无机材料学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 40 ›› Issue (9): 1022-1028.DOI: 10.15541/jim20250022 CSTR: 32189.14.jim20250022
收稿日期:2025-01-15
修回日期:2025-02-13
出版日期:2025-09-20
网络出版日期:2025-03-19
通讯作者:
杨长, 教授. E-mail: cyang@phy.ecnu.edu.cn作者简介:王亮君(1998-), 男, 博士研究生. E-mail: 1134420548@qq.com
基金资助:
WANG Liangjun1( ), OUYANG Yuzhao1, ZHAO Junliang2, YANG Chang1(
), OUYANG Yuzhao1, ZHAO Junliang2, YANG Chang1( )
)
Received:2025-01-15
Revised:2025-02-13
Published:2025-09-20
Online:2025-03-19
Contact:
YANG Chang, professor. E-mail: cyang@phy.ecnu.edu.cnAbout author:WANG Liangjun (1998-), male, PhD candidate. E-mail: 1134420548@qq.com
Supported by:摘要:
在光电子器件领域, 具有可控电学参数的p型透明半导体材料具有重要的应用价值。但以CuI为代表的该类材料在制备工艺与掺杂调控方面仍存在显著技术瓶颈。本研究通过锰阳离子掺杂, 成功制备出具有可调电学特性的新型p型透明半导体材料, 为透明电子学发展提供了新思路。采用反应磁控溅射技术制备的Cu1-xMnxI固溶体薄膜展现出独特的性能优势。首先, 该材料可以在室温条件下制备, 并保持优异的可见光透明性。其次, 随着锰掺杂量(x)的增加, 薄膜晶粒尺寸逐渐减小, 并且出现明显的晶粒团聚现象。通过X射线光电子能谱分析, 揭示了薄膜中锰离子以Mn2+和Mn3+混合价态存在。电学性能表征显示, 薄膜电阻率可在0.017~2.5 Ω·cm区间实现两个数量级的可控调节, 同时空穴载流子浓度稳定维持在1018~1019 cm-3较高数量级。与传统n型半导体掺杂规律不同, 引入高价态锰离子未显著影响材料的p型导电特性, 这可能源于锰取代亚铜离子后形成的非完全离域电子态。本研究表明CuI半导体的空穴导电特性不易受高价锰离子掺杂的影响, 有望在保持良好p型导电性的情况下在较大范围内实现材料组分的宽域调控, 为开发CuI基多功能透明电子器件提供了重要材料基础。
中图分类号:
王亮君, 欧阳玉昭, 赵俊亮, 杨长. Cu-Mn-I固溶体薄膜制备及其p型透明导电性质调控[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(9): 1022-1028.
WANG Liangjun, OUYANG Yuzhao, ZHAO Junliang, YANG Chang. Cu-Mn-I Solid Solution Thin Films: Preparation and Control of p-type Transparent Conductive Properties[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(9): 1022-1028.
