无机材料学报 ›› 2026, Vol. 41 ›› Issue (3): 322-330.DOI: 10.15541/jim20250228 CSTR: 32189.14.jim20250228
石金瑜1,2( ), 雷一明1, 王晨旭3, 张洁1(
), 雷一明1, 王晨旭3, 张洁1( ), 王京阳1
), 王京阳1
收稿日期:2025-05-26
修回日期:2025-07-14
出版日期:2025-07-31
网络出版日期:2025-07-31
通讯作者:
张 洁, 研究员. E-mail: jiezhang@imr.ac.cn作者简介:石金瑜(1996-), 男, 博士研究生. E-mail: jyshi19s@imr.ac.cn
基金资助:
SHI Jinyu1,2( ), LEI Yiming1, WANG Chenxu3, ZHANG Jie1(
), LEI Yiming1, WANG Chenxu3, ZHANG Jie1( ), WANG Jingyang1
), WANG Jingyang1
Received:2025-05-26
Revised:2025-07-14
Published:2025-07-31
Online:2025-07-31
Contact:
ZHANG Jie, professor. E-mail: jiezhang@imr.ac.cnAbout author:SHI Jinyu (1996-), male, PhD candidate. E-mail: jyshi19s@imr.ac.cn
Supported by:摘要:
第四代核反应堆服役环境苛刻, 高温和强辐照对结构材料提出了更高的要求, 亟需开发新型抗辐照材料。碳化钛(TiCx)陶瓷因其高熔点、优异的力学性能、良好的耐腐蚀性而成为先进核反应堆中极具潜力的结构材料。本研究采用3 MeV Au2+对不同化学计量TiCx薄膜进行辐照实验, 系统研究了TiCx结构缺陷、表面形貌和力学性能在不同辐照通量下的变化规律。结果表明: 随着辐照通量的增加, 近化学计量TiCx晶格无序化程度加剧, 而亚化学计量TiCx辐照后的结构稳定性优异。亚化学计量TiCx辐照后表面粗糙度无明显变化且未产生辐照裂纹。此外, TiCx辐照后的硬度和模量均呈现增加趋势, 其中亚化学计量TiCx的抗辐照硬化能力优于近化学计量TiCx。这主要是由于亚化学计量TiCx的本征碳空位有效抑制了辐照缺陷的累积, 从而维持了良好的稳定性。本研究为理解化学计量与过渡金属碳/氮化合物辐照损伤之间的关系, 以及设计新型抗强辐照陶瓷新材料提供了重要的参考依据。
中图分类号:
石金瑜, 雷一明, 王晨旭, 张洁, 王京阳. 不同化学计量碳化钛的离子辐照损伤行为研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2026, 41(3): 322-330.
SHI Jinyu, LEI Yiming, WANG Chenxu, ZHANG Jie, WANG Jingyang. Ion Irradiation Damage Behavior in Titanium Carbide with Different Stoichiometry[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2026, 41(3): 322-330.
