
Journal of Inorganic Materials ›› 2025, Vol. 40 ›› Issue (12): 1395-1404.DOI: 10.15541/jim20250004
• RESEARCH ARTICLE • Previous Articles Next Articles
LI Xueru( ), MA Zhejie, GUO Yujie, LI Ping(
), MA Zhejie, GUO Yujie, LI Ping( )
)
Received:2025-01-03
Revised:2025-03-20
Published:2025-12-20
Online:2025-04-15
Contact:
LI Ping, professor. E-mail: lipingunilab@ecust.edu.cnAbout author:LI Xueru (2000‒), female, Master candidate. E-mail: y82220019@mail.ecust.edu.cn
Supported by:CLC Number:
LI Xueru, MA Zhejie, GUO Yujie, LI Ping. Influence of Support Characteristics on Coverage of Ionomer and Oxygen Reduction Performance for Pt/C Catalysts[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(12): 1395-1404.
| Sample | VC | KB1 | KB2 | BP | SJR | AB |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Contact angle/(°) | 40 | 47 | 125 | 94 | 34 | 137 |
| Zeta potential/mV | 9.8 | 21.0 | 24.7 | 15.3 | -1.1 | - |
Table 1 Contact angles and Zeta potentials of different carbon supports
| Sample | VC | KB1 | KB2 | BP | SJR | AB |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Contact angle/(°) | 40 | 47 | 125 | 94 | 34 | 137 |
| Zeta potential/mV | 9.8 | 21.0 | 24.7 | 15.3 | -1.1 | - |
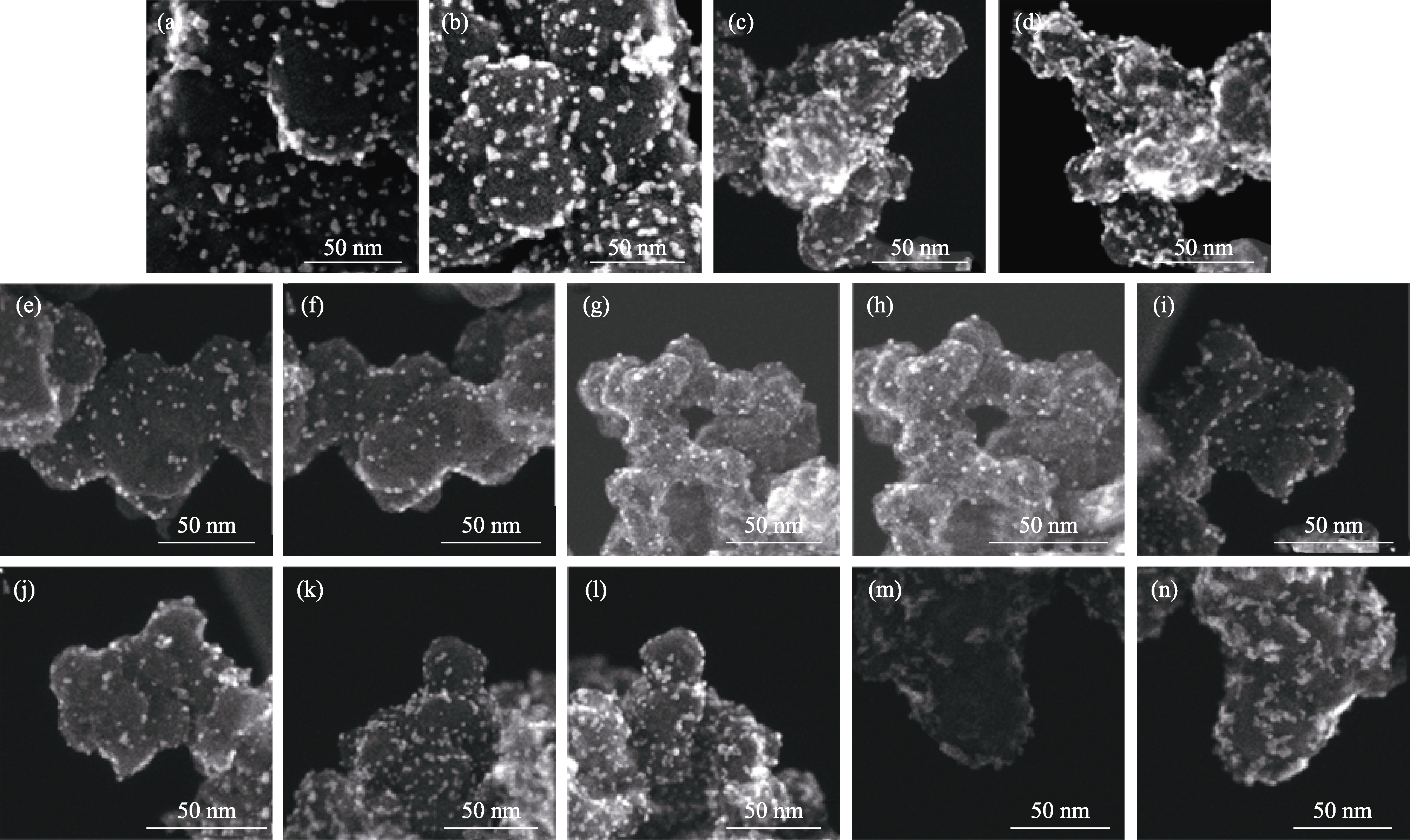
