无机材料学报 ›› 2020, Vol. 35 ›› Issue (4): 407-415.DOI: 10.15541/jim20190169 CSTR: 32189.14.10.15541/jim20190169
所属专题: 2020年能源材料论文精选(一) :金属离子电池&燃料电池
收稿日期:2019-04-22
修回日期:2019-08-03
出版日期:2020-04-20
网络出版日期:2020-04-10
作者简介:罗 燚(1994-), 男, 博士研究生. E-mail: nudtluoyi@163.com
基金资助:
LUO Yi,FENG Junzong,FENG Jian( ),JIANG Yonggang,LI Liangjun
),JIANG Yonggang,LI Liangjun
Received:2019-04-22
Revised:2019-08-03
Published:2020-04-20
Online:2020-04-10
Supported by:摘要:
质子交换膜燃料电池(PEMFC)具有能量转换效率高、功率密度大、室温启动快、噪音低和零污染等特点, 有望减少二氧化碳排放量, 缓解能源危机, 在轨道交通、航空航天等领域具有广阔的应用前景。催化剂是PEMFC的关键材料, Pt催化氧还原反应活性和稳定性好, 是广泛使用且很难被取代的电催化剂。然而Pt储量低、价格昂贵, 导致PEMFC成本较高, 使用Pt载体可减少PEMFC的Pt负载量, 提高Pt利用率。碳材料具有成本低廉、比表面积大、孔结构丰富、电导率和表面性质可调等特性, 是广泛应用的Pt载体。商用的炭黑载体对Pt的利用效率低, 抗电化学腐蚀性较差。为了进一步提高PEMFC的性能和持续性, 需要研发能够均匀负载Pt、高效利用Pt、抗电化学腐蚀性强且导电性好的碳载体, 进而实现PEMFC的大规模应用。炭气凝胶、碳纳米管和石墨烯等新型碳载体具有独特的结构和性质, 可以提高PEMFC性能和寿命, 引起了研究者的广泛关注。本文对近年来PEMFC新型碳材料Pt载体的研究进展进行了较为详细的综述, 并对其发展趋势作出了适当评论。
中图分类号:
罗燚,冯军宗,冯坚,姜勇刚,李良军. 新型碳材料质子交换膜燃料电池Pt催化剂载体的研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2020, 35(4): 407-415.
LUO Yi,FENG Junzong,FENG Jian,JIANG Yonggang,LI Liangjun. Research Progress on Advanced Carbon Materials as Pt Support for Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cells[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2020, 35(4): 407-415.
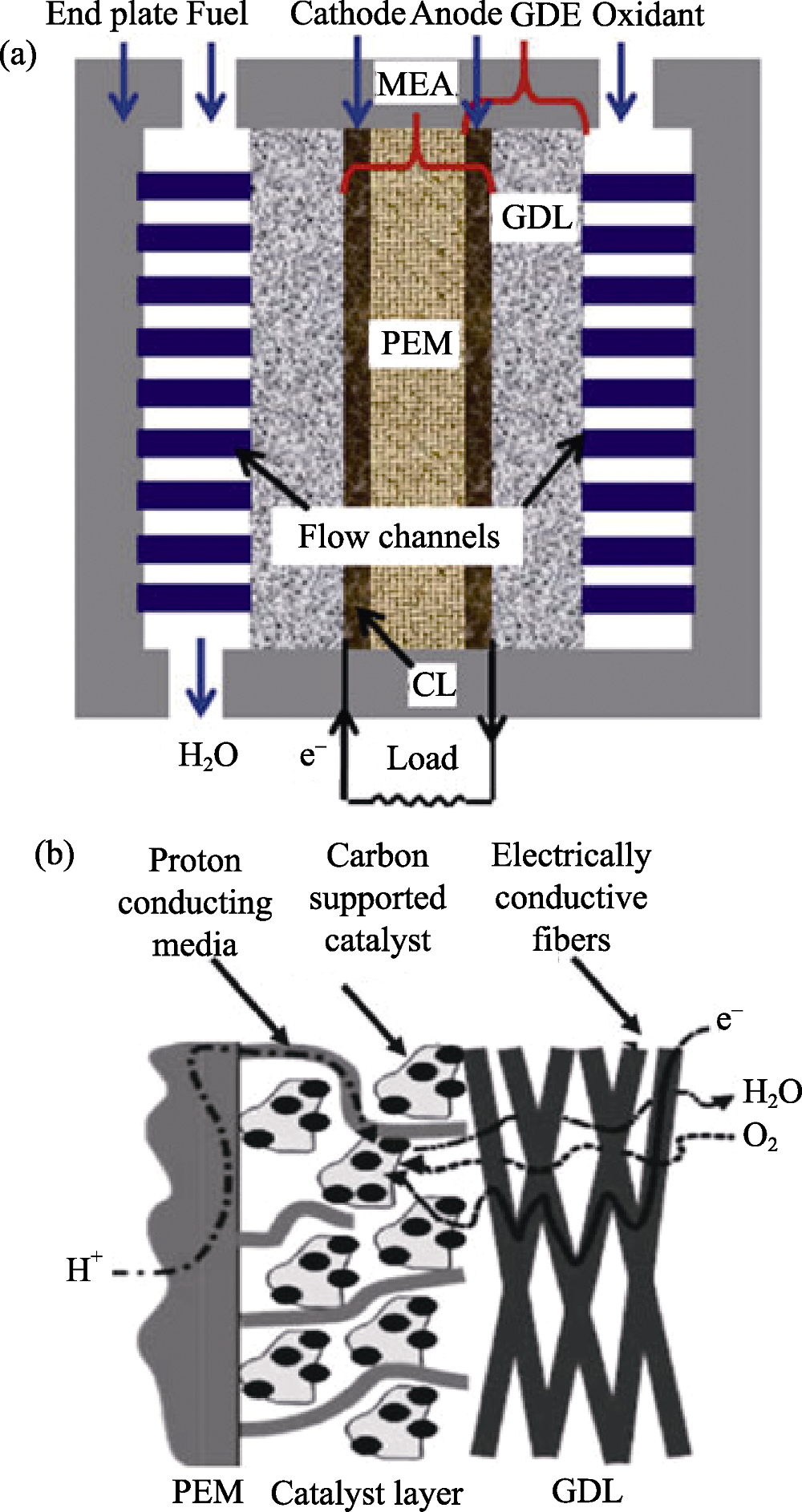
图1 PEMFC的组成结构示意图[6]
Fig. 1 Schematic diagram of PEMFC[6] PEM: Proton exchange membrane; MEA: Membrane electrode assembly; GDL: Gas diffusion layer; CL: Catalyst layer
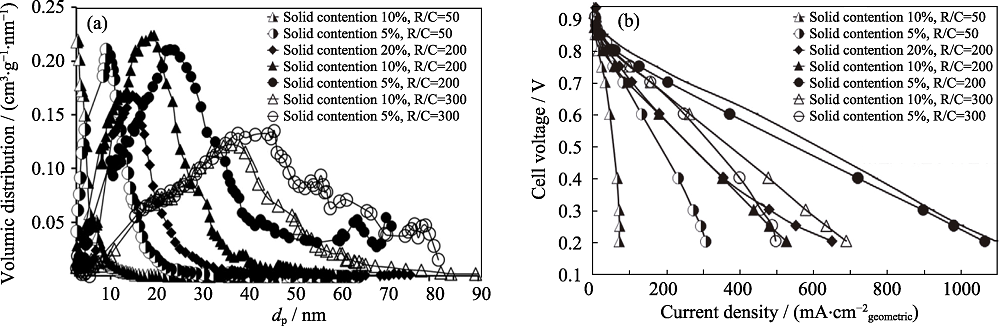
图5 压汞法测定的不同固含量、不同间苯二酚(R)和碳酸钠(C)摩尔比的炭气凝胶孔径分布曲线(a), 及其对应的单电池极化曲线(b)[29]
Fig. 5 Pore size distribution curves(a) of carbon aerogels determined by mercury porosimetry with different molar ratios of resorcinol (R) and sodium carbonate (C), and their corresponding single cell polarization curves(b)[29]
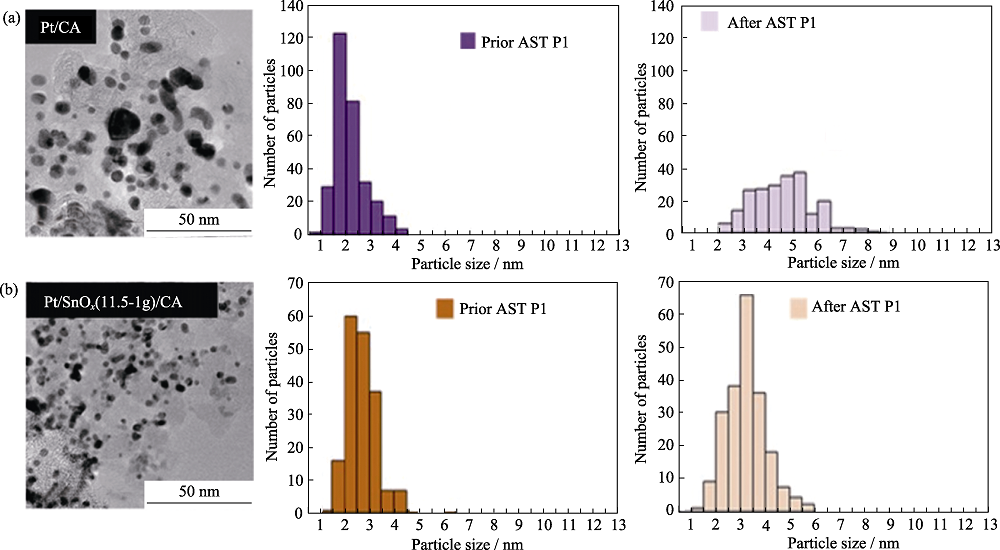
图6 炭气凝胶(a)及SnO2涂覆炭气凝胶(b)负载Pt催化剂加速氧化测试(AST P1)后的TEM照片和加速氧化测试前后的Pt粒子统计分布图[36]
Fig. 6 TEM images after accelerated stress tests (AST P1) and Pt nanoparticles statistical distributions before and after accelerated stress tests (AST P1)of carbon aerogels (a), SnO2 coated carbon aerogels (b) supported Pt catalysts[36]
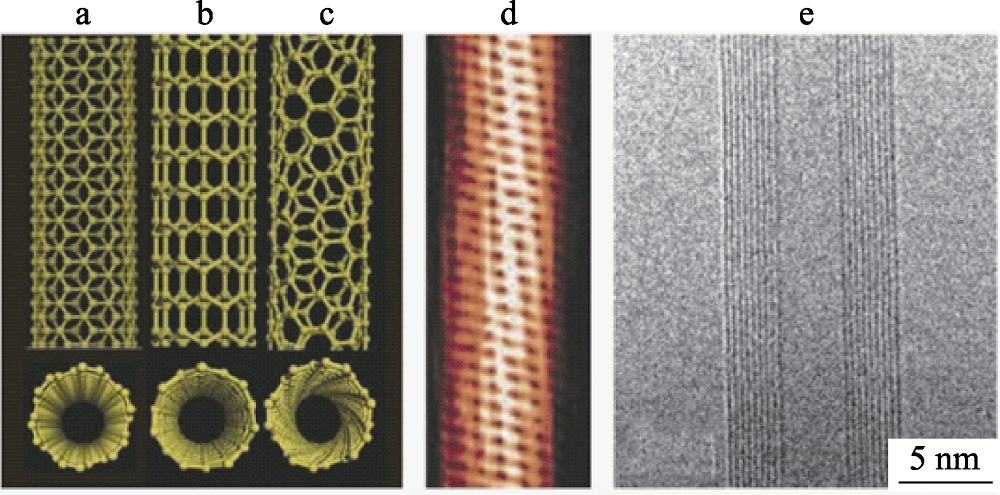
图7 碳纳米管原子结构示意图(a~c), 隧道电子显微镜照片(d), TEM微观形貌照片(e)[38]
Fig. 7 Schematic illustrations of the structures(a-c), tunneling electron microscope image(d), transmission electron microscope image (e) of carbon nanotubes[38]

图8 商业Pt/C(a), Pt/炭黑-石墨烯杂化材料(b)为阴极催化剂的PEMFC经加速氧化测试后的极化曲线; 不同循环次数后的电压保留值(c)[55]
