无机材料学报 ›› 2020, Vol. 35 ›› Issue (8): 847-856.DOI: 10.15541/jim20190554 CSTR: 32189.14.10.15541/jim20190554
所属专题: 功能材料论文精选(二):发光材料(2020)
• 综述 • 下一篇
姬海鹏1( ),张宗涛1,XU Jian2,TANABE Setsuhisa2,陈德良1(
),张宗涛1,XU Jian2,TANABE Setsuhisa2,陈德良1( ),解荣军3(
),解荣军3( )
)
收稿日期:2019-10-31
修回日期:2019-11-20
出版日期:2020-08-20
网络出版日期:2020-03-06
作者简介:姬海鹏(1989-), 男, 讲师. E-mail: <email>jihp@zzu.edu.cn</email><br/>JI Haipeng (1989–), male, lecturer. E-mail: <email>jihp@zzu.edu.cn</email>
基金资助:
JI Haipeng1( ),ZHANG Zongtao1,XU Jian2,TANABE Setsuhisa2,CHEN Deliang1(
),ZHANG Zongtao1,XU Jian2,TANABE Setsuhisa2,CHEN Deliang1( ),XIE Rongjun3(
),XIE Rongjun3( )
)
Received:2019-10-31
Revised:2019-11-20
Published:2020-08-20
Online:2020-03-06
Supported by:摘要:
稳定可靠的高光子能量发光(620~650 nm)红光荧光粉, 对于构建低色温、高显指荧光粉转换型白光发光二极管(WLED)至关重要。Mn 4+激活红光荧光粉是当前WLED用荧光粉研究热点之一。本文介绍了Mn 4+离子的能级跃迁与光致发光特性, 详细叙述了目前所报道的七种Mn 4+激活含d 0/d 10/s 0离子氧氟化物系列红色荧光粉(如Na2WO2F4:Mn 4+等)的制备方法、晶体结构及其发光特性。目前Mn 4+在氧氟化物结构中得到强R线发光的情况少, 微观配位体仍是[MnF6]或[MnO6], 其化学稳定性和量子效率研究也很缺乏。最后对Mn 4+激活氧氟化物红光荧光粉的研究进行了展望。
中图分类号:
姬海鹏, 张宗涛, XU Jian, TANABE Setsuhisa, 陈德良, 解荣军. Mn4+激活氧氟化物红光荧光粉的研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2020, 35(8): 847-856.
JI Haipeng, ZHANG Zongtao, XU Jian, TANABE Setsuhisa, CHEN Deliang, XIE Rongjun. Advance in Red-emitting Mn4+-activated Oxyfluoride Phosphors[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2020, 35(8): 847-856.
