
Journal of Inorganic Materials ›› 2020, Vol. 35 ›› Issue (10): 1099-1104.DOI: 10.15541/jim20190646
Special Issue: 结构陶瓷论文精选(2020)
Previous Articles Next Articles
LÜ Xiaoxu1( ),JIANG Zhuyu1,ZHOU Yiran1,QI Zhe1,ZHAO Wenqing1,2,JIAO Jian1
),JIANG Zhuyu1,ZHOU Yiran1,QI Zhe1,ZHAO Wenqing1,2,JIAO Jian1
Received:2019-12-23
Revised:2020-02-01
Published:2020-10-20
Online:2020-03-06
About author:Lü Xiaoxu(1988-), male, PhD. E-mail:xiaoxul@126.com
CLC Number:
LÜ Xiaoxu, JIANG Zhuyu, ZHOU Yiran, QI Zhe, ZHAO Wenqing, JIAO Jian. Effect of BN/SiC Multilayered Interphases on Mechanical Properties of SiC Fibers and Minicomposites by PIP[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2020, 35(10): 1099-1104.
| Linear density (g·m-1) Sample | PIP cycle | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | |
| SiCf/SiC | (0.303±0.028) | (1.26±0.11) | (1.30±0.14) | (1.32±0.17) | (1.33±0.12) | (1.33±0.13) |
| SiCf/BN/SiC | (0.330±0.023) | (1.31±0.10) | (1.34±0.11) | (1.35±0.15) | (1.36±0.10) | (1.36±0.13) |
| SiCf/(BN/SiC)/SiC | (0.346±0.035) | (1.25±0.08) | (1.28±0.11) | (1.30±0.15) | (1.30±0.14) | (1.31±0.10) |
Table 1 The linear density of Mini-composites after different PIP cycles
| Linear density (g·m-1) Sample | PIP cycle | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | |
| SiCf/SiC | (0.303±0.028) | (1.26±0.11) | (1.30±0.14) | (1.32±0.17) | (1.33±0.12) | (1.33±0.13) |
| SiCf/BN/SiC | (0.330±0.023) | (1.31±0.10) | (1.34±0.11) | (1.35±0.15) | (1.36±0.10) | (1.36±0.13) |
| SiCf/(BN/SiC)/SiC | (0.346±0.035) | (1.25±0.08) | (1.28±0.11) | (1.30±0.15) | (1.30±0.14) | (1.31±0.10) |
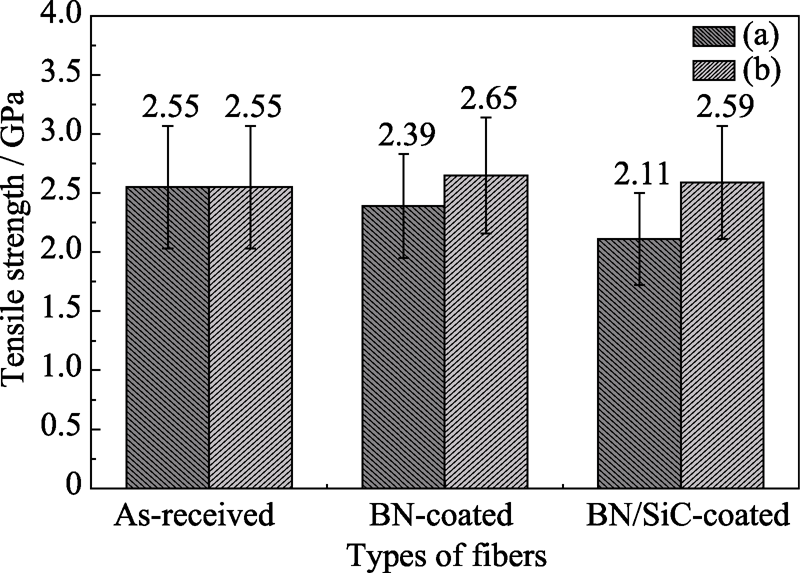
Fig. 4 Tensile strength of SiC fibers with different interphases (a) Tested strength value; (b) Calculated strength value after deducting the thickness of interphases
| [1] |
NASIRI N A, PATRA N, NI N , et al. Oxidation behaviour of SiC/SiC ceramic matrix composites in air. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2016,36(14):3293-3302.
