
Journal of Inorganic Materials ›› 2026, Vol. 41 ›› Issue (2): 225-233.DOI: 10.15541/jim20250169
• RESEARCH ARTICLE • Previous Articles Next Articles
WANG Zheng1,2,3( ), HOU Xiaoqi1,3(
), HOU Xiaoqi1,3( ), LIU Xuanyong1,2,3(
), LIU Xuanyong1,2,3( )
)
Received:2025-04-23
Revised:2025-05-27
Published:2025-06-05
Online:2025-06-05
Contact:
HOU Xiaoqi, associate professor. E-mail: houxiaoqi@ucas.ac.cn;About author:WANG Zheng (2000-), male, Master candidate. E-mail: wangzheng22@mails.ucas.ac.cn
Supported by:CLC Number:
WANG Zheng, HOU Xiaoqi, LIU Xuanyong. Functionalized Quantum Dot Fluorescent Probes with Dopamine Quinone: Construction and pH Response[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2026, 41(2): 225-233.
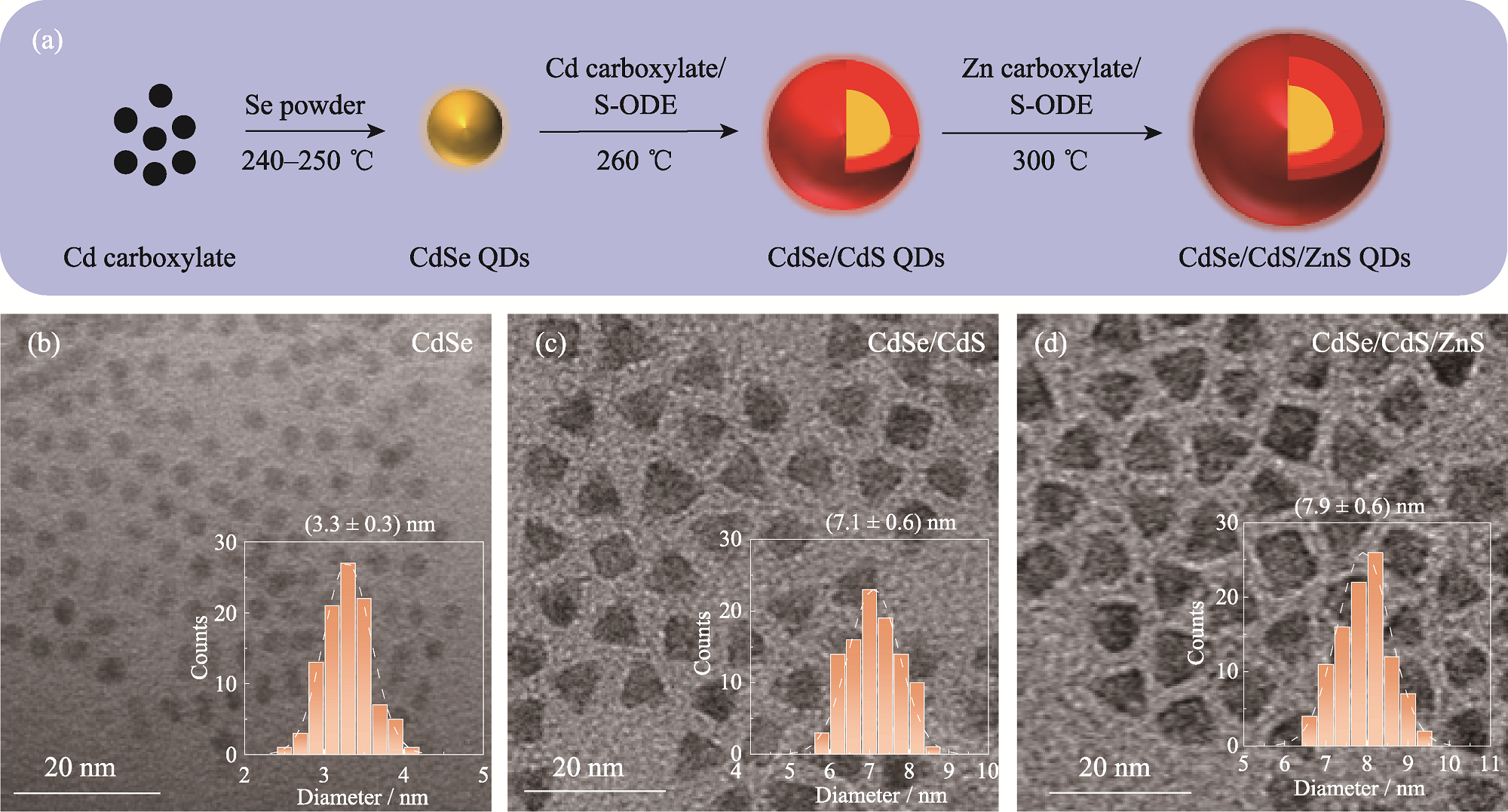
Fig. 1 Schematic of preparation, micromorphologies and size distributions of QDs (a) Preparation process of QDs; (b-d) TEM images of CdSe QDs (b), CdSe/CdS QDs (c) and CdSe/CdS/ZnS QDs (d),with insets showing size distribution histograms
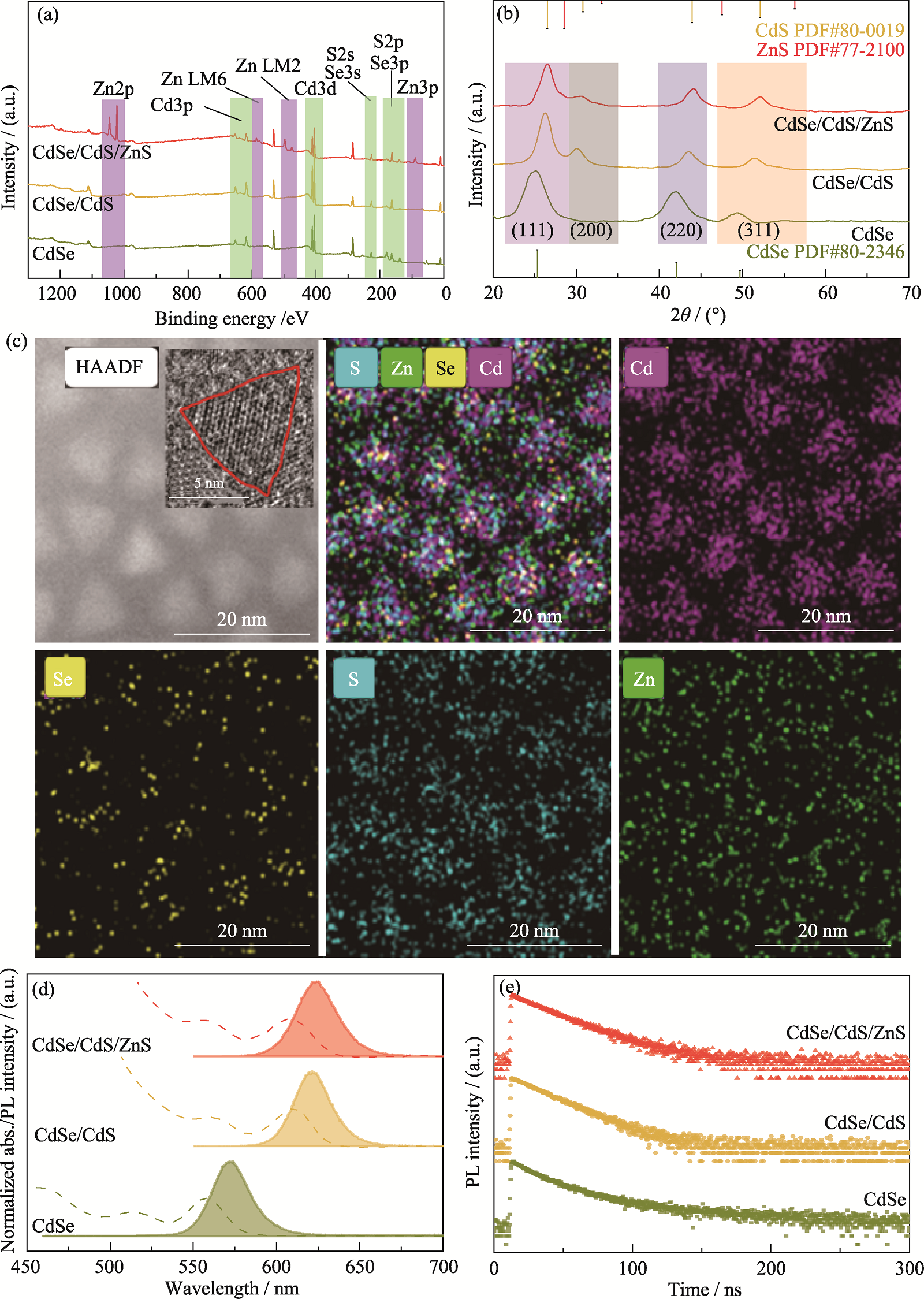
Fig. 2 Structural characterization, element distribution and optical properties of QDs (a) XPS spectra, (b) XRD patterns, (d) PL and UV-Vis spectra, and (e) transient PL spectra of QDs;(c) EDS mappings of CdSe/CdS/ZnS QDs with inset showing HRTEM image
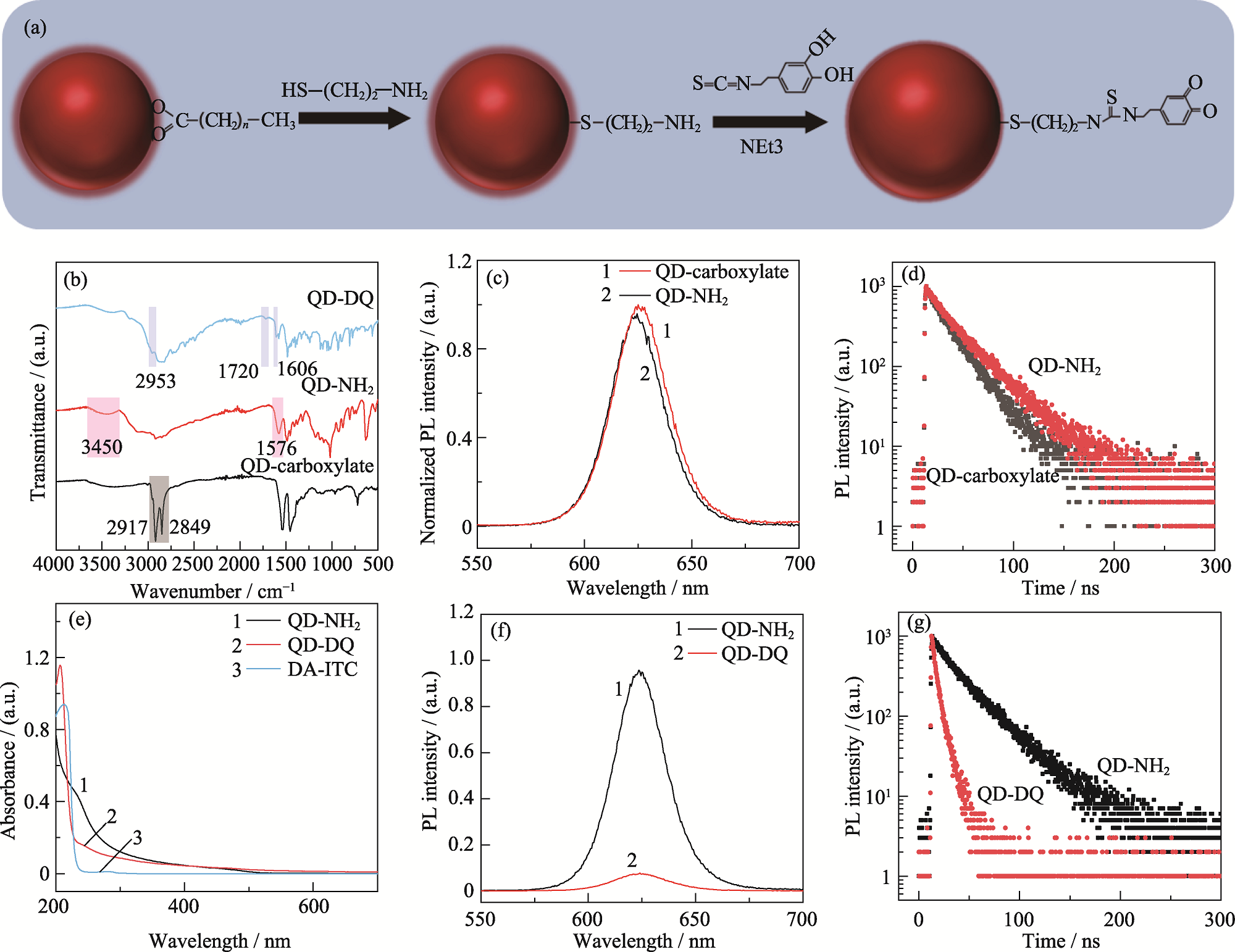
Fig. 3 Schematic of preparation, characterization and optical properties of QDs-based pH probes (a) Preparation of pH probe; (b) FT-IR spectra of pH probe at