无机材料学报 ›› 2017, Vol. 32 ›› Issue (7): 673-680.DOI: 10.15541/jim20160483 CSTR: 32189.14.10.15541/jim20160483
• • 下一篇
董 亮1,2, 王艳辉2, 臧建兵2
收稿日期:2016-08-29
修回日期:2016-11-10
出版日期:2017-07-20
网络出版日期:2017-06-23
作者简介:董 亮(1985–), 男, 讲师. E-mail: dongliang@neuq.edu.cn
基金资助:DONG Liang1,2, WANG Yan-Hui2, ZANG Jian-Bing2
Received:2016-08-29
Revised:2016-11-10
Published:2017-07-20
Online:2017-06-23
About author:DONG Liang. E-mail: dongliang@neuq.edu.cn
Supported by:摘要:
金刚石是由共价键方式连接的sp3杂化碳原子组成, 具有极强的稳定性。含硼金刚石(BDD)薄膜、BDD颗粒、非掺杂纳米金刚石(ND)等新型金刚石又兼具一定的导电性, 因此成为高稳定性燃料电池催化剂的理想载体材料。研究者进一步发现通过对上述新型金刚石进行适当功能化处理, 可以进一步提高催化剂的催化活性和稳定性。对金刚石进行掺杂处理, 既包括向金刚石晶格中掺杂, 也包括向金刚石衍生的石墨结构中进行掺杂, 能够得到新型高稳定性燃料电池非铂催化剂, 且金刚石sp3结构在提高非铂催化剂稳定性方面作用独特。本文总结介绍了相关研究成果, 希望能为后续研究提供参考借鉴。
中图分类号:
董 亮, 王艳辉, 臧建兵. 金刚石基燃料电池催化剂的研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2017, 32(7): 673-680.
DONG Liang, WANG Yan-Hui, ZANG Jian-Bing. Recent Progress in Diamond-based Electrocatalysts for Fuel Cells[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2017, 32(7): 673-680.
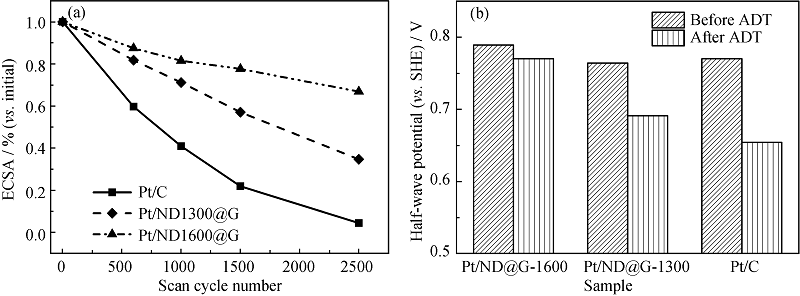
图3 (a)Pt/C、Pt/ND@G-1300和Pt/ND@G-1600在ADT过程中ESA变化情况对比图, (b)ADT完成前后三种催化剂的半波电位变化情况[51]
Fig. 3 (a) Changes of Pt/C, Pt/ND@G-1300 and Pt/ND@G-1600 ESA related (vs. initial) with cycle number, (b) half-wave potentials of Pt/GND1300, Pt/GND1600 and Pt/C before and after ADT[51]
| [1] | 黄镇江, 刘凤君. 燃料电池及其应用. 北京: 电子工业出版社, 2005: 5-14. |
| [2] | SHARAF O Z, ORHAN M F.An overview of fuel cell technology: fundamentals and applications.Renew. Sust. Energ. Rev., 2014, 32: 810-853. |
| [3] | O'HAYRE R, CHA S W, PRINZ F B, et al. Fuel Cell Fundamentals. The second edition. New York: John Wiley & Sons, 2016: 3-23. |
| [4] | ARICO A, SRINIVASAN S, ANTONUCCI V.DMFCs: From fundamental aspects to technology development.Fuel cells, 2001, 1(2): 133-161. |
| [5] | MCNICOL B, RAND D, WILLIAMS K.Direct methanol-air fuel cells for road transportation.J. Power Sources, 1999, 83(1): 15-31. |
| [6] | YU X, YE S.Recent advances in activity and durability enhancement of Pt/C catalytic cathode in PEMFC.J. Power Sources, 2007, 172(1): 133-144. |
| [7] | KANGASNIEMI K H, CONDIT D, JARVI T.Characterization of vulcan electrochemically oxidized under simulated pem fuel cell conditions.J. Electrochem. Soc., 2004, 151(4): E125-E132. |
| [8] | REISER C A, BREGOLI L, PATTERSON T W, et al.A reverse- current decay mechanism for fuel cells.Electrochem. Solid-State Lett., 2005, 8(6): A273-A276. |
| [9] | LIU M, CHEN W.Green synthesis of silver nanoclusters supported on carbon nanodots: enhanced photoluminescence and high catalytic activity for oxygen reduction reaction.Nanoscale, 2013, 5(24): 12558-12564. |
| [10] | SHAO Y, YIN G, GAO Y, et al.Durability study of Pt∕C and Pt∕CNTs catalysts under simulated pem fuel cell conditions.J. Electrochem. Soc., 2006, 153(6): A1093-A1097. |
