
Journal of Inorganic Materials ›› 2016, Vol. 31 ›› Issue (8): 834-840.DOI: 10.15541/jim20150611
• Orginal Article • Previous Articles Next Articles
SUN Li-Li1, YAN Kai1, LUO Wen2, ZHOU Jian3
Received:2015-12-03
Revised:2016-02-17
Published:2016-08-20
Online:2016-07-20
About author:SUN Li-Li. E-mail: 147393766@qq.com
CLC Number:
SUN Li-Li, YAN Kai, LUO Wen, ZHOU Jian. Hollow ZSM-5 Zeolite Microspheres with Improved Adsorption and
Catalytic Properties[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2016, 31(8): 834-840.
| Sample | Al contenta /% | SBETb/ (m2·g-1) | Smesoc/ (m2·g-1) | Vpored/ (cm3·g-1) | Vmesoc/ (cm3·g-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ZS | 1.74 | 347 | 152 | 0.21 | 0.09 |
| HZS | 2.01 | 335 | 167 | 0.37 | 0.29 |
Table1 Textural and structural properties of zeolite spheres(ZS) and hollow zeolite spheres(HZS)
| Sample | Al contenta /% | SBETb/ (m2·g-1) | Smesoc/ (m2·g-1) | Vpored/ (cm3·g-1) | Vmesoc/ (cm3·g-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ZS | 1.74 | 347 | 152 | 0.21 | 0.09 |
| HZS | 2.01 | 335 | 167 | 0.37 | 0.29 |
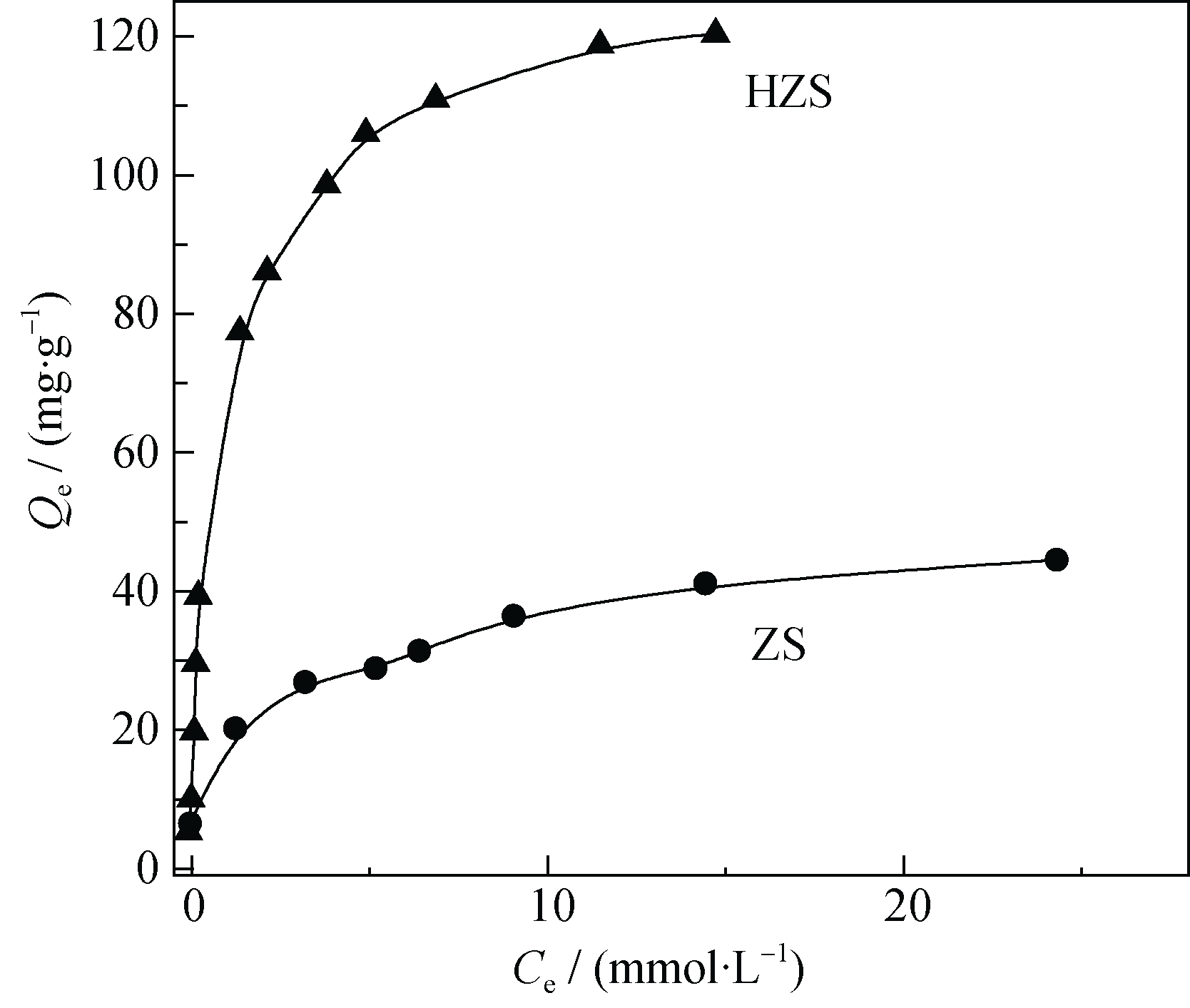
Fig. 6 Adsorption isotherms of benzene by zeolite spheres (ZS) and hollow zeolite spheres (HZS). Ce is the equilibrium concentration in the benzene/methanol solution and Qe is the amount of benzene adsorbed at equilibrium concentration
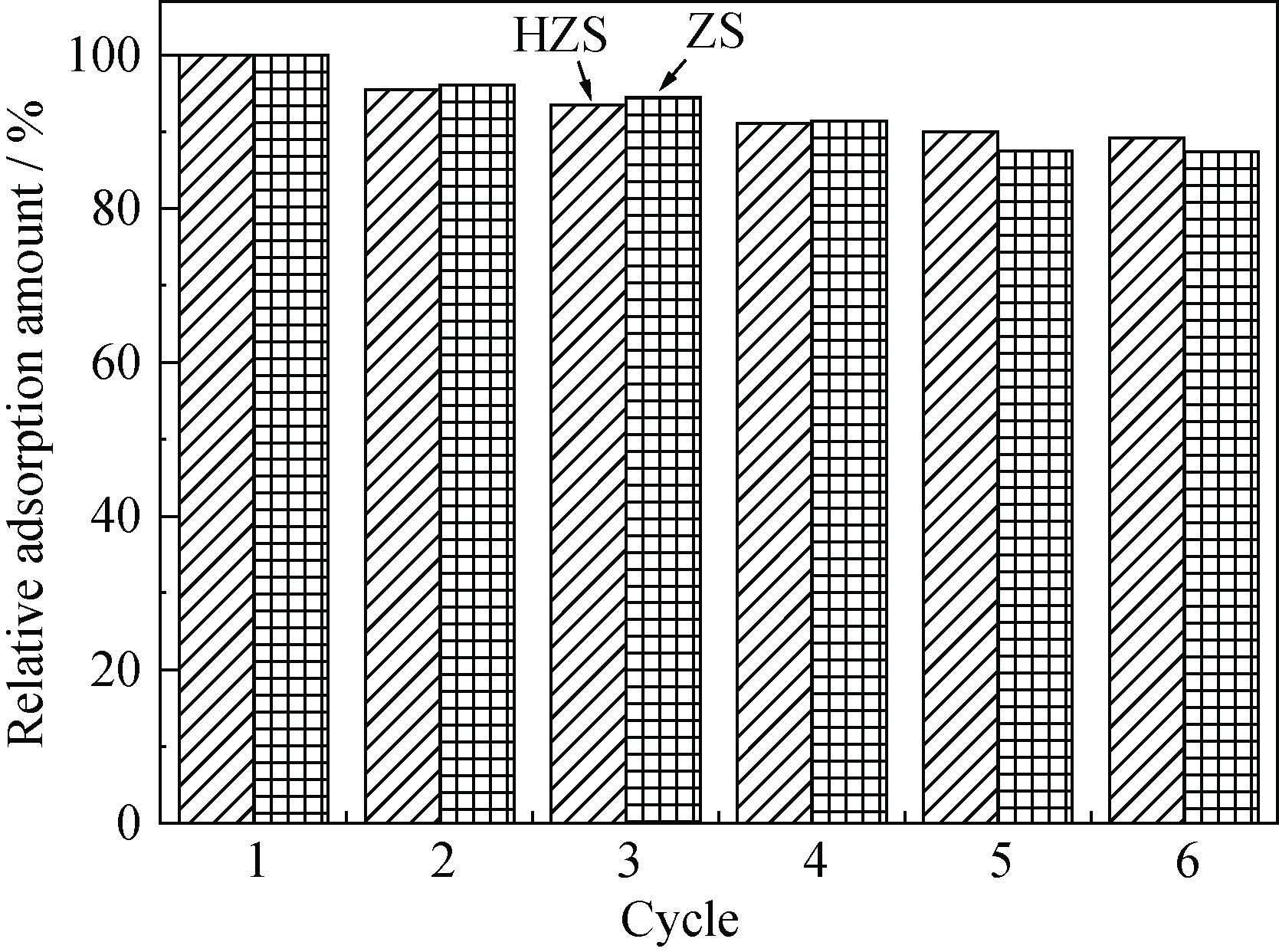
Fig. 7 Adsorption stability testing results of zeolite spheres (ZS) and hollow zeolite spheres (HZS). Relative adsorption amount is the ratio of adsorption amount in the single cycle to the adsorption amount in the first cycle
| Reaction | Conversion in cumene cracking /% | Conversion in triisopropylbenzene cracking /% | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Catalyst | ZS | HZS | ZS | HZS |
| 573 K | 55.1 | 66.9 | 12.6 | 34.8 |
| 623 K | 72.6 | 80.2 | 27.6 | 50.0 |
| 673 K | 82.7 | 90.0 | 39.9 | 61.1 |
| 723 K | 88.8 | 94.3 | 51.0 | 72.5 |
| 773 K | 92.2 | 97.3 | 61.0 | 78.4 |
Table2 Catalytic properties of zeolite spheres (ZS) and hollow zeolite spheres (HZS) in cracking reaction
| Reaction | Conversion in cumene cracking /% | Conversion in triisopropylbenzene cracking /% | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Catalyst | ZS | HZS | ZS | HZS |