Fig. 3 STEM images with secondary electron (SE) mode for Pt catalysts loaded on different carbon supports (a) 0° and (b) 180° of PK-Pt/VC; (c) 0° and (d) 180° of Pt/VC; (e) 0° and (f) 180° of PK-Pt/KB1; (g) 0° and (h) 180° of Pt/KB2; (i) 0° and (j) 180° of Pt/BP; (k) 0° and (l) 180° of Pt/SJR; (m) 0° and (n) 180° of Pt/AB
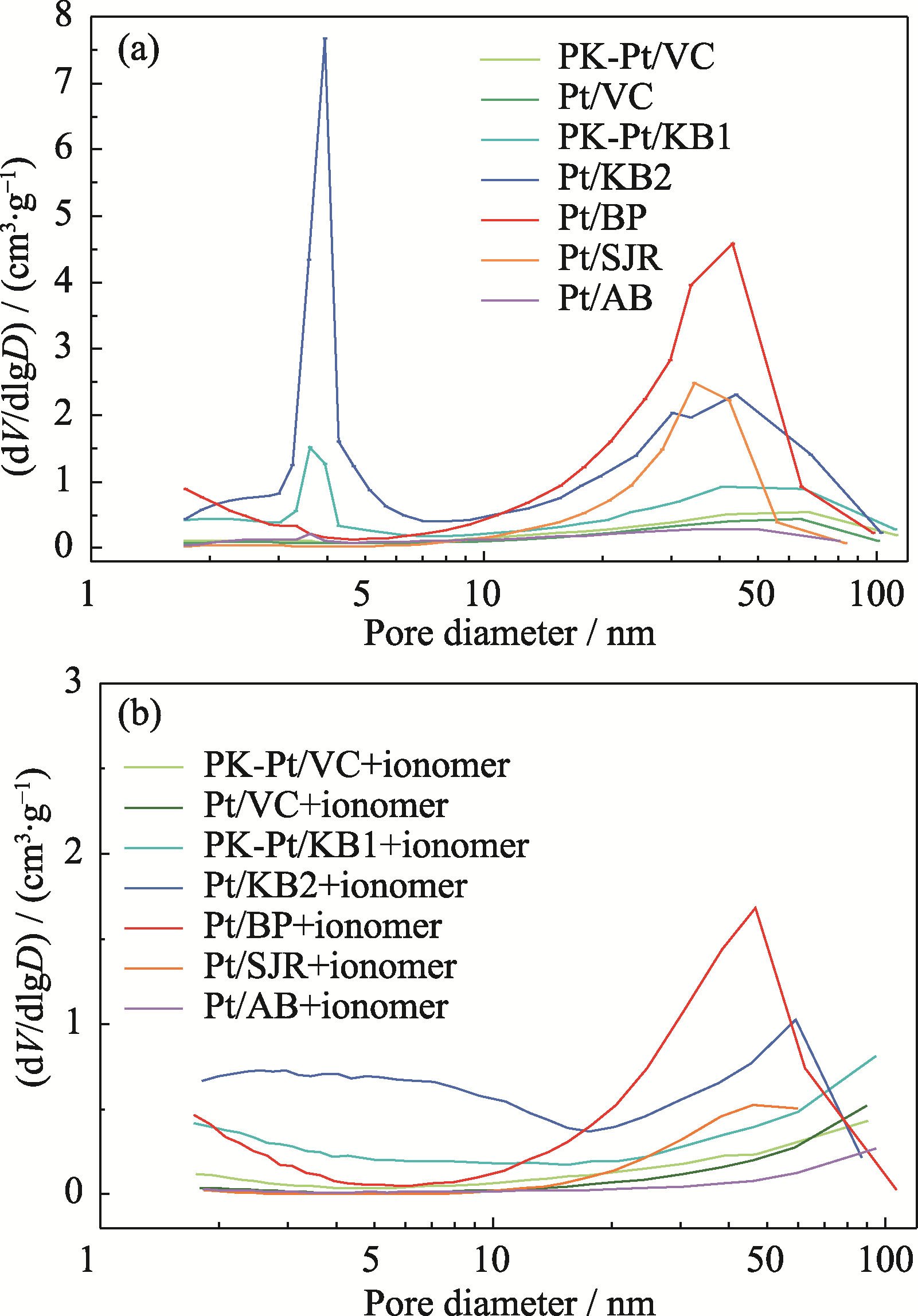
Fig. 5 Pore size distribution curves of different Pt/C catalysts (a) before and (b) after addition of ionomer Colorful figures are available on website
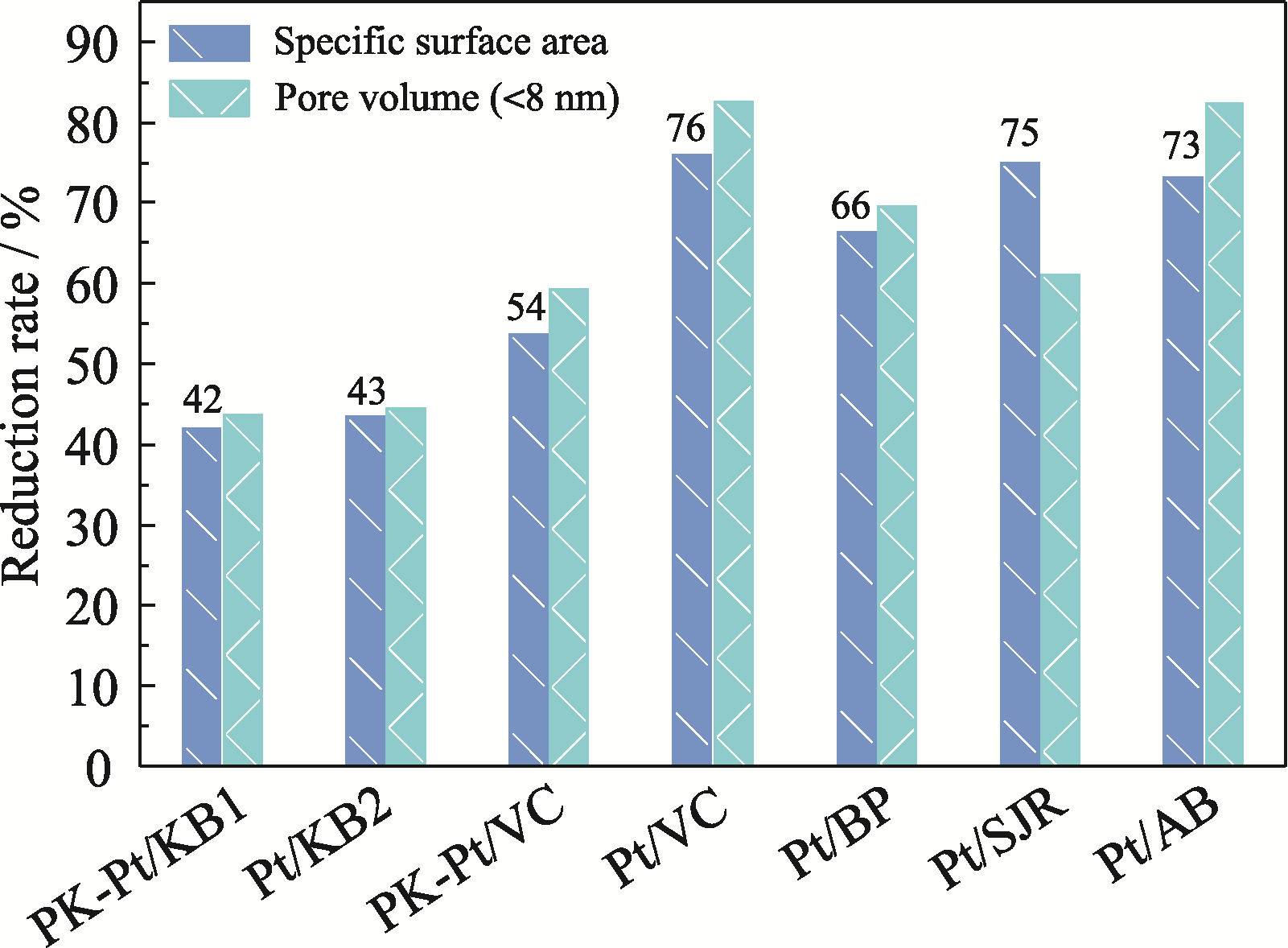
Fig. 6 Reduction rates of specific surface areas and pore volumes of different Pt/C catalysts after addition of ionomer Numbers in the figure represent coverages of ionomer
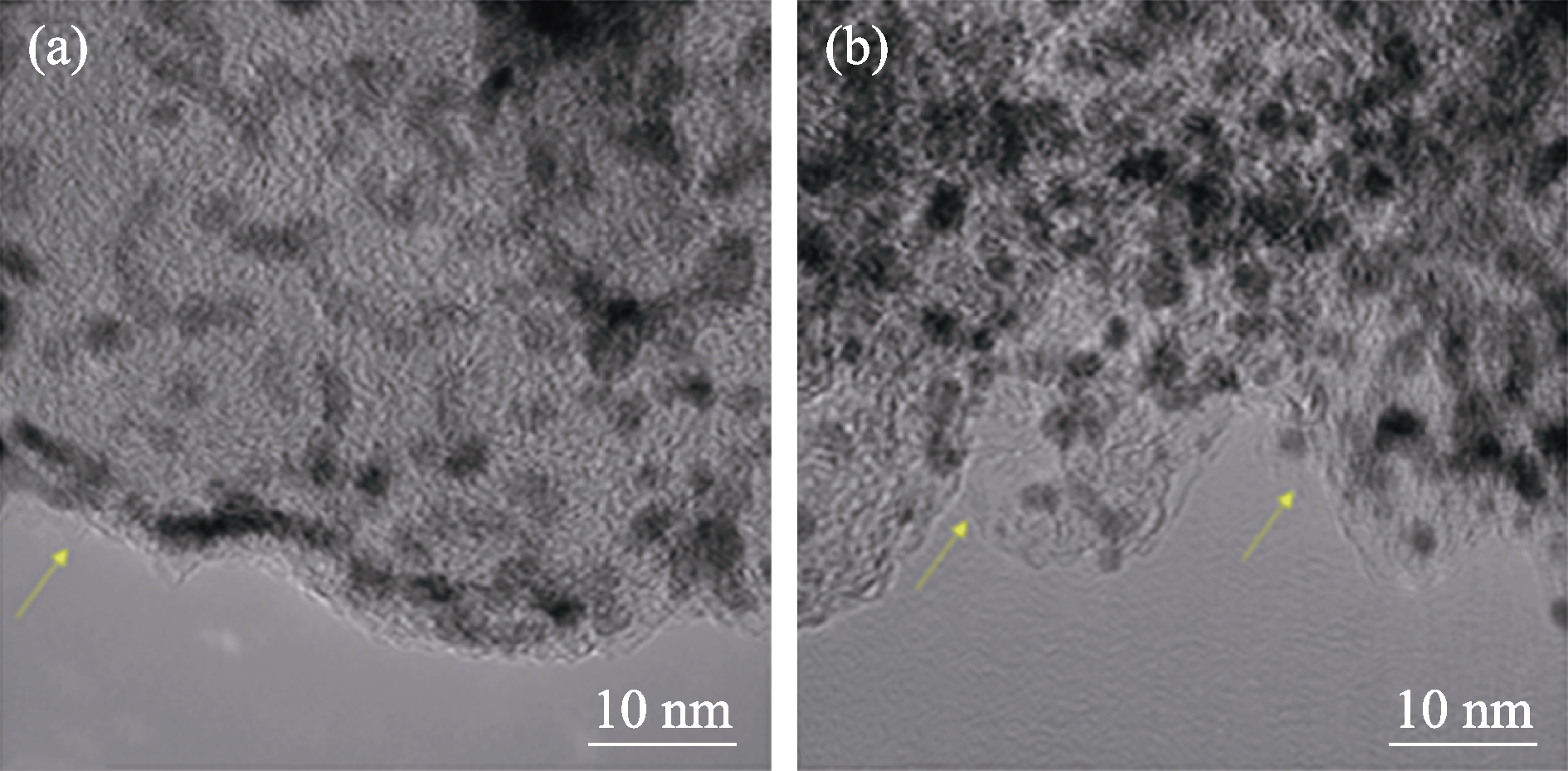
Fig. 7 TEM images of catalysts containing ionomer for (a) Pt/VC and (b) Pt/KB2 Yellow arrows: ionomer film covering the outer surface of the catalyst particles
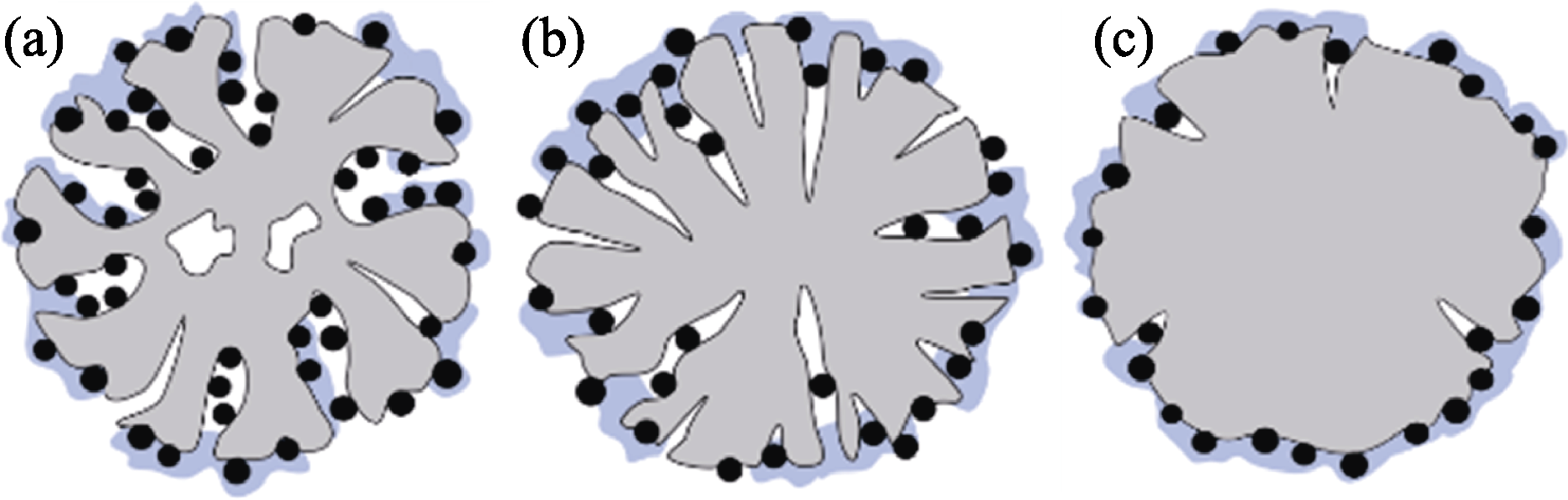
Fig. 8 Schematic diagrams of the coverage states of ionomer on catalysts with different characteristics (a) PK-Pt/KB1, Pt/KB2; (b) Pt/BP; (c) Pt/VC, Pt/SJR and Pt/AB Black dot: Pt particle; Blue area: ionomer; Gray area: C
| Sample | Specific surface area/(m2·g-1) | Pore area/(m2·g-1) | Pore volume/(cm3·g-1) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| <2 nm | 2-8 nm | >8 nm | <2 nm | 2-8 nm | >8 nm | Total | ||
| VC | 206.9 | 125.1 | 43.5 | 38.3 | 0.035 | 0.039 | 0.478 | 0.582 |