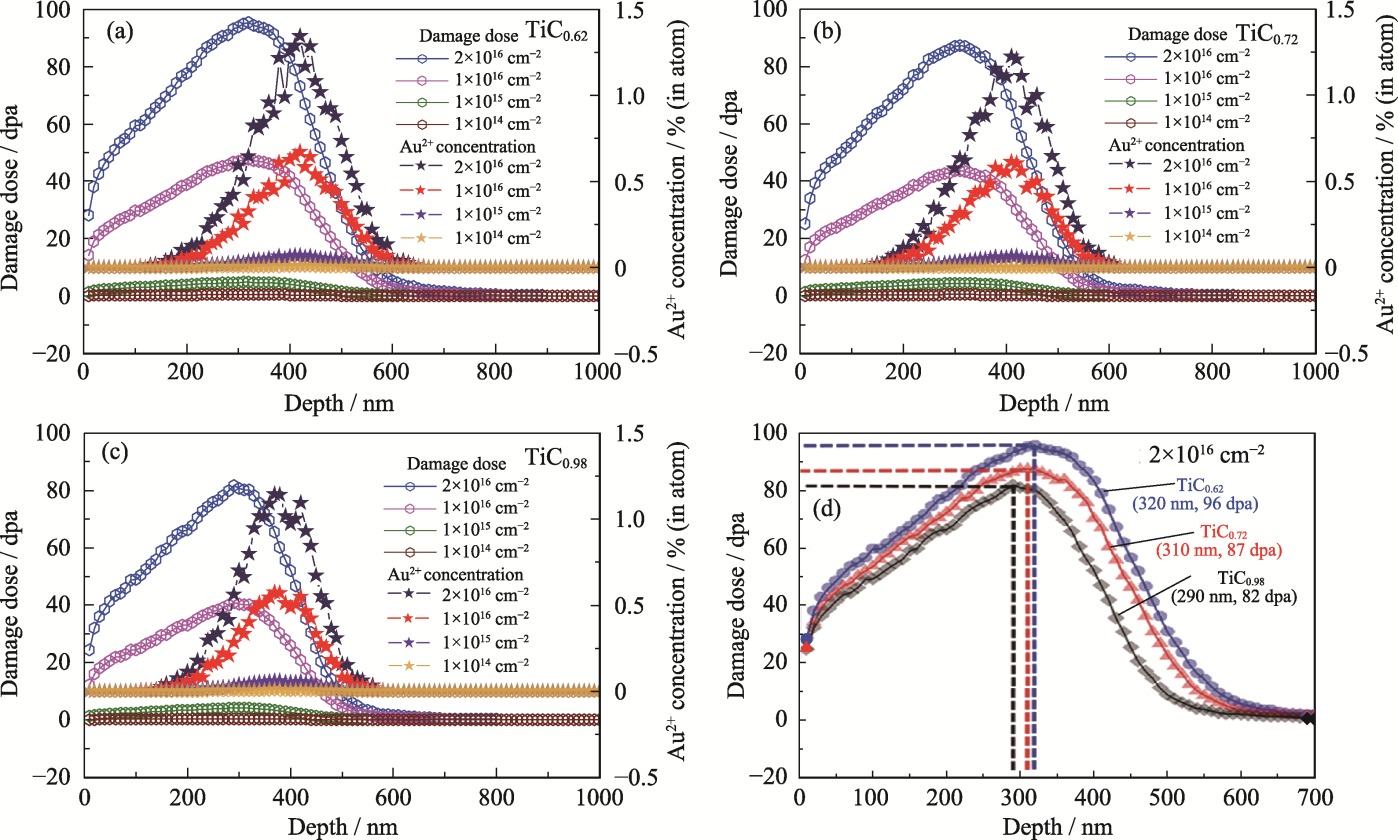
图1 (a~c)不同辐照通量(3 MeV Au2+)辐照后样品(a) TiC0.62、(b) TiC0.72、(c) TiC0.98的辐照损伤剂量和Au2+浓度随深度的变化; (d) 2×1016 cm-2辐照通量下样品的辐照损伤剂量随深度的变化
Fig. 1 (a-c) Damage dose and Au2+ concentration profiles induced by 3 MeV Au2+ irradiation in (a) TiC0.62, (b) TiC0.72, and (c) TiC0.98 at various fluences; (d) Damage dose profiles of samples at a fluence of 2×1016 cm-2 Colorful figures are available on website
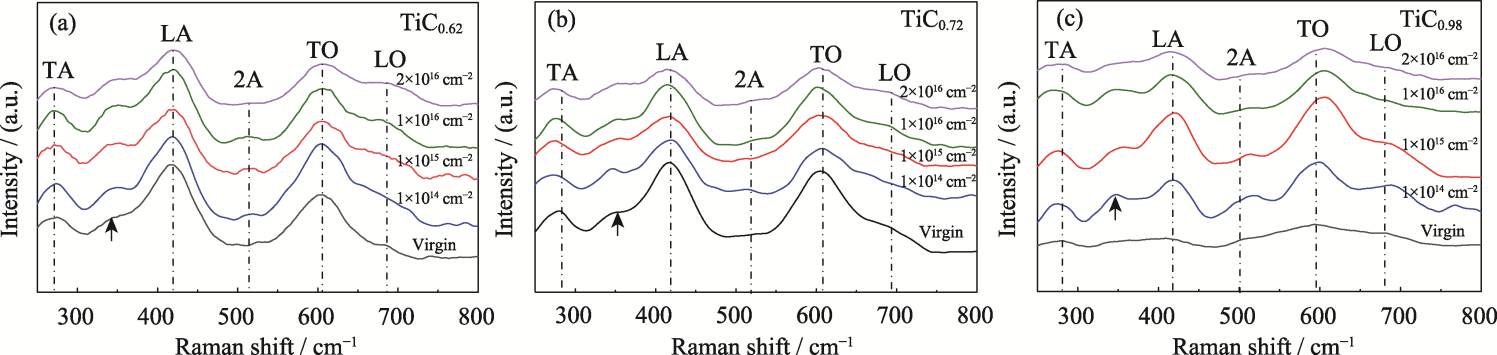
图2 制备态及不同辐照通量辐照后TiCx薄膜的拉曼谱图
Fig. 2 Raman spectra of TiCx films before and after irradiation with various fluences (a) TiC0.62; (b) TiC0.72; (c) TiC0.98
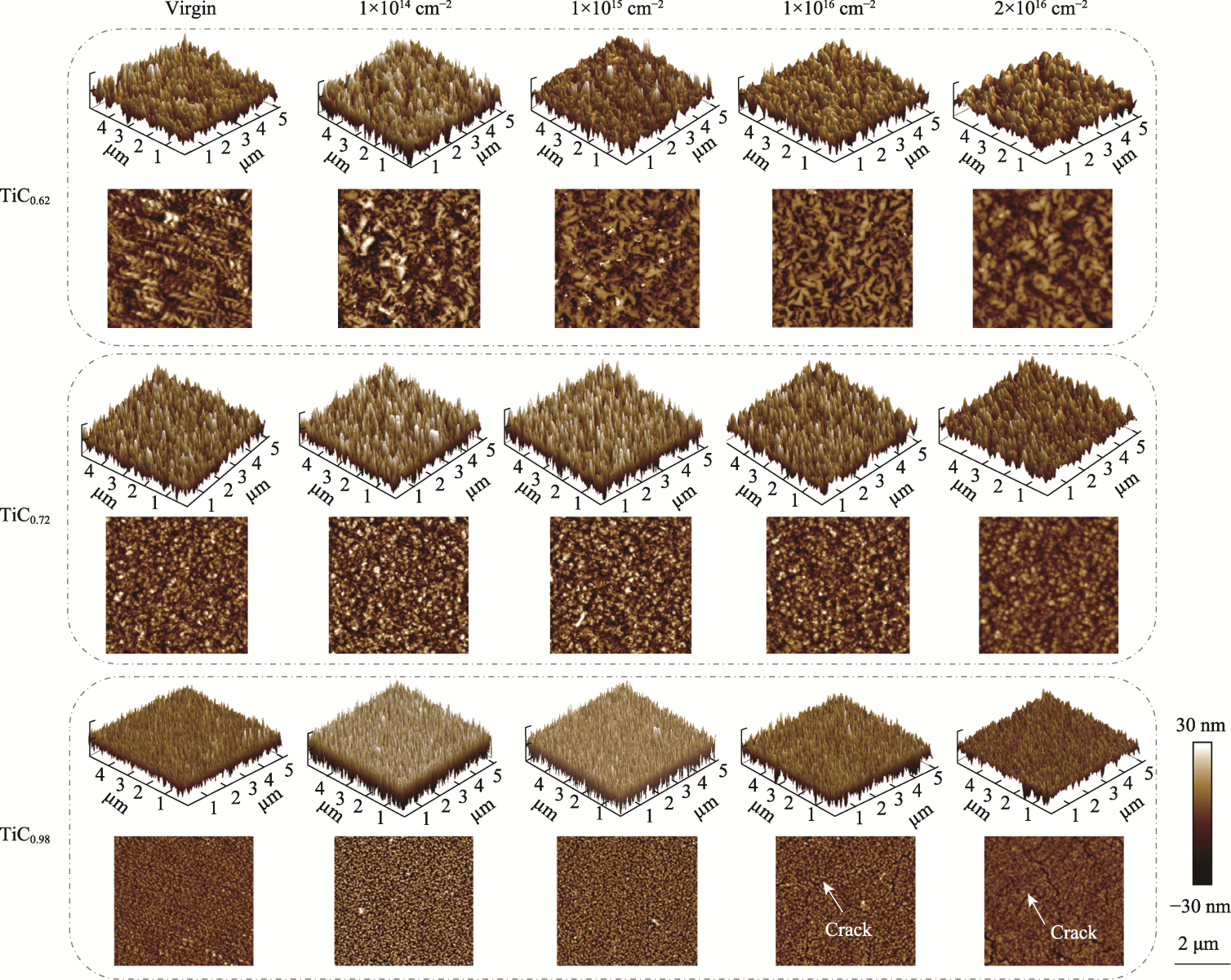

图3 制备态及不同辐照通量辐照后TiCx薄膜的AFM表面二维形貌及三维形貌图
Fig. 3 Surface two-dimensional morphologies and three-dimensional morphologies obtained by AFM of as-deposited and irradiated TiCx films with various fluences
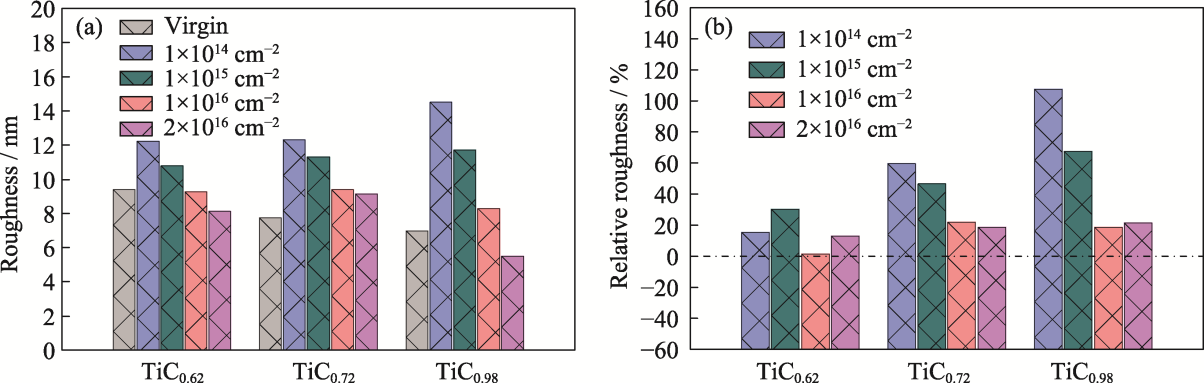
图4 不同辐照通量下TiCx薄膜的(a)粗糙度及(b)相对粗糙度
Fig. 4 (a) Roughness and (b) relative roughness of TiCx films under different fluences Colorful figures are available on website
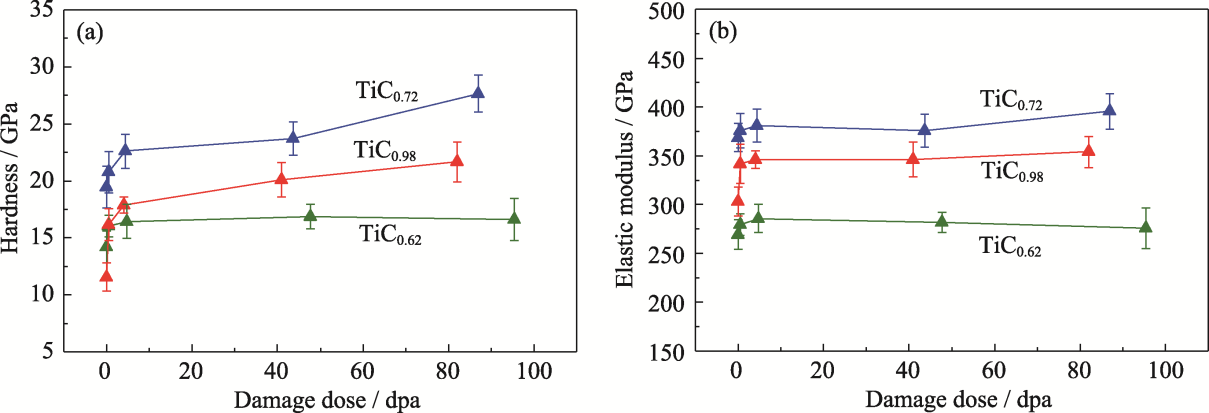
图6 辐照前后TiCx薄膜的(a)硬度和(b)弹性模量随辐照损伤剂量的变化
Fig. 6 (a) Variations of hardness and (b) elastic modulus of as-deposited and irradiated TiCx films with damage dose
| Sample | Fluence | Peak position/cm-1 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TA | LA | TO | ||
| TiC0.62 | Virgin | 273.69 | 418.55 | 605.78 |
| 1×1014 cm-2 | 273.58 | 418.32 | 605.83 | |
| 1×1015 cm-2 | 273.52 | 418.33 | 605.80 | |
| 1×1016 cm-2 | 273.60 | 418.22 | 605.81 | |
| 2×1016 cm-2 | 273.55 | 418.55 | 605.79 | |
| TiC0.72 | Virgin | 279.69 | 415.58 | 604.19 |
| 1×1014 cm-2 | 275.49 | 415.65 | 604.28 | |
| 1×1015 cm-2 | 274.86 | 415.32 | 604.54 | |
| 1×1016 cm-2 | 273.69 | 415.27 | 604.81 | |