| [11] | LIU M, LU Y, CHEN W.PdAg nanorings supported on graphene nanosheets: highly methanol‐tolerant cathode electrocatalyst for alkaline fuel cells.Adv. Funct. Mater., 2013, 23(10): 1289-1296. |
| [12] | LIU M, ZHANG R, CHEN W.Graphene-supported nanoelectrocatalysts for fuel cells: synthesis, properties, and applications.Chem. Rev., 2014, 114(10): 5117-5160. |
| [13] | LU Y, JIANG Y, WU H, et al.Nano-PtPd cubes on graphene exhibit enhanced activity and durability in methanol electrooxidation after Co stripping-cleaning.J. Phys. Chem. C, 2013, 117(6): 2926-2938. |
| [14] | LU Y, JIANG Y, CHEN W.Graphene nanosheet-tailored ptpd concave nanocubes with enhanced electrocatalytic activity and durability for methanol oxidation.Nanoscale, 2014, 6(6): 3309-3315. |
| [15] | ZHANG R, CHEN W.Non-Precious Ir-V bimetallic nanoclusters assembled on reduced graphene nanosheets as catalysts for the oxygen reduction reaction.J. Mater. Chem. A, 2013, 1(37): 11457-11464. |
| [16] | ZHANG R, HE S, LU Y, et al.Fe, Co, N-functionalized carbon nanotubes in situ grown on 3d porous N-doped carbon foams as a noble metal-free catalyst for oxygen reduction.J. Mater. Chem. A, 2015, 3(7): 3559-3567. |
| [17] | LIU M, HE S, CHEN W.Free-standing 3D hierarchical carbon foam-supported PtCo nanowires with “Pt Skin” as advanced electrocatalysts.Electrochim. Acta, 2016, 199: 218-226. |
| [18] | 方啸虎. 超硬材料科学与技术. 北京: 中国建材工业出版社, 1998: 17-21. |
| [19] | AVGOUROPOULOS G, IOANNIDES T.CO Tolerance of Pt and Rh catalysts: effect of co in the gas-phase oxidation of H2 over Pt and Rh supported catalysts.Appl. Catal. B- Environ., 2005, 56(1): 77-86. |
| [20] | GARC A G, SILVA-CHONG J, GUILL N-VILLAFUERTE O, et al. CO tolerant catalysts for PEM fuel cells: spectroelectrochemical studies.Catal. Today, 2006, 116(3): 415-421. |
| [21] | FERREIRA P, SHAO-HORN Y, MORGAN D, et al.Instability of Pt∕C electrocatalysts in proton exchange membrane fuel cells a mechanistic investigation.J. Electrochem. Soc., 2005, 152(11): A2256-A2271. |
| [22] | KOH S, YU C, MANI P, et al.Activity of ordered and disordered pt-co alloy phases for the electroreduction of oxygen in catalysts with multiple coexisting phases.J. Power Sources, 2007, 172(1): 50-56. |
| [23] | BAR-ON I, KIRCHAIN R, ROTH R.Technical cost analysis for pem fuel cells.J. Power Sources, 2002, 109(1): 71-75. |
| [24] | GONG K, DU F, XIA Z, et al.Nitrogen-doped carbon nanotube arrays with high electrocatalytic activity for oxygen reduction.Science, 2009, 323(5915): 760-764. |
| [25] | QU L, LIU Y, BAEK J B, et al.Nitrogen-doped graphene as efficient metal-free electrocatalyst for oxygen reduction in fuel cells.ACS Nano, 2010, 4(3): 1321-1326. |
| [26] | KRAMM U I, LEF VRE M, LAROUCHE N, et al.Correlations between mass activity and physicochemical properties of fe/n/c catalysts for the ORR in PEM fuel cell via 57Fe mößbauer spectroscopy and other techniques.J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2013, 136(3): 978-985. |
