
Journal of Inorganic Materials ›› 2016, Vol. 31 ›› Issue (3): 305-310.DOI: 10.15541/jim20150390
• RESEARCH PAPER • Previous Articles Next Articles
WANG Feng1,3( ), GAO Zhao-Fen2, XU Jia-Qiang1, ZENG Yu-Ping3(
), GAO Zhao-Fen2, XU Jia-Qiang1, ZENG Yu-Ping3( )
)
Received:2015-08-20
Revised:2015-11-03
Published:2016-03-20
Online:2016-02-24
CLC Number:
WANG Feng, GAO Zhao-Fen, XU Jia-Qiang, ZENG Yu-Ping. Porous SiC Ceramics with Multiple Pore Structure Fabricated via Gelcasting and Solid State Sintering[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2016, 31(3): 305-310.
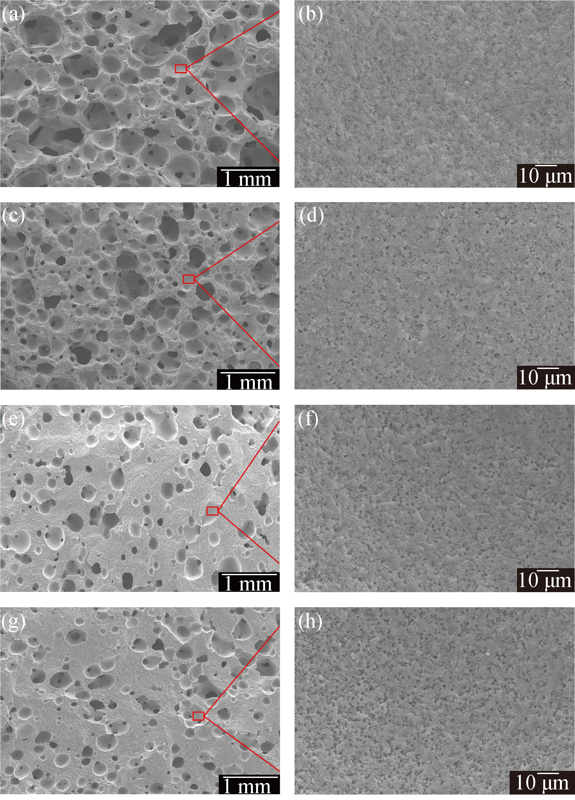
Fig. 2 Fracture surface microstructures of porous SiC ceramics with different PMMA contents, fabricated at rotation speed of 220 r/min and sintered at 2100℃(a, b) 5wt%; (c, d) 10wt%; (e, f) 15wt%; (g, h) 20wt%
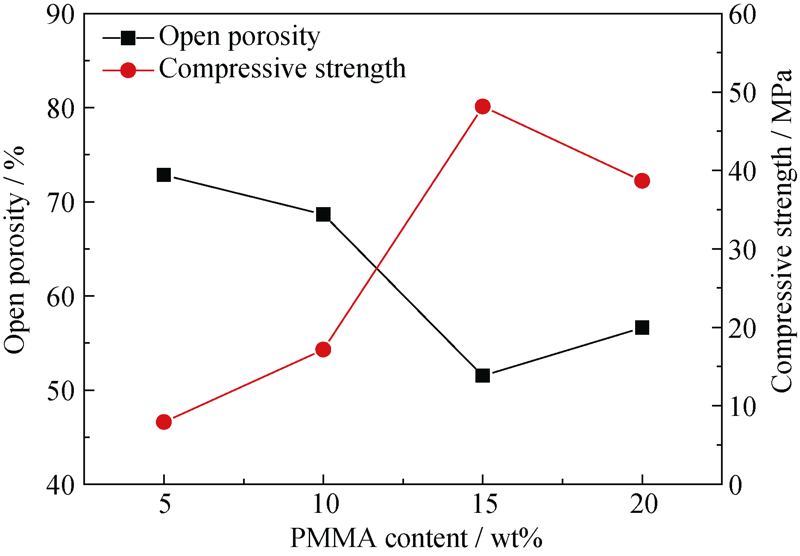
Fig. 3 Porosities and mechanical properties of porous SiC ceramics with different PMMA contents, fabricated at rotation speed of 220 r/min and sintered at 2100℃
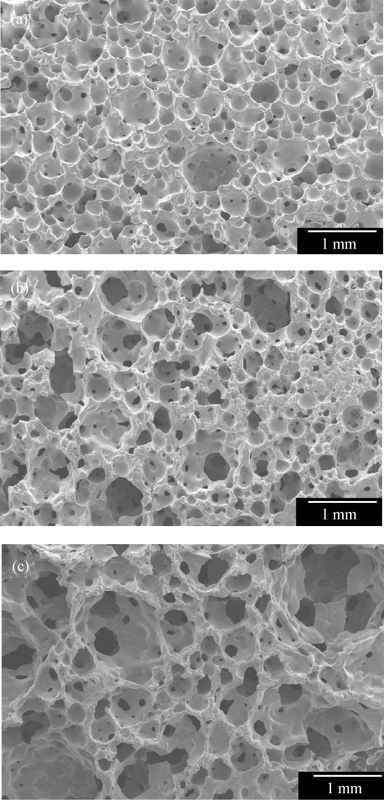
Fig. 4 Fracture surface microstructure of porous SiC ceramics with 20wt% PMMA fabricated at different rotation speeds and sintered at 2100℃ (a) 240 r/min; (b) 260 r/min; (c) 280 r/min
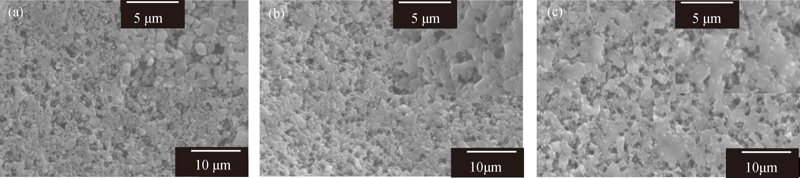
Fig. 6 Fracture surface microstructures of porous SiC ceramics with 20wt% PMMA sintered at different temperatures, fabricated at rotation speed of 220 r/min(a) 2050℃; (b) 2100℃; (c) 2150℃
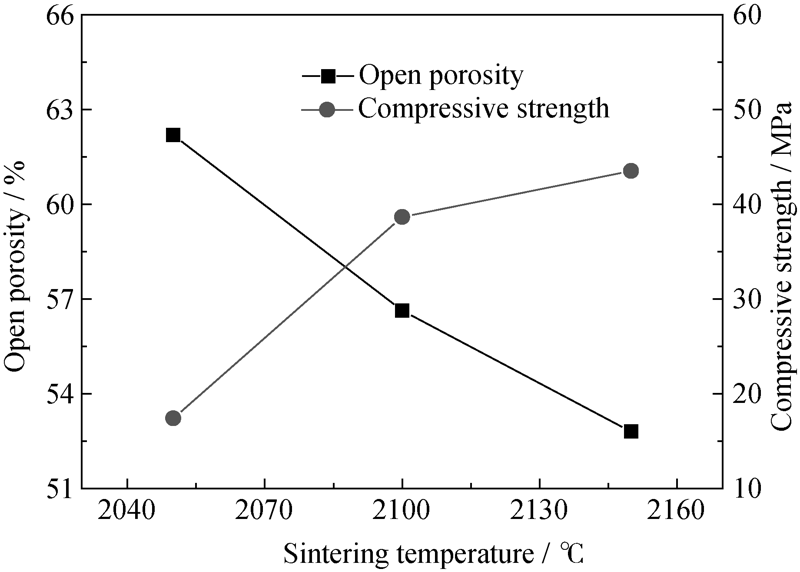
Fig. 7 Porosities and mechanical properties of porous SiC ceramics with 20wt% PMMA sintered at different temperatures, fabricated at rotation speed of 220 r/min
| [1] | KIM YOUNG-WOOK, Y S C, TOSHIYUKI NISHIMURA, et al. High-temperature strength of silicon carbide ceramics sintered with rare-earth oxide and aluminum nitride. Acta Materialia, 2007, 55(2): 727-736. |
| [2] | DING SHUQIANG, ZENG YUPING, JIANG DONGLIANG.Thermal shock resistance ofin situ reaction bonded porous silicon carbide ceramics. Materials Science and Engineering: A, 2006, 425(1/2): 326-329. |
| [3] | ALVIN M.Impact of char and ash fines on porous ceramic filter life.Fuel Processing Technology, 1998, 56(1/2): 143-168. |
| [4] | KELLER N, PHAM-HUU C, ROY S, et al. Influence of the preparation conditions on the synthesis of high surface area SiC for use as a heterogeneous catalyst support. Journal of Materials Science. 1999, 34(13): 3189-3202. |
