
Journal of Inorganic Materials ›› 2021, Vol. 36 ›› Issue (9): 981-990.DOI: 10.15541/jim20210020
Special Issue: 【虚拟专辑】抗菌材料(2020~2021)
• RESEARCH ARTICLE • Previous Articles Next Articles
ZHU Yutong( ), TAN Peijie, LIN Hai(
), TAN Peijie, LIN Hai( ), ZHU Xiangdong, ZHANG Xingdong
), ZHU Xiangdong, ZHANG Xingdong
Received:2021-01-11
Revised:2021-01-22
Published:2021-09-20
Online:2021-03-01
Contact:
LIN Hai, associate professor. E-mail: linhai028@scu.edu.cn
About author:ZHU Yutong (1997-), female, master. E-mail: 876073900@qq.com
Supported by:CLC Number:
ZHU Yutong, TAN Peijie, LIN Hai, ZHU Xiangdong, ZHANG Xingdong. Injectable Hyaluronan/Hydroxyapatite Composite: Preparation, Physicochemical Property and Biocompatibility[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(9): 981-990.
| Sample | HA/wt% | HAP/wt% | BDDE equivalent |
|---|---|---|---|
| HA-1.0 | 10 | 0 | 1.0 |
| HAP15-0.5 | 10 | 15 | 0.5 |
| HAP30-0.5 | 10 | 30 | 0.5 |
| HAP30-1.0 | 10 | 30 | 1.0 |
| HAP45-1.0 | 10 | 45 | 1.0 |
Table 1 Amount of HA, HAP and BDDE in preparing composite hydrogels
| Sample | HA/wt% | HAP/wt% | BDDE equivalent |
|---|---|---|---|
| HA-1.0 | 10 | 0 | 1.0 |
| HAP15-0.5 | 10 | 15 | 0.5 |
| HAP30-0.5 | 10 | 30 | 0.5 |
| HAP30-1.0 | 10 | 30 | 1.0 |
| HAP45-1.0 | 10 | 45 | 1.0 |
| Sample | Before dialysis | After dialysis | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HA/% | HAP/% | HA/% | HAP/% | |
| HA-1.0 | 10 | 0 | 2.01 | - |
| HAP15-0.5 | 10 | 15 | 1.58 | 2.38 |
| HAP30-0.5 | 10 | 30 | 1.54 | 4.63 |
| HAP30-1.0 | 10 | 30 | 2.19 | 7.73 |
| HAP45-1.0 | 10 | 45 | 3.00 | 15.8 |
Table 2 Contents of HA and HAP in different composites before and after dialysis
| Sample | Before dialysis | After dialysis | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HA/% | HAP/% | HA/% | HAP/% | |
| HA-1.0 | 10 | 0 | 2.01 | - |
| HAP15-0.5 | 10 | 15 | 1.58 | 2.38 |
| HAP30-0.5 | 10 | 30 | 1.54 | 4.63 |
| HAP30-1.0 | 10 | 30 | 2.19 | 7.73 |
| HAP45-1.0 | 10 | 45 | 3.00 | 15.8 |

Fig. 2 Appearance of composite hydrogels before and after autoclaving (A) Fully dialyzed; (B) Not dialyzed. From left to right: HA-1.0, HAP15-0.5, HAP30-0.5, HAP30-1.0, and HAP45-1.0

Fig. 3 Appearance of composite hydrogels HAP45-1.0 with remained crosslinking reagents From left to right: fully dialyzed, alkali-contained, cross linker-contained
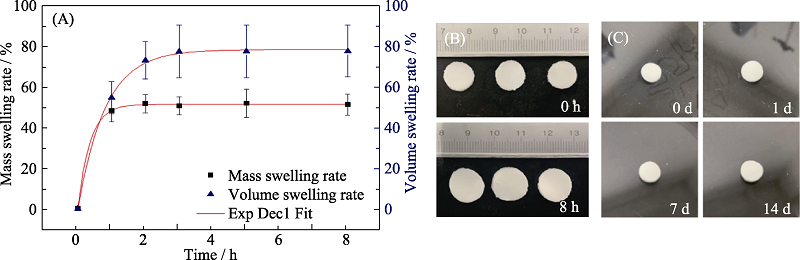
Fig. 7 Swelling behavior of composite hydrogel HAP45-1.0 and stabilization in vitro (A) Mass and volume swelling rate; (B) Sizes of samples before and after swelling for 8 h; (C) Stability of the samples immersed in PBS for different periods
| A | y0 | R2 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mass swelling rate | -51.64 | 51.64 | 0.9992 |
| Volume swelling rate | -78.81 | 78.66 | 0.9984 |
Table 3 The 1st order exponential decay equation fitting results of hydrogel HAP45-1.0 swelling behavior
| A | y0 | R2 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mass swelling rate | -51.64 | 51.64 | 0.9992 |
| Volume swelling rate | -78.81 | 78.66 | 0.9984 |
| [1] |
DE VRIES C G, GEERTSMA R E. Clinical data on injectable tissue fillers: a review. Expert Review of Medical Devices, 2013, 10(6):835-853.