different phases; (c) PL spectra and (d) transient PL spectra of QDs before and after MEA ligand exchange; (e) UV-Vis spectra, (f) PL spectra and (g) transient PL spectra of QDs before and after linking DA-ITC (40 μg/nmol)
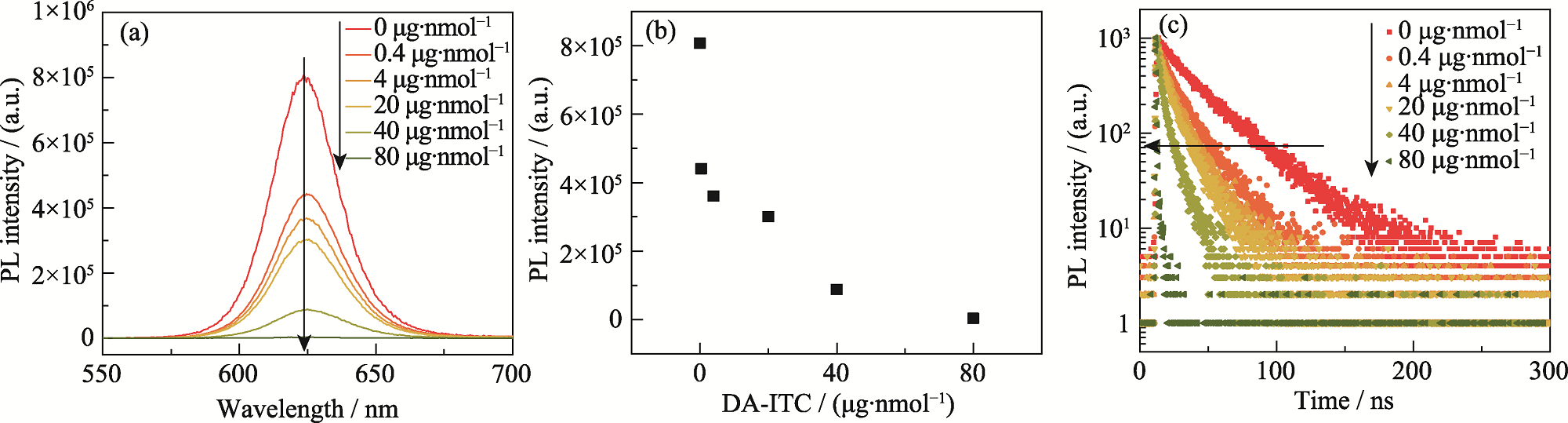
Fig. 4 Effect of DA-ITC input on optical properties of QDs-based pH probes (a) PL spectra; (b) Variation of PL peak intensity; (c) Transient PL spectra
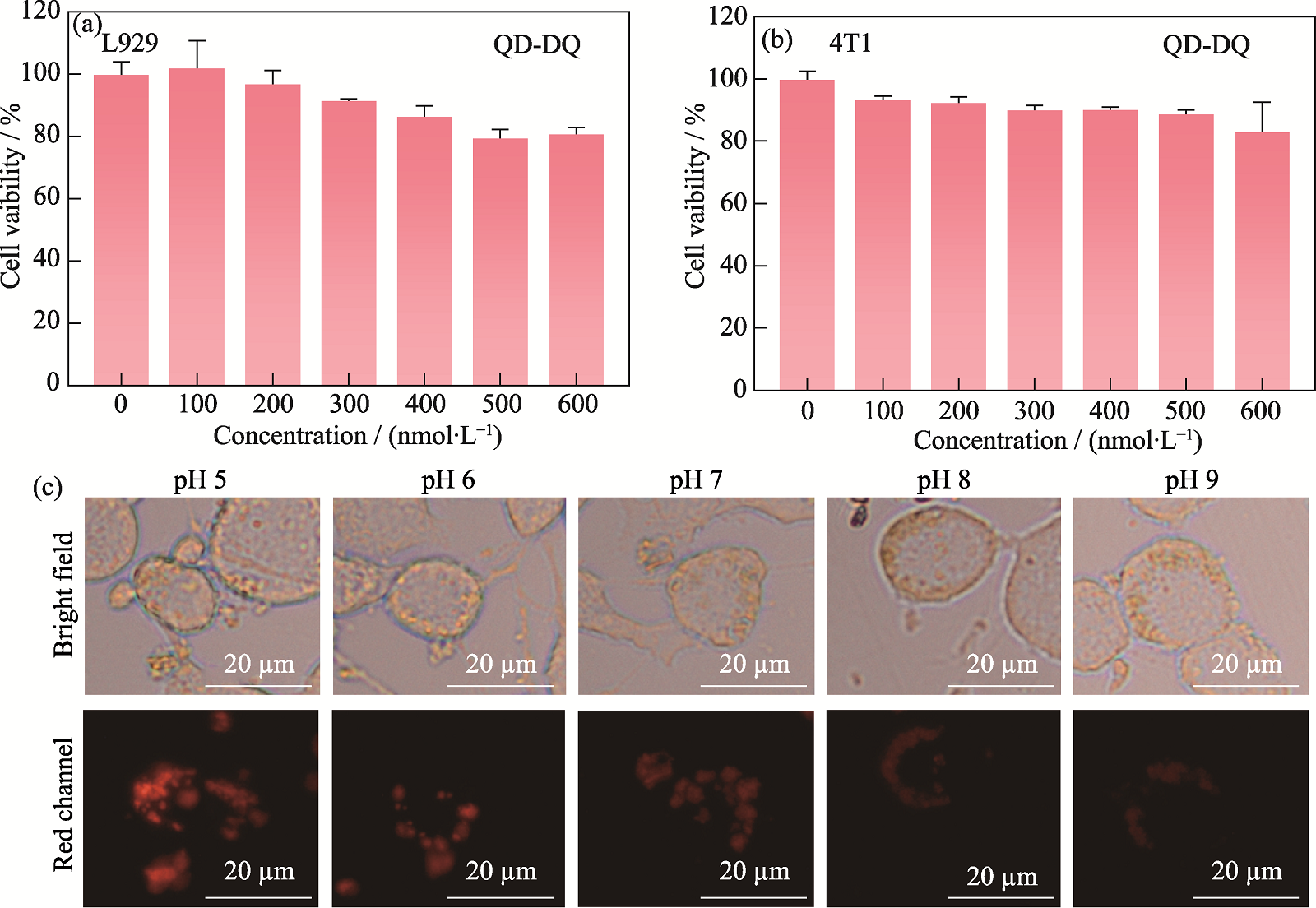
Fig. 6 Cytotoxicity of probe and its pH response effect in the cellular system (a, b) Cytotoxicity of probe to L929 cells (a) and 4T1 cells (b); (c) Fluorescence imaging of probe responses to intracellular pH change
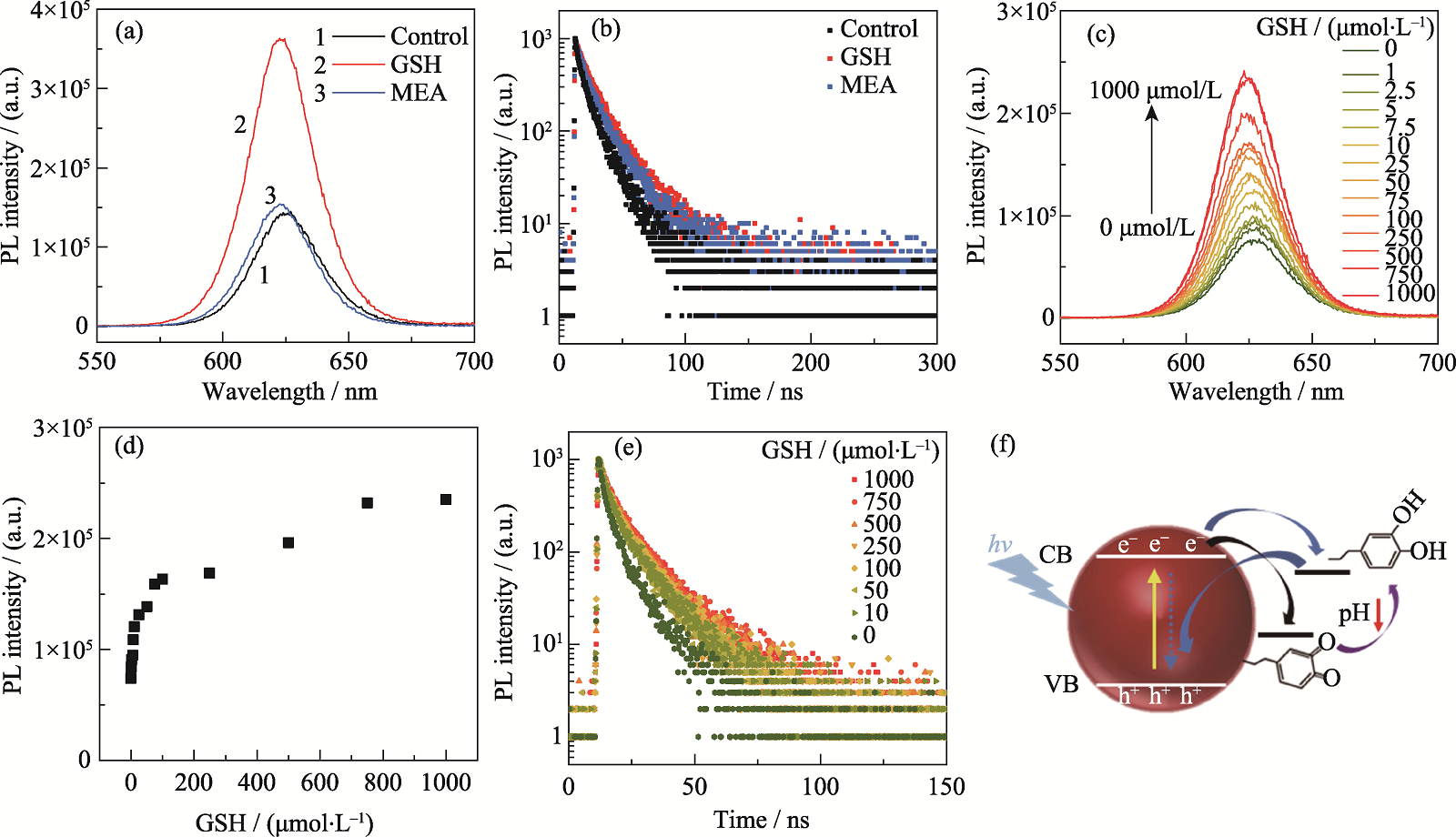