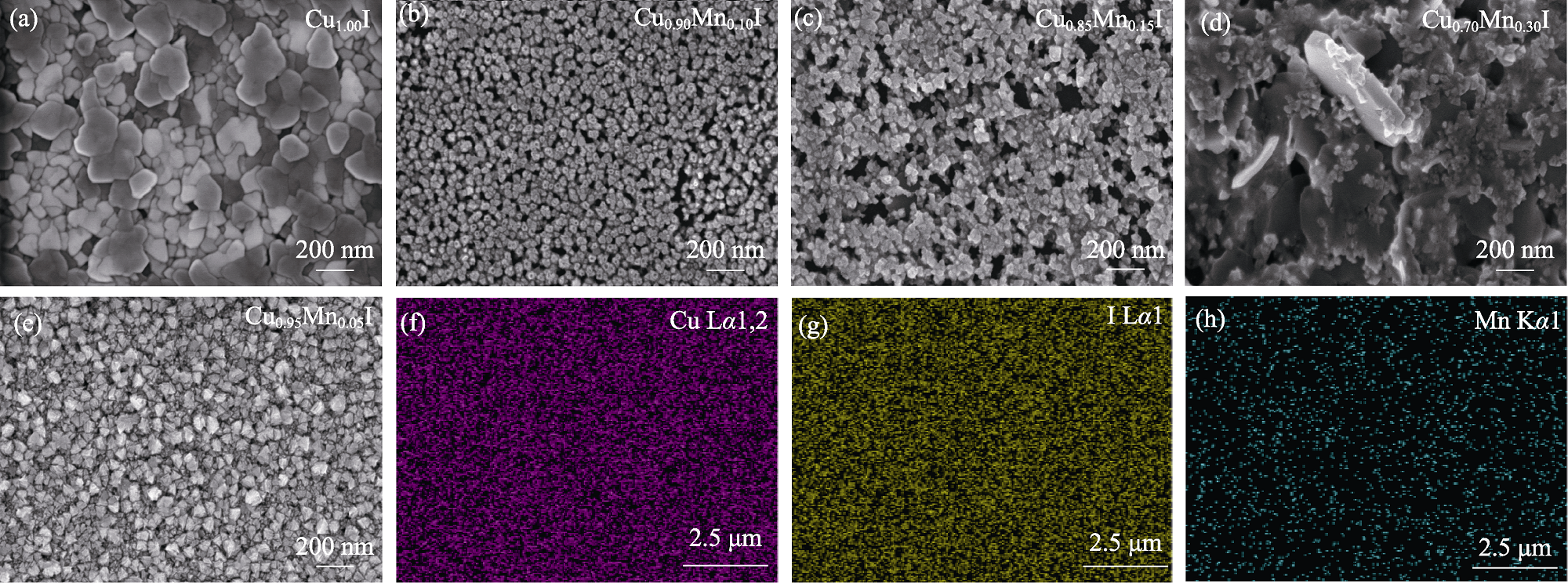
图1 Cu1-xMnxI薄膜的SEM照片(a~e)和Cu0.95Mn0.05I薄膜的元素面分布图(f~h)
Fig. 1 SEM images of Cu1-xMnxI thin films (a-e) and elemental distribution mappings of Cu0.95Mn0.05I thin films (f-h)
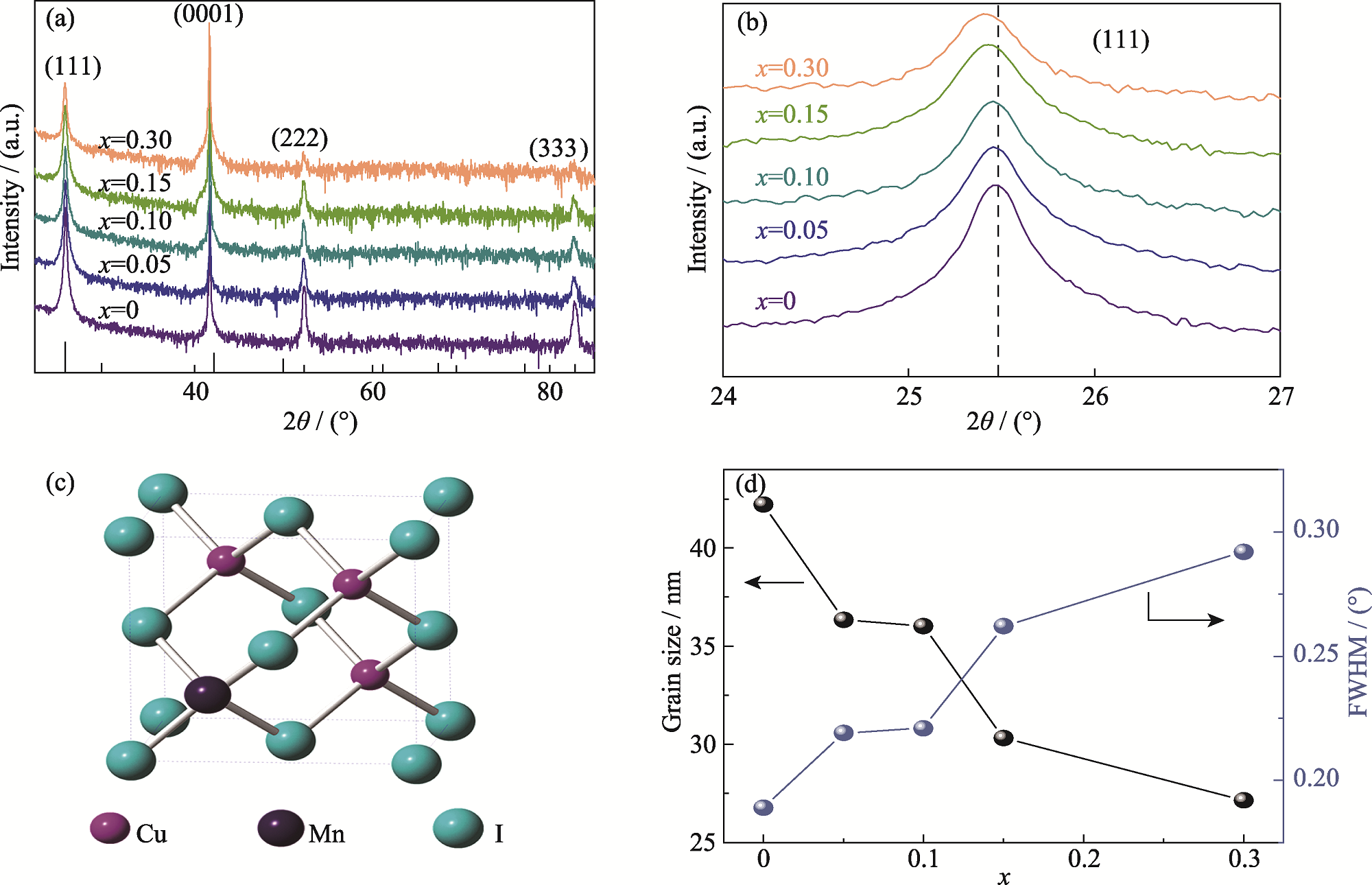
图2 Cu1-xMnxI薄膜晶体结构分析
Fig. 2 Crystal structure analyses of Cu1-xMnxI thin films (a) XRD patterns; (b) Localized magnified patterns of diffraction peak (111); (c) Schematic diagram of manganese ions replacing copper ions; (d) Dependence of grain size and FWHM on x
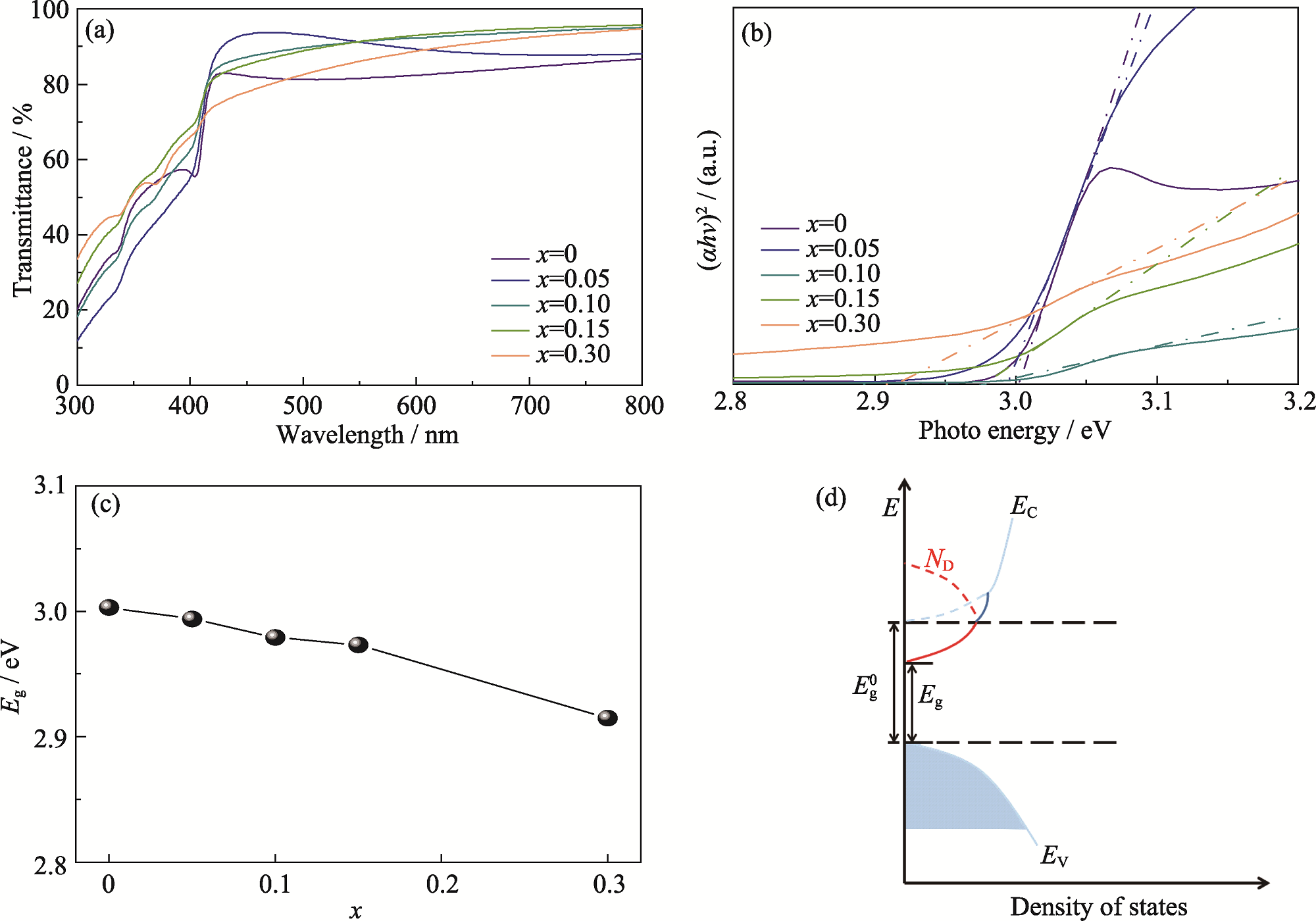
图3 Cu1-xMnxI薄膜光学带隙分析
Fig. 3 Analyses of optical bandgap of Cu1-xMnxI thin films (a) UV-Vis transmission spectra; (b) Tauc plots; (c) Dependence of Eg on x; (d) Schematic diagram of the influence of donor energy levels on Eg. Colorful figures are available on website
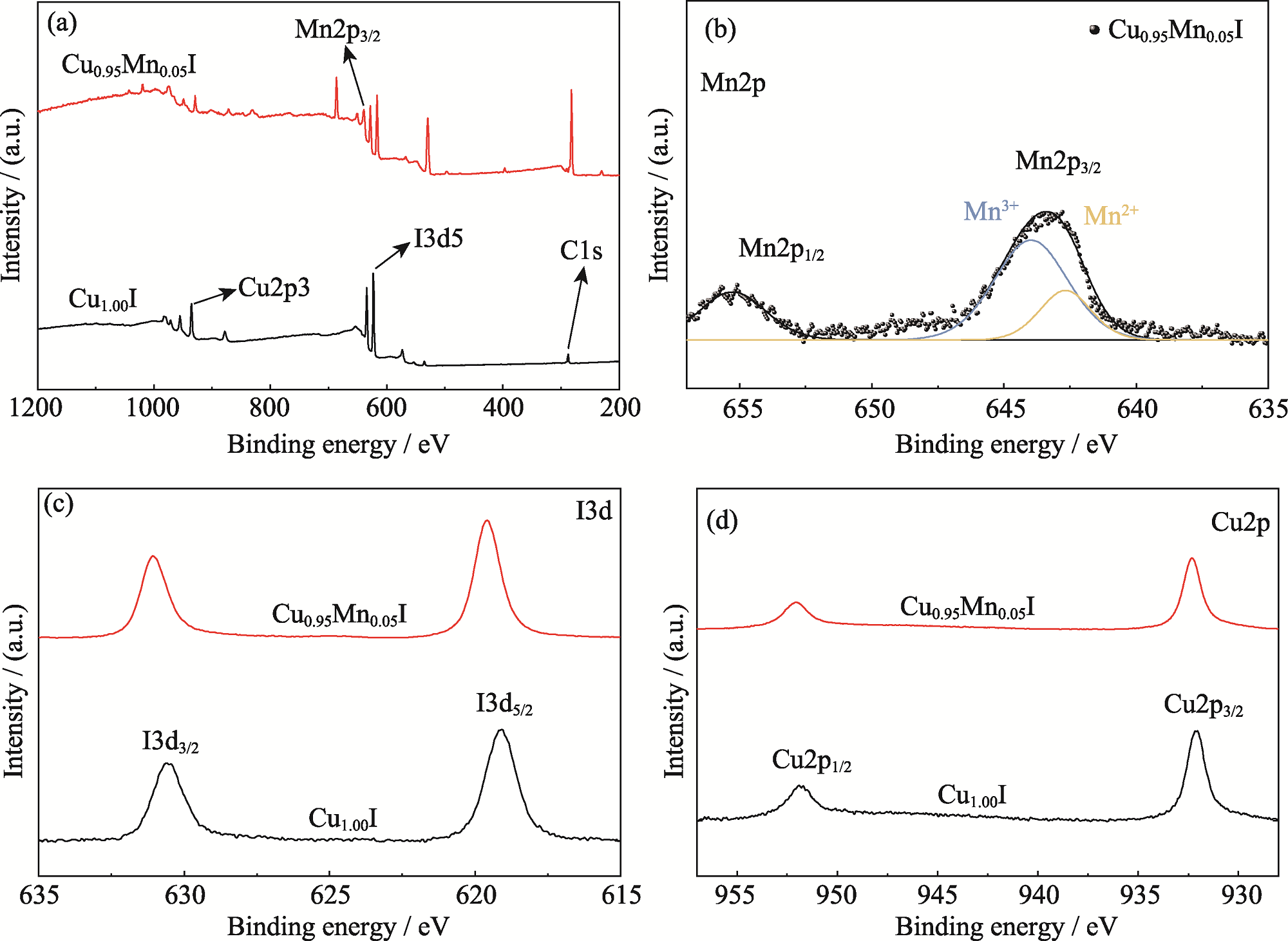
图4 Cu1.00I和Cu0.95Mn0.05I薄膜的XPS图谱
Fig. 4 XPS spectra of Cu1.00I and Cu0.95Mn0.05I thin films (a) XPS survey spectra; (b) High-resolution Mn2p XPS spectra of Cu0.95Mn0.05I films; (c, d) High-resolution I3d (c) and Cu2p (d) XPS spectra of Cu1.00I and Cu0.95Mn0.05I thin films
| [1] | LIU A, ZHU H H, KIM M G, et al. Engineering copper iodide (CuI) for multifunctional p-type transparent semiconductors and conductors. Advanced Science, 2021, 8(14): 2100546. |
| [2] | THOMAS G. Invisible circuits. Nature, 1997, 389(6654): 907. |