| [5] | PIRJO PASTILA, VESA HELANTI, ANTTI-PEKKA NIKKILÄ, et al. Environmental effects on microstructure and strength of SiC-based hot gas filters. Journal of European Ceramic Society, 2001, 21(9): 1261-1268. |
| [6] | DONG A, WANG Y, TANG Y, et al. Zeolitic tissue through wood cell templating. Advanced Materials, 2002, 14(12): 926-929. |
| [7] | SHIN YONGSOON, LIU JUN, WANG LI-QIONG, et al. Ordered hierarchical porous materials: towards tunable size- and shape- selective microcavities in nanoporous channels. Angewandte Chemie, 2000, 112(15): 2814-2819. |
| [8] | DESHPANDE A S, BURGERT I, PARIS O.Hierarchically structured ceramics by high-precision nanoparticte casting of wood.Small, 2006, 2(8/9): 994-998. |
| [9] | LIU SHIFENG, ZENG YUPING, DONGLIANG JIANG.Fabrication and characterization of cordierite-bonded porous SiC ceramics.Ceramics International, 2009, 35(2): 597-602. |
| [10] | BAUD S, THÉVENOT F, PISCH A, et al. High temperature sintering of SiC with oxide additives: I. Analysis in the SiC-Al2O3 and SiC-Al2O3-Y2O3 systems. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2003. 23(1): 1-8. |
| [11] | BAUD S, THÉVENOT F, CHATILLON C. High temperature sintering of SiC with oxide additives II. Vaporization processes in powder beds and gas.Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2003, 23(1): 9-18. |
| [12] | BAUD S, THÉVENOT F, CHATILLON C. High temperature sintering of SiC with oxide additives III. Quantitative vaporization of SiC-Al2O3 powder beds.Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2003, 23(1): 19-27. |
| [13] | DARIN A, RAY S K, RAYMOND A CUTLER, et al. Effect of additives on the activation energy for sintering of silicon carbide. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2008, 91(4): 1135-1140. |
| [14] | YOUNG ALBERT C, OMATETE OGBEMI O, JANNEY MARK A, et al. Gelcasting of alumina. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 1991, 74(3): 612-618. |
| [15] | OGBEMI O OMATETE, MARK A JANNEY, STEPHEN D NUNN.Gelcasting: from laboratory development toward industrial production.Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 1997, 17(2/3): 407-413. |
| [16] | YANG YAN, WANG SHI-WEI.Room temperature gelcasting of alumina with a water-soluble copolymer.Journal of Materials Research, 2013, 28(11): 1512-1516. |
| [17] | SUN YI, SHIMAI SHUNZO, PENG XIANG, et al. Fabrication of transparent Y2O3 ceramics via aqueous gelcasting. Ceramics International, 2014, 40(6): 8841-8845. |