DOI URL |
| [2] |
ORTIZ A E, AHLUWALIA J, SONG S S, et al. Analysis of U.S. food and drug administration data on soft-tissue filler complications. Dermatologic Surgery, 2020, 46(7):958-961.
DOI URL |
| [3] | BUCK D W, ALAM M, KIM J Y S. Injectable fillers for facial rejuvenation: a review. Journal of Plastic, Reconstructive & Aesthetic Surgery, 2009, 62(1):11-18. |
| [4] |
ALIJOTAS-REIG J, FERNÁNDEZ-FIGUERAS M T, PUIG L. Inflammatory, immune-mediated adverse reactions related to soft tissue dermalfillers. Seminars in Arthritis and Rheumatism, 2013, 43(2):241-258.
DOI URL |
| [5] |
BRANDT F S, CAZZANIGA A. Hyaluronic acid gel fillers in the management of facial aging. Clinical Interventions in Aging, 2008, 3(1):153-159.
DOI URL |
| [6] |
SHARMA P, SHARMA S. Comparative study of a new dermal filler uma jeunesse and juvéderm. Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology, 2011, 10(2):118-125.
DOI URL |
| [7] |
YANG R, TAN L, CEN L, et al. An injectable scaffold based on crosslinked hyaluronic acid gel for tissue regeneration. RSC Advances, 2016, 6(20):16838-16850.
DOI URL |
| [8] |
CHOI S C, YOO M A, LEE S Y, et al. Modulation of biomechanical properties of hyaluronic acid hydrogels by crosslinking agents. Journal of Biomedical Materials Research Part A, 2015, 103(9):3072-3080.
DOI URL |
| [9] |
YEOM J, BHANG S H, KIM B S, et al. Effect of cross-linking reagents for hyaluronic acid hydrogel dermal fillers on tissue augmentation and regeneration. Bioconjugate Chemistry, 2010, 21(2):240-247.
DOI URL |
| [10] | LOGHEM J V, YUTSKOVSKAYA Y A, WERSCHLER W P. Calcium hydroxylapatite: over a decade of clinical experience. Journal of Clinical and Aesthetic Dermatology, 2015, 8(1):38-49. |
| [11] | GRAIVIER M H, BASS L S, BUSSO M, et al. Calcium hydroxylapatite (radiesse) for correction of the mid- and lower face: consensus recommendations. Plastic & Reconstructive Surgery, 2007, 120(Suppl. 6):55S-66S. |
| [12] | EMER J, SUNDARAM H. Aesthetic applications of calcium hydroxylapatite volumizing filler: an evidence-based review and discussion of current concepts. Journal of Drugs in Dermatology Jdd., 2013, 12(12):1345-1354. |
| [13] |
LIU Y, WU Y H, LIN H, et al. Study on an injectable biomedical paste using cross-linked sodium hyaluronate as a carrier of hydroxyapatite particles. Carbohydrate Polymers, 2018, 195:378-386.
DOI URL |
| [14] |
REDBORD K P, BUSSO M, HANKO C W. Soft-tissue augmentation with hyaluronic acid and calcium hydroxyl apatite fillers. Dermatologic Therapy, 2011, 24(1):71-81.
DOI URL |
| [15] | EVIATAR J, LO C, KIRSZROT J. Radiesse: advanced techniques and applications for a unique and versatile implant. Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery, 2015, 136(Suppl. 5):164S-170S. |
| [16] |
JEONG S H, FAN Y F, BAEK J U, et al. Long-lasting and bioactive hyaluronic acid-hydroxyapatite composite hydrogels for injectable dermal fillers: physical properties and in vivo durability. Journal of Biomaterials Applications, 2016, 31(3):464-474.