Fig. 7 Effect of GSH on the optical properties of fluorescent probes and pH response mechanism of probes (a, b) Same concentration of GSH and MEA incubated with probe for 30 min: (a) PL spectra and (b) transient PL spectra of probe; (c-e) Different concentration of GSH incubated with probe for 30 min: (c) PL spectra, (d) variation of PL peak intensity and (e) transient PL spectra of probe; (f) Schematic of the mechanism of fluorescence probe response to pH change. Colorful figures are available on website
| QDs | The first exciton absorption peak/nm | PL peak/nm | FHWM/nm | PL decay lifetime/ns | χR2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CdSe | 558.0 | 571.5 | 26.0 | / | / |
| CdSe/CdS | 609.5 | 622.0 | 25.3 | 19.35 | 0.95 |
| CdSe/CdS/ZnS | 609.0 | 625.0 | 28.4 | 21.20 | 1.24 |
Table S1 Optical properties of oil-soluble QDs
| QDs | The first exciton absorption peak/nm | PL peak/nm | FHWM/nm | PL decay lifetime/ns | χR2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CdSe | 558.0 | 571.5 | 26.0 | / | / |
| CdSe/CdS | 609.5 | 622.0 | 25.3 | 19.35 | 0.95 |
| CdSe/CdS/ZnS | 609.0 | 625.0 | 28.4 | 21.20 | 1.24 |
| Amount of input/(μg·nmol-1) | y = b×x + a | R2 |
|---|---|---|
| 0.4 | y = -28309x + 587440 | 0.4777 |
| 4 | y = -56370x + 670873 | 0.9097 |
| 20 | y = -44246x + 522045 | 0.9869 |
| 40 | y = -11429x + 141699 | 0.9667 |
| 80 | y = -53.148x + 4116.5 | 0.0249 |
Table S2 Fitting of probe fluorescence response pH under different DA-ITC input amounts
| Amount of input/(μg·nmol-1) | y = b×x + a | R2 |
