
Journal of Inorganic Materials ›› 2012, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (4): 411-416.DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1077.2012.00411
• Orginal Article • Previous Articles Next Articles
DU Ji-Shi, WU Jie-Hua, ZHAO Li-Li, SONG Li-Xin
Received:2011-04-22
Revised:2011-06-04
Published:2012-04-10
Online:2012-03-12
About author:DU Ji-Shi. E-mail: flash6669@student.sic.ac.cn
CLC Number:
DU Ji-Shi, WU Jie-Hua, ZHAO Li-Li, SONG Li-Xin. Coloration of Glasses Induced by Space Ionizing Radiation[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2012, 27(4): 411-416.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
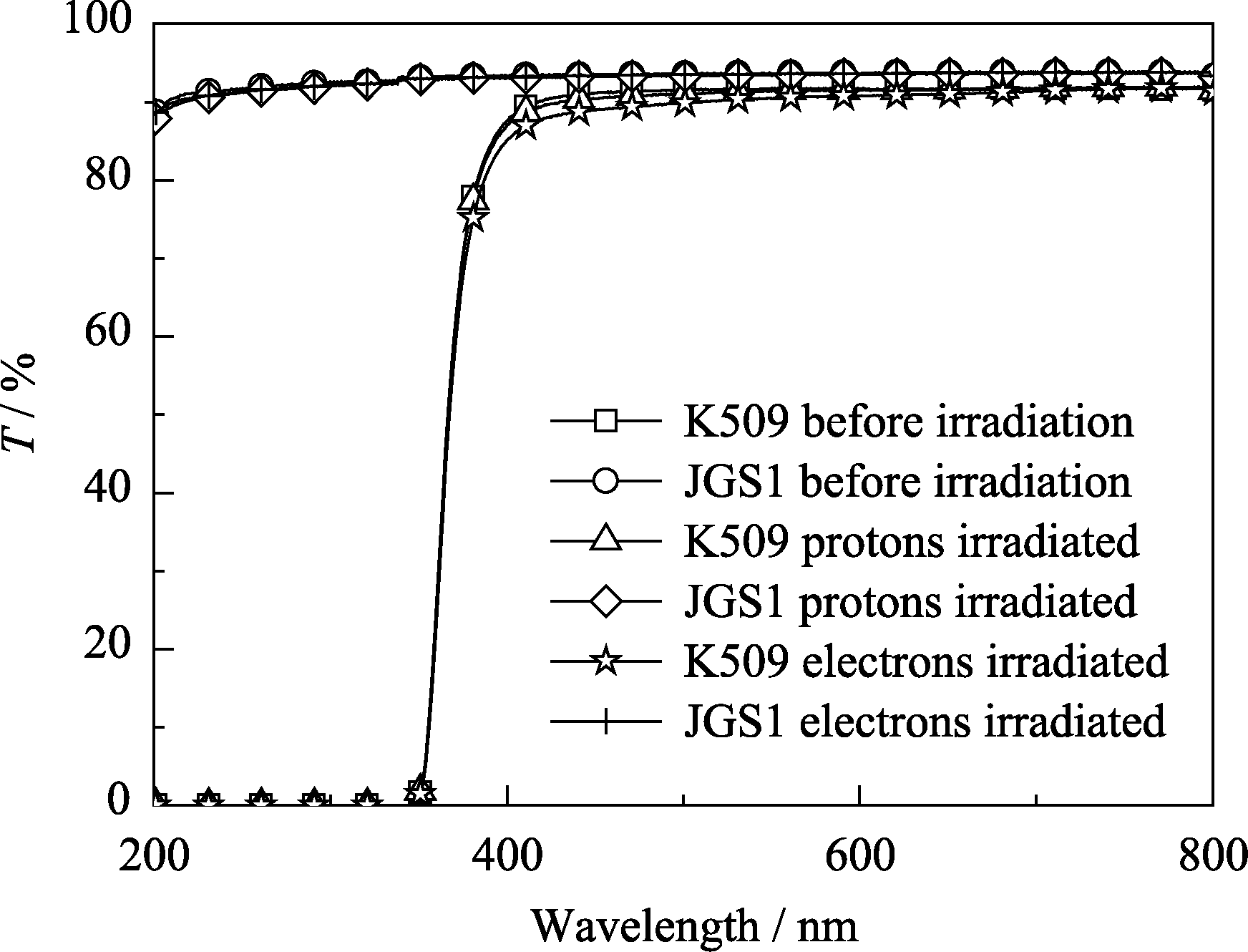
Fig. 3 Transmission Spectra of K509 glass, JGS1 silica glass before and after 1012 proton/cm2 10 MeV proton or 4×1012 electron/cm2 1.85 MeV electron irradiation
| Inclination /(o) | Altitude /km | Measured/AE8 |
|---|---|---|
| <40 | <750 | 2-10, or larger |
| <40 | 750-2000 | 2-10 |
| >40 | 300-750 | 0.5-1.5 |
| >40 | 750-2000 | 1-2 |
Table 1 Measured to predicted electron absorbed dose ratio based on satellite data and AE8 trapped electron model[12-13]
| Inclination /(o) | Altitude /km | Measured/AE8 |
|---|---|---|
| <40 | <750 | 2-10, or larger |
| <40 | 750-2000 | 2-10 |
| >40 | 300-750 | 0.5-1.5 |
| >40 | 750-2000 | 1-2 |
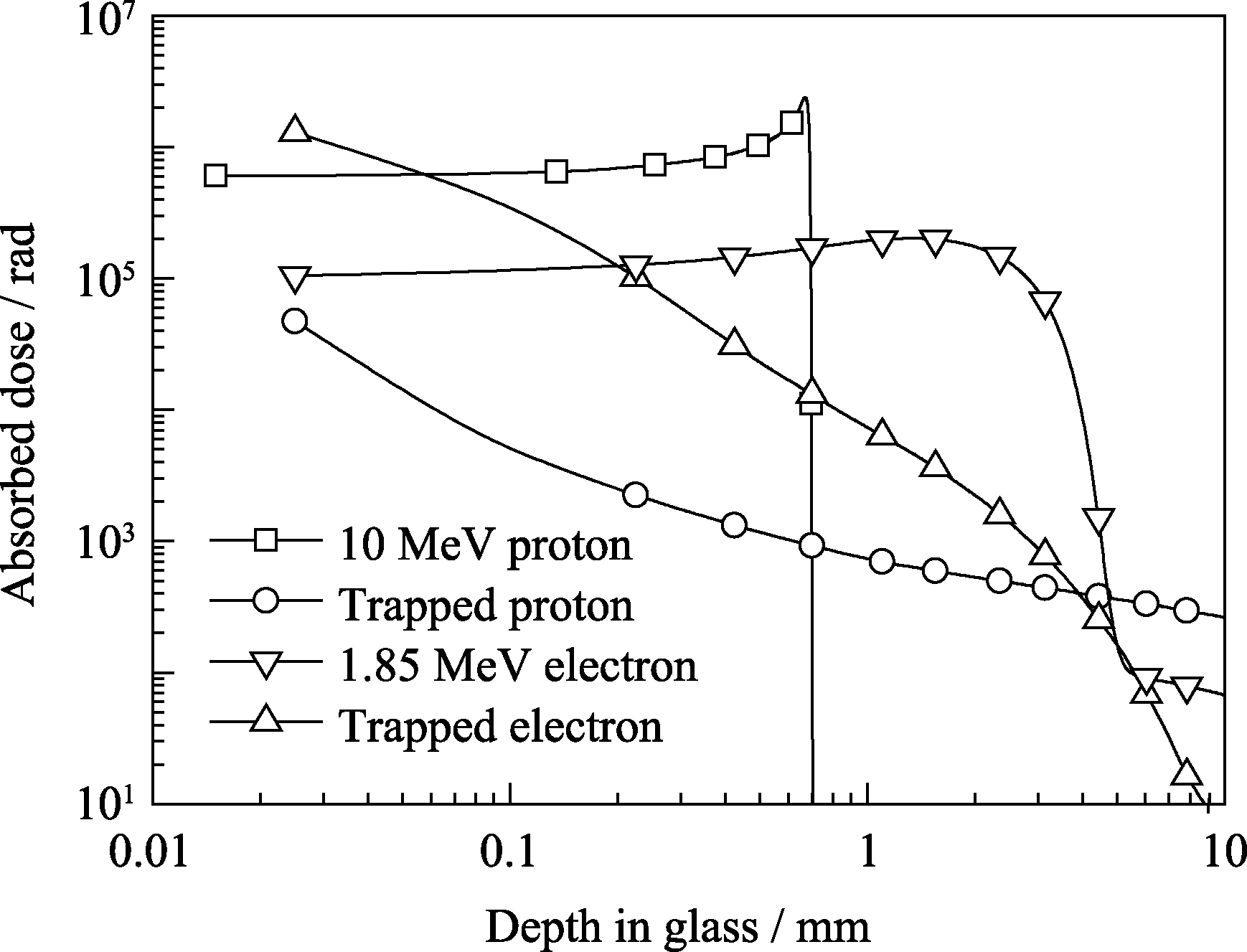
Fig. 6 MULASSIS simulated absorbed dose curves of 1012 proton/cm2 10 MeV proton, 20-year trapped proton in the given orbital, 4×1012 electron/cm2 1.85 MeV electron and 20-years trapped electron in the given orbital with depth in the silica glass
| [1] | 宋力昕, 胡行方, 吴国庭. 热钢化对载人航天器舷窗玻璃强度的影响. 中国空间科学技术, 1996(4): 43-49. |
| [2] | 吴国庭. 神舟飞船结构的研制. 航天器工程, 2004, 13(3): 14-19. |
| [3] | Schreurs J W H. Study of some trapped hole centers in X-irradiated alkali silicate glasses. J. Phys. Chem., 1967, 47(2): 818-830. |
| [4] | Bishay A. Radiation induced color centers in multicomponent glasses. J. Non-Cryst. Solids, 1970, 3: 54-114. |
| [5] | 葛世名. 石英玻璃的耐辐照性能. 原子能科学技术, 1983(2): 170-173. |