| KB1 | 811.1 | 372.8 | 353.1 | 85.2 | 0.194 | 0.308 | 0.730 | 1.232 |
| KB2 | 1361.0 | 291.3 | 834.3 | 235.4 | 0.167 | 0.807 | 1.613 | 2.587 |
| BP | 1313.1 | 903.6 | 249.0 | 160.5 | 0.444 | 0.204 | 1.909 | 2.577 |
| SJR | 121.2 | 15.1 | 33.4 | 72.7 | 0.009 | 0.032 | 0.757 | 0.798 |
| AB | 65.6 | 5.5 | 42.1 | 18.0 | 0.004 | 0.039 | 0.135 | 0.178 |
Table S1 Specific surface areas, pore volumes and distributions of different carbon supports
| Sample | Specific surface area/(m2·g-1) | Pore area/(m2·g-1) | Pore volume/(cm3·g-1) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| <2 nm | 2-8 nm | >8 nm | <2 nm | 2-8 nm | >8 nm | Total | ||
| VC | 206.9 | 125.1 | 43.5 | 38.3 | 0.035 | 0.039 | 0.478 | 0.582 |
| KB1 | 811.1 | 372.8 | 353.1 | 85.2 | 0.194 | 0.308 | 0.730 | 1.232 |
| KB2 | 1361.0 | 291.3 | 834.3 | 235.4 | 0.167 | 0.807 | 1.613 | 2.587 |
| BP | 1313.1 | 903.6 | 249.0 | 160.5 | 0.444 | 0.204 | 1.909 | 2.577 |
| SJR | 121.2 | 15.1 | 33.4 | 72.7 | 0.009 | 0.032 | 0.757 | 0.798 |
| AB | 65.6 | 5.5 | 42.1 | 18.0 | 0.004 | 0.039 | 0.135 | 0.178 |
| Catalyst | PK-Pt/VC | Pt/VC | PK-Pt/KB1 | Pt/KB2 | Pt/BP | Pt/SJR | Pt/AB |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pt loading/% (in mass) | 38.6 | 32.0 | 38.3 | 35.8 | 35.8 | 37.0 | 31.9 |
| Average Pt particle size/nm | 3.9 | 3.0 | 2.5 | 2.4 | 2.5 | 2.6 | 2.8 |
