhydrophobic surface. ACS Sustainable Chem. Eng., 2018,6(4):5173-5181. |
| [82] | TEISALA H, GEYER F, HAAPANEN J , et al. Ultrafast processing of hierarchical nanotexture for a transparent superamphiphobic coating with extremely low roll-off angle and high impalement pressure. Adv. Mater., 2018,30(14):1706529. |
| [83] | WU Y, ZENG J, SI Y , et al. Large-area preparation of robust and transparent superomniphobic polymer films. ACS Nano, 2018,12(10):10338-10346. |
| [84] | VARANASI K K, MING H, BHATE N , et al. Spatial control in the heterogeneous nucleation of water. Appl. Phys. Lett., 2009,95(9):144101. |
| [85] | LI Q, GUO Z . Fundamentals of icing and common strategies for designing biomimetic anti-icing surfaces. J. Mater. Chem. A, 2018,6(28):13549-13581. |
| [86] | JAMIL M I, ALI A, HAQ F , et al. Icephobic strategies and materials with superwettability: design principles and mechanism. Langmuir, 2018,34(50):15425-15444. |
| [87] | LI N, WU L, YU C , et al. Ballistic jumping drops on superhydrophobic surfaces via electrostatic manipulation. Adv. Mater., 2018,30(8):1703838. |
| [88] | SHEN Y, TAO J, WANG G , et al. Bioinspired fabrication of hierarchical-structured superhydrophobic surfaces to understand droplet bouncing dynamics for enhancing water repellency. J. Phys. Chem. C, 2018,122(13):7312-7320. |
| [89] | SHEN Y, LIU S, ZHU C , et al. Facile fabrication of hierarchical structured superhydrophobic surface and its ultra dynamic water repellency. Chem. Eng. J., 2017,313:47-55. |
| [90] | MISHCHENKO L, HATTON B, BAHADUR V , et al. Design of ice-free nanostructured surfaces based on repulsion of impacting water droplets. ACS Nano, 2010,4(12):7699-7707. |
| [91] | FAROKHIRAD S, LEE T . Computational study of microparticle effect on self-propelled jumping of droplets from superhydrophobic substrates. Int. J. Multiphas Flow, 2017,95:220-234. |
| [92] | RICHARD D, CLANET C, QUÉRÉ D . Surface phenomena: contact time of a bouncing drop. Nature, 2002,417(6891):811-811. |
| [93] | SCHUTZIUS T M, JUNG S, MAITRA T , et al. Spontaneous droplet trampolining on rigid superhydrophobic surfaces. Nature, 2015,527(7576):82-85. |
| [94] | WANG S, ZHANG W, YU X , et al. Sprayable superhydrophobic nano-chains coating with continuous self-jumping of dew and melting frost. Sci. Rep-UK, 2017,7(1):40300. |
| [95] | ZHANG W, WANG S, XIAO Z , et al. Frosting behavior of superhydrophobic nanoarrays under ultralow temperature. Langmuir, 2017,33(36):8891-8898. |
| [96] | ZHANG P, MAEDA Y, LÜ F , et al. Enhanced coalescence- induced droplet-jumping on nanostructured superhydrophobic surfaces in the absence of microstructures. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2017,9(40):35391-35403. |
| [97] | JUNG S, DORRESTIJN M, RAPS D , et al. Are superhydrophobic surfaces best for icephobicity. Langmuir, 2011,27(6):3059-3066. |
| [98] | EMELYANENKO A M, BOINOVICH L B, BEZDOMNIKOV A A , et al. Reinforced superhydrophobic coating on silicone rubber for longstanding anti-icing performance in severe conditions. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2017,9(28):24210-24219. |
| [99] | WU X, CHEN Z . A mechanically robust transparent coating for antiicing and self-cleaning applications. J. Mater. Chem. A, 2018,6:16043-16052. |
| [100] | RYZHKIN I A, PETRENKO V F . Proton ordering in ice at an ice-metal interface. J. Exp. Theor. Phys., 2005,101(2):317-321. |
| [101] | JIN M, SHEN Y, LUO X , et al. A combination structure of microblock and nanohair fabricated by chemical etching for excellent water repellency and icephobicity. Appl. Surf. Sci., 2018,455:883-890. |
| [102] | XI N, LIU Y, ZHANG X , et al. Steady anti-icing coatings on weathering steel fabricated by HVOF spraying. Appl. Surf. Sci., 2018,444:757-762. |
| [103] | WANG N, TANG L, TONG W , et al. Fabrication of robust and scalable superhydrophobic surfaces and investigation of their anti-icing properties. Mater. Des., 2018,156:320-328. |
| [104] | WU X, ZHAO X, HO J W C , et al. Design and durability study of environmental-friendly room-temperature processable icephobic coatings. Chem. Eng. J., 2019,355:901-909. |
| [105] | SONG J, LI Y, XU W , et al. Inexpensive and non-fluorinated superhydrophobic concrete coating for anti-icing and anti-corrosion. J. Colloid Interface Sci., 2019,541:86-92. |
