无机材料学报 ›› 2013, Vol. 28 ›› Issue (1): 12-20.DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1077.2013.12329 CSTR: 32189.14.SP.J.1077.2013.12329
郑学斌, 谢有桃
收稿日期:2012-05-18
修回日期:2012-07-03
出版日期:2013-01-10
网络出版日期:2012-12-20
基金资助:ZHENG Xue-Bin, XIE You-Tao
Received:2012-05-18
Revised:2012-07-03
Published:2013-01-10
Online:2012-12-20
摘要:
采用热喷涂技术在金属(合金)基材表面制备的生物陶瓷涂层, 兼具金属材料较高力学强度和陶瓷材料优良生物学性能, 作为骨植入材料的研究和应用备受关注。本文介绍骨植入涂层材料的研究概况, 重点阐述热喷涂羟基磷灰石(HA)涂层的研究现状, 并概述新型生物活性硅酸钙陶瓷涂层的研究进展。
中图分类号:
郑学斌, 谢有桃. 热喷涂生物陶瓷涂层的研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2013, 28(1): 12-20.
ZHENG Xue-Bin, XIE You-Tao. Progress on Biomedical Ceramic Coatings Prepared by Thermal Spraying[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2013, 28(1): 12-20.
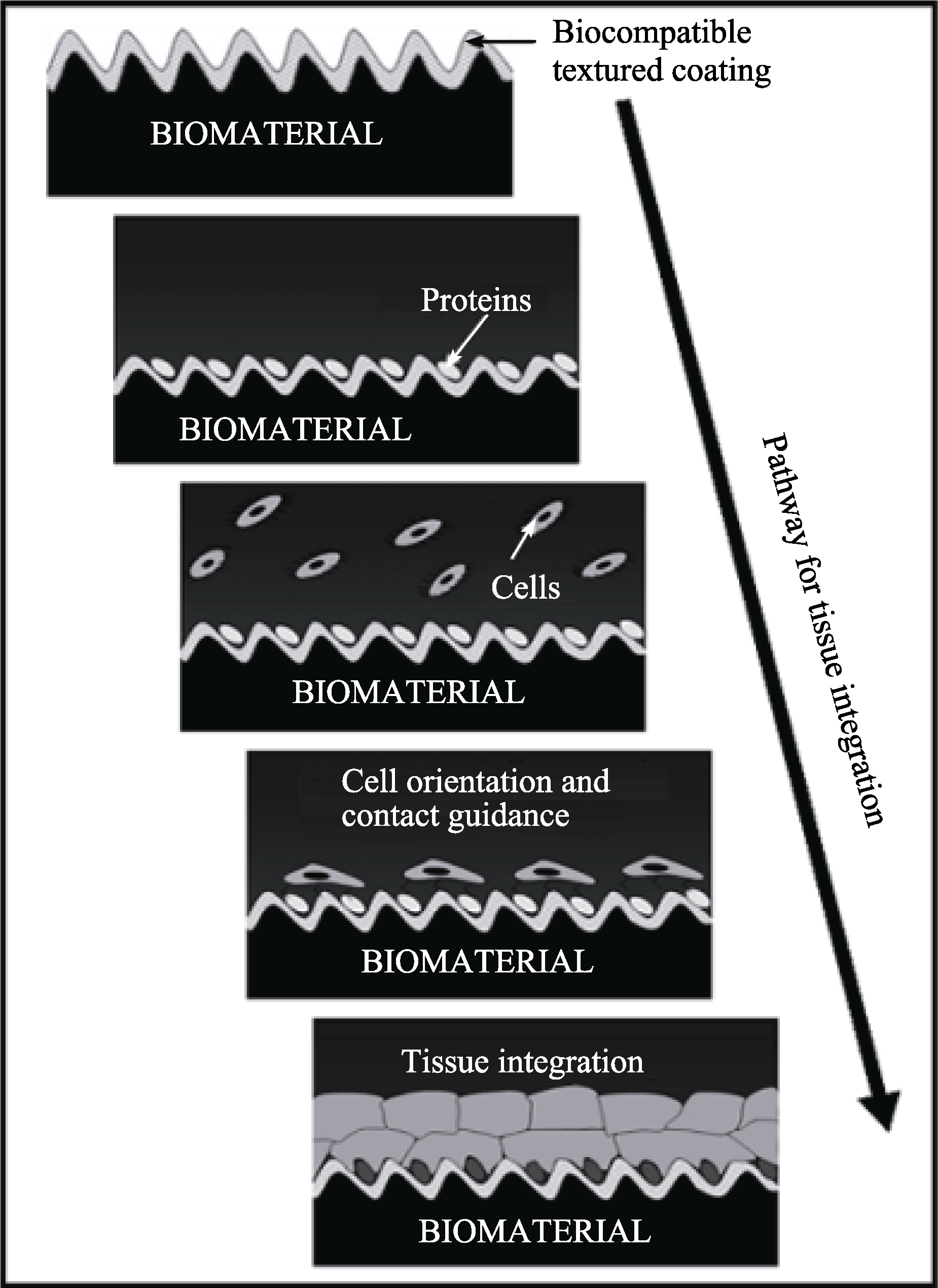
图1 生物材料植入生命系统后发生的系列反应示意图[3]
Fig. 1 Schematic illustration of the sequential reactions that taken place after the implantation of a biomaterial into a living system[3]
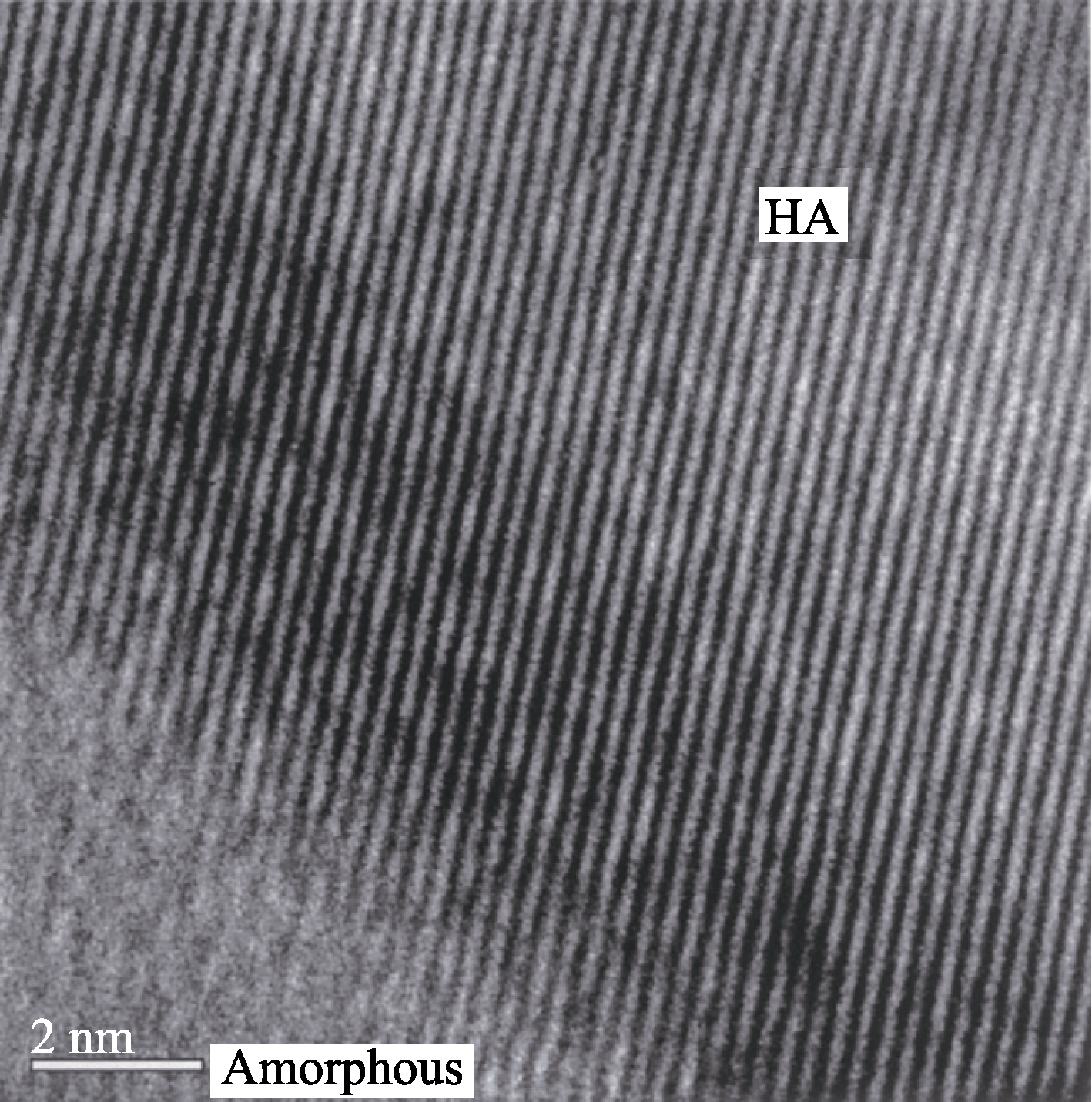
图2 非晶相/HA界面的TEM晶格像照片[27] 为控制HA的分解, 人们分别从组分设计[29]、粉体筛选[24]、喷涂方式改进[30]、工艺参数优化[26]以及后处理[31]等方面进行研究。HA涂层后处理是提高结晶度的重要方式。真空退火处理可将HA涂层的结晶度从44%提高到68%, 但处理温度超过600℃会使涂层应变增大、裂纹增多、结合强度下降[32]。蒸汽-火焰处理的HA涂层结晶度高达98.7%[33]。但过高结晶度的HA涂层早期骨整合性能不佳[34]。
Fig. 2 TEM lattice image showing amorphous/HA phases Lattice spacing is about 0.27 nm[27]
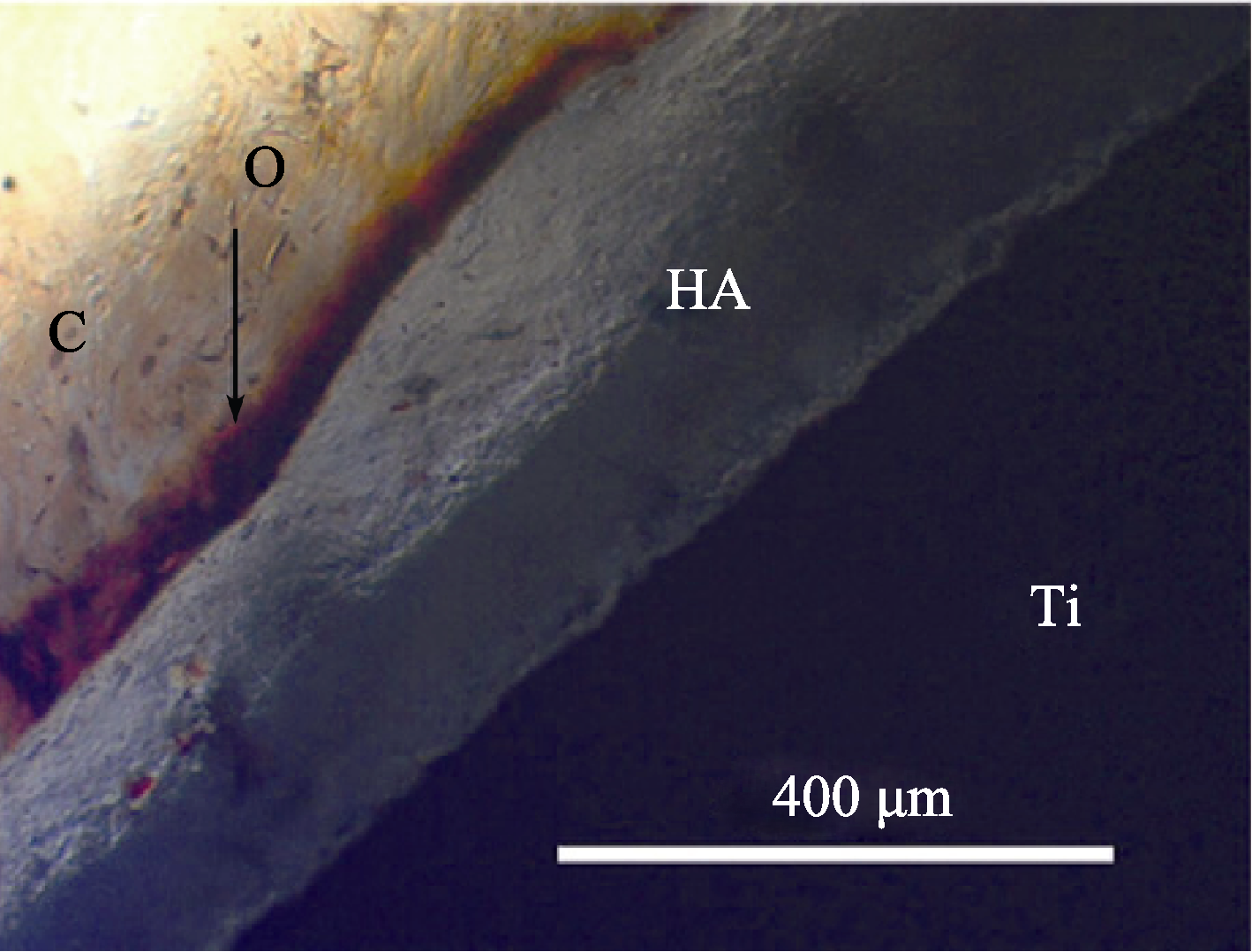
图4 加涂纳米HA涂层的钛植入鼠股骨2 w后的光学显微照片[30]
Fig. 4 Optical photomicrograph of a longitudinal section of nano-HA coated Ti implanted in rat femur at 2 w showing nonmineralized osteoid (O), and collagen matrix (C) [30]
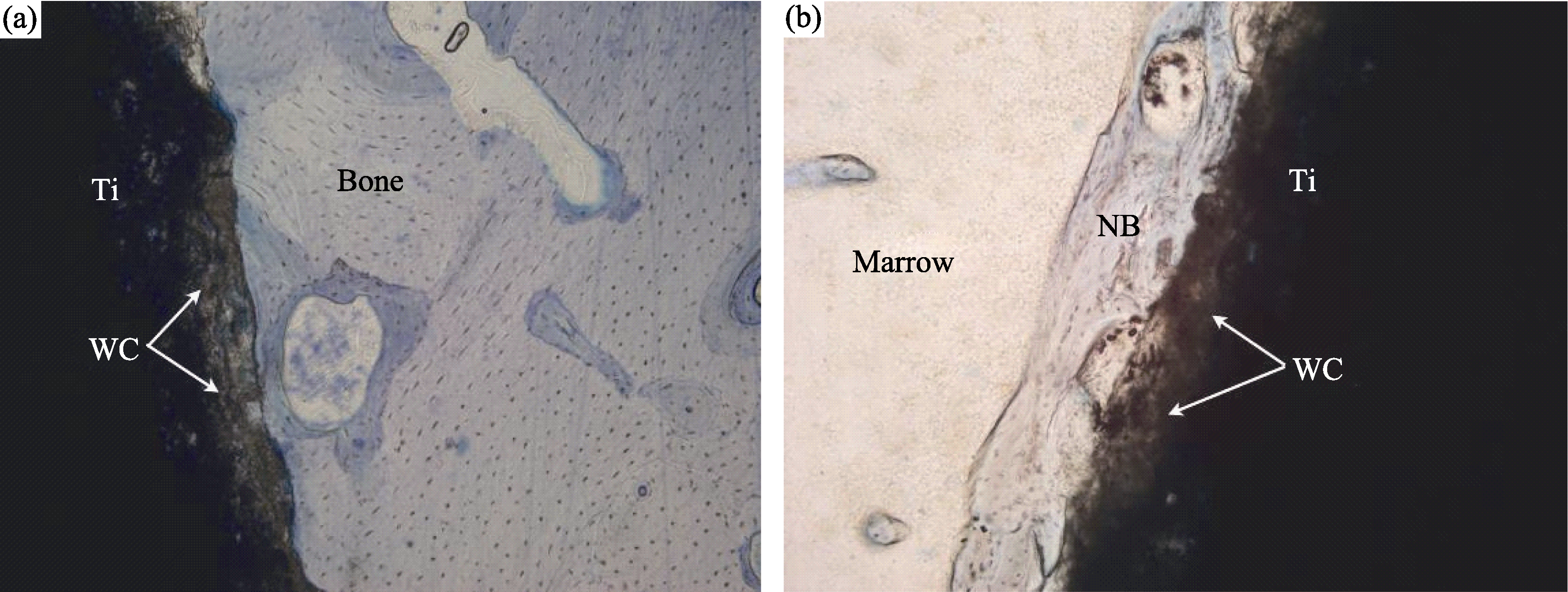
图5 硅灰石涂层在植入股骨(a)与骨髓(b)三个月后的组织学形貌[90]
Fig. 5 Histological morphologies of the cross-section of the wollastonite coating after implantation in cortical bone (a) and marrow (b) for 3 months[90]
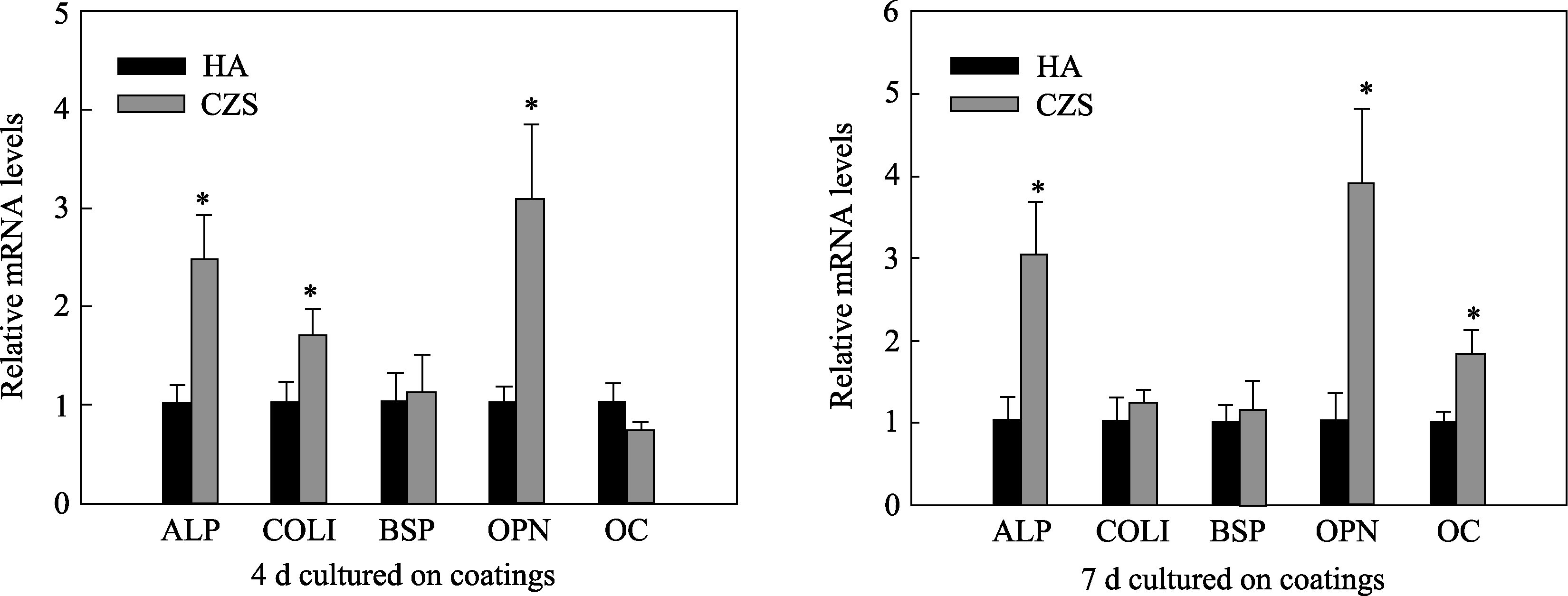
图6 人骨髓基质干细胞(hBMSCs)在CaO-ZrO2-SiO2和HA涂层表面的成骨标志基因表达: (A)4 d, (B)7 d [99]
Fig. 6 Expression levels of osteoblastic differentiation related genes of hBMSCs cultured on CaO-ZrO2-SiO2 and HA coatings for (A) 4 d and (B) 7 d [99]
| [1] | 吕厚山. 人工关节外科学. 北京: 科学出版社, 1998. |
| [2] | Kasemo B, Lausmaa J. Surface properties and processes of the biomaterial-tissue interface. Materials Science and Engineering C-Biommetic Materials Sensors and and Systems, 1994, 1(3): 115-119. |
| [3] | Paital S R, Dahotre N B. Calcium phosphate coatings for bio-implant applications: Materials, performance factors, and methodologies. Materials Science and Engineering R-Reports, 2009, 66(1/2/3): 1-70. |
| [4] | Gittens R A, McLachlan T, Olivares-Navarrete R, et al. The effects of combined micron-/submicron-scale surface roughness and nanoscale features on cell proliferation and differentiation. Biomaterials, 2011, 32(13): 3395-3403. |