Table S2 Average particle sizes and loading amounts of Pt particles on different carbon supports
| Catalyst | PK-Pt/VC | Pt/VC | PK-Pt/KB1 | Pt/KB2 | Pt/BP | Pt/SJR | Pt/AB |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pt loading/% (in mass) | 38.6 | 32.0 | 38.3 | 35.8 | 35.8 | 37.0 | 31.9 |
| Average Pt particle size/nm | 3.9 | 3.0 | 2.5 | 2.4 | 2.5 | 2.6 | 2.8 |
| Catalyst | PK-Pt/VC | Pt/VC | PK-Pt/KB1 | Pt/KB2 | Pt/BP | Pt/SJR | Pt/AB |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Exterior frequency/% | 92 | 90 | 34 | 28 | 85 | 100 | 100 |
| Interior frequency/% | 8 | 10 | 66 | 72 | 15 | 0 | 0 |
Table S3 Percentages of Pt particles distributed inside and outside of the carbon particles for different carbon supports
| Catalyst | PK-Pt/VC | Pt/VC | PK-Pt/KB1 | Pt/KB2 | Pt/BP | Pt/SJR | Pt/AB |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Exterior frequency/% | 92 | 90 | 34 | 28 | 85 | 100 | 100 |
| Interior frequency/% | 8 | 10 | 66 | 72 | 15 | 0 | 0 |
| Catalyst | jlim/(mA·cm-2) | jk/(mA·cm-2) | Eonset/V | E1/2/V |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PK-Pt/VC | 5.9 | 4.3 | 1.037 | 0.88 |
| Pt/VC | 5.9 | 3.5 | 1.033 | 0.88 |
| PK-Pt/KB1 | 6.0 | 5.6 | 1.048 | 0.90 |
| Pt/KB2 | 6.1 | 5.9 | 1.042 | 0.90 |
| Pt/BP | 6.1 | 4.5 | 1.039 | 0.88 |
| Pt/SJR | 6.0 | 4.0 | 1.046 | 0.87 |
