
Journal of Inorganic Materials ›› 2019, Vol. 34 ›› Issue (5): 509-514.DOI: 10.15541/jim20180345
Previous Articles Next Articles
Wei WANG1,Li-Li YUAN1,Qian-Yuan QIU1,Ming-Yang ZHOU1,Mei-Lin LIU1,2,Jiang LIU1( )
)
Received:2018-07-26
Revised:2018-10-28
Published:2019-05-20
Online:2019-05-14
Supported by:CLC Number:
Wei WANG, Li-Li YUAN, Qian-Yuan QIU, Ming-Yang ZHOU, Mei-Lin LIU, Jiang LIU. A Direct Carbon Solid Oxide Fuel Cell Stack Based on a Single Electrolyte Plate Fabricated by Tape Casting Technique[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2019, 34(5): 509-514.
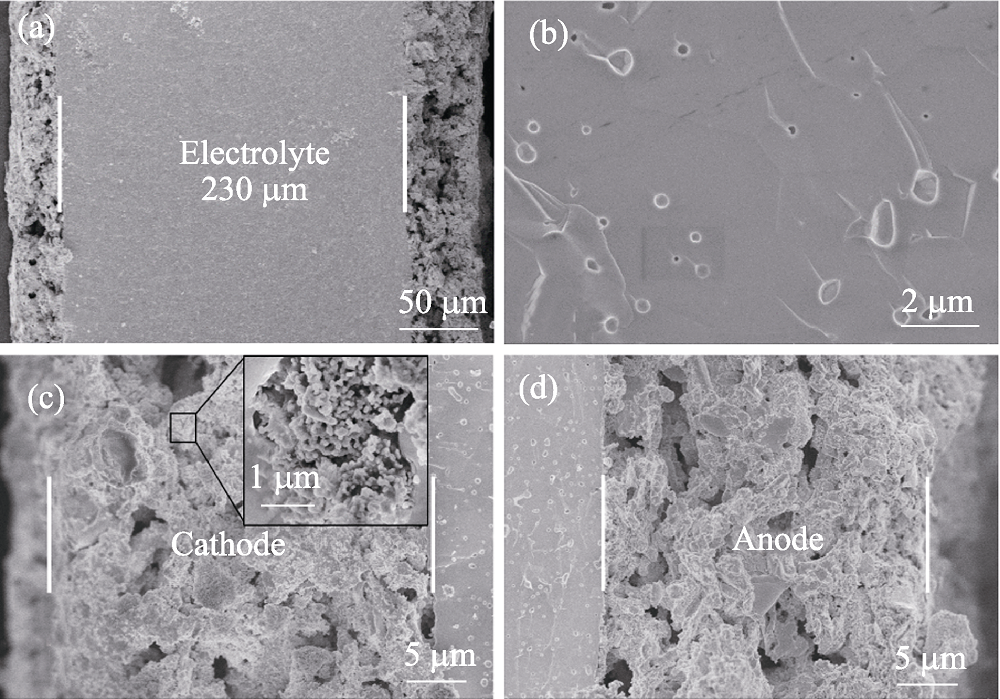
Fig. 3 Cross-sectional microstructures of DC-SOFC (a), YSZ electrolyte (b), interface between cathode and electrolyte (c), interface between anode and electrolyte (d)