| 2×1016 cm-2 | 273.80 | 415.55 | 604.54 | |
| TiC0.98 | Virgin | 277.29 | 416.55 | 595.40 |
| 1×1014 cm-2 | 275.49 | 416.55 | 598.87 | |
| 1×1015 cm-2 | 273.69 | 416.62 | 604.07 | |
| 1×1016 cm-2 | 271.89 | 416.55 | 605.81 | |
| 2×1016 cm-2 | 270.09 | 416.78 | 605.81 | |
表S1 制备态及不同辐照通量辐照后TiCx薄膜的拉曼光谱峰位
Table S1 Raman peak positions of as-deposited and irradiated TiCx films under different fluences
| Sample | Fluence | Peak position/cm-1 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TA | LA | TO | ||
| TiC0.62 | Virgin | 273.69 | 418.55 | 605.78 |
| 1×1014 cm-2 | 273.58 | 418.32 | 605.83 | |
| 1×1015 cm-2 | 273.52 | 418.33 | 605.80 | |
| 1×1016 cm-2 | 273.60 | 418.22 | 605.81 | |
| 2×1016 cm-2 | 273.55 | 418.55 | 605.79 | |
| TiC0.72 | Virgin | 279.69 | 415.58 | 604.19 |
| 1×1014 cm-2 | 275.49 | 415.65 | 604.28 | |
| 1×1015 cm-2 | 274.86 | 415.32 | 604.54 | |
| 1×1016 cm-2 | 273.69 | 415.27 | 604.81 | |
| 2×1016 cm-2 | 273.80 | 415.55 | 604.54 | |
| TiC0.98 | Virgin | 277.29 | 416.55 | 595.40 |
| 1×1014 cm-2 | 275.49 | 416.55 | 598.87 | |
| 1×1015 cm-2 | 273.69 | 416.62 | 604.07 | |
| 1×1016 cm-2 | 271.89 | 416.55 | 605.81 | |
| 2×1016 cm-2 | 270.09 | 416.78 | 605.81 | |
| [28] | LI Q, WEI Y, DING X, et al. Enhanced resistance to He ions irradi-ation damage of nanocrystalline SiC coating. Journal of Advanced Ceramics, 2025, 14: 9221067. |
| [29] | CHEN C C, LIANG N T, TSE W S, et al. Raman spectra of titanium nitride thin films. Chinese Journal of Physics, 1994, 32: 205. |
| [30] | KLEIN M V, HOLY J A, WILLIAMS W S. Raman scattering induced by carbon vacancies in TiCx. Physical Review B, 1978, 17(4): 1546. |
| [31] | WARD Y, YOUNG R J, SHATWELL R A. Application of Raman microscopy to the analysis of silicon carbide monofilaments. Journal of Materials Science, 2004, 39(22): 6781. |