|---|---|---|
| 0.4 | y = -28309x + 587440 | 0.4777 |
| 4 | y = -56370x + 670873 | 0.9097 |
| 20 | y = -44246x + 522045 | 0.9869 |
| 40 | y = -11429x + 141699 | 0.9667 |
| 80 | y = -53.148x + 4116.5 | 0.0249 |
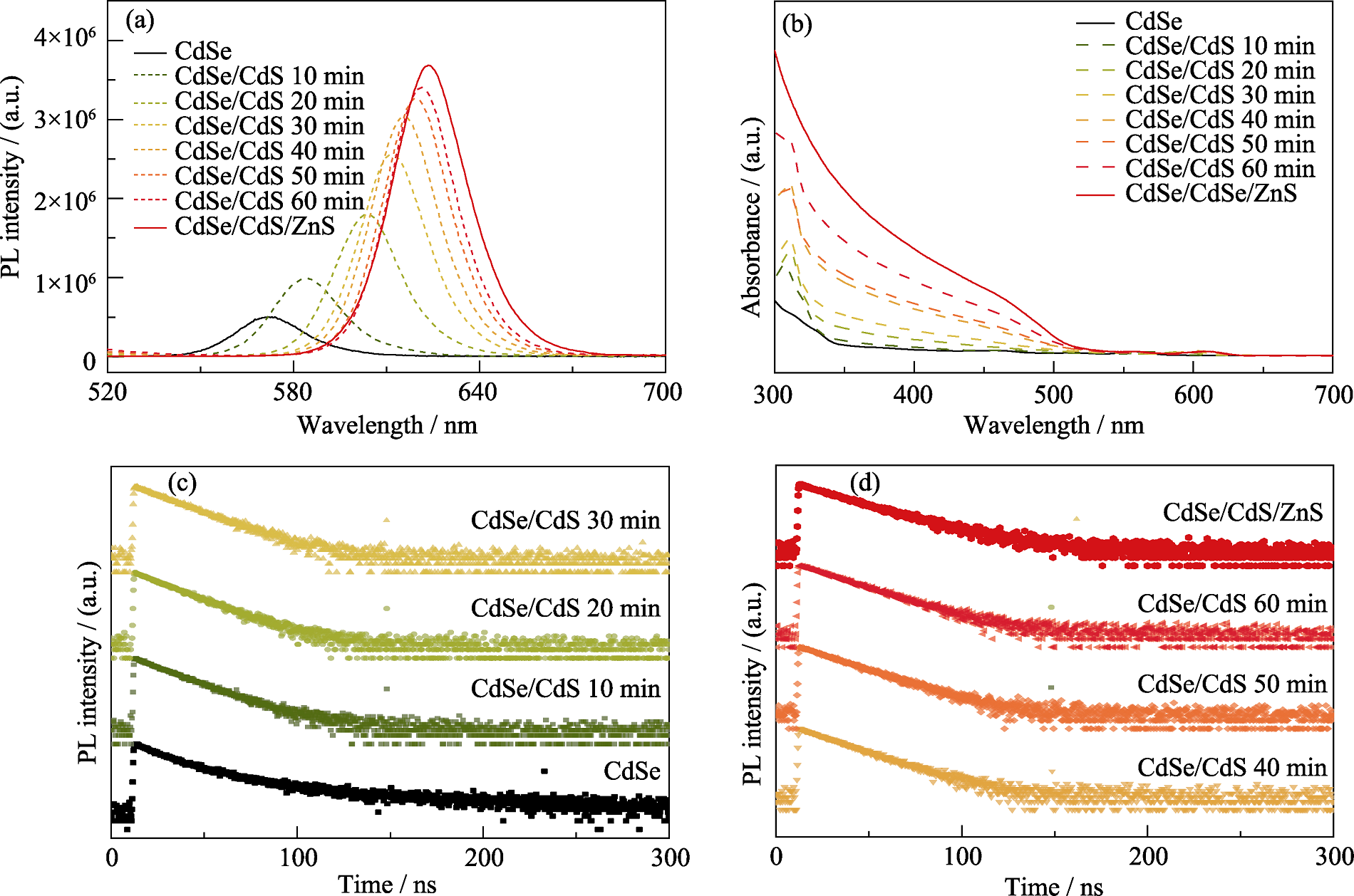
Fig. S2 Variation of optical properties during growth of CdS and ZnS layers on CdSe core QDs (a) PL spectra; (b) UV-Vis spectra; (c, d) Transient PL spectra
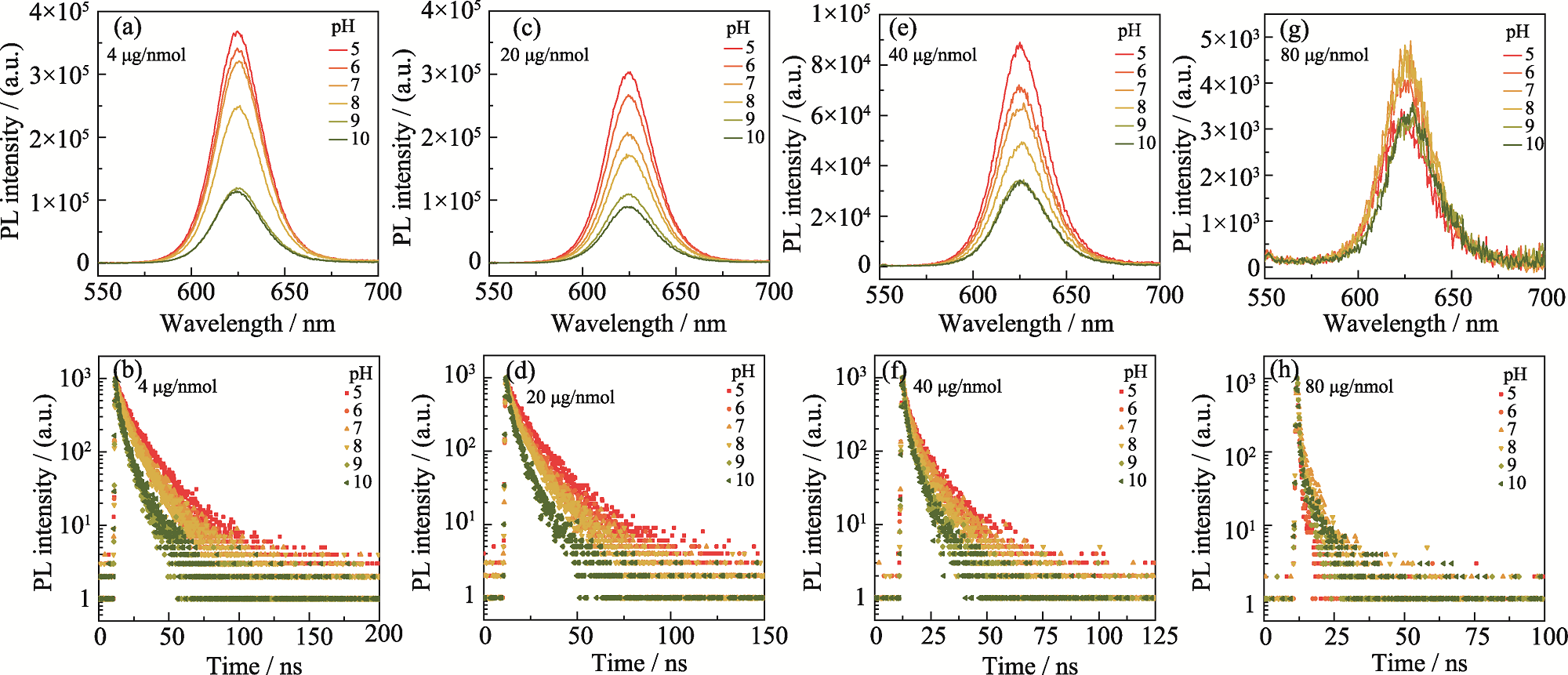
Fig. S3 Variation of optical properties of probes with different DA-ITC inputs in different pH environments (a, b) 4 μg/nmol; (c, d) 20 μg/nmol; (e, f) 40 μg/nmol; (g, h) 80 μg/nmol
| [1] |
ALIVISATOS A P. Semiconductor clusters, nanocrystals, and quantum dots. Science, 1996, 271(5251): 933.