Fig. 8 PEMFC polarization curves recorded after accelerated stress tests with cathode catalysts of commercial Pt/carbon black (a) and Pt/carbon black-graphene hybrid material (b); Voltage retention normalized with respect to initial performance after 10, 20, 100, 200, 500, and 1000 cycles(c)[55]
| Property | Carbon black | Carbon aerogel | Carbon nanotubes | Graphene |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Oxygen reduction reaction activity | √√ | √√ | √√ | |
| Proton transport | √ | √ | √√ | √√ |
| O2 transport | √ | √ | √√ | √√ |
| Water transport | √ | √ | √√ | √√ |
| Pt dispersion | √√ | |||
| Carbon corrosion | √ | √ | √√ | |
| Particle coalescence | √√ |
表1 不同碳载体的性能比较
Table 1 Comparison of some properties for four carbon supports
| Property | Carbon black | Carbon aerogel | Carbon nanotubes | Graphene |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Oxygen reduction reaction activity | √√ | √√ | √√ | |
| Proton transport | √ | √ | √√ | √√ |
| O2 transport | √ | √ | √√ | √√ |
| Water transport | √ | √ | √√ | √√ |
| Pt dispersion | √√ | |||
| Carbon corrosion | √ | √ | √√ | |
| Particle coalescence | √√ |
| [1] | DE L, ZHOU J R . Theoretical modeling of the PEMFC catalyst layer: a review of atomistic methods. Electrochimica Acta, 2015,177(7):4-20. |
| [2] | SHARMA S, POLLET B G . Support materials for PEMFC and DMFC electrocatalysts-a review. Journal of Power Sources, 2012,208(2):96-119. |
| [3] | CURTIN D E, LOUSENBERG R D, HENRY T J , et al. Advanced materials for improved PEMFC performance and life. Journal of Power Sources, 2004,131(1):41-48. |
| [4] | BARBIR F . PEM electrolysis for production of hydrogen from renewable energy sources. Solar Energy, 2005,78(5):661-669. |
| [5] | KNIGHTS S, BASHYAM R, HE P , et al. PEMFC MEA and System Design Considerations. 220th ECS Meeting, Boston, Massachusetts, USA, 2011. 39-53. |
| [6] | 马健新, 衣宝廉, 俞红梅 , 等. PEMFC膜电极组件(MEA)制备方法的评述. 化学进展, 2004,16(5):804-807. |
| [7] | KONGKANAN A . Encyclopedia of sustainability science and technology encyclopedia of sustainability science and technology, 1. New York: Springer, 2017, 1-20. |
| [8] | 孙世刚, 陈胜利 . 电催化, 1. 北京: 化学工业出版社, 2008, 242-253. |
| [9] | GASTEIGER H A, KOCHAS S, SOMPALLI B , et al. Activity benchmarks and requirements for Pt, Pt-alloy, and non-Pt oxygen reduction catalysts for PEMFCs. Applied Catalysis B Environmental, 2005,56(1):9-35. |
| [10] | SHAO Y, YIN G, GAO Y . Understanding and approaches for the durability issues of Pt-based catalysts for PEM fuel cell. Journal of Power Sources, 2007,171(2):558-566. |
| [11] | SHAO Y, LIU J, YONG W , et al. Novel catalyst support materials for PEM fuel cells: current status and future prospect. Journal of Materials Chemistry, 2008,19(1):46-59. |