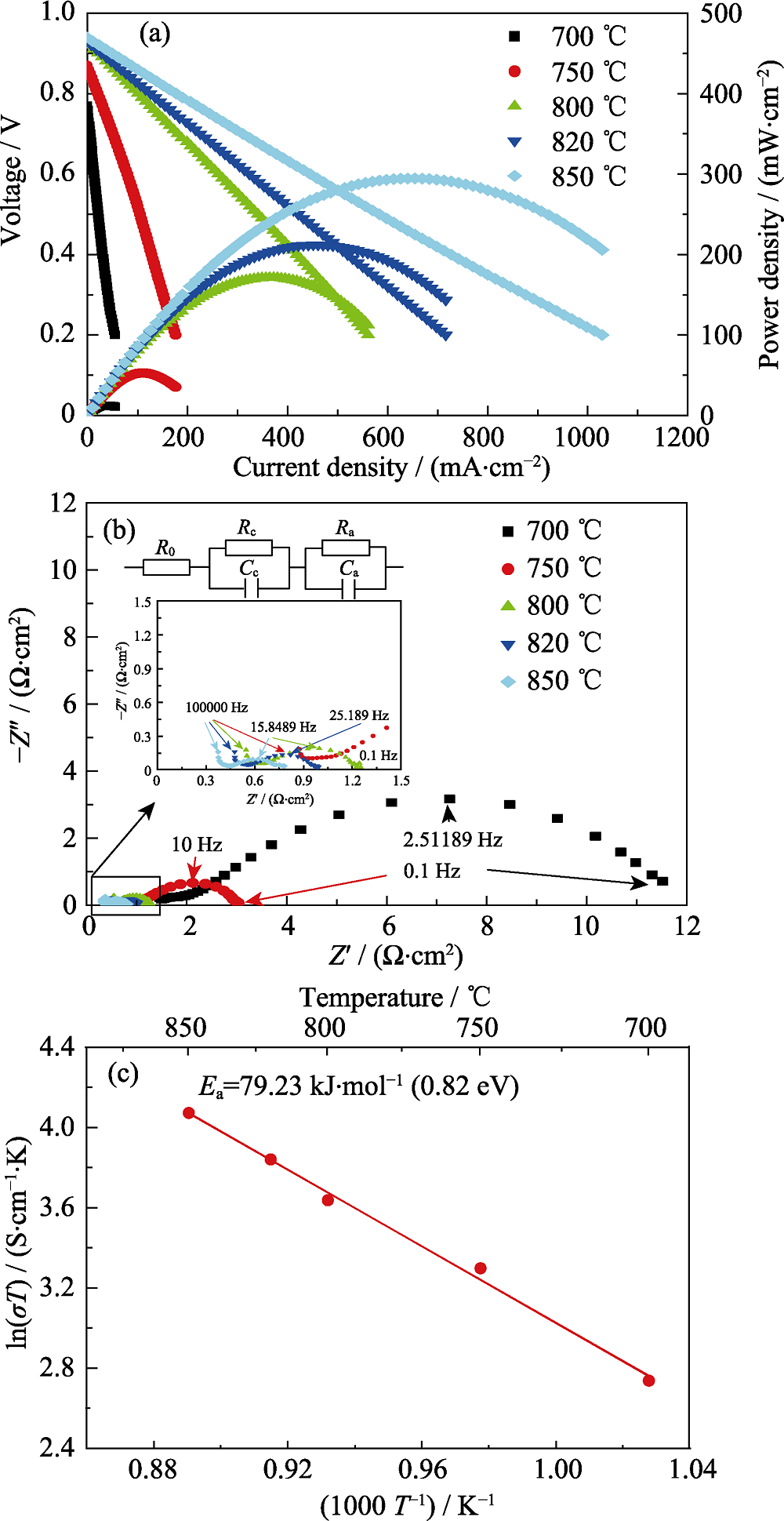
Fig. 4 Output performance (a), impedance spectra under OCV of the first cell of the 4-cell-stack with insets showing magnified spectra and equivalent circuit (b) and Arrhenius plot for YSZ (c)
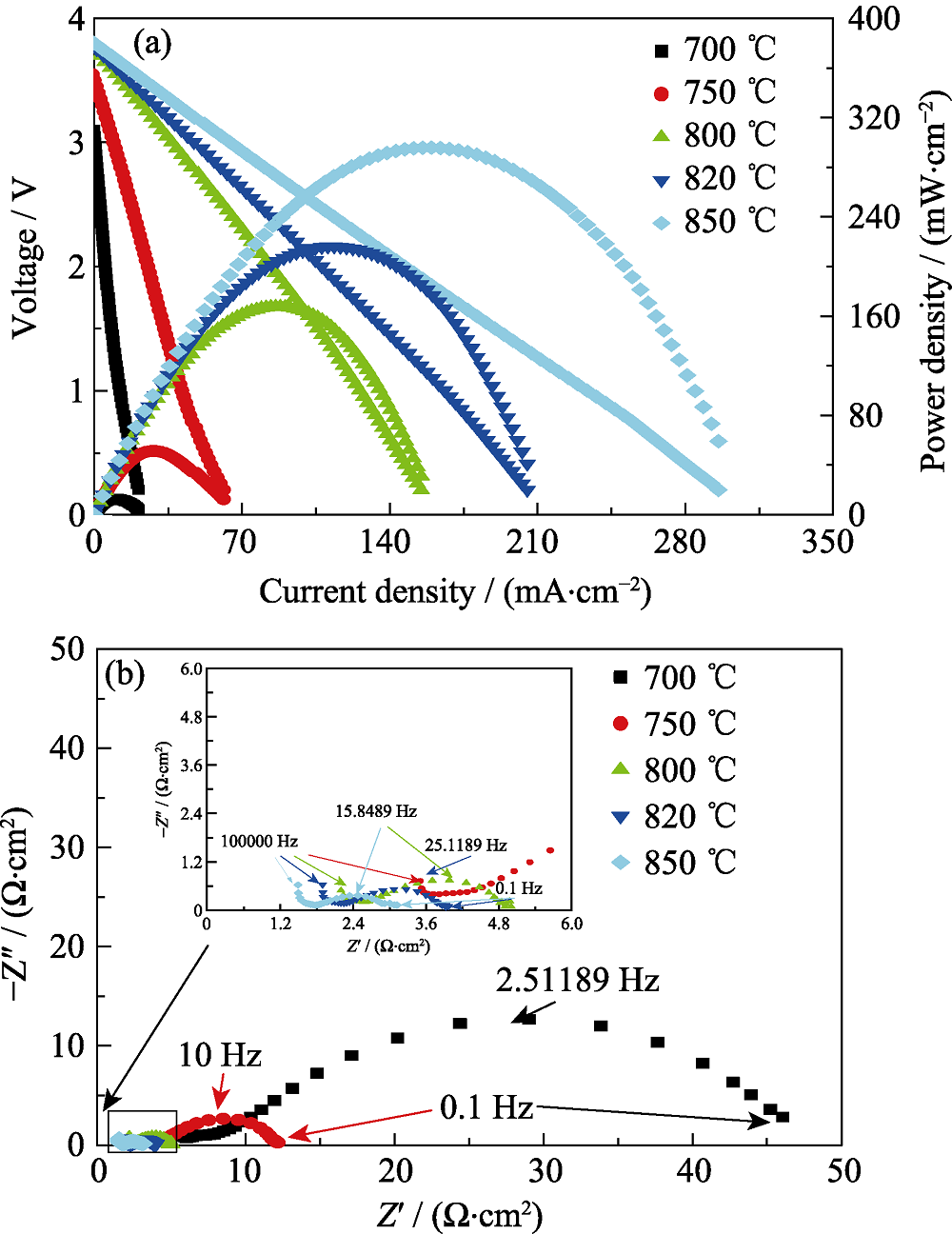
Fig. 5 Output performance (a) and impedance spectra under OCV (b) of 4-cell-stack of DC-SOFC operated at different temperatures with inset showing magnified spectra
| [1] |
LIU J, ZHOU M Y, ZHANG Y P , et al. Electrochemical oxidation of carbon at high temperature: principles and applications. Energ. Fuel, 2018,32:4107-4117.
DOI URL |
| [2] |
CAO T Y, HUANG K, SHI Y X , et al. Recent advances in high-temperature carbon-air fuel cells. Energy Environ. Sci., 2017,10(2):460-490.
DOI URL |
| [3] |
ZHOU Q, CAI W Z, ZHANG Y P , et al. Electricity generation from corn cob char though a direct carbon solid oxide fuel cell. Biomass Bioenerg., 2016,91:250-258.
DOI URL |
| [4] |
WANG X Q, LIU J, XIE Y M , et al. A high performance direct carbon solid oxide fuel cell stack for portable applications. Acta Phys. -Chim. Sin., 2017,33(8):1614-1620.
DOI URL |
| [5] |
TANG Y B, LIU J . Fueling solid oxide fuel cells with activated carbon. Acta Phys. -Chim. Sin., 2010,26(5):1191-1194.
DOI |
| [6] |
TANG Y B, LIU J . Effect of anode and boudouard reaction catalysts on the performance of direct carbon solid oxide fuel cells. Int. J. Hydrog.Energy, 2010,35(20):11188-11193.
DOI URL |
| [7] |
XIE Y M, TANG Y B, LIU J . A verification of the reaction mechanism of direct carbon solid oxide fuel cells.[J]. Solid State Electr., 2012,17(1):121-127.