| [5] | Hatano K, Inoue H, Kojo T, et al. Effect of surface roughness on proliferation and alkaline phosphatase expression of rat calvarial cells cultured on polystyrene. Bone, 1999, 25(4): 439-445. |
| [6] | Buser D, Schenk R K, Steinemann S, et al. Influence of surface characteristics on bone integration of titanium implants: a hostomorphometric study in miniature pigs. Journal of Biomedical Materials Research, 1991, 25(7): 889-902. |
| [7] | Keller J C, Young F A, Hansel B, et al. Systemic effects of porous Ti dental implants. Dental Materials, 1985, 1(2): 41-42. |
| [8] | Aebil N, Krebs J, Stich H, et al. In vivo comparison of the osseointegration of vacuum plasma sprayed titanium- and hydroxyapatite-coated implants. Journal of Biomedical Materials Research, 2003, 66A(2): 356-363. |
| [9] | SHI Jian-Min, DING Chuan-Xian, WU Yi-Hua. Bioactivity of titanium coating. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2001, 16(3): 515-521. |
| [10] | Chen Y K, Zheng X B, Ji H, et al. Effect of Ti-OH formation on bioactivity of vacuum plasma sprayed titanium coating after chemical treatment. Surface & Coating Technology, 2007, 202(3): 494-498. |
| [11] | Xue W C, Liu X Y, Zheng X B, et al. In vivo evaluation of plasma sprayed titanium coating after alkali modification. Biomaterials, 2005, 26(16): 3029-3037. |
| [12] | Schrooten J, Hesen J A. Adhesion of bioactive glass coating to Ti6Al4V oral implant. Biomaterials, 2000, 21(14): 1461-1469. |
| [13] | Wang G C, Liu X Y, Gao J H, et al. In vitro bioactivity and phase stability of plasma-sprayed nanostructured 3Y-TZP coatings. Acta Biomaterialia, 2009, 5(6): 2270-2278. |
| [14] | Han Y, Chen D, Sun J, et al. UV-enhanced bioactivity and cell response of micro-arc oxidized titania coatings. Acta Biomaterialia, 2008, 4(5): 1518-1529. |
| [15] | Feddes B, Vredenberg A M, Wolke J G C, et al. Bulk composition of r.f. magnetron sputter deposited calcium phosphate coatings on different substrates (polyethylene, polytetrafluoroethylene, silicon). Surface & Coatings Technology, 2004, 185(2/3): 346-355. |
| [16] | Guehennec L, Lopez-Heredia M A, Enkel B, et al. Osteoblastic cell behaviour on different titanium implant surfaces. Acta Biomaterialia, 2008, 4(3): 535-543. |
| [17] | Roy A, Singh S S, Datta M K, et al. Novel Sol-Gel derived calcium phosphate coatings on Mg4Y alloy. Materials Science and Engineering B-Advanced Functional Solid-State Materials, 2011, 176(20): 1679-1689. |
| [18] | Froimson M I, Garino J, Machenaud A, et al. Minimum 10-year results of a tapered, titanium, hydroxyapatite-coated hip stem: an independent review. The Journal of Arthroplasty, 2007, 22(1): 1-7. |
| [19] | Yu L G, Khor K A, Li H, et al. Effect of spark plasma sintering on the microstructure and in vitro behavior of plasma sprayed HA coatings. Biomaterials, 2003, 24(16): 2695-2705. |