| [3] | KAWAZOE H, YASUKAWA M, HYODO H, et al. P-type electrical conduction in transparent thin films of CuAlO2. Nature, 1997, 389(6654): 939. |
| [4] | UEDA K, HASE T, YANAGI H, et al. Epitaxial growth of transparent p-type conducting CuGaO2 thin films on sapphire (001) substrates by pulsed laser deposition. Journal of Applied Physics, 2001, 89(3): 1790. |
| [5] | YANAGI H, HASE T, IBUKI S, et al. Bipolarity in electrical conduction of transparent oxide semiconductor CuInO2 with delafossite structure. Applied Physics Letters, 2001, 78(11): 1583. |
| [6] | KUDO A, YANAGI H, HOSONO H, et al. SrCu2O2: a p-type conductive oxide with wide band gap. Applied Physics Letters, 1998, 73(2): 220. |
| [7] | RAGHUPATHY R K M, KÜHNE T D, FELSER C, et al. Rational design of transparent p-type conducting non-oxide materials from high-throughput calculations. Journal of Materials Chemistry C, 2018, 6(3): 541. |
| [8] | YANG C, KNEIß M, LORENZ M, et al. Room-temperature synthesized copper iodide thin film as degenerate p-type transparent conductor with a boosted figure of merit. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 2016, 113(46): 12929. |
| [9] | GENG F J, WANG L J, STRALKA, et al. (111)-oriented growth and acceptor doping of transparent conductive CuI:S thin films by spin coating and radio frequency-sputtering. Advanced Engineering Materials, 2023, 25(11): 2201666. |