| [32] | WIPF H, KLEIN M V, WILLIAMS W S. Vacancy-induced and two-phonon Raman scattering in ZrCx, NbCx, HfCx, and TaCx. Physica Status Solidi(b)-Basic Solid State Physics, 1981, 108(2): 489. |
| [33] | LANG E, BEECHEM T, MCDONALD A, et al. Defect structures as a function of ion irradiation and annealing in LiNbO3. Thin Solid Films, 2023, 768: 139719. |
| [34] | HU J, LI H, LI J, et al. Super-hard and tough Ta1-xWxCy films deposited by magnetron sputtering. Surface and Coatings Technology, 2020, 400: 126207. |
| [35] | LI H, ZHANG L, ZENG Q, et al. Structural, elastic and electronic properties of transition metal carbides TMC (TM=Ti, Zr, Hf and Ta) from first-principles calculations. Solid State Communications, 2011, 151(8): 602. |
| [36] | WANG R, LI B, LI P, et al. Effect of low-dose Xe20+ ion irradiation on the deformation behavior of the magnetron sputtered Cr coatings under nanoindentation. Surface and Coatings Technology, 2021, 428: 127907. |
| [37] | ZHANG Y, LI B, REN Y, et al. Evolution of structural and magnetic properties of NiFe/NiO exchange biased bilayer with medium energy C+ ion irradiation. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2025, 1018: 179180. |
| [38] | YANG J, LU S, YANG J. Irradiation response of microstructure and mechanical properties of NbMoVCr multi-principal element alloy coatings. Surface and Coatings Technology, 2024, 492: 131209. |
| [39] | ZHANG W, DENG J, ZHONG Y, et al. Microstructure response and LBE corrosion behavior of the FeCrAlY coating after Au-ions irradiation. Corrosion Science, 2024, 241: 112521. |
| [40] | ZHONG Y, ZHANG W, YANG J, et al. Study on LBE corrosion failure of FeAl/Al2O3 coatings after ion irradiation. Materials & Design, 2024, 242: 113019. |