| [106] | ZHENG S, BELLIDO-AGUILAR D A, WU X , et al. Durable waterborne hydrophobic bio-epoxy coating with improved anti-icing and self-cleaning performance. ACS Sustainable Chem. Eng., 2019,7(1):641-649. |
| [107] | SHEN Y, WU Y, TAO J , et al. Spraying fabrication of durable and transparent coatings for anti-icing application: dynamic water repellency, icing delay, and ice adhesion. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2019,11(3):3590-3598. |
| [108] | WEI C, JIN B, ZHANG Q , et al. Anti-icing performance of super- wetting surfaces from icing-resistance to ice-phobic aspects: robust hydrophobic or slippery surfaces. J. Alloys Compd., 2018,765:721-730. |
| [109] | WANG F, DING W, HE J , et al. Phase transition enabled durable anti-icing surfaces and its DIY design. Chem. Eng. J., 2019,360:243-249. |
| [110] | VAZIRINASAB E, JAFARI R, MOMEN G . Application of superhydrophobic coatings as a corrosion barrier: a review. Surf. Coat. Technol., 2018,341:40-56. |
| [111] | DING C, TAI Y, WANG D , et al. Superhydrophobic composite coating with active corrosion resistance for AZ31B magnesium alloy protection. Chem. Eng. J., 2019,357:518-532. |
| [112] | WEN Q, DI J, JIANG L , et al. Zeolite-coated mesh film for efficient oil-water separation. Chem. Sci., 2013,4(2):591-595. |
| [113] | ZHANG W, SHI Z, ZHANG F , et al. Superhydrophobic and superoleophilic PVDF membranes for effective separation of water- in-oil emulsions with high flux. Adv. Mater., 2013,25(14):2071-2076. |
| [114] | ZULFIQAR U, HUSSAIN S Z, SUBHANI T , et al. Mechanically robust superhydrophobic coating from sawdust particles and carbon soot for oil/water separation. Colloids Surf. A, 2018,539:391-398. |
| [115] | LI J, XU C, GUO C , et al. Underoil superhydrophilic desert sand layer for efficient gravity-directed water-in-oil emulsions separation with high flux. J. Mater. Chem. A, 2018,6(1):223-230. |
| [116] | LI X, CAO M, SHAN H , et al. Facile and scalable fabrication of superhydrophobic and superoleophilic PDMS-co-PMHS coating on porous substrates for highly effective oil/water separation. Chem. Eng. J., 2019,358:1103-1113. |
| [117] | ZHAO X, LI Y, LI B , et al. Environmentally benign and durable superhydrophobic coatings based on SiO2 nanoparticles and silanes. J. Colloid Interface Sci., 2019,542:8-14. |
| [118] | ZHANG L, LI H, LAI X , et al. Thiolated graphene-based superhydrophobic sponges for oil-water separation. Chem. Eng. J., 2017,316:736-743. |
| [1] | 朱文杰, 唐璐, 陆继长, 刘江平, 罗永明. 钙钛矿型氧化物催化氧化挥发性有机化合物的研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(7): 735-746. |
| [2] | 胡智超, 杨鸿宇, 杨鸿程, 孙成礼, 杨俊, 李恩竹. P-V-L键理论在微波介质陶瓷性能调控中的应用[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(6): 609-626. |
| [3] | 吴琼, 沈炳林, 张茂华, 姚方周, 邢志鹏, 王轲. 铅基织构压电陶瓷研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(6): 563-574. |
| [4] | 张碧辉, 刘小强, 陈湘明. Ruddlesden-Popper结构杂化非常规铁电体的研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(6): 587-608. |
| [5] | 吴杰, 杨帅, 王明文, 李景雷, 李纯纯, 李飞. 铅基织构压电陶瓷的发展历程、现状与挑战[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(6): 575-586. |
| [6] | 姜昆, 李乐天, 郑木鹏, 胡永明, 潘勤学, 吴超峰, 王轲. PZT陶瓷的低温烧结研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(6): 627-638. |
| [7] | 田睿智, 兰正义, 殷杰, 郝南京, 陈航榕, 马明. 基于微流控技术的纳米无机生物材料制备: 原理及其研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(4): 337-347. |
| [8] | 张继国, 吴田, 赵旭, 杨钒, 夏天, 孙士恩. 钠离子电池正极材料循环稳定性提升策略及产业化进程[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(4): 348-362. |
| [9] | 殷杰, 耿佳毅, 王康龙, 陈忠明, 刘学建, 黄政仁. SiC陶瓷的3D打印成形与致密化新进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(3): 245-255. |
| [10] | 谌广昌, 段小明, 朱金荣, 龚情, 蔡德龙, 李宇航, 杨东雷, 陈彪, 李新民, 邓旭东, 余瑾, 刘博雅, 何培刚, 贾德昌, 周玉. 直升机特定结构先进陶瓷材料研究进展与应用展望[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(3): 225-244. |
| [11] | 范晓波, 祖梅, 杨向飞, 宋策, 陈晨, 王子, 罗文华, 程海峰. 质子调控型电化学离子突触研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(3): 256-270. |
| [12] | 海热古·吐逊, 郭乐, 丁嘉仪, 周嘉琪, 张学良, 努尔尼沙·阿力甫. 上转换荧光探针辅助的光学成像技术在肿瘤显影中的应用研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(2): 145-158. |
| [13] | 孙树娟, 郑南南, 潘昊坤, 马猛, 陈俊, 黄秀兵. 单原子催化剂制备方法的研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(2): 113-127. |
| [14] | 陶桂龙, 支国伟, 罗添友, 欧阳佩东, 衣新燕, 李国强. 空腔型薄膜体声波滤波器的关键技术进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(2): 128-144. |
| [15] | 周帆, 田志林, 李斌. 热防护系统用碳化物超高温陶瓷抗烧蚀涂层研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(1): 1-16. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
