
Journal of Inorganic Materials ›› 2019, Vol. 34 ›› Issue (11): 1175-1180.DOI: 10.15541/jim20190037
Previous Articles Next Articles
DU Pei1,YAN Shu-Fang1,2( ),CHEN Wei-Dong1,2,LI Shi-Jiang1,MA Wen1,2
),CHEN Wei-Dong1,2,LI Shi-Jiang1,MA Wen1,2
Received:2019-01-18
Revised:2019-05-14
Published:2019-11-20
Online:2019-07-23
Supported by:CLC Number:
DU Pei, YAN Shu-Fang, CHEN Wei-Dong, LI Shi-Jiang, MA Wen. Graphene Concentration on Micro-arc Oxidation Ceramic Layer of ZrH1.8 Surface[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2019, 34(11): 1175-1180.
| Graphene concentration/(g·L-1) | Anode voltage/V | Cathode voltage/V | Frequency/Hz | Duty cycle | Time/min | Electrolyte composition |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 430 | 150 | 150 | 50 | 15 | Na5P3O10 KOH Na2EDTA |
| 0.05 | ||||||
| 0.10 | ||||||
| 0.15 | ||||||
| 0.20 |
Table 1 Electrolyte composition and micro-arc oxidation experimental parameters
| Graphene concentration/(g·L-1) | Anode voltage/V | Cathode voltage/V | Frequency/Hz | Duty cycle | Time/min | Electrolyte composition |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 430 | 150 | 150 | 50 | 15 | Na5P3O10 KOH Na2EDTA |
| 0.05 | ||||||
| 0.10 | ||||||
| 0.15 | ||||||
| 0.20 |
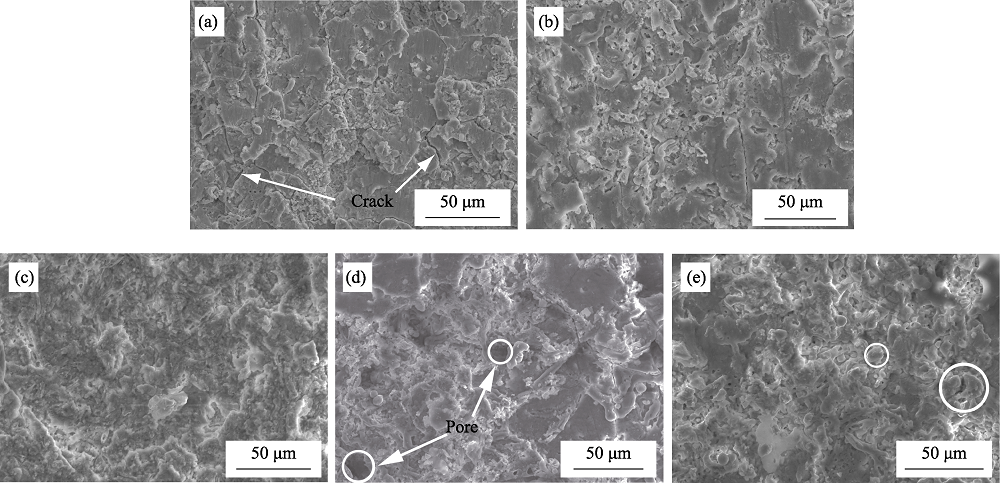
Fig. 1 Surface morphologies of micro-arc oxidation ceramic layer at different graphene concentrations (a) Without graphene; (b) 0.05 g/L; (c) 0.10 g/L; (d) 0.15 g/L; (e) 0.20 g/L
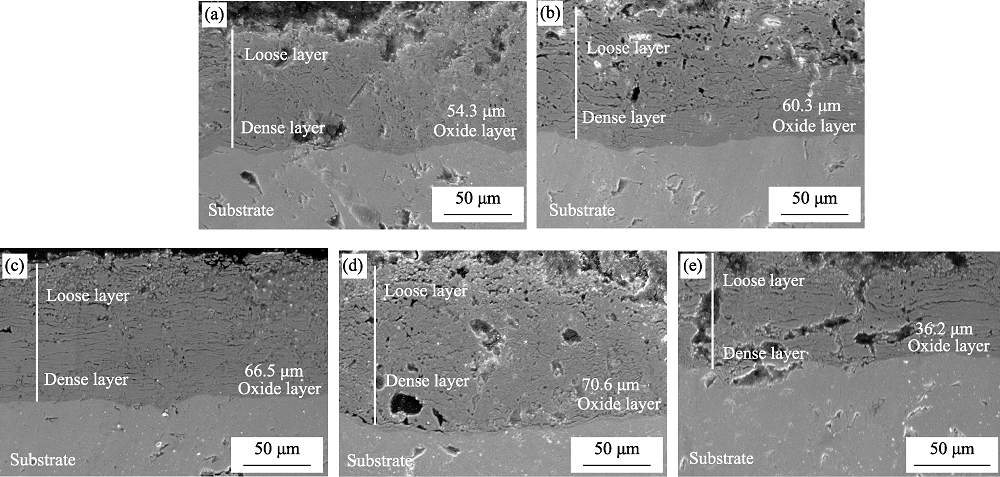

Fig. 2 Cross-section morphologies of micro-arc oxidation ceramic layer at different graphene concentrations (a) Without graphene; (b) 0.05 g/L; (c) 0.10 g/L; (d) 0.15 g/L; (e) 0.20 g/L
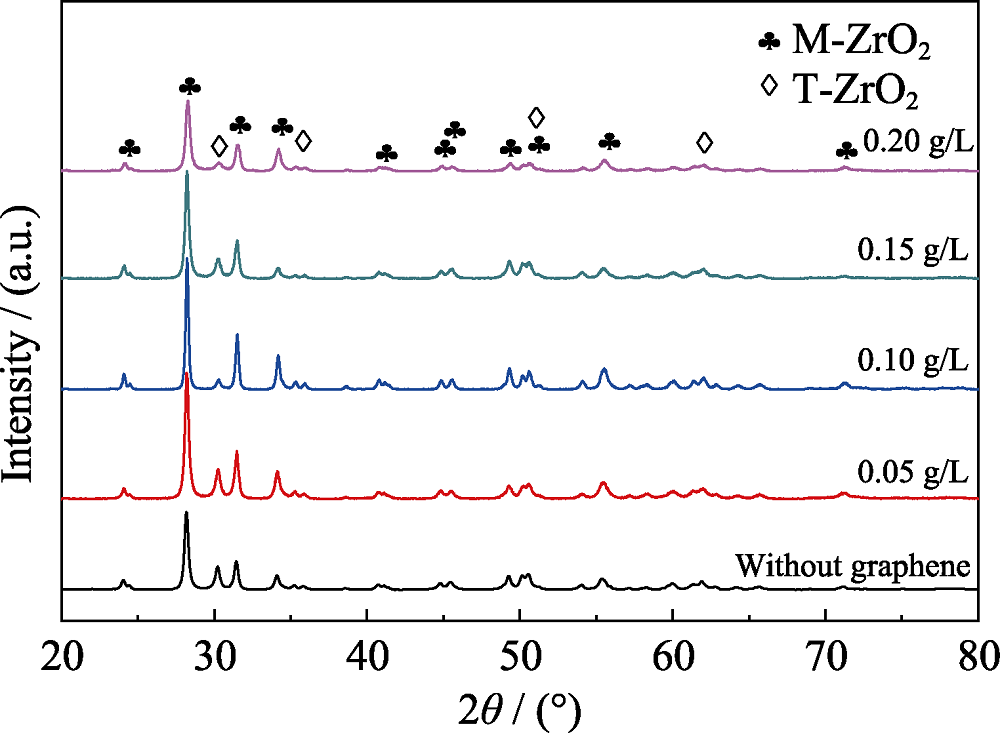
Fig. 3 XRD patterns of micro-arc oxidation ceramic layer at different graphene concentrations (a) Without graphene; (b) 0.05 g/L; (c) 0.10 g/L; (d) 0.15 g/L; (e) 0.20 g/L
| [1] | HAYASHI T, TOBITA K, NAKAMORI Y , et al. Advanced neutron shielding material using zirconium borohydride Advanced neutron shielding material using zirconium borohydride and zirconium hydride. Journal of Nuclear Materials, 2009, 386-388:119-121. |