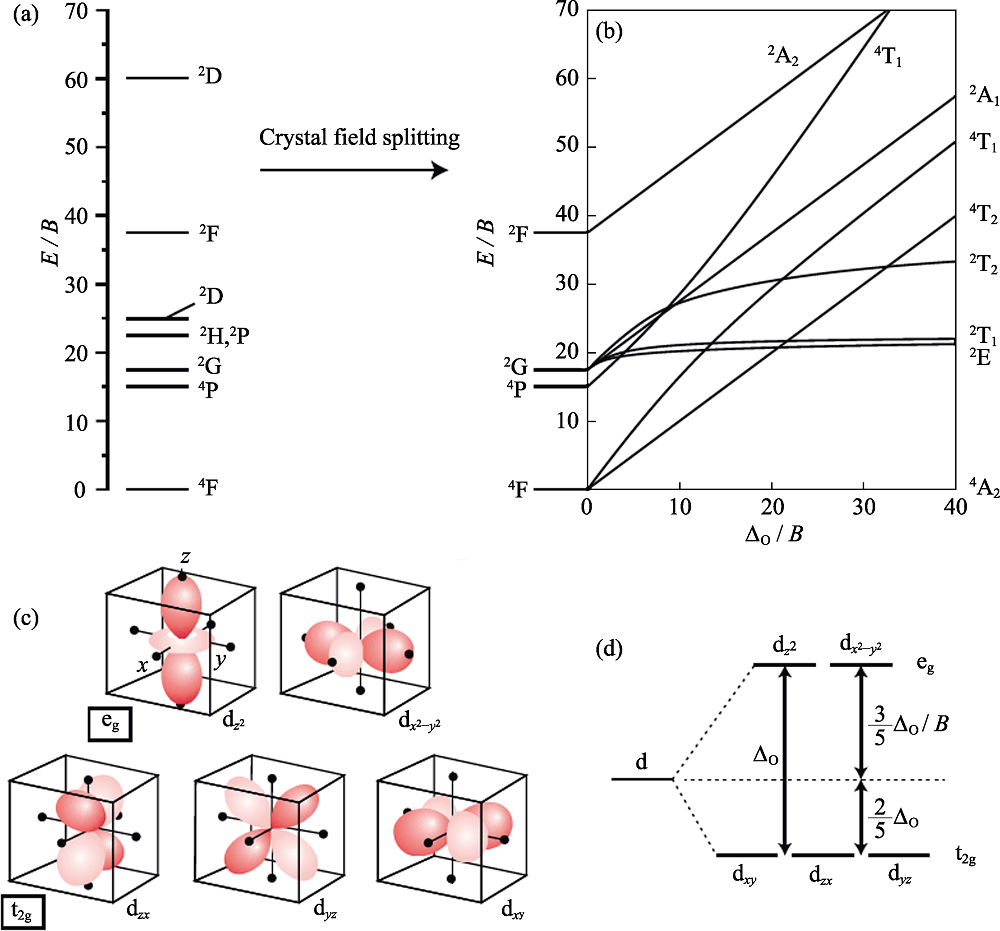
图1 d3离子的自由离子能级(C = 4.5B) (a), 描述d3离子在八面体晶体场中能级劈裂的Tanabe-Sugano图(C = 4.5B) (b), 八面体晶体场中五种d轨道相对于配体的取向(黑点表示配体离子)(c)和d轨道在八面体晶体场中的晶体场劈裂(d)[16]
Fig. 1 Energy levels arising from a d3 configuration for a free transition metal ion (C=4.5B) (a), Tanabe-Sugano diagram for the d3 electron configuration in an octahedral crystal field (C=4.5B) (b), orientation of the five d-orbitals with respect to the ligands of an octahedral complex (black dots showing the ligands around the transition metal ion) (c), and crystal field splitting for the d-orbitals in an octahedral crystal field (d)[16]
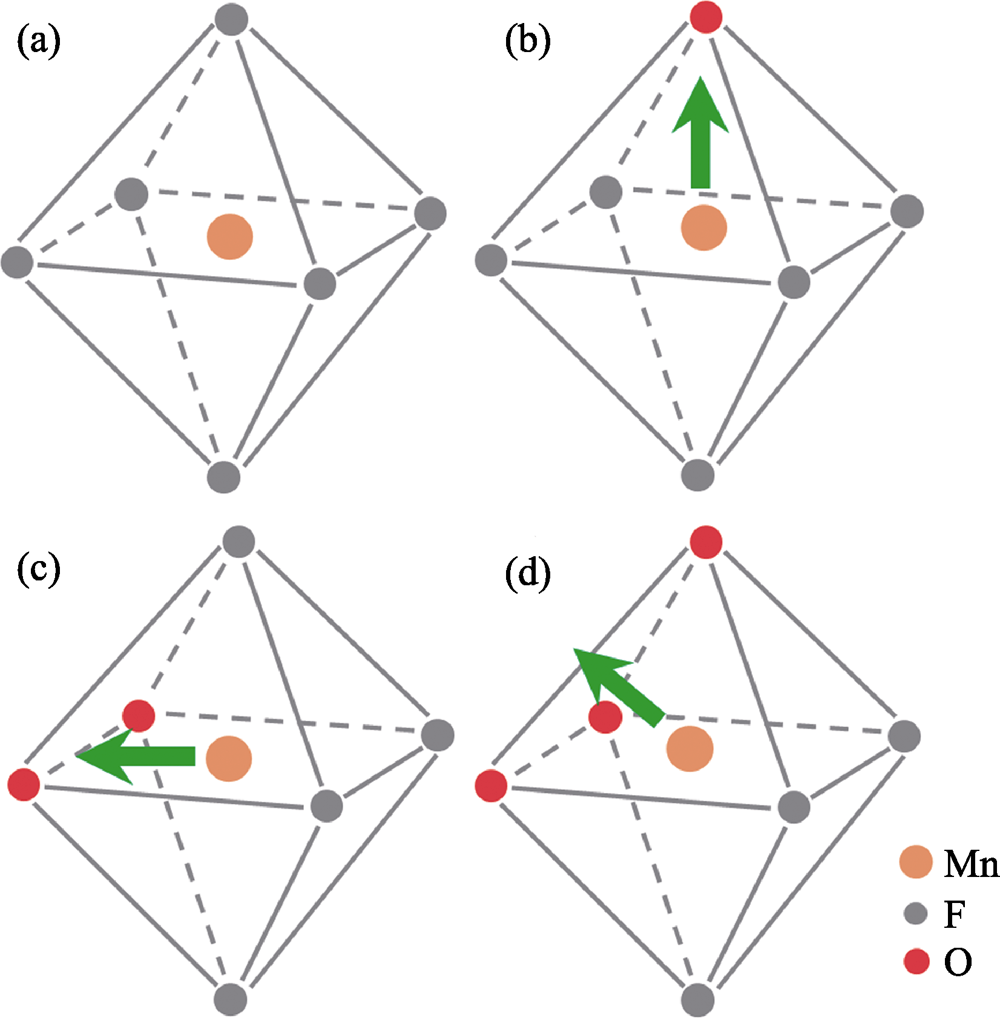
图2 规则八面体配位和畸变八面体配位
Fig. 2 Regular octahedron coordination and distorted octahedra coordination (a) Point symmetry of Oh; (b) Central cation shifting to a vertex, C4v; (c) Central cation shifting to an edge, C2v; (d) Central cation shifting to a face, C3v
| Cation | Phosphor host | Peaking wavelength/nm | (R-line/ν6 intensity ratio)/% | T50%/K | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| d0 | Na2WO2F4 | 619 | 125 | 340 | [21-22] |
| Cs2WO2F4 | 632 | 5 | 350 | [23] | |
| Cs2NbOF5 | 632 | 10 | - | [24-25] | |
| BaNbOF5 | 629 | 10 | - | [26] | |
| Sr2ScO3F | 690 | - | 320 | [27] | |
| BaTiOF4 | 632 | 5 | - | [28] | |
| d10 | Mg28Ge7.55O32F15.04 | 657 | - | 700 | [29] |