| [10] | YANG J L, JIANG X L, RUAN S Y, et al. Highly weak-light sensitive and dual-band switchable photodetector based on CuI/Si unilateral heterojunction. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(9): 1063. |
| [11] | GRUNDMANN M, SCHEIN F L, LORENZ M, et al. Cuprous iodide - a p-type transparent semiconductor: history and novel applications. Physica Status Solidi A, 2013, 210(9): 1671. |
| [12] | GRUNDMANN M. Karl Bädeker (1877-1914) and the discovery of transparent conductive materials. Physica Status Solidi A, 2015, 212(7): 1409. |
| [13] | CHEN D, WANG Y, LIN Z, et al. Growth strategy and physical properties of the high mobility p-type CuI crystal. Crystal Growth & Design, 2010, 10(5): 2057. |
| [14] | JUN T, KIM J, SASASE M, et al. Material design of p-type transparent amorphous semiconductor, Cu-Sn-I. Advance Materials, 2018, 30(12): 1706573. |
| [15] | YANG C, SOUCHAY D, KNEIß M, et al. Transparent flexible thermoelectric material based on non-toxic earth-abundant p-type copper iodide thin film. Nature Communications, 2017, 8: 16076. |
| [16] | ZENG G X, DOU W, GAN X M, et al. Low-voltage solution-processed NaxCu1-xI thin-film transistors for mimicking synaptic plasticity. Applied Physical Letters, 2024, 124(12): 123508. |
| [17] | JIANG G G, DOU W, GAN X M, et al. Low-voltage solution- processed p-type Mg-doped CuI thin film transistors with NAND logic function. Applied Physical Letters, 2023, 122(21): 213501. |