| [12] | DICKS A L . The role of carbon in fuel cells. Journal of Power Sources, 2006,156(2):128-141. |
| [13] | SHARMA S, POLLET B G . Support materials for PEMFC and DMFC electrocatalysts-a review. Journal of Power Sources, 2012,208(2):96-119. |
| [14] | SHAHGALDI S, HAMELIN J . Improved carbon nanostructures as a novel catalyst support in the cathode side of PEMFC: a critical review. Carbon, 2015,94(1):705-728. |
| [15] | SHARMA S, POLLET B G . Support materials for PEMFC and DMFC electrocatalysts-a review. Journal of Power Sources, 2012,208(2):96-119. |
| [16] | KONGKANAND A, MATHIAS M F . The priority and challenge of high-power performance of low-platinum proton-exchange membrane fuel cells. The Journal of Physical Chemistry Letters, 2016,7(7):1127-1137. |
| [17] | SHINOZAKI K, MORIMOTO Y, PIVOVAR B S , et al. Suppression of oxygen reduction reaction activity on Pt-based electrocatalysts from ionomer incorporation. Journal of Power Sources, 2016,325(1):745-751. |
| [18] | BRUJIN F A D, DAM V A T, JANSSEN G J M . Review: durability and degradation issues of PEM fuel cell components. Fuel Cells, 2010,8(1):3-22. |
| [19] | SHAO Y, YIN G, GAO Y . Understanding and approaches for the durability issues of Pt-based catalysts for PEM fuel cell. Journal of Power Sources, 2007,171(2):558-566. |
| [20] | XIN W, LI W, CHEN Z , et al. Durability investigation of carbon nanotube as catalyst support for proton exchange membrane fuel cell. Journal of Power Sources, 2006,158(1):154-159. |
| [21] | DUBAU L, CASTANHEIRA L, BERTHOME G , et al. An identical- location transmission electron microscopy study on the degradation of Pt/C nanoparticles under oxidizing, reducing and neutral atmosphere. Electrochimica Acta, 2013,110(1):273-281. |
| [22] | THOMMES M, MORLAY C, AHMAD R , et al. Assessing surface chemistry and pore structure of active carbons by a combination of physisorption (H2O, Ar, N2, CO2), XPS and TPD-MS. Adsorption-Journal of the International Adsorption Society, 2011,17(3):653-661. |
| [23] | MAILLAR F, BONNEFONT A, MICOUD F . An EC-FTIR study on the catalytic role of Pt in carbon corrosion. Electrochemistry Communications, 2011,13(10):1109-1111. |
| [24] | ZHAO Z, CASTANHEIRA L, DUBAU L , et al. Carbon corrosion and platinum nanoparticles ripening under open circuit potential conditions. Journal of Power Sources, 2013,230(20):236-243. |
| [25] | MITTERMEIER T, WEI A, HASCHE , et al. PEM fuel cell start-up/shut-down losses vs temperature for non-graphitized and graphitized cathode carbon supports. Journal of The Electrochemical Society, 2017,164(2):127-137. |
| [26] | TUAEV X, RUDI S, STRASSER P . The impact of the morphology of a carbon support on the activity and stability of nanoparticle fuel cell catalysts. Catalysis Science & Technology, 2016,6(23):1670-1679. |