| [20] | Daugaard H, Elmengaard B, Bechtold J E, et al. The effect on bone growth enhancement of implant coatings with hydroxyapatite and collagen deposited electrochemically and by plasma spray. Journal of Biomedical Materials Research, 2010, 92A(3): 913-921. |
| [21] | Groot K, Geesink R G T, Klein C P A T, et al. Plasma sprayed coating of hydroxyapatite. Journal of Biomedical Materials Research, 1987, 21(12): 1375-1387. |
| [22] | Lacefield W R. Hydroxyapatite coatings, In: An Introduction to Bioceramics, ed. Hench L L and Wilson J. Singapore: World Scientific, 1994. |
| [23] | 梁 星, 魏治统, 陈安玉. 生物活性陶瓷-钛复合人工牙的涂层初探. 华西口腔医学杂志, 1989, 7(4): 193-196. |
| [24] | Cheang P, Khor K A. Addressing processing problems associated with plasma spraying hydroxyapatite coatings. Biomaterials, 1996, 17(5): 537-544. |
| [25] | Feng C F, Khor K A, Liu E J, et al. Phase transformations in plasma sprayed hydroxyapatitecoatings. Scripta Materialia, 1999, 42(1): 103-109. |
| [26] | ZHENG Xue-Bin, HUANG Min-Hui, HUANG Jing-Qi, et al. Effect of spray distance and spray power on properties of plasma sprayed hydroxyapatite coatings. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 1999, 14(5): 783-788. |
| [27] | Dong Z L, Khor K A, Quek C H, et al. TEM and STEM analysis on heat-treated and in vitro plasma-sprayed hydroxyapatite/ Ti-6Al-4V composite coatings. Biomaterials, 2003, 24(1): 97-105. |
| [28] | Cizek J, Khor K A. Role of in-flight temperature and velocity of powder particles on plasma sprayed hydroxyapatite coating characteristics. Surface & Coatings Technology, 2012, 206(8/9): 2181-2191. |
| [29] | Bhadang K A, Gross K A. Influence of fluorapatite on the properties of thermally sprayed hydroxyapatite coatings. Biomaterials, 2004, 25(20): 4935-4945. |
| [30] | Roy M, Bandyopadhyay A, Bose S, et al. Induction plasma sprayed nano hydroxyapatite coatings on titanium for orthopaedic and dental implants. Surface & Coatings Technology, 2011, 205(8/9): 2785-2792. |
| [31] | Brossa F, Cigada A, Chiesa R, et al. Post-deposition treatment effects on hydroxyapatite vacuum plasma spray coatings. Journal of Materials Science - Materials in Medicine, 1994, 5(12): 855-857. |
| [32] | Yang Y C. Influence of residual stress on bonding strength of the plasma-sprayed hydroxyapatite coating after the vacuum heat treatment. Surface & Coatings Technology, 2007, 201(16/17): 7187-7193. |
| [33] | Tao S Y, Ji H, Ding C X. Effect of vapor-flame treatment on plasma sprayed hydroxyapatite coatings. Journal of Biomedical Materials Research, 2000, 52(3): 572-575. |
| [34] | Xue W C, Liu X Y, Zheng X B, et al. Effect of hydroxyapatite coating crystallinity on dissolution and osseointegration in vivo. Journal of Biomedical Materials Research Part A, 2005, 74A(4): 553-561. |
| [35] | Gross K A, Rodriguez-Lorenzo L M. Sintered hydroxyfluorapatites. Part I: Sintering ability of precipitated solid solution powders. Biomaterials, 2004, 25: 1375-1384. |