| s0 | LiAl4O6F | 662 | 5-10 | - | [30] |
表1 目前所报道的Mn4+激活氧氟化物荧光粉
Table 1 The reported Mn4+ activated oxyfluoride phosphors
| Cation | Phosphor host | Peaking wavelength/nm | (R-line/ν6 intensity ratio)/% | T50%/K | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| d0 | Na2WO2F4 | 619 | 125 | 340 | [21-22] |
| Cs2WO2F4 | 632 | 5 | 350 | [23] | |
| Cs2NbOF5 | 632 | 10 | - | [24-25] | |
| BaNbOF5 | 629 | 10 | - | [26] | |
| Sr2ScO3F | 690 | - | 320 | [27] | |
| BaTiOF4 | 632 | 5 | - | [28] | |
| d10 | Mg28Ge7.55O32F15.04 | 657 | - | 700 | [29] |
| s0 | LiAl4O6F | 662 | 5-10 | - | [30] |
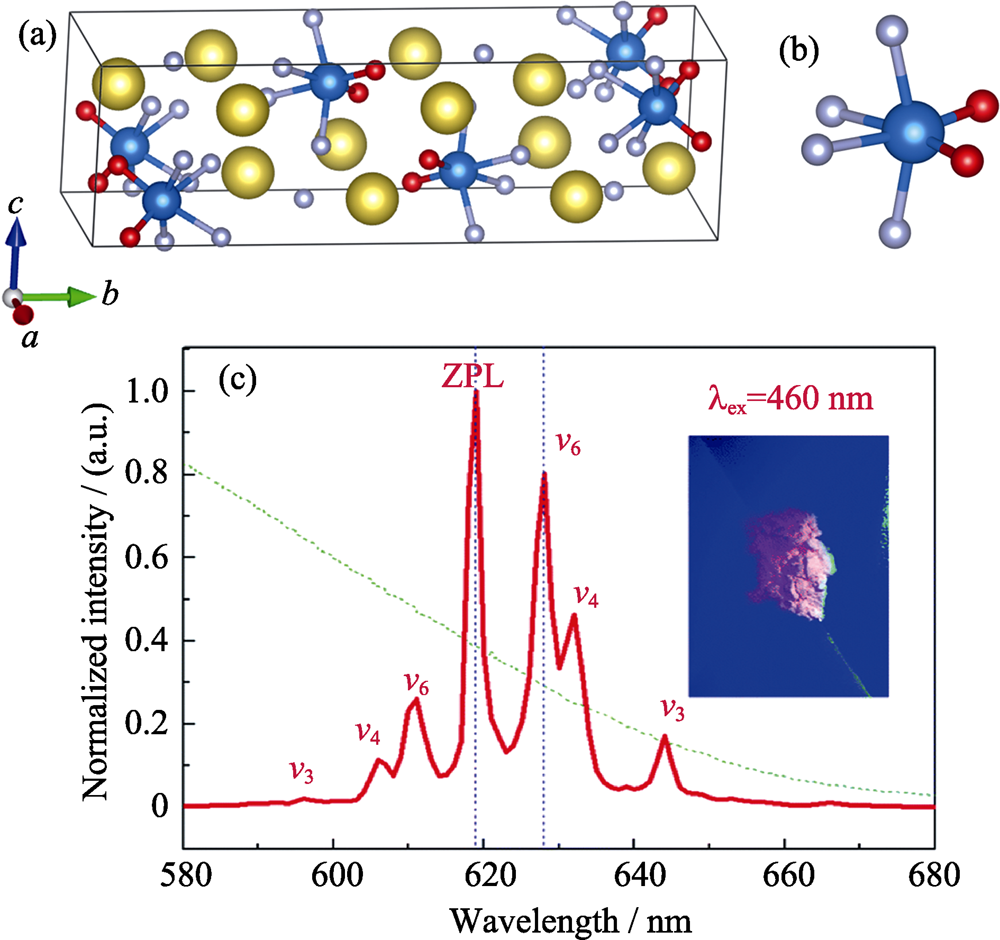
图3 Na2WO2F4的晶胞(a), 具有较大畸变的[WO2F4]八面体(b)和Na2WO2F4:Mn4+的发光光谱(c)(插图为其在460 nm激发下照片)[21]
Fig. 3 Unit cell of Na2WO2F4 (a), highly-distorted [WO2F4] octahedra (b), and emission spectrum of Na2WO2F4:Mn4+ (c) [21] with inset showing phosphor image under 460 nm light Na: yellow; W: blue; O: red; F: gray
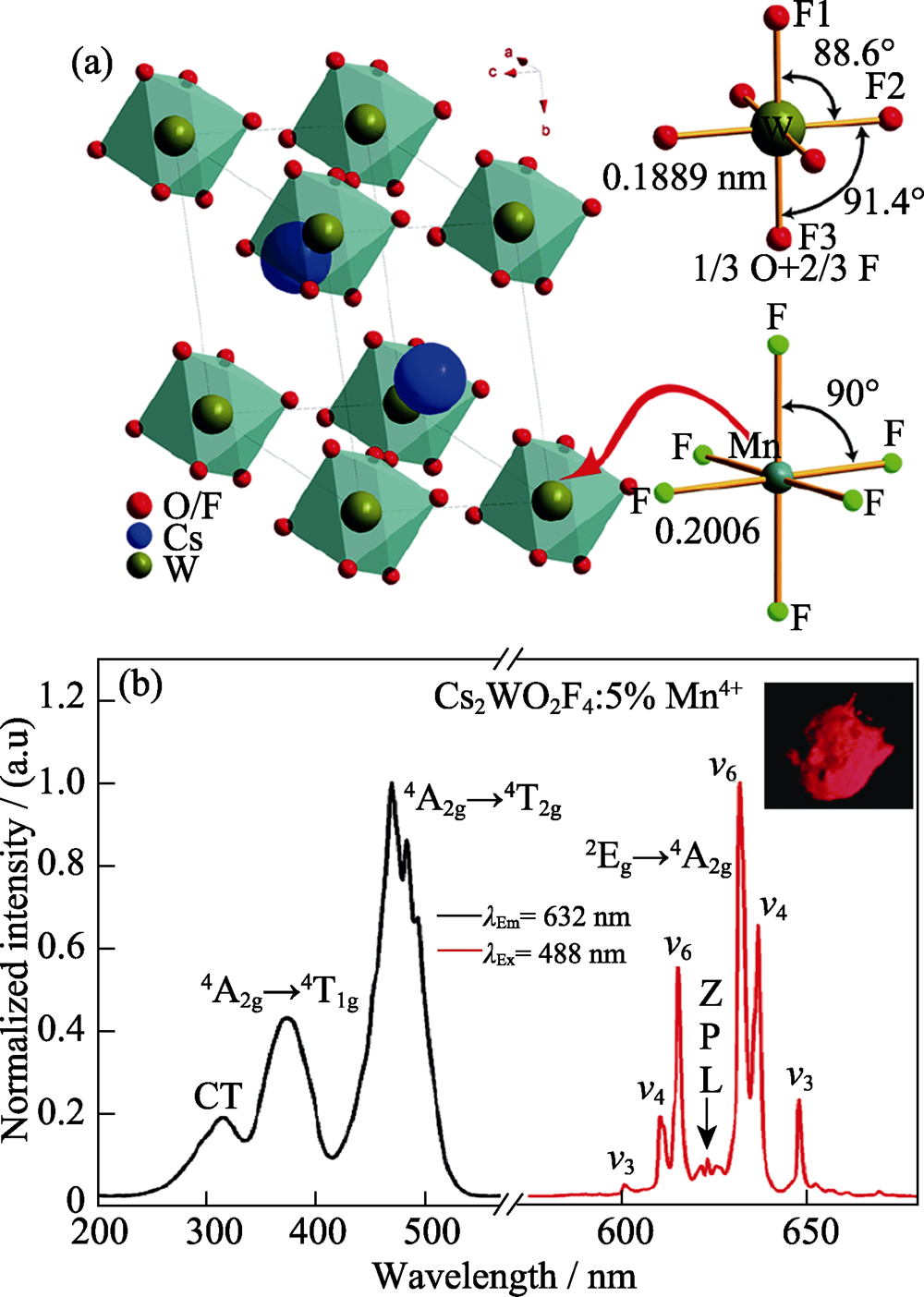
图4 (a) Cs2WO2F4的晶体结构, 其含有具有较小畸变的W(O,F)6配位八面体, 右下所示为Mn4+在K2MnF6中的微观配位八面体; (b) Cs2WO2F4:Mn4+的激发与发射光谱(插图为其在365 nm激发下照片)[23]
Fig. 4 (a) Unit cell of Cs2WO2F4 which contains slightly- distorted [W(O,F)6] octahedra, with the bottom-right showing the local coordination of Mn4+ in K2MnF6; (b) Excitation and emission spectra of Cs2WO2F4:Mn4+ with inset showing the phosphor image under 365 nm light[23]