| [27] | CHOO H S, KINUMOTO T, NOSE M , et al. Electrochemical oxidation of highly oriented pyrolytic graphite during potential cycling in sulfuric acid solution. Journal of Power Sources, 2008,185(2):740-746. |
| [28] | AZADEH S, AHMAD R B, ALIREZA S . Correlation between structure and oxidation behavior of carbon aerogels. Journal of Energy Storage, 2016,7(1):195-203. |
| [29] | OUATTARA B M, BERTHON F S, BEAYGER C , et al. Influence of the carbon texture of platinum/carbon aerogel electrocatalysts on their behavior in a proton exchange membrane fuel cell cathode. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2012,37(12):10-20. |
| [30] | SMIRNOVA A, WENDER T, GOBERMAN D , et al. Modification of carbon aerogel supports for PEMFC catalysts. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2009,34(21):8992-8997. |
| [31] | OUATTARA B M, BERTHON F S, BEAYGER C , et al. Correlations between the catalytic layer composition, the relative humidity and the performance for PEMFC carbon aerogel-based membrane electrode assemblies. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2014,39(3):1420-1429. |
| [32] | WANG Q C, CHEN Z Y, WU N , et al. N-doped 3D carbon aerogel with trace Fe as efficient catalyst for oxygen reduction reaction. ChemElectroChem, 2017,4(3):2373-2377. |
| [33] | OUATTARA B M, BEAYGER C, BERTHON F S , et al. Carbon aerogels as catalyst supports and first insights on their durability in proton exchange membrane fuel cells. Fuel Cells, 2015,11(6):726-734. |
| [34] | SINGH R, SINGH M K, BHARTIYA S , et al. Facile synthesis of highly conducting and mesoporous carbon aerogel as platinum support for PEM fuel cells. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2017,42(16):11110-11117. |
| [35] | WANG Q C, LEI Y P, ZHU Y G , et al. Edge defects engineering of nitrogen-doped carbon for oxygen electrocatalysts in Zn-air batteries. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2018,10(1):29448-29456. |
| [36] | FABIEN L, ASSET T, CHATENET M , et al. Activity and durability of platinum-based electrocatalysts with tin oxide-coated carbon aerogel materials as catalyst supports. Electrocatalysis, 2019(1):1-17. |
| [37] | BERTHON F S, DUBAU L, AHMAD Y , et al. First insight into fluorinated Pt/carbon aerogels as more corrosion-resistant electrocatalysts for proton exchange membrane fuel cell cathodes. Electrocatalysis, 2015,6(6):521-533. |
| [38] | BAUGHMAN R H . Carbon nanotubes-the route toward applications. Science, 2002,297(5582):787-792. |