| [36] | Robinson C, Shore R C, Brookes S J, et al. The chemistry of enamel caries. Crit. Rev. Oral. Biol. Med., 2000, 11(4): 481-495. |
| [37] | Landi E, Tampieri A, Mattioli-Belmonte, et al. Biomimetic Mg- and Mg, CO32- substituted hydroxyapatites: synthesis characterization and in vitro behavior. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc., 2006, 26(13): 2593-2601. |
| [38] | Jantova S, Theiszova M, Letasiova S. In vitro effects of fluor-hydroxyapatite, fluorapatite and hydroxyapatite on colony formation, DNA damage and mutagenicity. Mutation Research - Genetic Toxicology and Environmental Mutagenesis, 2008, 652(2): 139-144. |
| [39] | Landi E, Tampieri A, Celotti G, et al. Sr-substituted hydroxyapatites for osteoporotic bone replacement. Acta Biomater., 2007, 3(6): 961-969. |
| [40] | Oliveira A L, Reis R L, Li P. Strontium-substituted apatite coating grown on Ti6Al4V substrate through biomimetic synthesis. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B, 2007, 83(1): 258-265. |
| [41] | Xue W, Hosick H L, Bandyopadhyay A, et al. Preparation and cell-materials interactions of plasma sprayed strontium-containing hydroxyapatite coating. Surf. Coat. Technol., 2007, 201(8): 4685-4693. |
| [42] | Schwarz K, Milne D. Growth-promoting effects of silicon in rats. Nature, 1972, 239: 333-334. |
| [43] | Carlisle E. Silicon: a possible factor in bone calcification. Science, 1970, 167(3916): 279-280. |
| [44] | Pietak A M, Reid J W, Stott M J, et al. Silicon substitution in the calcium phosphate bioceramics. Biomaterials, 2007, 28: 4023-4032. |
| [45] | Jugdaohsingh R, Tucker K, Qiao N, et al. Dietary silicon intake is positevely associated with bone mineral density in men and premenopausal women of the Framingham offspring cohort. J. Bone. Miner. Res., 2004, 19(2): 297-307. |
| [46] | Darley W M, Volcani B E. Role of silicon in diatom metabolism. A silicon requirement for deoxyreibonucleic acid synthesis in diatom Cylindrotheca-fusiformis reimann and lewin. Exp. Cell. Res., 1969, 58(2/3): 334. |
| [47] | Keeting P, Oursler M, Wiegand K, et al. Zeolite a increases proliferation, differentiation, and transforming growth factor beta production in normal adult human osteoblastlike cells in vitro. J. Bone. Miner. Res., 1992, 7(11): 1281-1289. |
| [48] | Reffitt D, Ogston N, Jugdaohsingh R, et al. Orthosilicic acid stimulates collagen type I synthesis and osteoblastic differentiation in human osteoblastic-like cells in vitro. Bone, 2003, 32(2): 127-135. |
| [49] | Zheng X B, Huang M H, Ding C X. Bonding strength of plasma sprayed hydroxyapatite / Ti composite coatings. Biomaterials, 2000, 21(8): 841-849. |