| [18] | GHAZAL N, MADKOUR M, NAZEER A A, et al. Electrochemical capacitive performance of thermally evaporated Al-doped CuI thin films. RSC Advance, 2021, 11(62): 39262. |
| [19] | MIRZA A S, VISHAL B, DALLY P, et al. Cs-doped and Cs-S co-doped CuI p-type transparent semiconductors with enhanced conductivity. Advanced Functional Materials, 2024, 34(30): 2316144. |
| [20] | MUDE N N, BUKKE R N, JIANG J. Transparent, p-channel CuISn thin-film transistor with field effect mobility of 45 cm2·V-1·s-1 and excellent bias stability. Advanced Materials Technologies, 2022, 7(8): 2101434. |
| [21] | TAREY R D, RAJU T A. A method for the deposition of transparent conducting thin films of tin oxide. Thin Solid Films, 1985, 128(3/4): 181. |
| [22] | LIU A, ZHU H H, PARK W T, et al. Room-temperature solution-synthesized p-type copper(I) iodide semiconductors for transparent thin-film transistors and complementary electronics. Advanced Materials, 2018, 30(34): 1802379. |
| [23] | STRELCHUNK V, KOLOMYS O, RARATA S, et al. Raman submicron spatial mapping of individual Mn-doped ZnO nanorods. Nano Epress, 2017, 12: 1. |
| [24] | ZI M, LI J, ZHANG Z C, et al. Effect of deposition temperature on transparent conductive properties of γ-CuI film prepared by vacuum thermal evaporation. Physica Status Solidi A, 2015, 212(7): 1466. |
| [25] | SUNG S Y, KIM S Y, JO K M, et al. Fabrication of p-channel thin-film transistors using CuO active layers deposited at low temperature. Applied Physical Letters, 2010, 97(22): 222109. |