| [6] | Kreidl N J, Hensler J R. Formation of color centers in glasses exposed to gamma radiation. J. Am. Ceram. Soc., 1955, 38(12): 423-432. |
| [7] | Stroud J S. Color-center kinetics in cerium-containing glass. J. Phys. Chem. , 1965, 43(7): 2442-2450. |
| [8] | 王承遇,陶 瑛,主编. 玻璃材料手册. 北京: 化学工业出版社, 2007: 757. |
| [9] | 容超凡, 陈 军, 王志强, 等. 空间辐射剂量学浅谈. 辐射防护通讯, 2004, 24(1): 5-10. |
| [10] | Heynderickx D, Quaghebeur B, Wera J, et al. New Radiation Environment and Effects Models in ESA's Space Environment Information System (SPENVIS). Proceedings of the 7th European Conference on Radiation and its Effects on Components and Systems, Noordwijk, The Netherlands, 2003: 643-646. |
| [11] | Tylka A J, Adams J H, Jr, Boberg P R, et al. CREME96: a revision of the cosmic ray effects on micro-electronics code. IEEE Transactions on Nuclear Science, 1997, 44(6): 2150-2160. |
| [12] | Armstrong T W, Colborn B L, Bentont E V. Model calculations of the radiation dose and let spectra on ldef and comparisons with flight data. Radiat. Meas. , 1996, 26(6): 751-764. |
| [13] | Armstrong T W, Colborn B L. Evaluation of Trapped Radiation Model Uncertainties for Spacecraft Design. NASA/CR-2000- 210072, Alabama, USA: Marshall Space Flight Center, 2000. |
| [14] | Gusarov A, Doyle D, Fruit M. Towards a Database for Assessment of Nearearth Space Radiation Effects on Optical Glasses. In: Kleiman J I, Iskanderova Z. Protection of materials and structures from space environment: ICPMSE-6. Dordrecht, The Netherlands: Kluwer Academic Publishers, 2004: 113-122. |
| [15] | Gilard O, Caussanel M, Duval H, et al. New model for assessing dose, dose rate, and temperature sensitivity of radiation-induced absorption in glasses. J. Appl. Phys. , 2010, 108(9): 093115-1-5. |
| [16] | Kordas G, Camara B, Oel H J. Electron spin resonance of radiation damage in silicate glasses. J. Non-Cryst. Solids, 1982, 50(1): 79-95. |
| [17] | Davis E A, Mott N F. Conduction in non-crystalline systems V. conductivity, optical absorption and photoconductivity in amorphous semiconductors. Philos. Mag. , 1970, 22(179): 903-922. |