| [27] | SWAIN G M.The Susceptibility to surface corrosion in acidic fluoride media: a comparison of diamond, hopg, and glassy carbon electrodes.J. Electrochem. Soc., 1994, 141(12): 3382-3393. |
| [28] | GAO F, YANG N, SMIRNOV W, et al.Size-controllable and homogeneous platinum nanoparticles on diamond using wet chemically assisted electrodeposition.Electrochim. Acta, 2013, 90: 445-451. |
| [29] | LU X, HU J, FOORD J S, et al.Electrochemical deposition of Pt-Ru on diamond electrodes for the electrooxidation of methanol.J. Electroanal. Chem., 2011, 654(1): 38-43. |
| [30] | MAVROKEFALOS C K, NELSON G W, POLL C G, et al.Electrochemical aspects of Pt-Cu and Cu modified boron-doped diamond.Phys. Status Solidi A, 2015, 212(11): 2559-2567. |
| [31] | SIN G, FOTI G, COMNINELLIS C.Boron-doped diamond (bdd)-supported pt/sn nanoparticles synthesized in microemulsion systems as electrocatalysts of ethanol oxidation.J. Electroanal. Chem., 2006, 595(2): 115-124. |
| [32] | SALAZAR-BANDA G R, SUFFREDINI H B, AVACA L A, et al. methanol and ethanol electro-oxidation on Pt-SnO2 and Pt-Ta2O5 Sol-Gel-modified boron-doped diamond surfaces.Mater. Chem. Phys., 2009, 117(2): 434-442. |
| [33] | WANG J, SWAIN G, TACHIBANA T, et al.The incorporation of Pt nanoparticles into boron-doped diamond thin-films: dimensionally stable catalytic electrodes.J. New Mat. Electr. Sys, 2000, 3(1): 75-82. |
| [34] | LYU X, HU J, FOORD J S, et al.A novel electroless method to prepare a platinum electrocatalyst on diamond for fuel cell applications.J. Power Sources, 2013, 242: 631-637. |
| [35] | GONZALEZ-GONZALEZ I, TRYK D, CABRERA C R.Polycrystalline boron-doped diamond films as supports for methanol oxidation electrocatalysts.Diam. Relat. Mater., 2006, 15(2): 275-278. |
| [36] | EL ROUSTOM B, SINE G, FOTI G, et al.A novel method for the preparation of bi-metallic (Pt-Au) nanoparticles on boron doped diamond (BDD) substrate: application to the oxygen reduction reaction.J. Appl. Electrochem., 2007, 37(11): 1227-1236. |
| [37] | SPĂTARU T, PREDA L, OSICEANU P, et al. Electrochemical deposition of Pt-RuOxNh2O composites on conductive diamond and its application to methanol oxidation in acidic media.Electrocatalysis, 2016, 7(2): 140-148. |
| [38] | SALAZAR-BANDA G R, EGUILUZ K I, AVACA L A. Boron-doped diamond powder as catalyst support for fuel cell applications.Electrochem. Commun., 2007, 9(1): 59-64. |
| [39] | SPĂTARU N, ZHANG X, SPĂTARU T, et al. Platinum electrodeposition on conductive diamond powder and its application to methanol oxidation in acidic media.J. Electrochem. Soc., 2008, 155(3): B264-B269. |
| [40] | LA-TORRE-RIVEROS L, ABEL-TATIS E, M NDEZ-TORRES A E, et al. Synthesis of platinum and platinum-ruthenium-modified diamond nanoparticles.J. Nanopart. Res., 2011, 13(7): 2997-3009. |
| [41] | KIM J, CHUN Y S, LEE S K, et al.Improved electrode durability using a boron-doped diamond catalyst support for proton exchange membrane fuel cells.RSC Advances, 2015, 5(2): 1103-1108. |