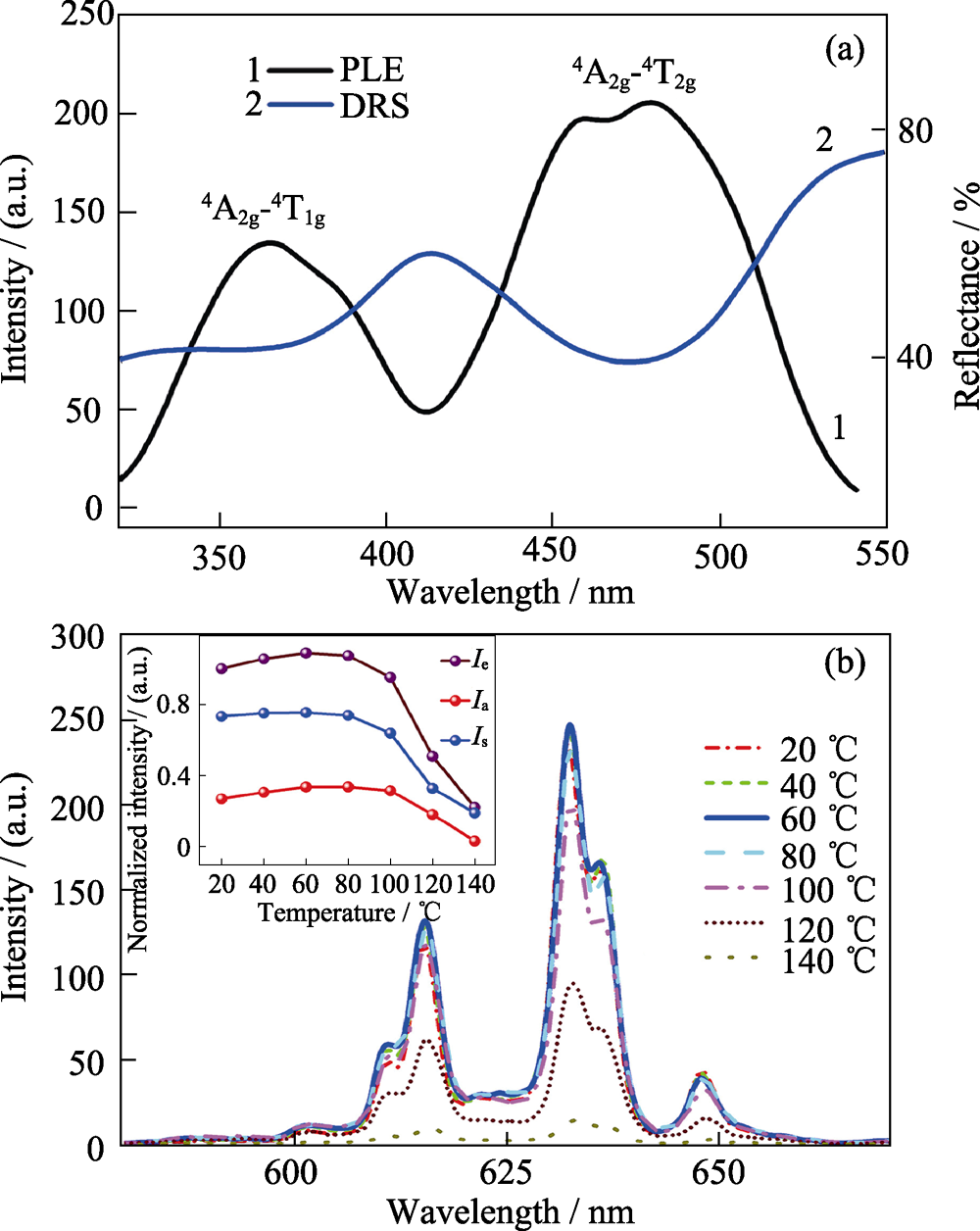
图5 Cs2NbOF5:Mn4+的激发光谱(PLE)与漫反射光谱(DRS) (a)和Cs2NbOF5:Mn4+的变温发光光谱(b)[24]
Fig. 5 PLE and DRS spectra of the Cs2NbOF5:Mn4+ phosphor (a) and temperature-dependent emission spectra of Cs2NbOF5:Mn4+ (b)[24] with the inset showing the intensity evolution of the integrated emission (Ie), the stokes emission (Is) and the anti-stokes emmission (Ia)
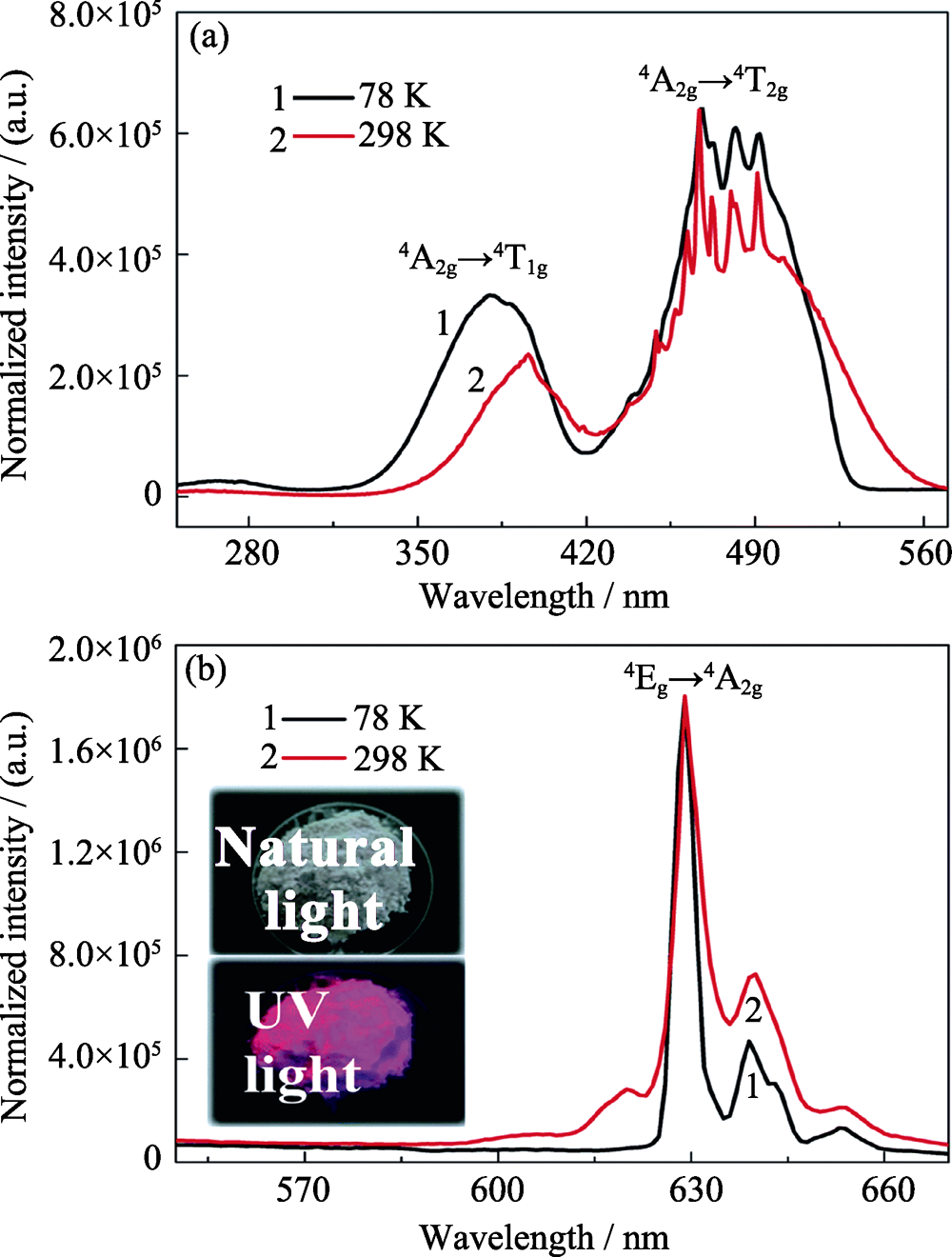
图6 T=78和298 K时BaNbOF5:Mn4+的激发光谱(a)与发光光谱(b) (插图为该荧光粉在自然光和紫外光照射下照片)[26]
Fig. 6 The PLE (a) and PL (b) spectra of the BaNbOF5:Mn4+ phosphor at temperature of 78 and 298 K with insets showing the phosphor images under natural or UV light[26]
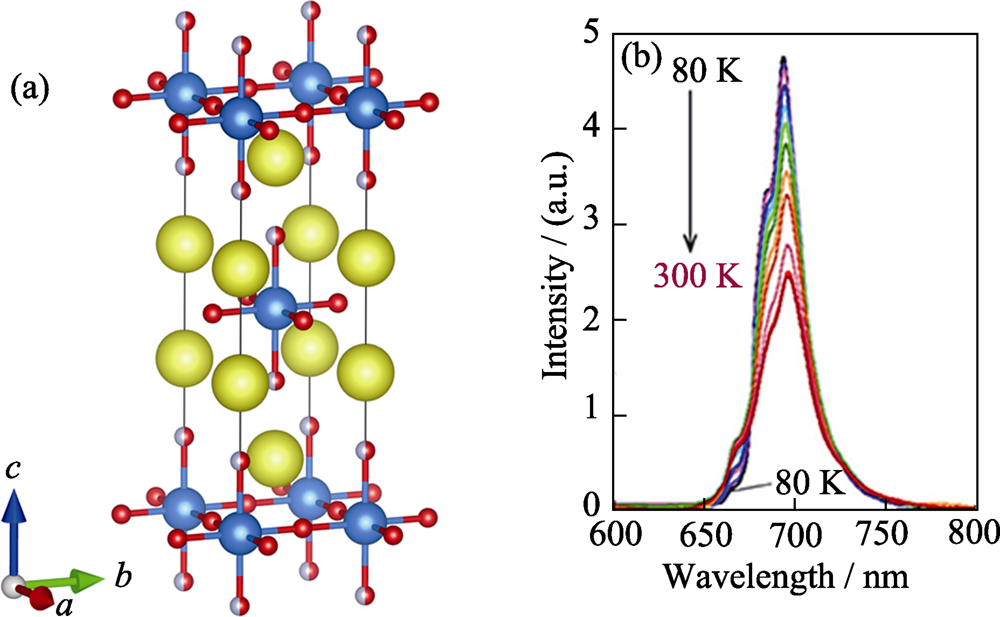
图7 Sr2ScO3F的晶胞(a)和Sr2ScO3F:Mn4+的变温发光光谱(b)[27]
Fig. 7 Unit cell of Sr2ScO3F (a) and temperature-dependent emission spectra of Sr2ScO3F:Mn4+ (b)[27]Sr: yellow; Sc: blue; O: red; F: gray
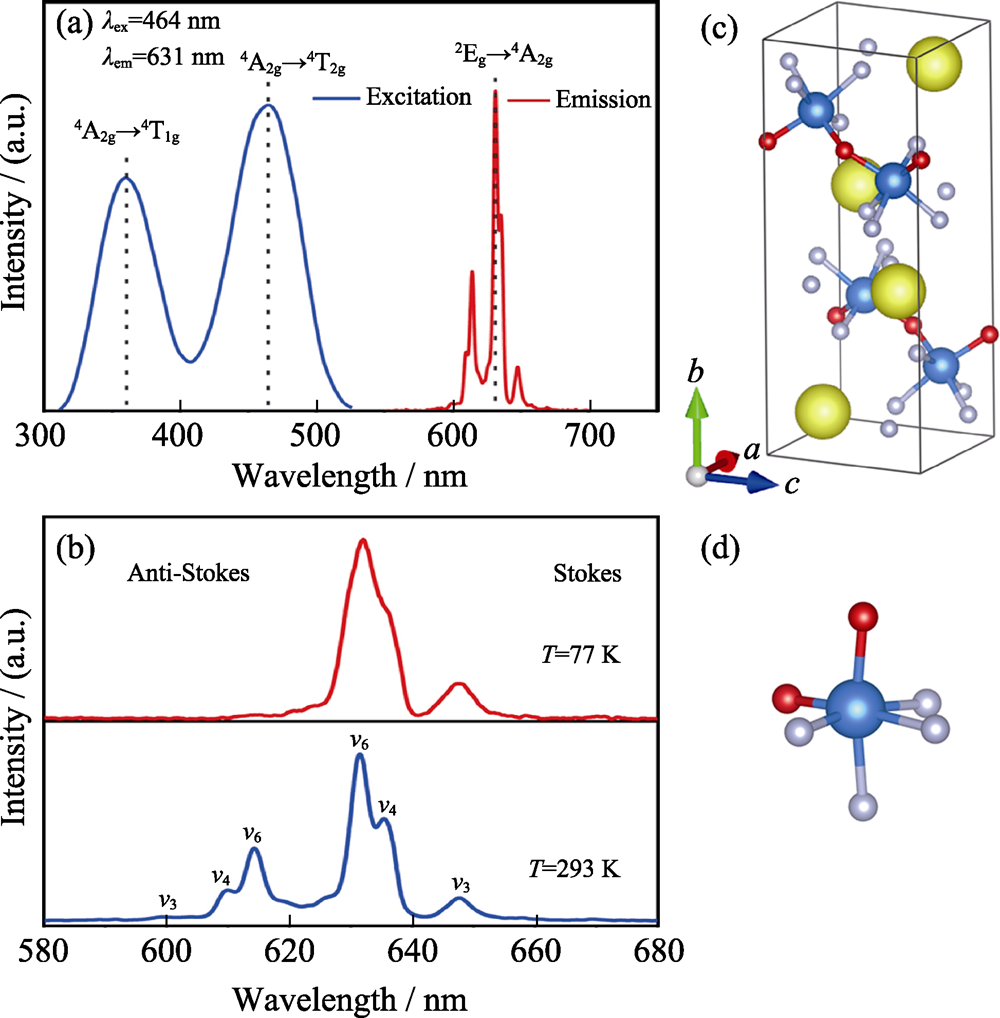
图8 BaTiOF4:Mn4+的室温激发与发射光谱(a), BaTiOF4:Mn4+的室温和低温发光光谱(b), BaTiOF4的晶胞(c)和[Ti2OF4]畸变八面体(d)[28]
Fig. 8 Excitation and emission spectra of BaTiOF4:Mn4+ at room temperature (a), emission spectra of BaTiOF4:Mn4+ at 77 K and 293 K (b), unit cell of BaTiOF4 (c), and distorted octahedron coordination of [Ti2OF4] (d)[28]Ba: yellow; Ti: blue; O: red; F: gray
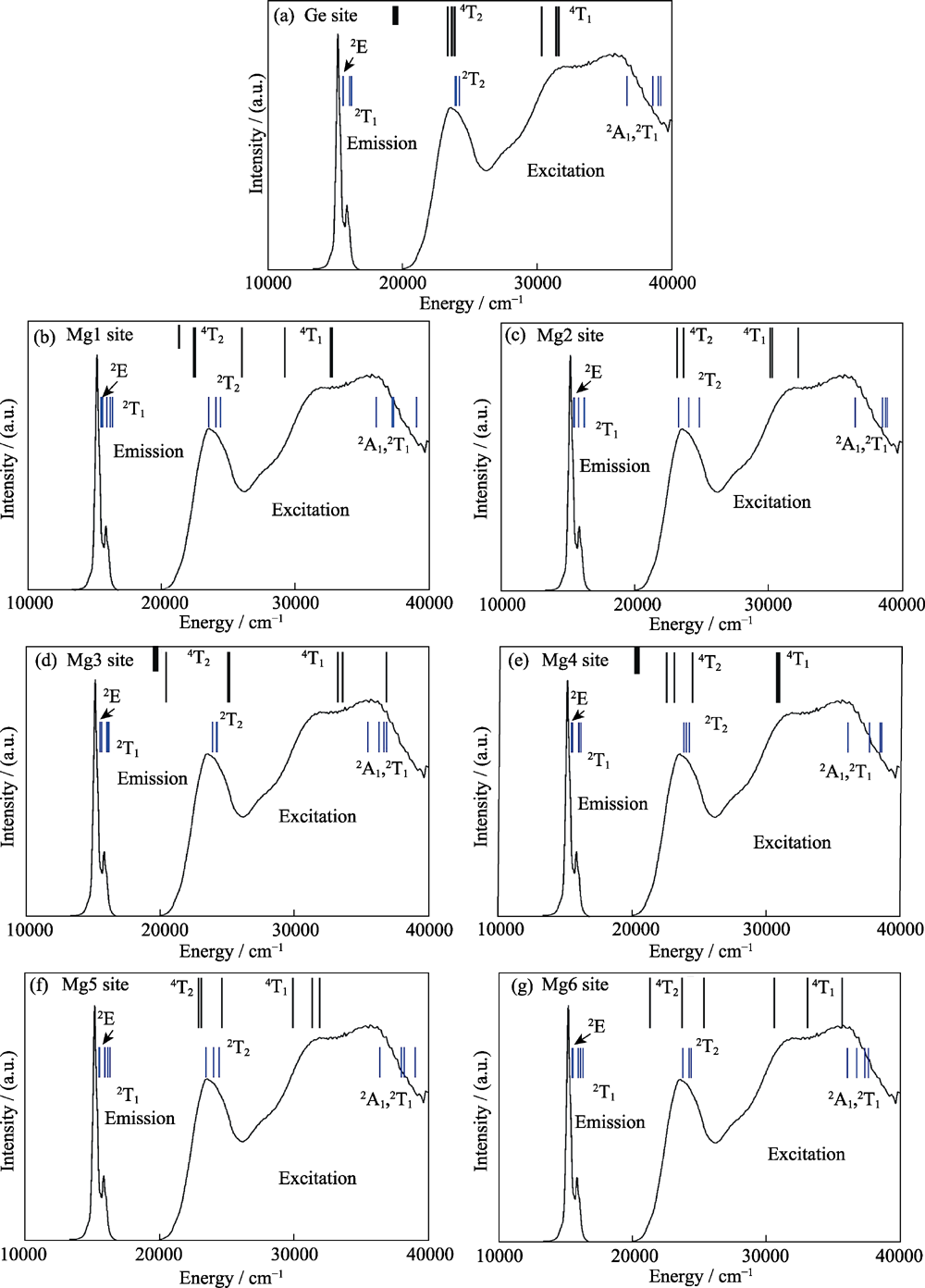