| [18] | QIN XIAN-PENG, ZHOU GUO-HONG, YANG YAN, et al. Gelcasting of transparent YAG ceramics by a new gelling system. Ceramics International, 2014, 40(8): 12745-12750. |
| [19] | WANG JUN, ZHANG FANG, CHEN FENG, et al. Fabrication of aluminum oxynitride(γ-AlON) transparent ceramics with modified gelcasting. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2014, 97(5): 1353-1355. |
| [20] | WAN TAO, YAO DONGXU, HU HAILONG, et al. Fabrication of porous Si3N4 ceramics through a novel gelcasting method. Materials Letters, 2014, 133(10): 190-192. |
| [21] | URS T GONZENBACH, ANDRÉ R STUDART, ELENA TERVOORT, et al. Tailoring the microstructure of particle-stabilized wet foams. Langmuir, 2007, 23(3): 1025-1032. |
| [22] | CHRISTOPHE SCHMITT, CLAUDINE BOVAY, MARTINE ROUVET.Bulk self-aggregation drives foam stabilization properties of whey protein microgels.Food Hydrocolloids, 2014, 42(1): 139-148. |
| [23] | LESOV I, TCHOLAKOVA S, DENKOV N.Factors controlling the formation and stability of foams used as precursors of porous materials, Journal of Colloid & Interface Science, 2014, 426(27): 9-21. |
| [1] | WANG Lujie, ZHANG Yuxin, LI Tongyang, YU Yuan, REN Pengwei, WANG Jianzhang, TANG Huaguo, YAO Xiumin, HUANG Yihua, LIU Xuejian, QIAO Zhuhui. Corrosion and Wear Behavior of Silicon Carbide Ceramic in Deep-sea Service Environment [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(7): 799-807. |
| [2] | LI Ziwei, GONG Weilu, CUI Haifeng, YE Li, HAN Weijian, ZHAO Tong. (Zr, Hf, Nb, Ta, W)C-SiC Composite Ceramics: Preparation via Precursor Route and Properties [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(3): 271-280. |
| [3] | WANG Hao, LIU Xuechao, ZHENG Zhong, PAN Xiuhong, XU Jintao, ZHU Xinfeng, CHEN Kun, DENG Weijie, TANG Meibo, GUO Hui, GAO Pan. Performance of Lateral 4H-SiC Photoconductive Semiconductor Switches by Extrinsic Backside Trigger [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(9): 1070-1076. |
| [4] | SUN Chuan, HE Pengfei, HU Zhenfeng, WANG Rong, XING Yue, ZHANG Zhibin, LI Jinglong, WAN Chunlei, LIANG Xiubing. SiC-based Ceramic Materials Incorporating GNPs Array: Preparation and Mechanical Characterization [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(3): 267-273. |
| [5] | NI Xiaoshi, LIN Ziyang, QIN Muyan, YE Song, WANG Deping. Bioactivity and Mechanical Property of PMMA Bone Cement: Effect of Silanized Mesoporous Borosilicate Bioglass Microspheres [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(8): 971-977. |
