
Journal of Inorganic Materials ›› 2017, Vol. 32 ›› Issue (11): 1128-1132.DOI: 10.15541/jim20160704
• RESEARCH PAPER • Previous Articles Next Articles
LI Guo-Chang, WANG Ping, LIU Chang-Bo
Received:2016-12-29
Revised:2017-03-13
Published:2017-11-20
Online:2017-10-20
CLC Number:
LI Guo-Chang, WANG Ping, LIU Chang-Bo. Hydrothermal Synthesis of Whitlockite[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2017, 32(11): 1128-1132.
| Sample | Unit cell parameters | |
|---|---|---|
| a/nm | c/nm | |
| Mg0.1 | 1.03705 | 3.71939 |
| Mg0.2 | 1.03707 | 3.71234 |
| Mg0.3 | 1.03542 | 3.71068 |
| Mg0.4 | 1.03431 | 3.70353 |
| Mg0.5 | 1.03412 | 3.70203 |
| PDF# 70-2064 | 1.03500 | 3.70850 |
Table 1 Unit cell parameters of samples
| Sample | Unit cell parameters | |
|---|---|---|
| a/nm | c/nm | |
| Mg0.1 | 1.03705 | 3.71939 |
| Mg0.2 | 1.03707 | 3.71234 |
| Mg0.3 | 1.03542 | 3.71068 |
| Mg0.4 | 1.03431 | 3.70353 |
| Mg0.5 | 1.03412 | 3.70203 |
| PDF# 70-2064 | 1.03500 | 3.70850 |
| MgL | Chemical constituents/wt% | Molar ratio | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CaO | P2O5 | MgO | MgS | MgL/MgS | (Ca+Mg)/P | |
| Mg0.1 | 53.95 | 43.85 | 1.85 | 0.041 | 0.41 | 1.62 |
| Mg0.2 | 50.95 | 45.64 | 3.16 | 0.076 | 0.38 | 1.59 |
| Mg0.3 | 49.34 | 46.04 | 4.21 | 0.102 | 0.34 | 1.51 |
| Mg0.4 | 48.54 | 46.34 | 4.89 | 0.119 | 0.30 | 1.51 |
| Mg0.5 | 46.74 | 46.8 | 6.03 | 0.136 | 0.27 | 1.49 |
Table 2 Chemical constituents of different Mg/(Ca+Mg) samples
| MgL | Chemical constituents/wt% | Molar ratio | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CaO | P2O5 | MgO | MgS | MgL/MgS | (Ca+Mg)/P | |
| Mg0.1 | 53.95 | 43.85 | 1.85 | 0.041 | 0.41 | 1.62 |
| Mg0.2 | 50.95 | 45.64 | 3.16 | 0.076 | 0.38 | 1.59 |
| Mg0.3 | 49.34 | 46.04 | 4.21 | 0.102 | 0.34 | 1.51 |
| Mg0.4 | 48.54 | 46.34 | 4.89 | 0.119 | 0.30 | 1.51 |
| Mg0.5 | 46.74 | 46.8 | 6.03 | 0.136 | 0.27 | 1.49 |
| Calcination temperature | Chemical formula | Unit cell parameters | |
|---|---|---|---|
| a/nm | c/nm | ||
| As-prepared sample | Ca18Mg2H2(PO4)14 | 1.03707 | 3.71234 |
| 950℃ | Ca18Mg2(PO4)12P2O7 | 1.03472 | 3.71176 |
| 1200℃ | Ca18Mg2(PO4)12P2O7 | 1.03412 | 3.71094 |
Table 3 Unit cell parameters of calcined samples
| Calcination temperature | Chemical formula | Unit cell parameters | |
|---|---|---|---|
| a/nm | c/nm | ||
| As-prepared sample | Ca18Mg2H2(PO4)14 | 1.03707 | 3.71234 |
| 950℃ | Ca18Mg2(PO4)12P2O7 | 1.03472 | 3.71176 |
| 1200℃ | Ca18Mg2(PO4)12P2O7 | 1.03412 | 3.71094 |
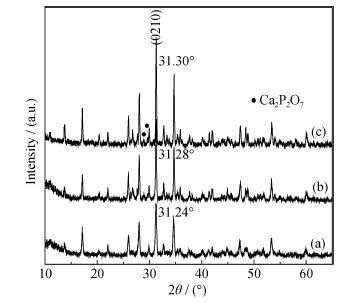
Fig. 6 XRD patterns of the calcined samples (a) As-prepared sample (Ca18Mg2H2(PO4)14); (b) Calcined at 950℃ (Ca18Mg2(PO4)12P2O7), 2 h; (c) Calcined at 1200℃, 2 h (Ca18Mg2(PO4)12P2O7)
| [1] | YASHIMA M, SAKAI A, KAMIYAMA T,et al. Crystal structure analysis of β-tricalcium phosphate Ca3 (PO4)2 by neutron powder diffraction. Journal of Solid State Chemistry, 2003, 175(2): 272-277. |
| [2] | ARAÚJO J C, SADER M S, MOREIRA E L,et al. Maximum substitution of magnesium for calcium sites in Mg-TCP structure determined by X-ray powder diffraction with the Rietveld refinement.Materials Chemistry and Physics, 2009, 118(2): 337-340. |
| [3] | MATSUNAGA K, KUBOTA T, TOYOURA K,et al. First-principles calculations of divalent substitution of Ca2+ in tricalcium phosphates. Acta Biomaterialia, 2015, 23(1): 329-337. |