| [41] | FU T, ZHU Y, PAN H, et al. Irradiation softening in a uranium containing NbTiZrU high entropy alloy induced by Xe ion implantation. Materials Today Communications, 2025, 42: 111231. |
| [42] | MONNET G. Multiscale modeling of irradiation hardening: application to important nuclear materials. Journal of Nuclear Materials, 2018, 508: 609. |
| [43] | HUANG Q, LEI G, LIU R, et al. Microstructure, hardness and modulus of carbon-ion-irradiated new SiC fiber (601-4). Journal of Nuclear Materials, 2018, 503: 91. |
| [44] | PELLEGRINO S, CROCOMBETTE J P, DEBELLE A, et al. Multi-scale simulation of the experimental response of ion-irradiated zirconium carbide: Role of interstitial clustering. Acta Materialia, 2016, 102: 79. |
| [1] | DONG D, GUAN J, WANG Z, et al. Current status and trends of nuclear energy under carbon neutrality conditions in China. Energy, 2025, 314: 134253. |
| [2] | OUYANG Q, WANG Y F, XU J, et al. Research progress of SiC fiber reinforced SiC composites for nuclear application. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(8): 822. |
| [3] | ZINKLE S J, SNEAD L L. Designing radiation resistance in materials for fusion energy. Annual Review of Materials Research, 2014, 44(1): 241. |
| [4] | ZINKLE S J, BUSBY J T. Structural materials for fission & fusion energy. Materials Today, 2009, 12(11): 12. |
| [5] | 杜进隆, 徐川, 付恩刚. 基于界面和纳米析出相材料的抗辐照损伤机制研究进展. 科学通报, 2023, 68(9): 1125. |
| [6] | HAN W Z, DEMKOWICZ M J, FU E G, et al. Effect of grain boundary character on sink efficiency. Acta Materialia, 2012, 60(18): 6341. |
| [7] | HAN W, DEMKOWICZ M J, MARA N A, et al. Design of radiation tolerant materials via interface engineering. Advanced Materials, 2013, 25(48): 6975. |
| [8] | YU K Y, BUFFORD D, KHATKHATAY F, et al. In situ studies of irradiation-induced twin boundary migration in nanotwinned Ag. Scripta Materialia, 2013, 69(5): 385. |