| Pt/AB | 5.5 | 2.7 | 1.014 | 0.84 |
Table S4 Testing results of ORR on various Pt/C catalytic electrodes
| Catalyst | jlim/(mA·cm-2) | jk/(mA·cm-2) | Eonset/V | E1/2/V |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PK-Pt/VC | 5.9 | 4.3 | 1.037 | 0.88 |
| Pt/VC | 5.9 | 3.5 | 1.033 | 0.88 |
| PK-Pt/KB1 | 6.0 | 5.6 | 1.048 | 0.90 |
| Pt/KB2 | 6.1 | 5.9 | 1.042 | 0.90 |
| Pt/BP | 6.1 | 4.5 | 1.039 | 0.88 |
| Pt/SJR | 6.0 | 4.0 | 1.046 | 0.87 |
| Pt/AB | 5.5 | 2.7 | 1.014 | 0.84 |

Fig. S1 HRTEM images and histograms of particle size distributions of different Pt catalysts (a, a1) PK-Pt/VC; (b, b1) Pt/VC; (c, c1) PK-Pt/KB1; (d, d1) Pt/KB2; (e, e1) Pt/BP; (f, f1) Pt/SJR; (g, g1) Pt/AB
| [1] |
HAO C, LIU Z R, LIU W, et al. Research progress of carbon- supported metal single atom catalysts for oxygen reduction reaction. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(8): 820.
DOI |
| [2] | YAO Y S, GUO R H, AN S L, et al. In-situ loaded Pt-Co high index facets catalysts: preparation and elec-trocatalytic performance. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(1): 71. |
| [3] |
李薛茹, 马哲杰, 李平. 质子交换膜燃料电池阴极催化层微观结构表征研究进展. 储能科学与技术, 2025, 14(2): 812.
DOI |
| [4] |
NORMILE S J, ZENYUK I V. Imaging ionomer in fuel cell catalyst layers with synchrotron nano transmission X-ray microscopy. Solid State Ionics, 2019, 335: 38.