DOI URL |
| [8] | BAI Y H, LIU Y, TANG Y B , et al. Direct carbon solid oxide fuel cell—a potential high performance battery. Int. J. Hydrog.Energy, 2011,36(15):9189-9194. |
| [9] | JAMES L, ANDREW D . Fuel Cell Systems Explained. Second edition. England: The Atrium, Southern Gate, Chichester, West Sussex PO19 8SQ, 2003: 6-14. |
| [10] | 刘江, 张莉, 刘燕, 苑莉莉 , 一种单片电解质固体氧化物燃料电池组. 中国 CN103956504A. 2014 -04-10. |
| [11] |
YU M X, ZHANG J X, LI X G , et al. Optimization of the tape casting process for development of high performance alumina ceramics. Ceram. Int., 2015,41(10):14845-14853.
DOI URL |
| [12] |
MOON H, KIM S, HYUN S , et al. Development of IT-SOFC unit cells with anode-supported thin electrolytes via tape casting and co-firing. Int. J. Hydrog.Energy, 2008,33(6):1758-1768.
DOI URL |
| [13] |
HOWATT G N, BREEKENRIDGE R G, BROWNLOW J M . Fabrication of thin ceramic sheets for capacitors.[J]. Am. Ceram. Soc., 1947,30(8):237-242.
DOI URL |
| [14] | LEE S, LEE K, JANG Y H , et al. Fabrication of solid oxide fuel cells (SOFCs) by solvent-controlled co-tape casting technique. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy, 2017,42(3):1648-1660. |
| [15] |
LOEY A, SALAM R D M, HUGH ROBERTSON . Pyrolysis of polyvinyl butyral (PVB) binder in thermoelectric green tapes. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc., 2000,20:1375-1383.
DOI URL |
| [16] |
HEDAYAT N, PANTHI D, DU Y . Fabrication of tubular solid oxide fuel cells by solvent-assisted lamination and co-firing a rolled multilayer tape cast. Int.[J]. Appl. Ceram. Tec., 2018,15(2):307-314.
DOI URL |
| [17] |
ALBANO M P, GARRIDO L B . Aqueous tape casting of yttria stabilized zirconia. Mater. Sci. Eng.,A, 2006,420(1/2):171-178.
DOI URL |
| [18] | MISTLER R E, TWINAME E R . Tape Casting: Theory and Practice. America: The American Ceramic Society, 2000: 37-39. |
| [19] |
MICH LEK M, BLUGAN G, GRAULE T , et al. Comparison of aqueous and non-aqueous tape casting of fully stabilized ZrO2 suspensions. Powder Technol., 2015,274:276-283.
DOI URL |
| [20] |
CEYLAN A, SUVACI E, MANDAL H . Role of organic additives on non-aqueous tape casting of Sialon ceramics.[J]. Eur. Ceram. Soc., 2011,31(1/2):167-173.
DOI URL |
| [21] |
WANG C C, LUO L H, WU Y F , et al. A novel multilayer aqueous tape casting method for anode-supported planar solid oxide fuel cell. Mater. Lett., 2011,65(14):2251-2253.
DOI URL |
| [22] |
NISHIHORA R K, RACHADEL P L, QUADRI M G N , et al. Manufacturing porous ceramic materials by tape casting—a review.[J]. Eur. Ceram. Soc., 2018,38(4):988-1001.
DOI URL |
| [23] |
CAI W Z, ZHOU Q, XIE Y M , et al. A facile method of preparing Fe-loaded activated carbon fuel for direct carbon solid oxide fuel cells. Fuel, 2015,159:887-893.
DOI URL |
| [24] |
CAI W Z, LIU J, XIE Y M , et al. An investigation on the kinetics of direct carbon solid oxide fuel cells.[J]. Solid State Electr., 2016,20(8):2207-2216.
DOI URL |
| [25] | JOON H K, GYEONG M C . Mixed ionic and electronic conductivity of [(ZrO2)0.92(Y2O3)0.08]1-y(MnO1.5)y. Solid State Ionics, 2000,130:157-168. |
| [26] |
LI X N, LIANG J W, HOU Z G , et al. The design of a high-energy Li-ion battery using germanium-based anode and LiCoO2 cathode.[J]. Power Sources, 2015,293:868-875.