图9 Mn4+占据Mg28Ge7.55O32F15.04结构中八面体配位Ge/Mg格位时计算所得4T2g和4T1g能级位置与实测光谱的比较[29]
Fig. 9 Comparison of the calculated Mn4+ energy levels in Mg28Ge7.55O32F15.04 for all possible Mn4+ positions in Ge/Mg sites with the measured spectrum[29]
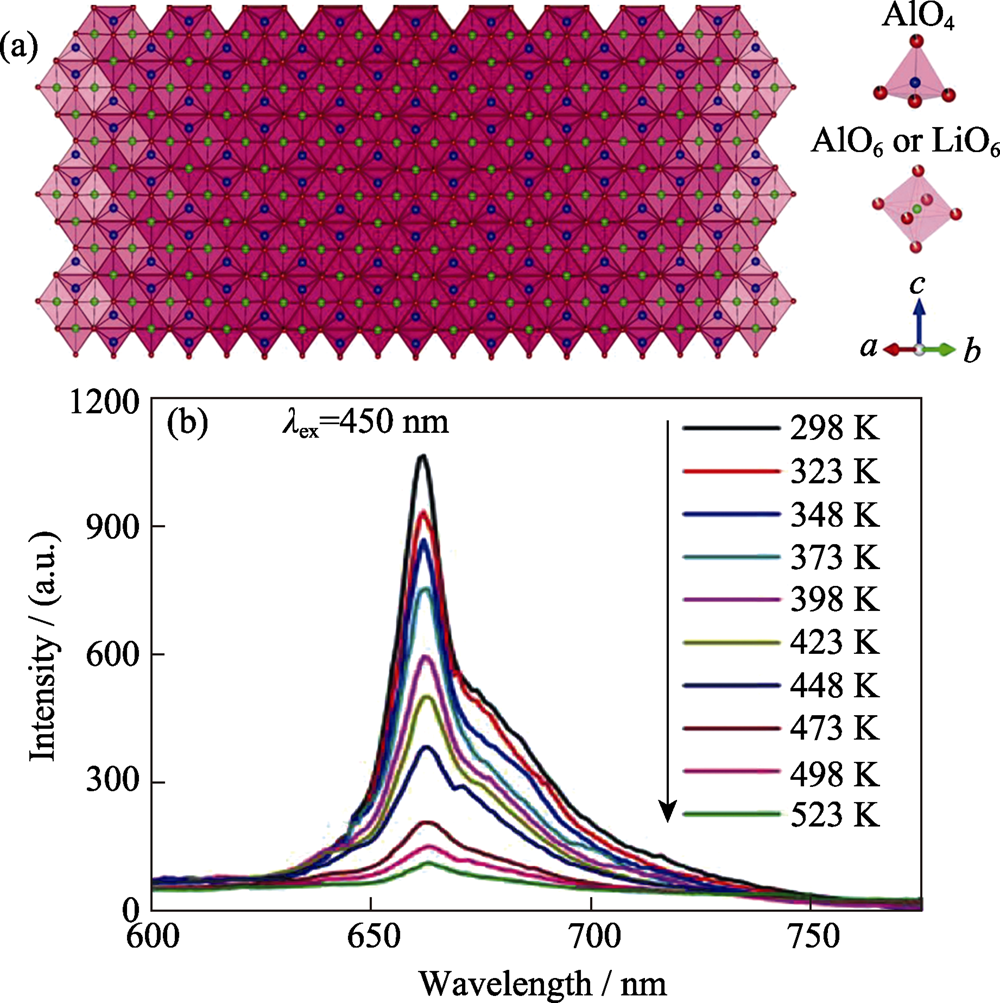
图10 LiAl4O6F的晶胞及Al3+/Li+的配位多面体(a)和LiAl4O6F:Mn4+的变温发光光谱(b)[30]
Fig. 10 Unit cell of LiAl4O6F and coordination of Al3+/Li+ (a) and emission spectra of LiAl4O6F:Mn4+ at temperature of 298-523 K (b) [30]
| [1] |
WANG L, XIE R J, SUEHIRO T, et al. Down-conversion nitride materials for solid state lighting: recent advances and perspectives. Chemical Reviews, 2018,1184:1951-2009.
DOI URL PMID |
| [2] |
XIA Z, LIU Q. Progress in discovery and structural design of color conversion phosphors for LEDs. Progress in Materials Science, 2016,84:59-117.
DOI URL |
| [3] |
LIN C C, MEIJERINK A, LIU R S. Critical red components for next-generation white LEDs. Journal of Physical Chemistry Letters, 2016,73:495-503.
DOI URL PMID |
| [4] |
HU Y, ZHUANG W, YE H, et al. Preparation and luminescent properties of (Ca1-xSrx)S:Eu 2+ red-emitting phosphor for white LED . Journal of Luminescence, 2005,1113:139-145.
DOI URL |
| [5] |
XIE R J, HINTZEN H T. Optical properties of (oxy)nitride materials: a review. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2013,963:665-687.
DOI URL |
| [6] |