| [9] | DU J, JIANG S, CAO P, et al. Superior radiation tolerance via reversible disordering-ordering transition of coherent superlattices. Nature Materials, 2023, 22(4): 442. |
| [10] | XUE J X, ZHANG G J, GUO L P, et al. Improved radiation damage tolerance of titanium nitride ceramics by introduction of vacancy defects. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2014, 34(3): 633. |
| [11] | 魏博鑫. 高抗辐照损伤容限ZrCx陶瓷的制备与环境损伤行为. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学博士学位论文, 2018. |
| [12] | 陈丽娜. 先进核能系统用碳化锆陶瓷涂层的制备与性能研究. 合肥: 中国科学技术大学博士学位论文, 2021. |
| [13] | SHI J, CHEN L, LEI Y, et al. Irradiation damage of zirconium carbide with different stoichiometry. Vacuum, 2025, 239: 114355. |
| [14] | AGARWAL S, KOYANAGI T, BHATTACHARYA A, et al. Neutron irradiation-induced microstructure damage in ultra-high temperature ceramic TiC. Acta Materialia, 2020, 186: 1. |
| [15] | NOSEK A, CONZEN J, DOESCHER H, et al. Thermomechanics of candidate coatings for advanced gas reactor fuels. Journal of Nuclear Materials, 2007, 371(1/2/3): 288. |
| [16] | TANG C, STUEBER M, SEIFERT H J, et al. Protective coatings on zirconium-based alloys as accident-tolerant fuel (ATF) claddings. Corrosion Reviews, 2017, 35(3): 141. |
| [17] | AGARWAL S, TROCELLIER P, VAUBAILLON S, et al. Diffusion and retention of helium in titanium carbide. Journal of Nuclear Materials, 2014, 448(1/2/3): 144. |
| [18] | WEINBERGER C R, THOMPSON G B. Review of phase stability in the group IVB and VB transition-metal carbides. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2018, 101(10): 4401. |
| [19] | LIPATNIKOV V N, KOTTAR A, ZUEVA L V, et al. Ordering effects in nonstoichiometric titanium carbide. Inorganic Materials, 2000, 36(2): 155. |