| [2] | MATHEUS A T, CHINTHAKA M S, PHILIP D E . Site specific dependencies of hydrogen concentrations in zirconium hydrides. Scripta Materialia, 2019,158:136-140. |
| [3] | OLANDER D, GREENSPAN E, GARKISCH H D , et al. Uranium- zirconium hydride fuel properties. Nuclear Engineering and Design, 2009,239(8):1406-1424. |
| [4] | KUMAR N A P K, SZPUNAR J A, HE Z . Preferential precipitation of hydrides in textured zircaloy-4 sheets. Journal of Nuclear Materials, 2010,403(1/2/3):101-107. |
| [5] | 单丽梅 . 氢化锆表面电镀铬膜阻止氢渗透的研究. 成都: 西华大学硕士学位论文, 2007. |
| [6] | WU M, PENG J Q, YAN G Q , et al. Preparation and properties of composite hydrogen permeation barrier on ZrH1.8 by Sol-Gel technique. Surface and Coatings Technology, 2018,352:159-165. |
| [7] | PENG J Q, CHEN Y, WU M , et al. Hydrogen desorption behavior of the hydrides of Zr-Y alloys under Ar and CO2 atmosphere. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2017,693:103-109. |
| [8] | SANTOSH P S, ETSUSHI T, YOSHITAKA A , et al. Cathodic pulse breakdown of anodic films on aluminium in alkaline silicate electrolyte-understanding the role of cathodic half-cycle in AC plasma electrolytic oxidation. Corrosion Science, 2012,55:90-96. |
| [9] | YANG W, XU D P, YAO X F , et al. Stable preparation and characterization of yellow micro arc oxidation coating on magnesium alloy. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2018,745:609-616. |
| [10] | LI H, SUN Y Z, ZHANG J . Effect of ZrO2 particle on the performance of micro-arc oxidation coatings on Ti6Al4V. Applied Surface Science, 2015,342:183-190. |
| [11] | YAN G Q, CHEN W D, ZHONG X K , et al. Properties of oxide coating on the surface of ZrH1.8 prepared by microarc oxidation with different positive voltages. Rare Metals, 2013,32(2):169-173. |
| [12] | CHEN Q Z, JIANG Z Q, TANG S G , et al. Influence of graphene particles on the micro-arc oxidation behaviors of 6063 aluminum alloy and the coating properties. Applied Surface Science, 2017,423:939-950. |
| [13] | CHEN F, ZHANG Y L, ZHANG Y , et al. Effect of graphene on micro-structure and properties of MAO coating prepared on Mg-Li alloy. International Journal of Electrochemical Science, 2017,12:6081-6091. |
| [14] | WANG Z G, CHEN W D, YAN S F , et al. Characterization of ZrO2 ceramic coatings on ZrH1.8 prepared in different electrolytes by micro-arc oxidation. Rare Metals, 2015, DOI: 10.1007/s12598- 015-0503-8. |