| [18] | Agostinelliae S, Allisonas J, Amakoe K, et al. Geant 4-a simulation toolkit. Nucl. Instr. and Meth. A, 2003, 506: 250-303. |
| [19] | Lei F, Truscott P R, Dyer C S, et al. Mulassis: a geant4-based multilayered shielding simulation tool. IEEE Trans. Nucl. Sci. , 2002, 49(6): 2788-2793. |
| [20] | 叶宗海. 空间粒子辐射探测技术. 北京: 科学出版社, 1986: 81. |
| [21] | 方书淦. 张启仁. 晶体色心物理. 上海: 上海交通大学出版社, 1989: 14. |
| [22] | 叶宗海. 空间粒子辐射探测技术. 北京: 科学出版社, 1986: 425-442. |
| [23] | Everhart T E, Hoff P H. Determination of kilovolt electron energy dissipation vs penetration distance in solid materials. J. Appl. Phys. , 1971, 42(13): 5837-5846. |
| [1] | LI Liuyuan, HUANG Kaiming, ZHAO Xiuyi, LIU Huichao, WANG Chao. Influence of RE-Si-Al-O Glass Phase on Microstructure and CMAS Corrosion Resistance of High Entropy Rare Earth Disilicates [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(7): 793-802. |
| [2] | YUE Zihao, YANG Xiaotu, ZHANG Zhengliang, DENG Ruixiang, ZHANG Tao, SONG Lixin. Effect of Pb2+ on the Luminescent Performance of Borosilicate Glass Coated CsPbBr3 Perovskite Quantum Dots [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(4): 449-456. |
| [3] | GUO Xiaoyang, ZHANG Xiaolin, JIANG Yan, TIAN Yuan, GENG Zhi. Ti-doped Hf(Zr)B2-SiC Anti-ablation Coatings: Preparation and Ablation Resistance Mechanism [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(12): 1357-1366. |
| [4] | NI Xiaoshi, LIN Ziyang, QIN Muyan, YE Song, WANG Deping. Bioactivity and Mechanical Property of PMMA Bone Cement: Effect of Silanized Mesoporous Borosilicate Bioglass Microspheres [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(8): 971-977. |
| [5] | LI Qianli, LI Naixin, LI Yucheng, LIU Shenye, CHENG Shuai, YANG Guang, REN Kuan, WANG Feng, ZHAO Jingtai. Research Progress of Radio-photoluminescence Materials and Their Applications [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(7): 731-749. |
| [6] | JIN Sai, LIU Xiaogen, QI Shuang, ZHAO Runchang, LI Zhijun. Fused Silica Glass: Laser-induced Damage on Bending Strength Weakening and Safety Design [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(6): 671-677. |