| [20] | GAVARINI S, MILLARD-PINARD N, GARNIER V, et al. Elaboration and behavior under extreme irradiation conditions of nano-and micro-structured TiC. Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research Section B: Beam Interactions with Materials and Atoms, 2015, 356/357: 114. |
| [21] | PELLEGRINO S, TROCELLIER P, THOMÉ L, et al. Raman investigation of ion irradiated TiC and ZrC. Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research Section B: Beam Interactions with Materials and Atoms, 2019, 454: 61. |
| [22] | SHI J, LEI Y, WANG C, et al. Microstructure evolution in titanium carbide with different stoichiometry under 3 MeV Au2+ ion irradiation. Journal of Nuclear Materials, 2025, 606: 155609. |
| [23] | 徐川, 付恩刚. 北京大学1.7 MV串列静电加速器的离子注入/辐照实验系统. 原子核物理评论, 2021, 38(4): 410. |
| [24] | WEBER W J, ZHANG Y. Predicting damage production in monoatomic and multi-elemental targets using stopping and range of ions in matter code: challenges and recommendations. Current Opinion in Solid State and Materials Science, 2019, 23(4): 100757. |
| [25] | JIANG M, XIAO H Y, ZHANG H B, et al. A comparative study of low energy radiation responses of SiC, TiC and ZrC. Acta Materialia, 2016, 110: 192. |
| [26] | HANSON W A, PATEL M K, CRESPILLO M L, et al. Ionizing vs collisional radiation damage in materials: separated, competing, and synergistic effects in Ti3SiC2. Acta Materialia, 2019, 173: 195. |
| [27] | KITAJIMA M. Defects in crystals studied by Raman scattering. Critical Reviews in Solid State and Materials Sciences, 1997, 22(4): 275. |
| [1] | 郑晨, 王湘宁, 苑贺楠, 杨嘉伟, 李传建, 王华栋. 氧化铝纤维增强二氧化硅复合材料力学性能失效研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2026, 41(3): 331-339. |
| [2] | 张韵铂, 王兵, 李威, 宋曲之, 杜贻昂, 王应德. BNNS/聚硼氮烷杂化先驱体转化BN纤维中的纳米片尺寸效应[J]. 无机材料学报, 2026, 41(3): 359-369. |