DOI URL |
| [5] |
MINAMI S, KAJIYA S, YAMADA H, et al. Measurement of ionomer coverage on carbon and Pt in catalyst layer of polymer electrolyte fuel cells by electrochemical impedance spectroscopy. Electrocatalysis, 2023, 14(4): 522.
DOI |
| [6] | KODAMA K, SHINOHARA A, HASEGAWA N, et al. Catalyst poisoning property of sulfonimide acid ionomer on Pt (111) surface. Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 2014, 161(5): F649. |
| [7] |
SHINOZAKI K, MORIMOTO Y, PIVOVAR B S, et al. Suppression of oxygen reduction reaction activity on Pt-based electrocatalysts from ionomer incorporation. Journal of Power Sources, 2016, 325: 745.
DOI URL |
| [8] |
OTT S, ORFANIDI A, SCHMIES H, et al. Ionomer distribution control in porous carbon-supported catalyst layers for high-power and low Pt-loaded proton exchange membrane fuel cells. Nature Materials, 2020, 19(1): 77.
DOI PMID |
| [9] |
SUN D D, WANG Z, JIN M, et al. Optimizing ionomer coverage in solid carbon-supported catalyst toward high performance for proton exchange membrane fuel cells. ACS Applied Energy Materials, 2024, 7(9): 4132.
DOI URL |
| [10] |
PARK Y C, TOKIWA H, KAKINUMA K, et al. Effects of carbon supports on Pt distribution, ionomer coverage and cathode performance for polymer electrolyte fuel cells. Journal of Power Sources, 2016, 315: 179.