| 573 K | 55.1 | 66.9 | 12.6 | 34.8 |
| 623 K | 72.6 | 80.2 | 27.6 | 50.0 |
| 673 K | 82.7 | 90.0 | 39.9 | 61.1 |
| 723 K | 88.8 | 94.3 | 51.0 | 72.5 |
| 773 K | 92.2 | 97.3 | 61.0 | 78.4 |
| Reaction | Selectivity of benzene: isopropylbenzene: diisopropylbenzene | |
|---|---|---|
| Catalyst | ZS | HZS |
| 300 | 11: 20: 69 | 13: 23: 64 |
| 350 | 15: 18: 67 | 16: 22: 62 |
| 400 | 19: 19: 62 | 19: 24: 57 |
| 450 | 22: 25: 55 | 25: 26: 49 |
| 500 | 28: 30: 42 | 28: 33: 39 |
Table3 Selectivity of products by zeolite spheres (ZS) and hollow zeolite spheres (HZS) in cracking reaction of TIPB
| Reaction | Selectivity of benzene: isopropylbenzene: diisopropylbenzene | |
|---|---|---|
| Catalyst | ZS | HZS |
| 300 | 11: 20: 69 | 13: 23: 64 |
| 350 | 15: 18: 67 | 16: 22: 62 |
| 400 | 19: 19: 62 | 19: 24: 57 |
| 450 | 22: 25: 55 | 25: 26: 49 |
| 500 | 28: 30: 42 | 28: 33: 39 |
| [1] | BAO Y, YANG Y, MA J.Research progress of hollow structural materials prepared via templating method.Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2013, 28(5): 459-468. |
| [2] | CAO F, LI D, WU Z, et al.Research progress on the preparation technique of hollow inorganic micropores.Bulletin of the Chinese ceramic society, 2014, 33(2): 821-825. |
| [3] | SHI J, CHEN Y, CHEN H.Progress on the multifunctional mesoporous silica-based nanotheranostics.Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2013, 28(1): 1-11. |
| [4] | YU J G, GUO H T, DAVIS S A, et al.Fabrication of holloew inorganic microapheres by chemically induced sell-trams for mationAdvanced Functional Materials, 2006, 16(15): 2035-2041. |
| [5] | CAO F, LI D, GUAN Z.Preparation of silica hollow microshperes with special surface morphology by biotemplate method.Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2009, 24(3): 501-506. |
| [6] | XIONG Y J, WILEY B, CHEN J Y, et al.Corrosion-based synthesis of single-crystal Pd nanoboxes and nanocages and their surface plasmon properties.Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2005, 44(48): 7913-7917. |
| [7] | ZHANG L D, FANG M.Nanomaterials in pollution trace detection and environmental improvement.Nano Today, 2010, 5(2): 128-142. |
| [8] | ZHAO Y, JIANG L.Hollow micro/Nanomaterials with multilevel interior structures.Advanced Materials, 2009, 21(36): 3621-3638. |