| [39] | GIRISHKUMAR G, VINODGOPAL K, KAMAT P V . Carbon nanostructures in portable fuel cells: single-walled carbon nanotube electrodes for methanol oxidation and oxygen reduction. The Journal of Physical Chemistry B, 2004,108(52):19960-19966. |
| [40] | GIGAEK L, HYEONJN C, YONG T . In situ durability of various carbon supports against carbon corrosion during fuel starvation in a PEM fuel cell cathode. Nanotechnology, 2019,30(8):1-12. |
| [41] | YILSER D, ELIF D . Multi-walled carbon nanotubes decorated by platinum catalyst for high temperature PEM fuel cell. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2019, doi: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2019.01.051. |
| [42] | YILSER D, ELIF D . Investigation of the effect of graphitized carbon nanotube catalyst support for high temperature PEM fuel cells. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2019, doi: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2019.01.111. |
| [43] | ZHAO L, WANG Q C, ZHANG X Q , et al. Combined electron and structure manipulation on Fe containing N-doped CNTs to boost bifunctional oxygen electrocatalysis. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2018,10(42):35888-35895. |
| [44] | MOHAMMAD N B, SUN S H, MENG X B , et al. TiSi2Ox coated N-doped carbon nanotubes as Pt catalyst support for the oxygen reduction reaction in PEMFCs. The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2013,117(30):15457-15467. |
| [45] | GAO W B, ZHANG Z P, DOU M L , et al. Highly dispersed and crystalline Ta2O5 anchored Pt electrocatalyst with improved activity and durability towards oxygen reduction: promotion by atomic- scale Pt-Ta2O5 interactions. ACS Catalysis, 2019, doi: 10.1021/acscatal.8b04505. |
| [46] | SAHOO M, SCOTT K, RAMAPRABHU S . Platinum decorated on partially exfoliated multiwalled carbon nanotubes as high- performance cathode catalyst for PEMFC. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2015,40(30):9435-9443. |
| [47] | PRIJI C, PUTHUSSERI D, RAMAPRABHU S . 1D-2D integrated hybrid carbon nanostructure supported bimetallic alloy catalyst for ethanol oxidation and oxygen reduction reactions. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2019,44(10):4951-4961. |
| [48] | MEENAKSHI S G, RAMAPRABHU S . Highly efficient and ORR active platinum-scandium alloy-partially exfoliated carbon nanotubes electrocatalyst for proton exchange membrane fuel cell. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2019, doi: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2019.02.161. |
| [49] | SHENG Z H, SHAO L, CHEN J J , et al. Catalyst-free synthesis of nitrogen-doped graphene via thermal annealing graphite oxide with melamine and its excellent electrocatalysis. ACS Nano, 2011,5(6):4350-4358. |