DOI URL |
| [17] |
FAKHARI A, BERKLAND C. Applications and emerging trends of hyaluronic acid in tissue engineering, as a dermal filler and in osteoarthritis treatment. Acta Biomaterialia, 2013, 9(7):7081-7092.
DOI URL |
| [18] |
BOULLE K, GLOGAU R, KONO T, et al. A review of the metabolism of 1,4-butanediol diglycidyl ether-crosslinked hyaluronic acid dermal fillers. Dermatologic Surgery, 2013, 39(12):1758-1766.
DOI URL |
| [19] | PAN H H, TAO J H, WU T, et al. Molecular simulation of water behaviours on hydroxyapatite crystal faces. Chinese Journal of Inorganic Chemistry, 2006, 22(8):1392-1400. |
| [20] |
DAI Z, RONHOLM J, TIAN Y P, et al. Sterilization techniques for biodegradable scaffolds in tissue engineering applications. J. Tissue Eng., 2016, 7:1-13.
DOI URL |
| [21] | GALANTE R, PINTO T J A, COLACO R, et al. Sterilization of hydrogels for biomedical applications: a review. J. Biomed. Mater. Res., 2017, B6:106. |
| [22] |
WENDE F J, COHIL S, NORD L I, et al. 1D NMR methods for determination of degree of cross-linking and BDDE substitution positions in HA hydrogels. Carbohyd. Polym., 2017, 157:1525-1530.
DOI URL |
| [23] |
HARIDAS J, ROSEMARY M J. Effect of steam sterilization and biocompatibility studies of hyaluronic acid hydrogel for viscosupplementation. Polymer Degradation and Stability, 2019, 163:220-227.
DOI URL |
| [24] | FENG X D. Study on the mechanism of initial dark oxidation of ether. Chemical Journal of Chinese Universities, 1998, 19(7):1181-1183. |
| [25] |
LÓPEZ J F, DEGLESNE P A, ARROYO R, et al. Detection of a new reaction by-product in BDDE cross-linked autoclaved hyaluronic acid hydrogels by LC-MS analysis. Medical Devices: Evidence and Research, 2018, 11:367-376.
DOI URL |
| [26] |
BAEK J, FAN Y F, JEONG S H, et al. Facile strategy involving low-temperature chemical cross-linking to enhance the physical and biological properties of hyaluronic acid hydrogel. Carbohyd. Polym., 2018, 202:545-553.
DOI URL |
| [27] | FERRY J D. Viscoelastic Properties of Polymers, 2nd edition. New York: Wiley-Interscience, 1970, 8:595. |
| [28] |
BARBUCCI R, LAMPONI S, BORZACCHIELLO A, et al. Hyaluronic acid hydrogel in the treatment of osteoarthritis. Biomaterials, 2002, 23:4503-4513.
DOI URL |
| [29] |
CHANG J W, KOO W Y, KIM E K, et al. Facial rejuvenation using a mixture of calcium hydroxylapatite filler and hyaluronic acid filler. Journal of Craniofacial Surgery, 2020, 31(1):e18-e21.
DOI URL |
| [30] |
WIBOWO A, KAPOOR K M, PHILIPP-DORMSTON W G. Reversal of post-filler vision loss and skin ischaemia with high-dose pulsed hyaluronidase injections. Aesthetic Plastic Surgery, 2019, 43(5):1337-1344.
DOI URL |
| [31] | KIM D W, YOON E S, JI Y H, et al. Vascular complications of hyaluronic acid fillers and the role of hyaluronidase in management. Journal of Plastic, Reconstructive & Aesthetic Surgery, 2011, 64:1590-1595. |
| [32] | TANO T, ONO K, HIRATSUKA Y, et al. Retinal vessel diameters in a Japanese population: the locomotive syndrome and health outcome in Aizu cohort study. Acta Ophthalmologica, 2016, 94(6):431-441. |
| [33] |
WANG M, LI W, ZHANG Y, et al. Comparison of intra-arterial and subcutaneous testicular hyaluronidase injection treatments and the vascular complications of hyaluronic acid filler. Dermatologic Surgery, 2017, 43(2):246-254.
DOI URL |
| [34] |
OHBA S, SUMITA Y, UMEBAYASHI M, et al. Onlay bone augmentation on mouse calvarial bone using a hydroxyapatite/ collagen composite material with total blood or platelet-rich plasma. Arch. Oral. Biol., 2016, 61:23-27.