| [7] | WU Rui, ZHANG Minhui, JIN Chenyun, LIN Jian, WANG Deping. Photothermal Core-Shell TiN@Borosilicate Bioglass Nanoparticles: Degradation and Mineralization [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(6): 708-716. |
| [8] | LUO Shuwen, MA Mingsheng, LIU Feng, LIU Zhifu. Corrosion Behavior and Mechanism of LTCC Materials in Ca-B-Si System [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(5): 553-560. |
| [9] | ZHU Qingong, ZHAO Gaoling, HAN Gaorong. Effect of Recombination Time on the Structure and Properties of P2O5-Al2O3 Heterogeneous Composite Glass [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(2): 170-176. |
| [10] | YANG Yanguo, REN Haishen, HE Daihua, LIN Huixing. Effect of Cation Field Strength on Structure and High-temperature Properties of BaO-SiO2-Ln2O3 Glass-ceramic [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(10): 1207-1215. |
| [11] | WAN Jiabao, ZHANG Minghui, SU Huaiyu, CAO Zhijun, LIU Xuechao, XIE Jiansheng, WANG Xiangyuan, SHI Yinghui, WANG Liang, LEI Shuijin. Structural, Thermal, and Optical Properties of GeO2-La2O3-TiO2 Glasses [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(10): 1230-1236. |
| [12] | DENG Taoli, CHEN Hexin, HEI Lingli, LI Shuxing, XIE Rongjun. Achieving High Light Uniformity Laser-driven White Lighting Source by Introducing Secondary Phases in Phosphor Converters [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(8): 891-896. |
| [13] | PANG Libin, WANG Deping. Drug Carrier Based on Mesoporous Borosilicate Glass Microspheres: Preparation and Performance [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(7): 780-786. |
| [14] | TANG Jieyin, WANG Gang, LIU Cong, ZOU Xuenong, CHEN Xiaofeng. Dentin Remineralization Induced by Micro-nano Bioactive Glass Spheres [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(4): 436-444. |
| [15] | SHI Jixiang, ZHAI Dong, ZHU Min, ZHU Yufang. Preparation and Characterization of Bioactive Glass-Manganese Dioxide Composite Scaffolds [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(4): 427-435. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||