| [15] | CHANG L . Growth regularity of ceramic coating on magnesium alloy by plasma electrolytic oxidation. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2009,468:462-465. |
| [16] | LÜ G H, CHEN H, GU W C , et al. Effects of graphite additives in electrolytes on the microstructure and corrosion resistance of alumina PEO coatings. Current Applied Physics, 2009,9(2):324-328. |
| [17] | HAN B J, YANG Y, HUANG Z G , et al. A composite anodic coating containing graphene on AZ31 magnesium alloy. International Journal of Electrochemical Science, 2017,12:9829-9843. |
| [1] | YANG Mingkai, HUANG Zeai, ZHOU Yunxiao, LIU Tong, ZHANG Kuikui, TAN Hao, LIU Mengying, ZHAN Junjie, CHEN Guoxing, ZHOU Ying. Co-production of Few-layer Graphene and Hydrogen from Methane Pyrolysis Based on Cu and Metal Oxide-KCl Molten Medium [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(5): 473-480. |
| [2] | GAO Chenguang, SUN Xiaoliang, CHEN Jun, LI Daxin, CHEN Qingqing, JIA Dechang, ZHOU Yu. SiBCN-rGO Ceramic Fibers Based on Wet Spinning Technology: Microstructure, Mechanical and Microwave-absorbing Properties [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(3): 290-296. |
| [3] | WANG Yue, WANG Xin, YU Xianli. Room-temperature Ferromagnetic All-carbon Films Based on Reduced Graphene Oxide [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(3): 305-313. |
| [4] | LI Honglan, ZHANG Junmiao, SONG Erhong, YANG Xinglin. Mo/S Co-doped Graphene for Ammonia Synthesis: a Density Functional Theory Study [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(5): 561-568. |
| [5] | SUN Chuan, HE Pengfei, HU Zhenfeng, WANG Rong, XING Yue, ZHANG Zhibin, LI Jinglong, WAN Chunlei, LIANG Xiubing. SiC-based Ceramic Materials Incorporating GNPs Array: Preparation and Mechanical Characterization [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(3): 267-273. |
| [6] | WANG Yanli, QIAN Xinyi, SHEN Chunyin, ZHAN Liang. Graphene Based Mesoporous Manganese-Cerium Oxides Catalysts: Preparation and Low-temperature Catalytic Reduction of NO [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(1): 81-89. |