PUST P, WEILER V, HECHT C, et al. Narrow-band red-emitting Sr[LiAl3N4]:Eu 2+ as a next-generation LED-phosphor material . Nature Materials, 2014,139:891-896.
DOI URL |
| [7] |
SCHMIECHEN S, SCHNEIDER H, WAGATHA P, et al. Toward new phosphors for application in illumination-grade white pc-LEDs: the nitridomagnesosilicates Ca[Mg3SiN4]:Ce 3+, Sr[Mg3SiN4]:Eu 2+, and Eu[Mg3SiN4] . Chemistry of Materials, 2014,268:2712-2719.
DOI URL |
| [8] |
ADACHI S. Photoluminescence spectra and modeling analyses of Mn 4+-activated fluoride phosphors: a review . Journal of Luminescence, 2018,197:119-130.
DOI URL |
| [9] | ADACHI S. Mn4+-activated red and deep red-emitting phosphors. ECS Journal of Solid State Science and Technology, 2020, 9(1): 016001-1-34. |
| [10] |
SIJBOM H F, VERSTRAETE R, JOOS J J, et al. K2SiF6:Mn 4+ as a red phosphor for displays and warm-white LEDs: a review of properties and perspectives . Optical Materials Express, 2017,79:3332-3365.
DOI URL |
| [11] |
PAULUSZ A G. Efficient Mn(IV) emission in fluorine coordination. Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 1973,1207:942-947.
DOI URL |
| [12] | LIU Y H, GAO W, CHEN G T, et al. Research progress and development trend of fluoride phosphor for white LED. China Light & Lighting, 2018(2):20-24. |
| [13] |
VERSTRAETE R, SIJBOM H F, KORTHOUT K, et al. K2MnF6 as a precursor for saturated red fluoride phosphors: the struggle for structural stability. Journal of Materials Chemistry C, 2017,541:10761-10769.