| [50] | Gu Y W, Khor K A, Cheang P. In vitro studies of plasma-sprayed hydroxyapatite/Ti-6Al-4V composite coatings in simulated body fluid (SBF). Biomaterials, 2003, 24(9): 1603-1611. |
| [51] | Khor K A, Gu Y W, Quek C H, et al. Plasma spraying of functionally graded hydroxyapatitey/Ti-6Al-4V coatings. Surface & Coatings Technology, 2003, 168(2/3): 195-201. |
| [52] | Lim V J P, Khor K A, Fu L, et al. Hydroxyapatite-zirconia composite coatings via the plasma spraying process. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 1999, 89-90 |
| (SI): 491-496. | |
| [53] | Li H, Khor K A, Kumar R, et al. Characterization of hydroxyapatite nano-zirconia composite coatings deposited by high velocity oxy-fuel (HVOF) spray process. Surface & Coatings Technology, 2004, 182(2/3): 227-236. |
| [54] | Zheng X B, Ding C X. Characterization of plasma sprayed hydroxyapatite / zirconium oxide composite coatings. Journal of the Korean Vacuum Society, 2000, 9(SI): 89-94. |
| [55] | Zheng X B, Ding C X. Characterization of plasma sprayed hydroxyapatite/TiO2 composite coatings. Journal of Thermal Spray Technology, 2000, 9(4): 520-525. |
| [56] | Tomaszek R, Pawlowski L, Gengembre L, et al. Microstructure of suspension plasma sprayed multilayer coatings of hydroxyapatite and titanium oxide. Surface & Coatings Technology, 2007, 201(16/17): 7432-7440. |
| [57] | Morks M F, Fahim N F, Kobayashi A. Structure, mechanical performance and electrochemical characterization of plasma sprayed SiO2/Ti-reinforced hydroxyapatite biomedical coatings. Applied Surface Science, 2008, 255(5): 3426-3433. |
| [58] | Gristina A G. Biomaterial-centered infection: microbial adhesion versus tissue integration. Science, 1987, 237(4822): 1588-1595. |
| [59] | Gruessner U, Clemens M, Pahlplatz P V, et al. Improvement of peripheral wound healing by local administration of gentamicin- impregnated collagen fleeces after abdominoperineal excision of rectal cancer. American Journal of Surgery, 2001, 182: 502-509. |
| [60] | Oyane A, Yokoyama Y, Uchida M, et al. The formation of an antibacterial agent-apatite composite coating on a polymer surface using a metastable calcium phosphate solution. Biomaterials, 2006, 27(17): 3295-3303. |
| [61] | Sorensen T S, Sorensen A L. Rapid release of gentamycin from collagen sponge: in vitro comparison with plastic beads. Acta Orthopaedice Scandinavica, 1990, 61(4): 353-356. |
| [62] | Frédéric L, Aurélien B, Jérémy G, et al. A new concept of gentamicin loaded HAP/TCP bone substitute for prophylactic action: in vitro release validation. Journal of Materials Science - Materials in Medicine, 2008, 19(2): 947-951. |
| [63] | Cambell A A, Song L, Li X S, et al. Development, characterization, and anti-microbial efficacy of hydroxyapatite-chlorhexidine coatings produced by surface-induced mineralization. Journal of Biomedical Materials Research, 2000, 53(4): 400-407. |