| [9] | XU R, PANG W, YU J, et al.Zeolite and Porous Materials Chemistry. Science Press, 2004: 13-18. |
| [10] | CARUSO F.Hollow capsule processing through colloidal templating and self-assembly.Chemistry-A European Journal, 2000, 6(3): 413-419. |
| [11] | VALTCHEV V, MINTOVA S.Layer-by-layer preparation of zeolite coatings of nanosized crystals,Microporous and Mesoporous Materials, 2001, 43(1): 41-49. |
| [12] | CHU N B, WANG J Q, ZHANG Y, et al.Nestlike hollow hierarchical MCM-22 microspheres: synthesis and exceptional catalytic properties.Chemical Materials, 2010, 22(9): 2757-2763. |
| [13] | DONG A G, WANG D J, TANG Y.Hollow zeolite capsules: a novel approach for fabrication and guest encapsulation.Chemical Materials, 2002, 14(8): 3217-3219. |
| [14] | REN N, YANG Y H, SHEN J.Novel, efficient hollow zeolitically microcapsulized noble metal catalysts.Journal of Catalysis, 2007, 251(1): 182-188. |
| [15] | MEI C S, LIU Z C, WEN P Y, et al.Regular HZSM-5 microboxes prepared via a mild alkaline treatment.Journal of Material Chemistry, 2008, 18(29): 3496-3500. |
| [16] | GROEN J C, BACH T, ZIESE U, et al.Creation of hollow zeolite arthitetures by controlled desilication of alzoned ZSM-5 crystalsJournal of the American Chemical Society, 2005, 127: 10792-10793. |
| [17] | DAI C Y, ZHANG A F, GUO X W, et al.Synthesis of hollow nanocubes and macroporous monoliths of silicalite-1 by alkaline Treatment.Chemical Materials, 2013, 25(21): 4197-4205. |
| [18] | WANG Y R, TUEL A.Nanoporous zeolite single crystals: ZSM-5 nanoboxes with uniform intracrystalline hollow structures.Microporous and Mesoporous Materials, 2008(113): 286-295. |
| [19] | LI S W, TUEL A, LAPRUNE D, et al.Transition-metal nanoparticles in hollow zeolite single crystals as bifunctional and size-selective hydrogenation Catalysts.Chemical Materials, 2015, 27: 276-282. |
| [20] | ZUO Y, SONG W C, GUO X W, et al. Modification of small-crystal titanium silicalite-1 with organic bases: recrystallization and catalytic properties in the hydroxylation of phenol.Applied Catalysis A: General, 453: 272-279. |
| [21] | FODOR D, PACOSOVA L, VAN BOKHOVEN J A, et al. Facile synthesis of nano-sized hollow single crystal zeolites under mild conditions.Chemical Communications, 2014, 50: 76-78. |