DOI URL |
| [11] |
UCHIDA M, PARK Y C, KAKINUMA K, et al. Effect of the state of distribution of supported Pt nanoparticles on effective Pt utilization in polymer electrolyte fuel cells. Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics, 2013, 15(27): 11236.
DOI PMID |
| [12] |
YARLAGADDA V, CARPENTER M K, MOYLAN T E, et al. Boosting fuel cell performance with accessible carbon mesopores. ACS Energy Letters, 2018, 3(3): 618.
DOI URL |
| [13] |
RAMASWAMY N, GU W B, ZIEGELBAUER J M, et al. Carbon support microstructure impact on high current density transport resistances in PEMFC cathode. Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 2020, 167(6): 064515.
DOI |
| [14] |
WANG M N, ZHANG J G, FAVERO S, et al. Resolving optimal ionomer interaction in fuel cell electrodes via operando X-ray absorption spectroscopy. Nature Communications, 2024, 15: 9390.
DOI |
| [15] | 朱凤鹃, 吴爱明, 吴若飞. 催化剂中碳载体类型对燃料电池性能的影响研究. 现代工程科技, 2023, 2(2): 5. |
| [16] | XIANG Q, JIANG S K, LIU J, et al. Probing impact of support pore diameter on three-phase interfaces of Pt/C catalysts by molecular dynamic simulation. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2025, 17(5): 7619. |
| [17] |
BERLINGER S A, GARG S, WEBER A Z. Multicomponent, multiphase interactions in fuel-cell inks. Current Opinion in Electrochemistry, 2021, 29: 100744.
DOI URL |
| [18] |
SCHEIBA F, BENKER N, KUNZ U, et al. Electron microscopy techniques for the analysis of the polymer electrolyte distribution in proton exchange membrane fuel cells. Journal of Power Sources, 2008, 177(2): 273.
DOI URL |
| [19] |
GUÉTAZ L, LOPEZ-HARO M, ESCRIBANO S, et al. Catalyst- layer ionomer imaging of fuel cells. ECS Transactions, 2015, 69(17): 455.
DOI URL |
| [20] |
LOPEZ-HARO M, GUÉTAZ L, PRINTEMPS T, et al. Three- dimensional analysis of Nafion layers in fuel cell electrodes. Nature Communications, 2014, 5: 5229.
DOI |
| [21] | TAKESHITA T, KAMITAKA Y, SHINOZAKI K, et al. Evaluation of ionomer coverage on Pt catalysts in polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cells by CO stripping voltammetry and its effect on oxygen reduction reaction activity. Journal of Electroanalytical Chemistry, 2020, 871: 7. |
| [22] | 刘楠, 王宏伟. 单颗粒冷冻电镜技术的研究现状和未来展望. 中国基础科学, 2019, 21(5): 1. |
| [23] |
ZHAO X K, MA Z J, LI X R, et al. Optimization of atomic layer deposited Pt-shell thickness of PtCu3@Pt/C catalyst for oxygen reduction reaction. Materials Chemistry and Physics, 2025, 329: 130145.
DOI URL |
| [24] |
ITO T, MATSUWAKI U, OTSUKA Y, et al. Three-dimensional spatial distributions of Pt catalyst nanoparticles on carbon substrates in polymer electrolyte fuel cells. Electrochemistry, 2011, 79(5): 374.
DOI URL |
| [25] |
SING K S W. Reporting physisorption data for gas/solid systems with special reference to the determination of surface area and porosity. Pure and Applied Chemistry, 2013, 54(11): 2201.
DOI URL |
| [26] |
SHIN S, JANG J, YOON S H, et al. A study on the effect of heat treatment on functional groups of pitch based activated carbon fiber using FTIR. Carbon, 1997, 35(12): 1739.
DOI URL |
| [27] |
LI P, ZHAO T J, ZHOU J H, et al. Characterization of carbon nanofiber composites synthesized by shaping process. Carbon, 2005, 43(13): 2701.
DOI URL |
| [28] |
XIA G F, SHEN S Y, ZHU F J, et al. Effect of oxygen-containing functional groups of carbon materials on the performance of Li-O2 batteries. Electrochemistry Communications, 2015, 60: 26.
DOI URL |
| [29] |
VINAYAN B P, JAFRI R I, NAGAR R, et al. Catalytic activity of platinum-cobalt alloy nanoparticles decorated functionalized multiwalled carbon nanotubes for oxygen reduction reaction in PEMFC. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2012, 37(1): 412.
DOI URL |
| [30] |
TERZYK A P. The influence of activated carbon surface chemical composition on the adsorption of acetaminophen (paracetamol) in vitro: part II. TG, FTIR, and XPS analysis of carbons and the temperature dependence of adsorption kinetics at the neutral pH. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 2001, 177(1): 23.