| [4] | GRIGG A T, MEE M, MALLINSON P M,et al. Cation substitution in β-tricalcium phosphate investigated using multi-nuclear, solid-state NMR. Journal of Solid State Chemistry, 2014, 212: 227-236. |
| [5] | NABIYOUNI M, REN Y, BHADURI S B.Magnesium substitution in the structure of orthopedic nanoparticles: a comparison between amorphous magnesium phosphates, calcium magnesium phosphates, and hydroxyapatites.Materials Science and Engineering C, 2015, 52: 11-17. |
| [6] | HABRAKEN W, HABIBOVIC P, EPPLE M,et al. Calcium phosphates in biomedical applications: materials for the future? Materials Today, 2016, 19(2): 70-87. |
| [7] | QIN S, LU A H, WANG C Q.The minerals in the human body.Earth Science Frontiers, 2008, 15(6): 32-39. |
| [8] | XIE X D, CHEN M.Formation conditions of tuite.Geochimica, 2008, 37(4): 297-303. |
| [9] | JANG H L, JIN K, LEE J,et al. Revisiting whitlockite, the second most abundant biomineral in bone: nanocrystal synthesis in physiologically relevant conditions and biocompatibility evaluation. Acs Nano, 2014, 8(1): 634-641. |
| [10] | KIM H D, JANG H L, AHN HY,et al. Biomimetic whitlockite inorganic nanoparticles-mediated in situ remodeling and rapid bone regeneration. Biomaterials, 2017, 112: 31-43. |
| [11] | ZHANG J T, LIU W Z, SCHNITZLER V,et al. Calcium phosphate cements for bone substitution: chemistry, handling and mechanical properties. Acta Biomaterialia, 2013, 10(3): 1035-1049. |
| [12] | FURUZONO T, WALSH D, YASUDA S,et al. Preparation of plated β-tricalcium phosphate containing hydroxyapatite for use in bonded inorganic-organic composites. Journal of Materials Science, 2005, 40(9): 2595-2597. |
| [13] | SWAIN S K, GOTMAN I, UNGER R,et al. Microstructure, mechanical characteristics and cell compatibility of β-tricalcium phosphate reinforced with biodegradable Fe-Mg metal phase. Journal of the Mechanical Behavior of Biomedical Materials, 2016, 53: 434-444. |
| [14] | SHAVANDI A, BEKHIT E D A, ALI A,et al. Microwave-assisted synthesis of high purity β-tricalcium phosphate crystalline powder from the waste of green mussel shells. Powder Technology, 2015, 273: 33-39. |
| [15] | TORRES P M, GOUVEIA S, OLHERO S,et al. Injectability of calcium phosphate pastes: effects of particle size and state of aggregation of β-tricalcium phosphate powders. Acta Biomaterialia, 2015, 21: 204-216. |
| [16] | HASHIMOTO K, KOBAYASHI T, TODA Y.Chemical composition of synthetic whitlockite prepared by hydrothermal method.Inorganic Materials, 1999, 6(279): 110-116. |
| [17] | GOPAL R, CALVO C, ITO J,et al. Crystal structure of synthetic Mg-whitlockite, Cal8Mg2H2(PO4)14. Canadian Journal of Chemistry, 2011, 52(7): 1155-1164. |
| [18] | BOANINI E, GAZZANO M, BIGI A.Ionic substitutions in calcium phosphates synthesized at low temperature.Acta Biomaterialia, 2010, 6: 1882-1894. |
| [1] | LI Yuejun, CAO Tieping, SUN Dawei. Bi4O5Br2/CeO2 Composite with S-scheme Heterojunction: Construction and CO2 Reduction Performance [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(8): 963-970. |
| [2] | WU Wei, BAKHET Shahd, ASANTE Naomi Addai, KAREEM Shefiu, KOMBO Omar Ramadhan, LI Binbin, DAI Honglian. In vitro Study of Biphasic Calcium Magnesium Phosphate Microspheres for Angiogenesis and Bone Formation [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(7): 830-838. |