| [22] | AN J, GAO X, LI Y, et al.Mesoporous zeolite ZSM-5 synthesized via gel conversion with polyethyleneglycol as template and its catalytic performance. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2015, 30(3): 1148-1154. |
| [23] | VON BALLMOOS R, MEIER W M.Zoned aluminium distribution in synthetic zeolite ZSM-5.Nature, 1981, 289: 782. |
| [24] | ZHOU J, HUA Z, WU W, et al.Hollow mesoporous zeolite microshperes: hierarchical macro-/meso-/microporous structure and exceptionally enhanced adsorption properties.Dalton Transactions, 2011, 40: 12667-12669. |
| [25] | TU W.Progress on the high concentration organic wastewater treatment technology. Science and Technology Innovation, 2014, 14: 153-154. |
| [26] | ZHAO Y, SUN Y, WANG H, et al.The application of hollow microshperes. Science & Technology in Chemical Industry, 2014, 22(5): 68-72. |
| [27] | WANG H, ZHOU W, LINGHU W.Adsorption of terephthalic acid waste water over activated carbon. Hebei Chemical Engineering and Industry, 2009, 32(4): 74-76. |
| [28] | XIE Z, CHEN Z, DAI Y.Preparation of sepiolite complex sorbent and its treatment properties for dyeing wastewater. Environmental Science & Technology, 2009, 32(2): 130-133. |
| [1] | WEI Jianwen, ZHANG Lijuan, GENG Linlin, LI Yu, LIAO Lei, WANG Dunqiu. Novel CO2 Adsorbent Prepared with ZSM-5/MCM-48 as Support: High Adsorption Property and Its Mechanism [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(7): 833-839. |
| [2] | JIANG Zongyu, HUANG Honghua, QING Jiang, WANG Hongning, YAO Chao, CHEN Ruoyu. Aluminum Ion Doped MIL-101(Cr): Preparation and VOCs Adsorption Performance [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(7): 747-753. |
| [3] | HONG Peiping, LIANG Long, WU Lian, MA Yingkang, PANG Hao. Structure Regulation of ZIF-67 and Adsorption Properties for Chlortetracycline Hydrochloride [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(4): 388-396. |
| [4] | WU Guangyu, SHU Song, ZHANG Hongwei, LI Jianjun. Enhanced Styrene Adsorption by Grafted Lactone-based Activated Carbon [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(4): 390-398. |
| [5] | XIE Tian, SONG Erhong. Effect of Elastic Strains on Adsorption Energies of C, H and O on Transition Metal Oxides [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(11): 1292-1300. |