DOI URL |
| [14] | ZHOU Z, ZHOU N, XIA M, et al. Research progress and application prospects of transition metal Mn 4+-activated luminescent materials . Journal of Materials Chemitry C, 2016,439:9143-9161. |
| [15] | ZHOU Y Y, WANG L Y, DENG T T, et al. Recent advances in Mn 4+-doped fluoride narrow-band red-emitting phosphors . Scientia Sinica Technologica, 2017,4711:1111-1125. |
| [16] | TIM S. New Narrow Band Red Phosphors for White Light Emitting Diodes. Utrecht: Doctoral Dissertation of Utrecht University, 2018. |
| [17] |
TANABE Y, SUGANO S. On the absorption spectra of complex ions II. Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 1954,9:766-779.
DOI URL |
| [18] |
BRIK M G, CAMARDELLO S J, SRIVASTAVA A M. Spin-forbidden transitions in the spectra of transition metal ions and nephelauxetic effect. ECS Journal of Solid State Science and Technology, 2016,51:R3067-R3077.
DOI URL |
| [19] |
BRIK M G, BEERS W W, COHEN W, et al. On the Mn 4+ R-line emission intensity and its tunability in solids . Optical Materials, 2019,91:338-343.
DOI URL |
| [20] |
JI H, UEDA J, BRIK M G, et al. Intense deep-red zero phonon line emission of Mn 4+ in double perovskite La4Ti3O12 . Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics, 2019,2145:25108-25117.