DOI URL |
| [31] | MOHAMED E. Characterization of porous solids and powders: surface area, pore size and density. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2005, 127(40): 14117. |
| [32] |
MA P C, SIDDIQUI N A, MÄDER E, et al. Correlation between electrokinetic potential, dispersibility, surface chemistry and energy of carbon nanotubes. Composites Science and Technology, 2011, 71(14): 1644.
DOI URL |
| [33] |
GIROD R, LAZARIDIS T, GASTEIGER H A, et al. Three- dimensional nanoimaging of fuel cell catalyst layers. Nature Catalysis, 2023, 6(5): 383.
DOI |
| [34] |
ZHONG G Y, XU S R, LIU L, et al. Effect of experimental operations on the limiting current density of oxygen reduction reaction evaluated by rotating-disk electrode. ChemElectroChem, 2020, 7(5): 1107.
DOI URL |
| [1] | LIU Lei, GUO Ruihua, WANG Li, WANG Yan, ZHANG Guofang, GUAN Lili. Oxygen Reduction Reaction on Pt3Co High-index Facets by Density Functional Theory [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(1): 39-46. |
| [2] | YANG Daihui, SUN Tian, TIAN Hexin, SHI Xiaofei, MA Dongwei. Iron-nitrogen-codoped Mesoporous Carbon: Facile Synthesis and Catalytic Performance of Oxygen Reduction Reaction [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(11): 1309-1315. |
| [3] | SUN Lian, GU Quanchao, YANG Yaping, WANG Honglei, YU Jinshan, ZHOU Xingui. Two-dimensional Transition Metal Dichalcogenides for Electrocatalytic Oxygen Reduction Reaction [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(7): 697-709. |
| [4] | JIANG Lili, XU Shuaishuai, XIA Baokai, CHEN Sheng, ZHU Junwu. Defect Engineering of Graphene Hybrid Catalysts for Oxygen Reduction Reactions [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(2): 215-222. |
| [5] | LIU Ziruo, LIU Wei, HAO Ce, HU Jinwen, SHI Yantao. Honeycomb-like Carbon-supported Fe Single Atom Catalyst: Preparation and Electrocatalytic Performance in Oxygen Reduction Reaction [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(9): 943-949. |
| [6] | HAO Ce, LIU Ziruo, LIU Wei, SHI Yantao. Research Progress of Carbon-supported Metal Single Atom Catalysts for Oxygen Reduction Reaction [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(8): 820-834. |
| [7] | ZHU Yong, GU Jun, YU Tao, HE Haitong, YAO Rui. Synthesis and Property of Platinum-cobalt Alloy Nano Catalyst [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(3): 299-305. |
| [8] | DING Sheng, NING Kai, YUAN Binxia, PAN Weiguo, YIN Shibin, LIU Jianfeng. Durability of Fe-N/C Catalysts with Different Nanostructures for Electrochemical Oxygen Reduction in Alkaline Solution [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2020, 35(8): 953-958. |
| [9] | LUO Yi,FENG Junzong,FENG Jian,JIANG Yonggang,LI Liangjun. Research Progress on Advanced Carbon Materials as Pt Support for Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cells [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2020, 35(4): 407-415. |
| [10] | HE Wang-Tao, MA Ru-Guang, ZHU Yu-Fang, YANG Ming-Jie, WANG Jia-Cheng. Renewable Porous Carbons Prepared by KOH Activation as Oxygen Reduction Electrocatalysts [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2019, 34(10): 1115-1122. |
| [11] | LI Shu-Ling, YUAN Xian-Xia, KONG Hai-Chuan, XU Jin, MA Zi-Feng. Fe-PPy-TsOH/C as Cathode Catalyst for Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cells [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2017, 32(4): 393-399. |
| [12] | SHI Qi, LEI Yong-Peng, WANG Ying-De, WANG Zhong-Min. In-situ Preparation and Electrocatalytic Oxygen Reduction Performance of N-doped Graphene@CNF [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2016, 31(4): 351-357. |
| [13] | ZHANG Yu-Hui, YI Qing-Feng, LIU Xiao-Ping, XIANG Bai-Lin. Carbonizing Products of the Fe/Co Doped Polypyrrole as Efficient Electrocatalysts for Oxygen Reduction Reaction [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2014, 29(3): 269-274. |
| [14] | LI Lin, YUAN Xian-Xia, XIA Xiao-Yun, DU Juan, MA Zhong, MA Zi-Feng. Effects of Mo Doping on Properties of Pt/C as Catalyst towards Electro-oxidation of Ethanol [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2014, 29(10): 1044-1048. |
| [15] | ZHAO Wen-Wen, ZHANG Hua, LI Mei. Potentiostatic Electrodeposition of Pt-Fe Alloy Catalyst and Application in PEMFC Cathode [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2013, 28(11): 1217-1222. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||