| [6] | CHAO Shaofei, XUE Yanhui, WU Qiong, WU Fufa, MUHAMMAD Sufyan Javed, ZHANG Wei. Efficient Potassium Storage through Ti-O-H-O Electron Fast Track of MXene Heterojunction [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(11): 1212-1220. |
| [7] | DING Ningning, SUN Jianhua, WEI Xu, SUN Lixia. Monitoring Ammonia at Room Temperature of p-Aminobenzene Sulfonic Acid Modified MoO3/PPy Composites [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(11): 1245-1253. |
| [8] | MA Xiaosen, ZHANG Lichen, LIU Yanchao, WANG Quanhua, ZHENG Jiajun, LI Ruifeng. 13X@SiO2: Synthesis and Toluene Adsorption [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(5): 537-543. |
| [9] | GUO Chunxia, CHEN Weidong, YAN Shufang, ZHAO Xueping, YANG Ao, MA Wen. Adsorption of Arsenate in Water by Zirconia-halloysite Nanotube Material [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(5): 529-536. |
| [10] | WANG Shiyi, FENG Aihu, LI Xiaoyan, YU Yun. Pb (II) Adsorption Process of Fe3O4 Supported Ti3C2Tx [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(5): 521-528. |
| [11] | YU Yefan, XU Ling, NI Zhongbing, SHI Dongjian, CHEN Mingqing. Prussian Blue Modified Biochar: Preparation and Adsorption of Ammonia Nitrogen from Sewage [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(2): 205-212. |
| [12] | LING Jie, ZHOU Anning, WANG Wenzhen, JIA Xinyu, MA Mengdan. Effect of Cu/Mg Ratio on CO2 Adsorption Performance of Cu/Mg-MOF-74 [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(12): 1379-1386. |
| [13] | TANG Ya, SUN Shengrui, FAN Jia, YANG Qingfeng, DONG Manjiang, KOU Jiahui, LIU Yangqiao. PEI Modified Hydrated Calcium Silicate Derived from Fly Ash and Its adsorption for Removal of Cu (II) and Catalytic Degradation of Organic Pollutants [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(11): 1281-1291. |
| [14] | DAI Jieyan, FENG Aihu, MI Le, YU Yang, CUI Yuanyuan, YU Yun. Adsorption Mechanism of NaY Zeolite Molecular Adsorber Coating on Typical Space Contaminations [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(10): 1237-1244. |
| [15] | WANG Hongning, HUANG Li, QING Jiang, MA Tengzhou, HUANG Weiqiu, CHEN Ruoyu. Mesoporous Organic-inorganic Hybrid Siliceous Hollow Spheres: Synthesis and VOCs Adsorption [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(9): 991-1000. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||