| [26] | KYKYNESHI R, MCINTYRE D H, TATE J, et al. Electrical and optical properties of epitaxial transparent conductive BaCuTeF thin films deposited by pulsed laser deposition. Solid State Sciences, 2008, 10(7): 921. |
| [27] | ZAKUTAYEV A, MCINTYRE D H, SCHNEIDER G, et al. Tunable properties of wide-band gap p-type BaCu(Ch1-xChx′)F (Ch=S, Se, Te) thin-film solid solutions. Thin Solid Films, 2010, 518(19): 5494. |
| [28] | YANG C, KNEIß M, SCHEIN F L, et al. Room-temperature domain-epitaxy of copper iodide thin films for transparent CuI/ZnO heterojunctions with high rectification ratios larger than 109. Scientific Reports, 2016, 6: 21937. |
| [29] | YANG C, ROSE E, YU W L, et al. Controllable growth of copper iodide for high-mobility thin films and self-assembled microcrystals. ACS Applied Electronic Materials, 2020, 2(11): 3627. |
| [1] | 凌意瀚, 郭胜, 曹志强, 田云峰, 刘方升, 金芳军, 高源. 固体氧化物电池直孔电极结构的制备技术与性能研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(12): 1311-1323. |
| [2] | 张海丰, 蒋蒙, 孙婷婷, 王连军, 江莞. 稳定立方相p型GeMnTe2基热电材料制备[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(11): 1245-1251. |
| [3] | 李成明, 周闯, 刘鹏, 郑礼平, 赖泳机, 陈良贤, 刘金龙, 魏俊俊. CVD金刚石膜应力的产生、抑制、应用及测量[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(11): 1188-1200. |
| [4] | 吴明轩, 李珺杰, 陈硕, 鄢永高, 苏贤礼, 张清杰, 唐新峰. 区熔n型Bi1.96Sb0.04Te2.70Se0.30热电材料均匀性研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(11): 1252-1260. |