| [3] | NIU Haibin, HUANG Jiahui, LI Qianwen, MA Dongyun, WANG Jinmin. Directly Hydrothermal Growth and Electrochromic Properties of Porous NiMoO4 Nanosheet Films [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(12): 1427-1433. |
| [4] | YAO Yishuai, GUO Ruihua, AN Shengli, ZHANG Jieyu, CHOU Kuochih, ZHANG Guofang, HUANG Yarong, PAN Gaofei. In-situ Loaded Pt-Co High Index Facets Catalysts: Preparation and Electrocatalytic Performance [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(1): 71-78. |
| [5] | ZHANG Xian, ZHANG Ce, JIANG Wenjun, FENG Deqiang, YAO Wei. Synthesis, Electronic Structure and Visible Light Photocatalytic Performance of Quaternary BiMnVO5 [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(1): 58-64. |
| [6] | WU Zhongcao, HUAN Zhiguang, ZHU Yufang, WU Chengtie. 3D Printing and Characterization of Microsphere Hydroxyapatite Scaffolds [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(6): 601-607. |
| [7] | GUO Xiaowei, LI Yuyan, CHEN Nanchun, WANG Xiuli, XIE Qinglin. Construction of Sustainable Release Antimicrobial Microspheres Loaded with Potassium Diformate [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(2): 181-187. |
| [8] | XIAO Yumin, Li Bin, QIN Lizhao, LIN Hua, LI Qing, LIAO Bin. Efficient Preparation of CuGeO3 with Controllable Morphology Using CuCl2 as Copper Source [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(1): 69-74. |
| [9] | WANG Juhan,WEN Xiong,LIU Chengchao,ZHANG Yuhua,ZHAO Yanxi,LI Jinlin. Preparation and Fischer-Tropsch Synthesis Performance of Hierarchical Co/Al-SiO2 Catalyst [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2020, 35(9): 999-1004. |
| [10] | PAN Bichen,REN Penghe,ZHOU Tejun,CAI Zhenyang,ZHAO Xiaojun,ZHOU Hongming,XIAO Lairong. Microstructure and Property of Thermal Insulation Coating on the Carbon Fiber Reinforced Epoxy Resin Composites [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2020, 35(8): 947-952. |
| [11] | HU Yaping, TIAN Zhengfang, ZHU Min, ZHU Yufang. Controllable Preparation and in Vitro Bioactivity of Bioglass Microspheres via Spray Drying Method [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2020, 35(11): 1268-1276. |
| [12] | GAO Long, ZHANG Zhaowenbin, CHANG Jiang. Bioglass/Polylactic Acid Porous Microspheres: Preparation and Their Application as Cell Microcarriers [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2020, 35(10): 1163-1168. |
| [13] | XU Yun-Qing,WANG Hai-Zeng. Sodium Magnesium Fluoride Particles of Different Morphologies: Prepared by EDTA-assisted Hydrothermal Method [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2019, 34(9): 933-937. |
| [14] | XIAO Wen-Qian,ZHANG Jing,LI Ke-Jiang,ZOU Xin-Yu,CAI Yu-Dong,LI Bo,LIU Xue,LIAO Xiao-Ling. Litchi-like Superparamagnetic Hydroxyapatite Microspheres with Hierarchically Mesoporous Microspheres [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2019, 34(9): 925-932. |
| [15] | GOU Sheng-Lian, NAI Xue-Ying, XIAO Jian-Fei, YE Jun-Wei, DONG Ya-Ping, LI Wu. Preparation and Thermal Decomposition of Basic Magnesium Chloride Whiskers [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2019, 34(7): 781-785. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||