| [64] | Feng Q L, Kim T N, Wu J, et al. Antibacterial effects of Ag-HAp thin films on alumina substrates. Thin Sold Films, 1998, 335(1/2): 214-219. |
| [65] | Wan Y Z, Xiong G Y, Liang H, et al. Modification of medical metals by ion implantation of copper. Applied Surface Science, 2007, 253(24): 9426-9429. |
| [66] | Chen Yikai, Zheng Xuebin, Xie Youtao, et al. Anti-bacterial and cytotoxic properties of plasma sprayed silver-containing HA coatings. Journal of Materials Science - Materials in Medicine, 2008, 19(12): 3603-3609. |
| [67] | 阮洪江, 刘俊建, 范存义, 等. 载银羟基磷灰石抗菌涂层体外抗菌性能及生物相容性研究. 中国修复重建外科杂志, 2009, 23(2): 226-230. |
| [68] | 陈益凯. 抗菌型钛和羟基磷灰石涂层制备和性能研究. 上海: 中国科学院上海硅酸盐研究所博士论文, 2009: 91-92. |
| [69] | Tercero J E, Namin S, Lahiri D, et al. Effect of carbon nanotube and aluminum oxide addition on plasma-sprayed hydroxyapatite coating's mechanical properties and biocompatibility. Materials Science and Engineering C, 2009, 29(7): 2195-2202. |
| [70] | Balani K, Anderson R, Laha T, et al. Plasma-sprayed carbon nanotube reinforced hydroxyapatite coatings and their interaction with human osteoblasts in vitro. Biomaterials, 2007, 28(4): 618-624. |
| [71] | Li H, Khor K A, Cheang P. Adhesive and bending failure of thermal sprayed hydroxyapatite coatings: Effect of nanostructures at interface and crack propagation phenomenon during bending. Engineering Fracture Mechanics, 2007, 74(12): 1894-1903. |
| [72] | 杨 晖, 陈礼洲. 液相等离子喷涂制备纳米涂层的研究进展. 材料导报, 2008, 22(9): 58-60. |
| [73] | Gadow R, Killinger A, Stiegler N. Hydroxyapatite coatings for biomedical applications deposited by different thermal spray techniques. Surface & Coatings Technology, 2010, 205(4): 1157-1164. |
| [74] | Huang Y, Song L, Huang T. Characterization and formation mechanism of nano-structured hydroxyapatite coatings deposited by the liquid precursor plasma spraying process. Biomedical Materials, 2010, 5(5): 054113-1-10. |
| [75] | Huang Y, Song L, Liu X Y, et al. Hydroxyapatite coatings deposited by liquid precursor plasma spraying: controlled dense and porous microstructures and osteoblastic cells responses. Biofabrication, 2010, 2(4): 045003-1-3. |
| [76] | Liu X Y, Zhao X, Ding C X, et al. Light-induced bioactive TiO2 surface. Applied Physics Letters, 2006, 88(1): 013905. |
| [77] | Zhao X B, Liu X Y, Chen Z G, et al. Study on bioactivity of plasma-sprayed titania coating. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2008, 23(5): 1021-1026. |
| [78] | Hu X X, Shen H, Cheng Y, et al. One-step modification of nano-hydroxyapatite coating on titanium surface by hydrothermal method. Surf Coat Technol, 2010, 205(7): 2000-2006. |
| [79] | Wang G, Liu X, Zreiqat H, et al. Enhanced effects of nano-scale topography on the bioactivity and osteoblast behaviors of micron rough ZrO2 coatings. Colloids and Surfaces B: Biointerfaces, 2011, 86(2): 267-274. |