DOI URL |
| [2] | 刘虎, 杨金华, 周怡然 , 等. 国外航空发动机用SiCf/SiC复合材料的材料级性能测试研究进展. 材料工程, 2018,46(11):1-12. |
| [3] |
STAEHLER J M, ZAWADA L P . Performance of four ceramic-matrix composite divergent flap inserts following ground testing on an F110 turbofan engine. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2000,83(7):1727-1738.
DOI URL |
| [4] | 焦健, 陈明伟 . 新一代发动机高温材料-陶瓷基复合材料的制备、性能及应用. 航空制造技术, 2014,451(7):62-69. |
| [5] |
CHARLES H, HENAGER J, KURTZ R J . Low-activation joining of SiC/SiC composites for fusion applications. Journal of Nuclear Materials, 2011,417(1/2/3):375-378.
DOI URL |
| [6] |
LAMON J . A micromechanics-based approach to the mechanical behavior of brittle matrix composites. Composites Science Technology, 2001,61(15):2259-2272.
DOI URL |
| [7] |
REBILLAT F, LAMON J, NASLAIN R , et al. Interfacial bond strength in SiC/C/SiC composite materials, as studied by single-fibre push-out tests. Journal of American Ceramic Society , 1998,81(4):965-978.
DOI URL |
|
SREEJITH K, VIPIN V, SUBRAMANIA S , et al. A comparative study on Cf/PyC/SiC minicomposites prepared via CVI process for hypersonic engine application. International Journal of Applied Ceramic Technology, 2018,15(5):1110-1123.
DOI URL |
|
| [8] |
WINDISCH C F, HENAGER C, SPRINGER G D , et al. Oxidation of the carbon interface in Nicalon fiber reinforced silicon carbide composite. Journal of the American Ceramic Society , 1997,80(3):569-574.
DOI URL |
| [9] | SHI YING, ARAKI HIROSHI, YANG WEN , et al. Influence of fiber pre-coating on mechanical properties and interfacial structures of SiC(f)/SiC composites. Journal of Inorganic Materials , 2001,16(5):883-888. |
| [10] |
OPILA E J, VERRILLI M J . Borosilicate glass-induced fiber degradation of SiC/BN/SiC composites exposed in combustion environments. International Journal of Applied Ceramic Technology, 2016,13(3):434-442.
DOI URL |
| [11] |
WING B L, HALLORAN J W . Subsurface oxidation of boron nitride coatings on silicon carbide fibers in SiC/SiC ceramic matrix composites. Ceramics International, 2018,44(14):17499-17505.
DOI URL |
| [12] |
NASLAIN R R, PAILLER R J F, LAMON J L. Single and multilayered interphases in SiC/SiC composites exposed to severe environmental conditions: an overview. International Journal of Applied Ceramic Technology, 2010,7(3):263-275.
DOI URL |
| [13] |
BERTRAND S, FORIO P, PAILLER R , et al. Hi-Nicalon/SiC minicomposites with (pyrocarbon/SiC)n nanoscale multilayered interphases. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 1999,82(9):2465-2473.
DOI URL |
| [14] |
BERTRAND S, PAILLER R, LAMON J . SiC/SiC minicomposites with nanoscale multilayered fibre coatings. Composites Science and Technology, 2001,61(3):363-367.
DOI URL |
| [15] |
YU HAIJIAO, ZHOU XINGUI, ZHANG WEI , et al. Mechanical behavior of SiCf/SiC composites with alternating PyC/SiC multilayer interphases. Materials and Design, 2013,44:320-324.
DOI URL |
| [16] |
YANG M, ZHOU W C, LUO F , et al. Effects of BN/SiC dual-layer interphase on mechanical and dielectric properties of SiCf/SiC composites. Ceramic International, 2014,40(2):3411-3418.
DOI URL |
| [17] | BERTRAND S, BOISRON O, PAILLER R , et al. (PyC-SiC)n and(BN-SiC) n nano-scale multilayered interphases by pressure pulsed-CVI. Key Engineering Materials, 1999, 164-165:357-360. |
| [18] |
AMJAD A, EMMANUEL M, SIVAKUMAR R , et al. Effect of fiber content on single tow SiC minicomposite mechanical and damage properties using acoustic emission. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2015,35(13):3389-3399.
DOI URL |
| [19] | LV X X, QI Z, JIANG Z Y , et al. The Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Silicon Carbide Fibers with Boron Nitride Interphase. IOP Conf. Series: Materials Science and Engineering, 2019,678, 012061. |
| [20] |
WANG GUODONG, SONG YONGCAI . Enhancing mechanical property of SiC fiber by decreasing fiber diameter through a modified melt-spinning process. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2018,33(7):721-727.