DOI URL |
| [2] |
EFROS A L, BRUS L E. Nanocrystal quantum dots: from discovery to modern development. ACS Nano, 2021, 15(4): 6192.
DOI PMID |
| [3] |
BRUS L E. Electron-electron and electron-hole interactions in small semiconductor crystallites: the size dependence of the lowest excited electronic state. The Journal of Chemical Physics, 1984, 80(9): 4403.
DOI URL |
| [4] |
MICHALET X, PINAUD F F, BENTOLILA L A, et al. Quantum dots for live cells, in vivo imaging, and diagnostics. Science, 2005, 307: 538.
DOI URL |
| [5] | WEGNER K D, HILDEBRANDT N. Quantum dots: bright and versatile in vitro and in vivo fluorescence imaging biosensors. Chemical Society Reviews, 2015, 44(14): 4792. |
| [6] |
LIU H, WANG Z, LIU S, et al. Single-virus tracking with quantum dots in live cells. Nature Protocols, 2022, 18(2): 458.
DOI |
| [7] |
OU W, ZHU K, LU X, et al. Alloyed geometric structure strategy enables high-quality water-soluble quantum dots for ultrasensitive fluorescence immunoassay. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2024, 502: 157799.
DOI URL |
| [8] | LIU Z, HOU X, YOU H, et al. Surface copassivation strategy for developing water-soluble InP colloidal quantum dots with high luminescence and suppressed blinking. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2025, 147(6): 4778. |
| [9] |
DING C, CHENG S, ZHANG C, et al. Ratiometric upconversion luminescence nanoprobe with near-infrared Ag2S nanodots as the energy acceptor for sensing and imaging of pH in vivo. Analytical Chemistry, 2019, 91(11): 7181.
DOI URL |
| [10] |
HOU S L, DONG J, TANG M H, et al. Triple-interpenetrated lanthanide-organic framework as dual wave bands self-calibrated pH luminescent probe. Analytical Chemistry, 2019, 91(8): 5455.
DOI URL |
| [11] |
STEINEGGER A, WOLFBEIS O S, BORISOV S M. Optical sensing and imaging of pH values: spectroscopies, materials, and applications. Chemical Reviews, 2020, 120(22): 12357.
DOI PMID |
| [12] |
YANG R, HE X, NIU G, et al. A single fluorescent pH probe for simultaneous two-color visualization of nuclei and mitochondria and monitoring cell apoptosis. ACS Sensors, 2021, 6(4): 1552.
DOI PMID |
| [13] | LYAGIN I, MASLOVA O, STEPANOV N, et al. Reassessing of enzymes degrading mycotoxins at acidic pH. International Biodeterioration & Biodegradation, 2025, 198: 105994. |
| [14] |
RUIZ-GUERRERO C D, ESTRADA-OSORIO D V, GUTIÉRREZ A, et al. Novel cobalt-based aerogels for uric acid detection in fluids at physiological pH. Biosensors and Bioelectronics, 2025, 267: 116850.
DOI URL |
| [15] |
CHEN H, YE Z, SUN L, et al. Synthesis of chitosan-based micelles for pH responsive drug release and antibacterial application. Carbohydrate Polymers, 2018, 189: 65.
DOI PMID |
| [16] |
KAY E R, LEE J, NOCERA D G, et al. Conformational control of energy transfer: a mechanism for biocompatible nanocrystal-based sensors. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2012, 52(4): 1165.
DOI URL |
| [17] | ORTE A, ALVAREZ-PEZ J M, RUEDAS-RAMA M J. fluorescence lifetime imaging microscopy for the detection of intracellular pH with quantum dot. ACS Nano, 2013, 7(7): 6387. |
| [18] |
PAEK K, YANG H, LEE J, et al. Efficient colorimetric pH sensor based on responsive polymer quantum dot integrated graphene oxide. ACS Nano, 2014, 8(3): 2848.
DOI URL |
| [19] |
SUSUMU K, FIELD L D, OH E, et al. Purple-, blue-, and green- emitting multishell alloyed quantum dots: synthesis, characterization, and application for ratiometric extracellular pH sensing. Chemistry of Materials, 2017, 29(17): 7330.
DOI URL |
| [20] |
MEDINTZ I L, STEWART M H, TRAMMELL S A, et al. Quantum-dot/dopamine bioconjugates function as redox coupled assemblies for in vitro and intracellular pH sensing. Nature Materials, 2010, 9(8): 676.
DOI |
| [21] |
LI D, XU H, LI D, et al. p-Aminothiophenol-coated CdSe/ZnS quantum dots as a turn-on fluorescent probe for pH detection in aqueous media. Talanta, 2017, 166: 54.
DOI PMID |
| [22] |
ZHOU J, ZHU M, MENG R, et al. Ideal CdSe/CdS core/shell nanocrystals enabled by entropic ligands and their core size-, shell thickness-, and ligand-dependent photoluminescence properties. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2017, 139(46): 16556.
DOI PMID |
| [23] |
HOU X, KANG J, QIN H, et al. Engineering Auger recombination in colloidal quantum dots via dielectric screening. Nature Communications, 2019, 10: 1750.