| [42] | CELORRIO V, PLANA D, FL REZ-MONTA O J, et al. Methanol oxidation at diamond-supported Pt nanoparticles: effect of the diamond surface termination.J. Phys. Chem. C, 2013, 117(42): 21735-21742. |
| [43] | WANG J, SWAIN G M.Fabrication and evaluation of platinum/diamond composite electrodes for electrocatalysis preliminary studies of the oxygen-reduction reaction.J. Electrochem. Soc., 2003, 150(1): E24-E32. |
| [44] | ZANG J, WANG Y, ZHAO S, et al.Electrochemical properties of nanodiamond powder electrodes.Diam. Relat. Mater., 2007, 16(1): 16-20. |
| [45] | BIAN L, WANG Y, ZANG J, et al.Microwave synthesis and characterization of pt nanoparticles supported on undoped nanodiamond for methanol electrooxidation.Int. J. Hydrogen. Energ, 2012, 37(2): 1220-1225. |
| [46] | LU R, ZANG J, WANG Y, et al.Microwave synthesis and properties of nanodiamond supported ptru electrocatalyst for methanol oxidation.Electrochim. Acta, 2012, 60: 329-333. |
| [47] | ZANG J, WANG Y, BIAN L, et al.Graphene growth on nanodiamond as a support for a Pt electrocatalyst in methanol electro-oxidation.Carbon, 2012, 50(8): 3032-3038. |
| [48] | ZHAO Y, WANG Y, CHENG X, et al.Platinum nanoparticles supported on epitaxial TiC/nanodiamond as an electrocatalyst with enhanced durability for fuel cells.Carbon, 2014, 67: 409-416. |
| [49] | ZHAO Y, WANG Y, DONG L, et al.Core-shell structural nanodiamond@tin supported pt nanoparticles as a highly efficient and stable electrocatalyst for direct methanol fuel cells.Electrochim. Acta, 2014, 148: 8-14. |
| [50] | ZHAO Y, WANG Y, ZANG J, et al.A novel support of nano titania modified graphitized nanodiamond for Pt electrocatalyst in direct methanol fuel cell.Int. J. Hydrogen. Energy, 2015, 40(13): 4540-4547. |
| [51] | DONG L, ZANG J, WANG Y, et al.Graphitized nanodiamond as highly efficient support of electrocatalysts for oxygen reduction reaction.J. Electrochem. Soc., 2014, 161(3): F185-F191. |
| [52] | LIU Y, CHEN S, QUAN X, et al.Tuning the electrochemical properties of a boron and nitrogen codoped nanodiamond rod array to achieve high performance for both electro-oxidation and electro-reduction.J. Mater. Chem. A, 2013, 1(46): 14706-14712. |
| [53] | GAN P, FOORD J S, COMPTON R G.Surface modification of boron-doped diamond with microcrystalline copper phthalocyanine: oxygen reduction catalysis.Chemistry Open, 2015, 4(5): 606-612. |
| [54] | KOH J, PARK S H, CHUNG M W, et al.Diamond@carbon-onion hybrid nanostructure as a highly promising electrocatalyst for the oxygen reduction reaction.RSC Advances, 2016, 6(33): 27528-27534. |
| [55] | DONG L, ZANG J, SU J, et al.Nanodiamond/ nitrogen-doped graphene (core/shell) as an effective and stable metal-free electrocatalyst for oxygen reduction reaction.Electrochim. Acta, 2015, 174: 1017-1022. |