| [7] | YANG Pingjun, LI Tiehu, LI Hao, DANG Alei. Effect of Graphene on Graphitization, Electrical and Mechanical Properties of Epoxy Resin Carbon Foam [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(1): 107-112. |
| [8] | DONG Yiman, TAN Zhan’ao. Research Progress of Recombination Layers in Two-terminal Tandem Solar Cells Based on Wide Bandgap Perovskite [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(9): 1031-1043. |
| [9] | DU Jiaheng, FAN Xinli, XIAO Dongqin, YIN Yiran, LI Zhong, HE Kui, DUAN Ke. Electrophoretic Coating of Magnesium Oxide on Microarc-oxidized Titanium and Its Biological Properties [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(12): 1441-1448. |
| [10] | CHEN Saisai, PANG Yali, WANG Jiaona, GONG Yan, WANG Rui, LUAN Xiaowan, LI Xin. Preparation and Properties of Green-yellow Reversible Electro-thermochromic Fabric [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(9): 954-960. |
| [11] | SUN Ming, SHAO Puzhen, SUN Kai, HUANG Jianhua, ZHANG Qiang, XIU Ziyang, XIAO Haiying, WU Gaohui. First-principles Study on Interface of Reduced Graphene Oxide Reinforced Aluminum Matrix Composites [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(6): 651-659. |
| [12] | AN Lin, WU Hao, HAN Xin, LI Yaogang, WANG Hongzhi, ZHANG Qinghong. Non-precious Metals Co5.47N/Nitrogen-doped rGO Co-catalyst Enhanced Photocatalytic Hydrogen Evolution Performance of TiO2 [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(5): 534-540. |
| [13] | WANG Hongli, WANG Nan, WANG Liying, SONG Erhong, ZHAO Zhankui. Hydrogen Generation from Formic Acid Boosted by Functionalized Graphene Supported AuPd Nanocatalysts [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(5): 547-553. |
| [14] | DONG Shurui, ZHAO Di, ZHAO Jing, JIN Wanqin. Effect of Ionized Amino Acid on the Water-selective Permeation through Graphene Oxide Membrane in Pervaporation Process [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(4): 387-394. |
| [15] | JIANG Lili, XU Shuaishuai, XIA Baokai, CHEN Sheng, ZHU Junwu. Defect Engineering of Graphene Hybrid Catalysts for Oxygen Reduction Reactions [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(2): 215-222. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||