| [50] | LIU J F, DAIO T, KAZUNARI S , et al. Defective graphene foam: a platinum catalyst support for PEMFCs. Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 2014,161(9):838-844. |
| [51] | EYLUL S Ö, ŞANSIM B B, SELMI E B , et al. Graphene aerogel supported Pt electrocatalysts for oxygen reduction reaction by supercritical deposition. Electrochimica Acta, 2017,250(1):174-184. |
| [52] | ECE A, BEGUM Y K, AHMET M M , et al. An effective electrocatalyst based on platinum nanoparticles supported with graphene nanoplatelets and carbon black hybrid for PEM fuel cells. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2019, doi: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2018.11.210. |
| [53] | MELIKE S Y, BEGÜM Y K, SELMIYE A G , et al. Binary CuPt alloy nanoparticles assembled on reduced graphene oxide-carbon black hybrid as efficient and cost-effective electrocatalyst for PEMFC. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2018,44(27):14184-14192. |
| [54] | SEVIM Y M, KAPLAN B Y, METIN , et al. A facile synthesis and assembly of ultrasmall Pt nanoparticles on reduced graphene oxide- carbon black hybrid for enhanced performance in PEMFC. Materials and Design, 2018,151(1):29-36. |
| [55] | LI Z F, XIN L, YANG F , et al. Hierarchical polybenzimidazole- grafted graphene hybrids as supports for Pt nanoparticle catalysts with excellent PEMFC performance. Nano Energy, 2015,16(1):281-292. |
| [56] | EMELINE R, YOHANN R J, LAURE G , et al. Optimization and tunability of 2D graphene and 1D carbon nanotube electrocatalysts structure for PEM Fuel Cells. Catalysts, 2018,8(9):377-387. |
| [57] | YANG H N, KO Y D, KIM W J . 3D structured Pt/rGO-polyethyleneimine-functionalized MWCNTs prepared with different mass ratio of rGO and MWCNT for proton exchange membrane fuel cell. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2018,43(9):4439-4447. |
| [58] | OH E J, HEMPELMANN R, NICA V , et al. New catalyst supports prepared by surface modification of graphene and carbon nanotube structures with nitrogen containing carbon coatings. Journal of Power Sources, 2017(1):240-249. |
| [59] | FU K, WANG Y, MAO L , et al. Facile one-pot synthesis of graphene-porous carbon nanofibers hybrid support for Pt nanoparticles with high activity towards oxygen reduction. Electrochimica Acta, 2016(1):427-434. |
| [60] | FU K, WANG Y, QIAN Y , et al. Synergistic effect of nitrogen doping and MWCNT intercalation for the graphene hybrid support for Pt nanoparticles with exemplary oxygen reduction reaction performance. Materials, 2018,11(4):1-13. |