| [56] | LIU X, WANG Y, DONG L, et al.One-step synthesis of shell/core structural boron and nitrogen co-doped graphitic carbon/ nanodiamond as efficient electrocatalyst for the oxygen reduction reaction in alkaline media.Electrochim. Acta, 2016, 194: 161-167. |
| [57] | WU Y, ZANG J, DONG L, et al.High performance and bifunctional cobalt-embedded nitrogen doped carbon/nanodiamond electrocatalysts for oxygen reduction and oxygen evolution reactions in alkaline media.J. Power Sources, 2016, 305: 64-71. |
| [58] | ZHU Y, LIN Y, ZHANG B, et al.Nitrogen-doped annealed nanodiamonds with varied Sp2/Sp3 ratio as metal‐free electrocatalyst for the oxygen reduction reaction.ChemCatChem, 2015, 7(18): 2840-2845. |
| [59] | JANG D M, IM H S, BACK S H, et al.Laser-induced graphitization of colloidal nanodiamonds for excellent oxygen reduction reaction.Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2014, 16(6): 2411-2416. |
| [1] | 朱文杰, 唐璐, 陆继长, 刘江平, 罗永明. 钙钛矿型氧化物催化氧化挥发性有机化合物的研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(7): 735-746. |
| [2] | 江宗玉, 黄红花, 清江, 王红宁, 姚超, 陈若愚. 铝离子掺杂MIL-101(Cr)的制备及其VOCs吸附性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(7): 747-753. |
| [3] | 柴润宇, 张镇, 王孟龙, 夏长荣. 直接组装法制备氧化铈基金属支撑固体氧化物燃料电池[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(7): 765-771. |
| [4] | 胡智超, 杨鸿宇, 杨鸿程, 孙成礼, 杨俊, 李恩竹. P-V-L键理论在微波介质陶瓷性能调控中的应用[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(6): 609-626. |
| [5] | 吴琼, 沈炳林, 张茂华, 姚方周, 邢志鹏, 王轲. 铅基织构压电陶瓷研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(6): 563-574. |
| [6] | 张碧辉, 刘小强, 陈湘明. Ruddlesden-Popper结构杂化非常规铁电体的研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(6): 587-608. |
| [7] | 吴杰, 杨帅, 王明文, 李景雷, 李纯纯, 李飞. 铅基织构压电陶瓷的发展历程、现状与挑战[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(6): 575-586. |
| [8] | 姜昆, 李乐天, 郑木鹏, 胡永明, 潘勤学, 吴超峰, 王轲. PZT陶瓷的低温烧结研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(6): 627-638. |
| [9] | 渠吉发, 王旭, 张维轩, 张康喆, 熊永恒, 谭文轶. 掺杂改性NaYTiO4增强固体氧化物燃料电池阳极抗硫中毒性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(5): 489-496. |
| [10] | 薛柯, 蔡长焜, 谢满意, 李舒婷, 安胜利. 固体氧化物燃料电池Pr1+xBa1-xFe2O5+δ阴极材料的制备及电化学性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(4): 363-371. |
| [11] | 田睿智, 兰正义, 殷杰, 郝南京, 陈航榕, 马明. 基于微流控技术的纳米无机生物材料制备: 原理及其研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(4): 337-347. |
| [12] | 张继国, 吴田, 赵旭, 杨钒, 夏天, 孙士恩. 钠离子电池正极材料循环稳定性提升策略及产业化进程[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(4): 348-362. |
| [13] | 信震宇, 郭瑞华, 乌仁托亚, 王艳, 安胜利, 张国芳, 关丽丽. Pt-Fe/GO纳米催化剂的制备及其电催化乙醇氧化性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(4): 379-387. |
| [14] | 殷杰, 耿佳毅, 王康龙, 陈忠明, 刘学建, 黄政仁. SiC陶瓷的3D打印成形与致密化新进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(3): 245-255. |
| [15] | 谌广昌, 段小明, 朱金荣, 龚情, 蔡德龙, 李宇航, 杨东雷, 陈彪, 李新民, 邓旭东, 余瑾, 刘博雅, 何培刚, 贾德昌, 周玉. 直升机特定结构先进陶瓷材料研究进展与应用展望[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(3): 225-244. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||