DOI URL |
|
MU Y, ZHOU W C, WANG C , et al. Mechanical and electromagnetic shielding properties of SiCf/SiC composites fabricated by combined CVI and PIP process. Ceramics International, 2014,40(7):10037-10041.
DOI URL |
| [1] | WEI Zhifan, CHEN Guoqing, ZU Yufei, LIU Yuan, LI Minghao, FU Xuesong, ZHOU Wenlong. ZrB2-HfSi2 Ceramics: Microstructure and Formation Mechanism of Core-rim Structure [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(7): 817-825. |
| [2] | HONG Peiping, LIANG Long, WU Lian, MA Yingkang, PANG Hao. Structure Regulation of ZIF-67 and Adsorption Properties for Chlortetracycline Hydrochloride [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(4): 388-396. |
| [3] | LI Jianjun, CHEN Fangming, ZHANG Lili, WANG Lei, ZHANG Liting, CHEN Huiwen, XUE Changguo, XU Liangji. Peroxymonosulfate Activation by CoFe2O4/MgAl-LDH Catalyst for the Boosted Degradation of Antibiotic [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(4): 440-448. |
| [4] | HOU Jiaqi, CHEN Ruicong, ZENG Yaoying, ZHOU Lei, ZHANG Jiaping, FU Qiangang. Thermal Shock and Ablation Resistance of SiC Coating Repaired by Gaseous Silicon Infiltration [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(2): 168-176. |
| [5] | LUAN Xingang, HE Dianwei, TU Jianyong, CHENG Laifei. 2D Plain and 3D Needle-punched C/SiC Composites: Low-velocity Impact Damage Behavior and Failure Mechanism [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(2): 205-214. |
| [6] | WANG Wenting, XU Jingjun, MA Ke, LI Meishuan, LI Xingchao, LI Tongqi. Oxidation Behavior at 1000-1300 ℃ in air of Ti2AlC-20TiB2 Synthesized by in-situ Reaction/Hot Pressing [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(1): 31-38. |
| [7] | ZHANG Li, GUAN Haoyang, ZHENG Qining, HONG Zhiliang, WANG Jiaxuan, XING Ning, LI Mei, LIU Yongsheng, ZHANG Chengyu. Creep Properties and Damage Mechanisms of SiCf/SiC-SiYBC Prepared by Melt Infiltration [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(1): 23-30. |
| [8] | WEN Zhipeng, WEI Yi, HOU Xianghua, GUO Jiawen, LI Qu, ZHU Manqing, ZHANG Jiahao, PAN Kai, WU Lian. Research Progress of Bentonite-based Functional Materials in Electrochemical Energy Storage [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(12): 1301-1315. |
| [9] | MA Yongjie, LIU Yongsheng, GUAN Kang, ZENG Qingfeng. Gas-phase Kinetic Study of Pyrolysis in the System of CH4+C2H5OH+Ar [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(11): 1235-1244. |
| [10] | DING Ningning, SUN Jianhua, WEI Xu, SUN Lixia. Monitoring Ammonia at Room Temperature of p-Aminobenzene Sulfonic Acid Modified MoO3/PPy Composites [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(11): 1245-1253. |
| [11] | ZHOU Yunkai, DIAO Yaqi, WANG Minglei, ZHANG Yanhui, WANG Limin. First-principles Calculation Study of the Oxidation Resistance of PANI Modified Ti3C2(OH)2 [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(10): 1151-1158. |
| [12] | WEI Xiangxia, ZHANG Xiaofei, XU Kailong, CHEN Zhangwei. Current Status and Prospects of Additive Manufacturing of Flexible Piezoelectric Materials [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(9): 965-978. |
| [13] | QUAN Wenxin, YU Yiping, FANG Bing, LI Wei, WANG Song. Oxidation Behavior and Meso-macro Model of Tubular C/SiC Composites in High-temperature Environment [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(8): 920-928. |
| [14] | MA Binbin, ZHONG Wanling, HAN Jian, CHEN Liangyu, SUN Jingjing, LEI Caixia. ZIF-8/TiO2 Composite Mesocrystals: Preparation and Photocatalytic Activity [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(8): 937-944. |
| [15] | YOU Bojie, LI Bo, LI Xuqin, MA Xuehan, ZHANG Yi, CHENG Laifei. Thermal Shock Damage and In-plane Shear Performance Degradation of 2D SiCf/SiC at Medium Temperature [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(12): 1367-1376. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||