| [80] | Liu X Y, Tao S Y, Ding C X. Bioactivity of plasma sprayed dicalcium silicate coating. Biomaterials, 2002, 23(3): 963-968. |
| [81] | Liu X Y, Ding C X. Reactivity of plasma sprayed wollastonite in simulated body fluid. J. Biomed. Mater. Res., 2002, 59(2): 259-264. |
| [82] | Liu X Y, Ding C X. Apatite formed on the surface of plasma sprayed wollastonite coating immersed in simulated body fluid. Biomaterials, 2001, 22(14): 2007-2012. |
| [83] | Xue W C, Liu X Y, Zheng X B, et al. Dissolution and mineralization of plasma-sprayed wollastonite coatings with different crystallinity. Surf. Coat. Technol, 2004, 200(7): 2420-2427. |
| [84] | Xue W C, Ding C X, Cao C, et al. Bioactivity of plasma-sprayed diopside coating in vitro. Key Eng. Mater., 2005, 288-289: 319-322. |
| [85] | Liu X Y, Ding C X. Phase compositions and microstructure of plasma sprayed wollastonite coating. Surf. Coat. Technol., 2001, 141(2/3): 269-274. |
| [86] | Liu X Y, Ding C X. Characterization of plasma sprayed wollastonite powder and coating. Surf. Coat. Technol., 2002, 153(2/3): 173-177. |
| [87] | 刘宣勇. 等离子喷涂生物活性硅灰石涂层研究. 上海: 中国科学院上海硅酸盐研究所博士论文, 2002: 96-98. |
| [88] | Xue W C, Liu X Y, Zheng X B, et al. Plasma-sprayed diopside coatings for biomedical applications. Surf. Coat. Technol., 2004, 185(2/3): 340-345. |
| [89] | Liu X Y, Ding C X. Thermal properties and microstructure of a plasma sprayed wollastonite coating. J. Therm. Spray. Technol., 2002, 11(3): 375-379. |
| [90] | Xue W C, Liu X Y, Zheng X B, et al. In vivo evaluation of plasma-sprayed wollastonite coating. Biomaterials, 2005, 26(17): 3455-3460. |
| [91] | Xie Y T, Liu X Y, Zheng X B, et al. Bioconductivity of plasma sprayed dicalcium silicate/titanium composite coatings on Ti-6Al-4V alloy. Surf. Coat. Technol., 2005, 199(1): 105-111. |
| [92] | Xie Y T, Liu X Y, Chu P K, et al. Bioactive titanium-particle- containing dicalcium silicate coatings. Surface & Coatings Technology, 2005, 200(5/6): 1950-1953. |
| [93] | Xie Y T, Liu X Y, Ding C X, et al. Bioconductivity and mechanical properties of plasma-sprayed dicalcium silicate/zirconia composite coatings. Mater. Sci. Eng., C, 2005, 25(4): 509-515. |
| [94] | Xie Y T, Chu P K, Liu X Y, et al. Improved stability of dicalcium silicate/zirconia composite coatings by post-spraying heat treatment. Solid State Phenomena, 2005, 107: 141-144. |
| [95] | Liang Y, Xie Y T, Ji H, et al. Chemical Stability and biological properties of plasma-sprayed CaO-SiO2-ZrO2 Coatings. J. Therm. Spray Technol., 2010, 19(6): 1171-1178. |
| [96] | Xie Y T, Zheng X B, Ding C X, et al. Preparation and characterization of CaO-ZrO2-SiO2 coating for potential application in biomedicine. J. Therm. Spray Technol., 2009, 18(4): 678-685. |