DOI URL PMID |
| [21] |
HU T, LIN H, CHENG Y, et al. A highly-distorted octahedron with a C2v group symmetry inducing an ultra-intense zero phonon line in Mn 4+-activated oxyfluoride Na2WO2F4 . Journal of Materials Chemistry C, 2017,540:10524-10532.
DOI URL |
| [22] |
CAI P, WANG X, SEO H J. Excitation power dependent optical temperature behaviors in Mn 4+ doped oxyfluoride Na2WO2F4 . Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics, 2018,203:2028-2035.
DOI URL PMID |
| [23] | CAI P, QIN L, CHEN C, et al. Luminescence, energy transfer and optical thermometry of a novel narrow red emitting phosphor: Cs2WO2F4:Mn 4+ . Dalton Transcations, 2017,4641:14331-14340. |
| [24] |
WANG Q, YANG Z, WANG H, et al. Novel Mn 4+-activated oxyfluoride Cs2NbOF5:Mn 4+ red phosphor for warm white light- emitting diodes . Optical Materials, 2018,85:96-99.
DOI URL |
| [25] | MING H, ZHANG J, LIU L, et al. A novel Cs2NbOF5:Mn 4+ oxyfluoride red phosphor for light-emitting diode devices . Dalton Transcations, 2018,4745:16048-16056. |
| [26] |
DONG X, PAN Y, LI D, et al. A novel red phosphor of Mn 4+ ion-doped oxyfluoroniobate BaNbOF5 for warm WLED applications . CrystEngComm, 2018,2037:5641-5646.
DOI URL |
| [27] |
KATO H, TAKATA Y, KOBAYASHI M, et al. Photoluminescence properties of layered perovskite-type strontium scandium oxyfluoride activated with Mn 4+ . Frontiers in Chemistry, 2018,6:467.
DOI URL PMID |
| [28] |
LIANG Z, YANG Z, TANG H, et al. Synthesis, luminescence properties of a novel oxyfluoride red phosphor BaTiOF4:Mn 4+ for LED backlighting . Optical Materials, 2019,90:89-94.
DOI URL |
| [29] |
BRIK M G, SRIVASTAVA A M. A computation study of site occupancy in the commercial Mg28Ge7.55O32F15.04:Mn 4+ phosphor . Optical Materials, 2016,54:245-251.
DOI URL |
| [30] |
WANG Q, LIAO J, KONG L, et al. Luminescence properties of a non-rare-earth doped oxyfluoride LiAl4O6F:Mn 4+ red phosphor for solid-state lighting . Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2019,772:499-506.
DOI URL |
| [31] |
SRIVASTAVA A M, ACKERMAN J F. Synthesis and luminescence properties of Cs2NbOF5 and Cs2NbOCl5 with isolated [NbOX5] -2 (X=F -, Cl -) octahedra . Materials Research Bulletin, 1991,266:443-448.
DOI URL |
| [32] | SRIVASTAVA A M, ACKERMAN J F. Synthesis and luminescence properties of barium niobium oxide fluoride (BaNbOF5) with isolated [NbOF5] 2- octahedra . Chemitry of Materials, 1992,45:1011-1013. |
| [33] |
BLESS P W, VON DREELE R B, KOSTINER E, et al. Anion and cation defect structure in magnesium fluorogermanate. Journal of Solid State Chemistry, 1972,42:262-268.
DOI URL |
| [34] |
BEERS W W, SMITH D, COHEN W E, et al. Temperature dependence (13-600 K) of Mn 4+ lifetime in commercial Mg28Ge7.55O32F15.04 and K2SiF6 phosphors . Optical Materials, 2018,84:614-617.
DOI URL |
| [1] | 朱文杰, 唐璐, 陆继长, 刘江平, 罗永明. 钙钛矿型氧化物催化氧化挥发性有机化合物的研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(7): 735-746. |
| [2] | 胡智超, 杨鸿宇, 杨鸿程, 孙成礼, 杨俊, 李恩竹. P-V-L键理论在微波介质陶瓷性能调控中的应用[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(6): 609-626. |
| [3] | 吴琼, 沈炳林, 张茂华, 姚方周, 邢志鹏, 王轲. 铅基织构压电陶瓷研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(6): 563-574. |
| [4] | 张碧辉, 刘小强, 陈湘明. Ruddlesden-Popper结构杂化非常规铁电体的研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(6): 587-608. |
| [5] | 吴杰, 杨帅, 王明文, 李景雷, 李纯纯, 李飞. 铅基织构压电陶瓷的发展历程、现状与挑战[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(6): 575-586. |
| [6] | 姜昆, 李乐天, 郑木鹏, 胡永明, 潘勤学, 吴超峰, 王轲. PZT陶瓷的低温烧结研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(6): 627-638. |
| [7] | 范小暄, 郑永炅, 徐丽荣, 姚子敏, 曹硕, 王可心, 王绩伟. 基于富氧空位LiYScGeO4: Bi3+长余辉光催化剂的自激活余辉驱动有机污染物芬顿降解[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(5): 481-488. |
| [8] | 田睿智, 兰正义, 殷杰, 郝南京, 陈航榕, 马明. 基于微流控技术的纳米无机生物材料制备: 原理及其研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(4): 337-347. |
| [9] | 张继国, 吴田, 赵旭, 杨钒, 夏天, 孙士恩. 钠离子电池正极材料循环稳定性提升策略及产业化进程[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(4): 348-362. |
| [10] | 殷杰, 耿佳毅, 王康龙, 陈忠明, 刘学建, 黄政仁. SiC陶瓷的3D打印成形与致密化新进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(3): 245-255. |
| [11] | 谌广昌, 段小明, 朱金荣, 龚情, 蔡德龙, 李宇航, 杨东雷, 陈彪, 李新民, 邓旭东, 余瑾, 刘博雅, 何培刚, 贾德昌, 周玉. 直升机特定结构先进陶瓷材料研究进展与应用展望[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(3): 225-244. |
| [12] | 潘泽晟, 游雅萍, 郑雅, 陈海杰, 王连军, 江莞. 面向紫光激发白光LED用荧光材料的耐候性[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(3): 314-322. |
| [13] | 范晓波, 祖梅, 杨向飞, 宋策, 陈晨, 王子, 罗文华, 程海峰. 质子调控型电化学离子突触研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(3): 256-270. |
| [14] | 海热古·吐逊, 郭乐, 丁嘉仪, 周嘉琪, 张学良, 努尔尼沙·阿力甫. 上转换荧光探针辅助的光学成像技术在肿瘤显影中的应用研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(2): 145-158. |
| [15] | 孙树娟, 郑南南, 潘昊坤, 马猛, 陈俊, 黄秀兵. 单原子催化剂制备方法的研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(2): 113-127. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||