DOI |
| [24] |
HOU X, QIN H, PENG X. Enhancing dielectric screening for Auger suppression in CdSe/CdS quantum dots by epitaxial growth of ZnS shell. Nano Letters, 2021, 21(9): 3871.
DOI PMID |
| [25] |
SNEE P T, SOMERS R C, NAIR G, et al. A ratiometric cdse ZnS nanocrystal pH sensor. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2006, 128: 13320.
DOI URL |
| [26] |
SYKORA M, PETRUSKA M A, ALSTRUM-ACEVEDO J, et al. Photoinduced charge transfer between CdSe nanocrystal quantum dots and Ru-polypyridine complexes. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2006, 128: 9984.
PMID |
| [27] |
MEDINTZ I L, PONS T, TRAMMELL S A, et al. Interactions between redox complexes and semiconductor quantum dots coupled via a peptide bridge. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2008, 130: 16745.
DOI URL |
| [28] |
SCHWABACHER J C, KODAIMATI M S, WEISS E A. Origin of the pH dependence of emission of aqueous dihydrolipoic acid-capped PbS quantum dots. The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2019, 123(28): 17574.
DOI URL |
| [29] |
JI X, PALUI G, AVELLINI T, et al. On the pH-dependent quenching of quantum dot photoluminescence by redox active dopamine. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2012, 134(13): 6006.
DOI PMID |
| [30] |
BANERJEE S, KAR S, PEREZ J M, et al. Quantum dot based off on probe for detection of glutathione. The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2009, 113: 9659.
DOI URL |
| [1] | YUAN Zihao, XU Yinsheng, LI Xinkuo, TAN Dezhi. Femtosecond Laser Modulation on Luminescence Properties of CdS Quantum Dot Glasses [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2026, 41(1): 105-112. |
| [2] | CHEN Zi, ZHANG Aidi, GONG Ke, LIU Haihua, YU Gang, SHAN Qingsong, LIU Yong, ZENG Haibo. High-brightness and Monodisperse Quaternary CuInZnS@ZnS Quantum Dots with Tunable and Long-lived Emission [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(4): 433-339. |
| [3] | ZHANG Yuting, LI Xiaobin, LIU Zunyi, LI Ning, ZHAO Yu. Composite Yolk-shell NiCo2V2O8@TiO2@NC Material as Anode for Lithium-ion Batteries [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(11): 1221-1228. |
| [4] | HU Xuemin, ZHANG Xingjian, JIANG Zhihao, HUANG Liwen, DING Kaining, ZHANG Shengli. First-principles Study on Oxygen Evolution Reaction Activity of CoPS3 Quantum Dots Edge States Modified with Oxygen [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(11): 1229-1236. |
| [5] | LÜ Xinyi, XIANG Hengyang, ZENG Haibo. Long-range Ordered Films Boost Efficient Perovskite Quantum Dot Light-emitting Devices [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(1): 111-112. |
| [6] | YANG Endong, LI Baole, ZHANG Ke, TAN Lu, LOU Yongbing. ZnCo2O4-ZnO@C@CoS Core-shell Composite: Preparation and Application in Supercapacitors [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(5): 485-493. |
| [7] | ZHANG Tingting, WANG Fangyuan, LIU Changyou, ZHANG Guorong, LÜ Jiahui, SONG Yuchen, JIE Wanqi. Hydrothermal-sintering Preparation of Cr2+:ZnSe/ZnSe Nanotwins with Core-shell Structure [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(4): 409-415. |
| [8] | YUE Zihao, YANG Xiaotu, ZHANG Zhengliang, DENG Ruixiang, ZHANG Tao, SONG Lixin. Effect of Pb2+ on the Luminescent Performance of Borosilicate Glass Coated CsPbBr3 Perovskite Quantum Dots [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(4): 449-456. |
| [9] | YUE Quanxin, GUO Ruihua, WANG Ruifen, AN Shengli, ZHANG Guofang, GUAN Lili. 3D Core-shell Structured NiMoO4@CoFe-LDH Nanorods: Performance of Efficient Oxygen Evolution Reaction and Overall Water Splitting [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(11): 1254-1264. |
| [10] | WU Rui, ZHANG Minhui, JIN Chenyun, LIN Jian, WANG Deping. Photothermal Core-Shell TiN@Borosilicate Bioglass Nanoparticles: Degradation and Mineralization [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(6): 708-716. |
| [11] | MA Xiaosen, ZHANG Lichen, LIU Yanchao, WANG Quanhua, ZHENG Jiajun, LI Ruifeng. 13X@SiO2: Synthesis and Toluene Adsorption [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(5): 537-543. |
| [12] | CHI Congcong, QU Panpan, REN Chaonan, XU Xin, BAI Feifei, ZHANG Danjie. Preparation of SiO2@Ag@SiO2@TiO2 Core-shell Structure and Its Photocatalytic Degradation Property [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(7): 750-756. |
| [13] | ZHANG Fengjuan, HAN Boning, ZENG Haibo. Perovskite Quantum Dot Photovoltaic and Luminescent Concentrator Cells: Current Status and Challenges [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(2): 117-128. |
| [14] | CHEN Xiaomei, CHEN Ying, YUAN Xia. Decomposition of Cyclohexyl Hydroperoxide Catalyzed by Core-shell Material Co3O4@SiO2 [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(1): 65-71. |
| [15] | TIAN Jianjian, MA Xia, WANG Min, YAO Heliang, HUA Zile, ZHANG Lingxia. Sn Quantum Dots for Electrocatalytic Reduction of CO2 to HCOOH [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(12): 1337-1342. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||