| [97] | Liang Y, Xie Y T, Ji H, et al. Excellent stability of plasma-sprayed bioactive Ca3ZrSi2O9 ceramic coating on Ti-6Al-4V. Appl. Surf. Sci., 2010, 256(14): 4677-4681. |
| [98] | 梁 莹. 等离子体喷涂氧化锆改性钙-硅基涂层制备与性能研究. 上海: 中国科学院上海硅酸盐研究所硕士论文, 2010: 34-36. |
| [99] | Yang F, Xie Y T, Li H, et al. Human bone marrow-derived stromal cells cultured with a plasma sprayed CaO-ZrO2-SiO2 coating. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B, 2010, 95B(1): 192-201. |
| 100 | Li K, Yu J, Xie Y T, et al. Chemical stability and antimicrobial activity of plasma sprayed bioactive Ca2ZnSi2O7 coating. J. Mater. Sci. - Mater. Med., 2011, 22(12): 2781-2789. |
| 101 | 作者学术成就介绍:郑学斌, 男, 博士, 中国科学院上海硅酸盐研究所研究员、博士生导师.主要从事生物涂层材料研究, 负责完成的“等离子喷涂羟基磷灰石生物材料制备中的关键技术研究”和“骨植入体生物活性涂层材料研究及应用”项目, 分别获2002和2009年度上海市科技进步二等奖.主持的真空等离子体喷涂钛(Ti)和羟基磷灰石(HA)涂层研发项目效果显著, 已进入批量生产阶段, 累计制备骨植入体产品十万余件, 临床应用效果优良. 在Biomaterials、JBMR、Acta Biomaterialia等国内外学术刊物发表论文120余篇, 申请国家发明专利30余项. |
| [1] | 朱文杰, 唐璐, 陆继长, 刘江平, 罗永明. 钙钛矿型氧化物催化氧化挥发性有机化合物的研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(7): 735-746. |
| [2] | 胡智超, 杨鸿宇, 杨鸿程, 孙成礼, 杨俊, 李恩竹. P-V-L键理论在微波介质陶瓷性能调控中的应用[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(6): 609-626. |
| [3] | 吴琼, 沈炳林, 张茂华, 姚方周, 邢志鹏, 王轲. 铅基织构压电陶瓷研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(6): 563-574. |
| [4] | 张碧辉, 刘小强, 陈湘明. Ruddlesden-Popper结构杂化非常规铁电体的研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(6): 587-608. |
| [5] | 吴杰, 杨帅, 王明文, 李景雷, 李纯纯, 李飞. 铅基织构压电陶瓷的发展历程、现状与挑战[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(6): 575-586. |
| [6] | 姜昆, 李乐天, 郑木鹏, 胡永明, 潘勤学, 吴超峰, 王轲. PZT陶瓷的低温烧结研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(6): 627-638. |
| [7] | 田睿智, 兰正义, 殷杰, 郝南京, 陈航榕, 马明. 基于微流控技术的纳米无机生物材料制备: 原理及其研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(4): 337-347. |
| [8] | 张继国, 吴田, 赵旭, 杨钒, 夏天, 孙士恩. 钠离子电池正极材料循环稳定性提升策略及产业化进程[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(4): 348-362. |
| [9] | 殷杰, 耿佳毅, 王康龙, 陈忠明, 刘学建, 黄政仁. SiC陶瓷的3D打印成形与致密化新进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(3): 245-255. |
| [10] | 谌广昌, 段小明, 朱金荣, 龚情, 蔡德龙, 李宇航, 杨东雷, 陈彪, 李新民, 邓旭东, 余瑾, 刘博雅, 何培刚, 贾德昌, 周玉. 直升机特定结构先进陶瓷材料研究进展与应用展望[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(3): 225-244. |
| [11] | 范晓波, 祖梅, 杨向飞, 宋策, 陈晨, 王子, 罗文华, 程海峰. 质子调控型电化学离子突触研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(3): 256-270. |
| [12] | 海热古·吐逊, 郭乐, 丁嘉仪, 周嘉琪, 张学良, 努尔尼沙·阿力甫. 上转换荧光探针辅助的光学成像技术在肿瘤显影中的应用研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(2): 145-158. |
| [13] | 孙树娟, 郑南南, 潘昊坤, 马猛, 陈俊, 黄秀兵. 单原子催化剂制备方法的研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(2): 113-127. |
| [14] | 陶桂龙, 支国伟, 罗添友, 欧阳佩东, 衣新燕, 李国强. 空腔型薄膜体声波滤波器的关键技术进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(2): 128-144. |
| [15] | 周帆, 田志林, 李斌. 热防护系统用碳化物超高温陶瓷抗烧蚀涂层研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(1): 1-16. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||