DOI URL |
| [1] | CHAI Runyu, ZHANG Zhen, WANG Menglong, XIA Changrong. Preparation of Ceria Based Metal-supported Solid Oxide Fuel Cells by Direct Assembly Method [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(7): 765-771. |
| [2] | QU Jifa, WANG Xu, ZHANG Weixuan, ZHANG Kangzhe, XIONG Yongheng, TAN Wenyi. Enhanced Sulfur-resistance for Solid Oxide Fuel Cells Anode via Doping Modification of NaYTiO4 [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(5): 489-496. |
| [3] | XUE Ke, CAI Changkun, XIE Manyi, LI Shuting, AN Shengli. Pr1+xBa1-xFe2O5+δ Cathode Materials for Solid Oxide Fuel Cells: Preparation and Electrochemical Performance [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(4): 363-371. |
| [4] | ZHANG Jinghui, LU Xiaotong, MAO Haiyan, TIAN Yazhou, ZHANG Shanlin. Effect of Sintering Additives on Sintering Behavior and Conductivity of BaZr0.1Ce0.7Y0.2O3-δ Electrolytes [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(1): 84-90. |
| [5] | PAN Jianlong, MA Guanjun, SONG Lemei, HUAN Yu, WEI Tao. High Stability/Catalytic Activity Co-based Perovskite as SOFC Anode: In-situ Preparation by Fuel Reducing Method [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(8): 911-919. |
| [6] | YE Zibin, ZOU Gaochang, WU Qiwen, YAN Xiaomin, ZHOU Mingyang, LIU Jiang. Preparation and Performances of Tubular Cone-shaped Anode-supported Segmented-in-series Direct Carbon Solid Oxide Fuel Cell [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(7): 819-827. |
| [7] | ZHANG Kun, WANG Yu, ZHU Tenglong, SUN Kaihua, HAN Minfang, ZHONG Qin. LaNi0.6Fe0.4O3 Cathode Contact Material: Electrical Conducting Property Manipulation and Its Effect on SOFC Electrochemical Performance [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(4): 367-373. |
| [8] | CHEN Zhengpeng, JIN Fangjun, LI Mingfei, DONG Jiangbo, XU Renci, XU Hanzhao, XIONG Kai, RAO Muming, CHEN Chuangting, LI Xiaowei, LING Yihan. Double Perovskite Sr2CoFeO5+δ: Preparation and Performance as Cathode Material for Intermediate-temperature Solid Oxide Fuel Cells [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(3): 337-344. |
| [9] | XUE Dingxi, YI Bingyao, LI Guojun, MA Shuai, LIU Keqin. Numerical Simulation of Thermal Stress in Solid Oxide Fuel Cells with Functional Gradient Anode [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(11): 1189-1196. |
| [10] | GUO Tianmin, DONG Jiangbo, CHEN Zhengpeng, RAO Mumin, LI Mingfei, LI Tian, LING Yihan. Enhanced Compatibility and Activity of High-entropy Double Perovskite Cathode Material for IT-SOFC [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(6): 693-700. |
| [11] | FAN Shuai, JIN Tian, ZHANG Shanlin, LUO Xiaotao, LI Chengxin, LI Changjiu. Effect of Li2O Sintering Aid on Sintering Characteristics and Electrical Conductivity of LSGM Electrolyte for Solid Oxide Fuel Cell [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(10): 1087-1092. |
| [12] | ZHENG Qifan, LI Chaoqun, BAN Xiaokuan, ZHAN Zhongliang, CHEN Chusheng. Preparation and Property of GDC-LSF Dual-phase Composite Membrane with Straight Pores and Sandwich Structure [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(5): 497-501. |
| [13] | CAO Dan,ZHOU Mingyang,LIU Zhijun,YAN Xiaomin,LIU Jiang. Fabrication and Characterization of Anode-supported Solid Oxide Fuel Cell Based on Proton Conductor Electrolyte [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2020, 35(9): 1047-1052. |
| [14] | XIA Tian, MENG Xie, LUO Ting, ZHAN Zhongliang. La 3+-substituted Sr2Fe1.5Ni0.1Mo0.4O6-δ as Anodes for Solid Oxide Fuel Cells [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2020, 35(5): 617-622. |
| [15] | Kai LI, Xiao LI, Jian LI, Jia-Miao XIE. Structural Stability of Ni-Fe Supported Solid Oxide Fuel Cells Based on Stress Analysis [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2019, 34(6): 611-617. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||