DOI URL |
| [35] | FLINT P W, CORIO R L, CUMMINGS C W. Comparison of soft tissue response in rabbits following laryngeal implantation with hydroxylapatite, silicone rubber, and Teflon. Ann. Oto. Rhinol. Laryn., 1997, 106(5):399-407. |
| [36] | REBELLATO P R O, TORRE D S, RASTELLI G J C, et al. Calcium hydroxylapatite for collagen biostimulation in the neck. Int. J. Dermatol. Venereology Leprosy Sci., 2020, 3(1):27-31. |
| [1] | AN Ran, LIN Si, GUO Shigang, ZHANG Chong, ZHU Shun, HAN Yingchao. Iron-doped Nano-hydroxyapatite: Preparation and Ultraviolet Absorption Performance [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(5): 457-465. |
| [2] | LI Chengyu, DING Ziyou, HAN Yingchao. In vitro Antibacterial and Osteogenic Properties of Manganese Doped Nano Hydroxyapatite [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(3): 313-320. |
| [3] | LIU Yan, ZHANG Yufan, WANG Ximan, LI Ting, MA Wenting, YANG Fuwei, CHEN Liang, ZHAO Dongyue, YAN Xiaoqin. Consolidation of Fragile Weathered Bone Relics Using Hydroxyapatite Material as Consolidant [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(11): 1345-1354. |
| [4] | CHEN Yaling, SHU Song, WANG Shaoxin, LI Jianjun. Mn-HAP SCR Catalyst: Preparation and Sulfur Resistance [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(10): 1065-1072. |
| [5] | LIN Ziyang, CHANG Yuchen, WU Zhangfan, BAO Rong, LIN Wenqing, WANG Deping. Different Simulated Body Fluid on Mineralization of Borosilicate Bioactive Glass-based Bone Cement [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(7): 745-752. |
| [6] | WANG Endian, CHANG Jiang. Mo Doped Cuprorivaite: Preparation, Antibacterial and Cytocompatibility [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(7): 738-744. |
| [7] | WU Zhongcao, HUAN Zhiguang, ZHU Yufang, WU Chengtie. 3D Printing and Characterization of Microsphere Hydroxyapatite Scaffolds [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(6): 601-607. |
| [8] | WU Yonghao, LI Xiangfeng, ZHU Xiangdong, ZHANG Xingdong. Construction of Hydroxyapatite Nanoceramics with High Mechanical Strength and Efficiency in Promoting the Spreading and Viability of Osteoblasts [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(5): 552-560. |
| [9] | SONG Keke, HUANG Hao, LU Mengjie, YANG Anchun, WENG Jie, DUAN Ke. Hydrothermal Preparation and Characterization of Zn, Si, Mg, Fe Doped Hydroxyapatite [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(10): 1091-1096. |
| [10] | SHAO Yueting, ZHU Yingjie, DONG Liying, CAI Anyong. Nanocomposite “Xuan Paper” Made from Ultralong Hydroxyapatite Nanowires and Cellulose Fibers and Its Anti-mildew Properties [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(1): 107-112. |
| [11] | SUN Tuanwei,ZHU Yingjie. One-step Solvothermal Synthesis of Strontium-doped Ultralong Hydroxyapatite Nanowires [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2020, 35(6): 724-728. |
| [12] | LIU Ziyang, GENG Zhen, LI Zhaoyang. Preparing Biomedical CaCO3/HA Composite with Oyster Shell [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2020, 35(5): 601-607. |
| [13] | DAI Zhao,WANG Ming,WANG Shuang,LI Jing,CHEN Xiang,WANG Da-Lin,ZHU Ying-Chun. Zirconia Reinforced Trace Element Co-doped Hydroxyapatite Coating [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2020, 35(2): 179-186. |
| [14] | FU Ya-Kang,WENG Jie,LIU Yao-Wen,ZHANG Ke-Hong. hBMP-2 Contained Composite Coatings on Titanium Mesh Surface: Preparation and hBMP-2 Release [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2020, 35(2): 173-178. |
| [15] | ZHOU Zihang, WANG Qun, GE Xiang, LI Zhaoyang. Strontium Doped Hydroxyapatite Nanoparticles: Synthesis, Characterization and Simulation [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2020, 35(11): 1283-1289. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||