| [61] | CATIA A, SARA R, FRANCESCA S , et al. Graphene and carbon nanotube structures supported on mesoporous xerogel carbon as catalysts for oxygen reduction reaction in proton-exchange- membrane fuel cells. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2011,36(8):5038-5046. |
| [62] | GHOSHL A, BASU S, VERMAL A . Graphene and functionalized graphene supported platinum catalyst for PEMFC. Fuel Cells, 2013,13(3):355-363. |
| [63] | GRIGORIEV S A, FATEEV V N, PUSHKAREV A S , et al. Reduced graphene oxide and its modifications as catalyst supports and catalyst layer modifiers for PEMFC. Materials, 2018,11(8):1-15. |
| [64] | XIN L, YANG F, RASOULI S , et al. Understanding Pt nanoparticle anchoring on graphene supports through surface functionalization. ACS Catalysis, 2016,6(4):2642-2653. |
| [65] | SERGRY A G, VLADIMIR N F, ARTEM S . Reduced graphene oxide and its modifications as catalyst supports and catalyst layer modifiers for PEMFC. Materials, 2018,11(10):1045-1056. |
| [66] | WANG Q C, LEI Y P, WANG D S , et al. Defect engineering in earth-abundant electrocatalysts for CO2 and N2 reduction. Energy& Environment Science, 2019, doi: 10.1039/c8ee03781g. |
| [67] | XU X, YAN X M, ZHONG Z , et al. The construction of porous graphene tri-doped with B, N and Co for enhanced oxygen reduction reaction. Carbon, 2019, doi: 10.1016/j.carbon.2019.01.039. |
| [68] | LEI Y P, SHI Q, HAN C , et al. N-doped graphene grown on silk cocoon-derived interconnected carbon fibers for oxygen reduction reaction and photocatalytic hydrogen production. Nano Research, 2016,9(8):2498-2509. |
| [69] | WANG Q C, JI Y J, LEI Y P , et al. Pyridinic-N-dominated doped graphene with abundant defects as superior oxygen electrocatalyst for ultrahigh-energy-density Zn-air batteries. ACS Energy Letters, 2018,3(1):1183-1191. |
| [70] | YANG X D, ZHENG Y P, YANG J , et al. Modeling Fe/N/C catalysts in monolayer graphene. ACS Catalysis, 2017,7(1):139-145. |
| [71] | WANG Y, JIN J, YANG , et al. Highly active and stable platinum catalyst supported on porous carbon nanofibers for improved performance of PEMFC. Electrochimica Acta, 2015,177(1):181-189. |
| [72] | WANG Y, LI G, JIN J H , et al. Hollow porous carbon nanofibers as novel support for platinum-based oxygen reduction reaction electrocatalysts. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2017,42(9):5938-5947. |
| [73] | WANG Y, JIN J H, YANG S L , et al. Nitrogen-doped porous carbon nanofiber based oxygen reduction reaction electrocatalysts with high activity and durability. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2016,41(26):11174-11189. |