| [6] | XU Hao, QIAN Wei, HUA Yinqun, YE Yunxia, DAI Fengze, CAI Jie. Effects of Micro Texture Processed by Picosecond Laser on Hydrophobicity of Silicon Carbide [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(8): 923-930. |
| [7] | CHEN Qiang, BAI Shuxin, YE Yicong. Highly Thermal Conductive Silicon Carbide Ceramics Matrix Composites for Thermal Management: a Review [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(6): 634-646. |
| [8] | GU Xuesu, YIN Jie, WANG Kanglong, CUI Chong, MEI Hui, CHEN Zhongming, LIU Xuejian, HUANG Zhengren. Effect of Particle Grading on Properties of Silicon Carbide Ceramics by Binder Jetting Printing [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(12): 1373-1378. |
| [9] | WANG Shiwei. Progress of Spontaneous Coagulation Casting of Ceramic Slurries Based on Hydrophobic Interaction [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(8): 809-820. |
| [10] | OUYANG Qin, WANG Yanfei, XU Jian, LI Yinsheng, PEI Xueliang, MO Gaoming, LI Mian, LI Peng, ZHOU Xiaobing, GE Fangfang, ZHANG Chonghong, HE Liu, YANG Lei, HUANG Zhengren, CHAI Zhifang, ZHAN Wenlong, HUANG Qing. Research Progress of SiC Fiber Reinforced SiC Composites for Nuclear Application [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(8): 821-840. |
| [11] | RUAN Jing, YANG Jinshan, YAN Jingyi, YOU Xiao, WANG Mengmeng, HU Jianbao, ZHANG Xiangyu, DING Yusheng, DONG Shaoming. Porous SiC Ceramic Matrix Composite Reinforced by SiC Nanowires with High Strength and Low Thermal Conductivity [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(4): 459-466. |
| [12] | LUO Qing,YUAN Qing,JIANG Qian-Qin,YU Nai-Sen. Cu-SSZ-13/SiC-waste Composite: Synthesis and Application for NH3-SCR [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2019, 34(9): 953-960. |
| [13] | XIE Yu-Zhou, PENG Chao-Qun, WANG Xiao-Feng, WANG Ri-Chu, LUO Feng. Porous Alumina Ceramic Prepared by HEMA-TBA Gelcasting System [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2017, 32(7): 731-738. |
| [14] | WU Ying-Ying, YE Song,YAO Ai-Hua, LI Hai-Bin, JIA Wei-Tao, HUANG Wen-Hai, WANG De-Ping. Effect of Gas-foaming Porogen-NaHCO3 and Citric Acid on the Properties of Injectable Macroporous Borate Bioactive Glass Cement [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2017, 32(7): 777-784. |
| [15] | HE Fei, LI Ya, LUO Jin, FANG Min-Han, HE Xiao-Dong. Development of SiO2/C and SiC/C Composites Featuring Aerogel Structures [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2017, 32(5): 449-458. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||