| [3] | 袁旺, 胡建宝, 周亮, 阚艳梅, 张翔宇, 董绍明. 氩气气氛热处理对Shicolon-II SiC纤维机械性能和微观结构演变的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2026, 41(1): 119-128. |
| [4] | 张永恒, 陈继新. 镱铝硅酸盐玻璃和SiC改性h-BN基复合材料的制备与性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2026, 41(1): 37-44. |
| [5] | 陈义, 邱海鹏, 陈明伟, 徐昊, 崔恒. SiC/SiC复合材料基体硼改性方法及其力学性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(5): 504-510. |
| [6] | 崔宁, 张玉新, 王鲁杰, 李彤阳, 于源, 汤华国, 乔竹辉. (TiVNbMoW)Cx高熵陶瓷的单相形成过程与碳空位调控[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(5): 511-520. |
| [7] | 李紫薇, 弓伟露, 崔海峰, 叶丽, 韩伟健, 赵彤. 前驱体法制备(Zr, Hf, Nb, Ta, W)C-SiC复相陶瓷及性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(3): 271-280. |
| [8] | 高晨光, 孙晓亮, 陈君, 李达鑫, 陈庆庆, 贾德昌, 周玉. 基于湿法纺丝技术的SiBCN-rGO陶瓷纤维的组织结构、力学和吸波性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(3): 290-296. |
| [9] | 穆浩洁, 张源江, 喻彬, 付秀梅, 周世斌, 李晓东. ZrO2掺杂Y2O3-MgO纳米复相陶瓷的制备及性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(3): 281-289. |
| [10] | 李伟, 许志明, 苟燕子, 尹森虎, 余艺平, 王松. SiC纤维烧结陶瓷的制备及其性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(2): 177-183. |
| [11] | 范武刚, 曹雄, 周响, 李玲, 赵冠楠, 张兆泉. 8YSZ陶瓷在模拟压水堆水环境中的耐腐蚀性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(7): 803-809. |
| [12] | 王伟明, 王为得, 粟毅, 马青松, 姚冬旭, 曾宇平. 以非氧化物为烧结助剂制备高导热氮化硅陶瓷的研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(6): 634-646. |
| [13] | 孙海洋, 季伟, 王为民, 傅正义. TiB-Ti周期序构复合材料设计、制备及性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(6): 662-670. |
| [14] | 蔡飞燕, 倪德伟, 董绍明. 高熵碳化物超高温陶瓷的研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(6): 591-608. |
| [15] | 刘国昂, 王海龙, 方成, 黄飞龙, 杨欢. B4C含量对(Ti0.25Zr0.25Hf0.25Ta0.25)B2-B4C陶瓷力学性能及抗氧化性能的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(6): 697-706. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||