| [74] | SONG J, LI G, QIAO J . Ultrafine porous carbon fiber and its supported platinum catalyst for enhancing performance of proton exchange membrane fuel cells. Electrochimica Acta, 2015,177(13):46861-46878. |
| [75] | YING J, LI J, JIANG G P , et al. Metal-organic frameworks derived platinum-cobalt bimetallic nanoparticles in nitrogen-doped hollow porous carbon capsules as a highly active and durable catalyst for oxygen reduction reaction. Applied Catalysis B-Environmental, 2018,225(1):496-503. |
| [76] | CHEN Z Y, WANG Q C, ZHANG X B , et al. N-doped defective carbon with trace Co for efficient rechargeable liquid electrolyte-/all-solid-state Zn-air batteries. Science Bulletin, 2018,60(9):548-555. |
| [1] | 朱文杰, 唐璐, 陆继长, 刘江平, 罗永明. 钙钛矿型氧化物催化氧化挥发性有机化合物的研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(7): 735-746. |
| [2] | 胡智超, 杨鸿宇, 杨鸿程, 孙成礼, 杨俊, 李恩竹. P-V-L键理论在微波介质陶瓷性能调控中的应用[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(6): 609-626. |
| [3] | 吴琼, 沈炳林, 张茂华, 姚方周, 邢志鹏, 王轲. 铅基织构压电陶瓷研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(6): 563-574. |
| [4] | 张碧辉, 刘小强, 陈湘明. Ruddlesden-Popper结构杂化非常规铁电体的研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(6): 587-608. |
| [5] | 吴杰, 杨帅, 王明文, 李景雷, 李纯纯, 李飞. 铅基织构压电陶瓷的发展历程、现状与挑战[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(6): 575-586. |
| [6] | 姜昆, 李乐天, 郑木鹏, 胡永明, 潘勤学, 吴超峰, 王轲. PZT陶瓷的低温烧结研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(6): 627-638. |
| [7] | 杨茗凯, 黄泽皑, 周芸霄, 刘彤, 张魁魁, 谭浩, 刘梦颖, 詹俊杰, 陈国星, 周莹. 基于Cu与金属氧化物-KCl熔融介质的甲烷热解制备少层石墨烯与氢气联产研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(5): 473-480. |
| [8] | 田睿智, 兰正义, 殷杰, 郝南京, 陈航榕, 马明. 基于微流控技术的纳米无机生物材料制备: 原理及其研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(4): 337-347. |
| [9] | 张继国, 吴田, 赵旭, 杨钒, 夏天, 孙士恩. 钠离子电池正极材料循环稳定性提升策略及产业化进程[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(4): 348-362. |
| [10] | 殷杰, 耿佳毅, 王康龙, 陈忠明, 刘学建, 黄政仁. SiC陶瓷的3D打印成形与致密化新进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(3): 245-255. |
| [11] | 高晨光, 孙晓亮, 陈君, 李达鑫, 陈庆庆, 贾德昌, 周玉. 基于湿法纺丝技术的SiBCN-rGO陶瓷纤维的组织结构、力学和吸波性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(3): 290-296. |
| [12] | 谌广昌, 段小明, 朱金荣, 龚情, 蔡德龙, 李宇航, 杨东雷, 陈彪, 李新民, 邓旭东, 余瑾, 刘博雅, 何培刚, 贾德昌, 周玉. 直升机特定结构先进陶瓷材料研究进展与应用展望[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(3): 225-244. |
| [13] | 王悦, 王欣, 于显利. 室温铁磁性还原氧化石墨烯基全碳膜[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(3): 305-313. |
| [14] | 范晓波, 祖梅, 杨向飞, 宋策, 陈晨, 王子, 罗文华, 程海峰. 质子调控型电化学离子突触研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(3): 256-270. |
| [15] | 海热古·吐逊, 郭乐, 丁嘉仪, 周嘉琪, 张学良, 努尔尼沙·阿力甫. 上转换荧光探针辅助的光学成像技术在肿瘤显影中的应用研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(2): 145-158. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||