| [5] | 袁龙, 贾如, 袁梦, 张健, 段羽, 孟祥东. X射线诱导光致变色材料的机理与应用[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(10): 1097-1110. |
| [6] | 艾伊昭彤, 任九龙, 强林芽, 张小珍, 杨凯, 高彦峰. 高承载下Al2O3-GdAlO3(GAP)非晶陶瓷涂层的摩擦磨损性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(10): 1111-1118. |
| [7] | 曹路涵, 孟佳, 薛玉冬, 盛晓晨, 崔苑苑, 乐军, 宋力昕. SiC过渡层对SiC/SiC陶瓷基复合材料表面MoSi2-SABB涂层结合性能的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(10): 1119-1128. |
| [8] | 宛心怡, 王文奇, 李加诚, 赵俊亮, 马董云, 王金敏. 基于WO3·xH2O与可逆金属电沉积的无色/黑色转换电致变色器件[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(10): 1163-1174. |
| [9] | 赵丽华, 王言帅, 尹昕妩, 毛叶琼, 牛德超. 负载硫化铋纳米簇的硅基杂化胶束的制备及其光热抗菌性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(10): 1129-1136. |
| [10] | 吴华鑫, 张骐昊, YAN Haixue, 王连军, 江莞. 纳米复合MgAgSb基合金的热电输运性能优化[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(9): 997-1004. |
| [11] | 余升阳, 苏海军, 姜浩, 余明辉, 姚佳彤, 杨培鑫. 激光增材制造超高温氧化物陶瓷孔隙缺陷形成及抑制研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(9): 944-956. |
| [12] | 李廷松, 王文丽, 刘强, 王雁斌, 周真真, 胡辰, 李江. Cr3+掺杂浓度对YAGG:Ce3+,Cr3+发光陶瓷余辉性能的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(9): 1037-1044. |
| [13] | 马景阁, 吴成铁. 无机生物材料用于毛囊和毛发再生的研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(8): 901-910. |
| [14] | 张洪健, 赵梓壹, 吴成铁. 无机生物材料调控神经细胞功能及神经化组织再生的研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(8): 849-859. |
| [15] | 马文平, 韩雅卉, 吴成铁, 吕宏旭. 无机活性材料在类器官研究领域的应用[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(8): 888-900. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||