无机材料学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 40 ›› Issue (10): 1079-1096.DOI: 10.15541/jim20240525 CSTR: 32189.14.jim20240525
所属专题: 【信息功能】透明与闪烁陶瓷(202512)
田甜1( ), 方辰恺1, 张杰1, 王维维2, 伍霆锋1, 徐家跃1(
), 方辰恺1, 张杰1, 王维维2, 伍霆锋1, 徐家跃1( )
)
收稿日期:2024-12-18
修回日期:2025-01-02
出版日期:2025-10-20
网络出版日期:2025-03-19
通讯作者:
徐家跃, 教授. E-mail: xujiayue@sit.edu.cn作者简介:田 甜(1985-), 男, 教授. E-mail: tiant@sit.edu.cn
基金资助:
TIAN Tian1( ), FANG Chenkai1, ZHANG Jie1, WANG Weiwei2, WU Tingfeng1, XU Jiayue1(
), FANG Chenkai1, ZHANG Jie1, WANG Weiwei2, WU Tingfeng1, XU Jiayue1( )
)
Received:2024-12-18
Revised:2025-01-02
Published:2025-10-20
Online:2025-03-19
Contact:
XU Jiayue, professor. E-mail: xujiayue@sit.edu.cnAbout author:TIAN Tian (1985-), male, professor. E-mail: tiant@sit.edu.cn
Supported by:摘要:
铌酸锂(LiNbO3, LN)是一种集声光、电光、弹光、光折变等优越物理特性于一身的多功能晶体, 不仅被誉为“光学硅”, 更有学者提出人类正在进入“铌酸锂谷”时代, 其优异的光电性能使基于其的各类光电器件在人工智能、光电混合集成等新兴领域具有广阔的应用前景。光折变效应是LN晶体非常重要的特性。随着基于LN的光电器件向微纳级尺寸迅速发展, 光折变效应在微纳级尺寸也已逐渐显现。LN单晶是在非绝缘体上采用铌酸锂单晶薄膜(Lithium Niobate on Insulator, LNOI)技术制备各类器件的基材, 可通过掺杂合适的杂质离子来调控光折变性能。相对于传统的低价态阳离子(化合价<铌离子+5价), 近年来发现掺入高价态阳离子(化合价≥铌离子+5价)更有利于提升LN晶体的光折变性能。本文综述了已有报道的高价态阳离子掺杂LN晶体光折变性能的研究成果, 归纳总结出掺钒、钼、铀、铋等高价态离子可以显著提升LN晶体的光折变性能, 尤其是能够有效缩短光折变响应时间, 这有利于LN在微环谐振器、可编程光子器件、非线性光子器件等微纳器件领域的应用。同时, 提出未来可围绕高价态离子掺杂LN, 在高质量大尺寸晶体生长技术、光折变机理、其他具有孤对电子的离子掺杂、基于高价态离子掺杂LN的光电器件这四方面进行研究。
中图分类号:
田甜, 方辰恺, 张杰, 王维维, 伍霆锋, 徐家跃. 高价态离子掺杂铌酸锂晶体光折变性能的研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(10): 1079-1096.
TIAN Tian, FANG Chenkai, ZHANG Jie, WANG Weiwei, WU Tingfeng, XU Jiayue. Research Progress on Photorefraction of Lithium Niobate Crystal Doped with High Valence Ion[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(10): 1079-1096.
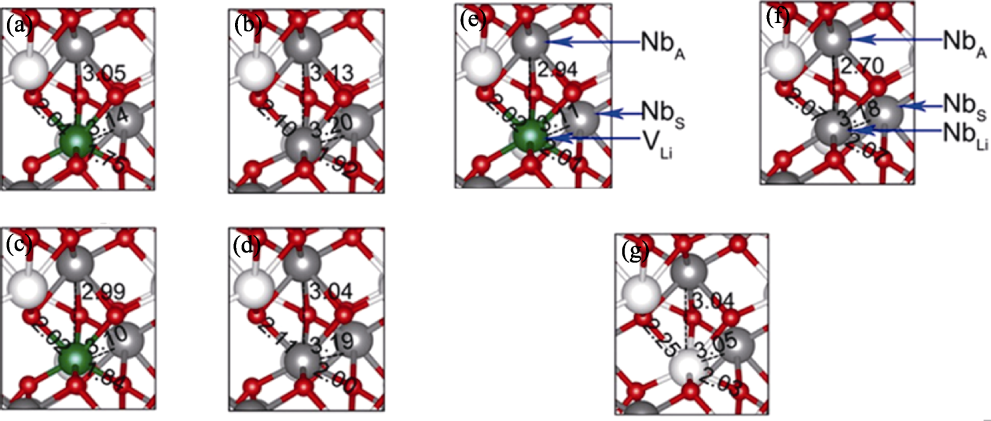
图3 VLi、NbLi晶格与通过HSE06自旋极化计算的铌酸锂主体晶格结构对比[69]
Fig. 3 Comparison between the local lattice distortions of VLi, NbLi and the bulk LiNbO3 calculated by spin-polarized HSE06[69] (a) Lattice of ${\text{V}}_{\text{Li}}^{4+}$; (b) Lattice of ${\text{Nb}}_{\text{Li}}^{4+}$; (c) Lattice of ${\text{V}}_{\text{Li}}^{3+}$; (d) Lattice of ${\text{Nb}}_{\text{Li}}^{3+}$; (e) Lattice of ${\text{V}}_{\text{Li}}^{2+}$; (f) Lattice of ${\text{Nb}}_{\text{Li}}^{2+}$; (g) Lattice of bulk lithium niobate. Red balls refer to O, green balls refer to V, grey balls refer to Nb, and white balls refer to Li
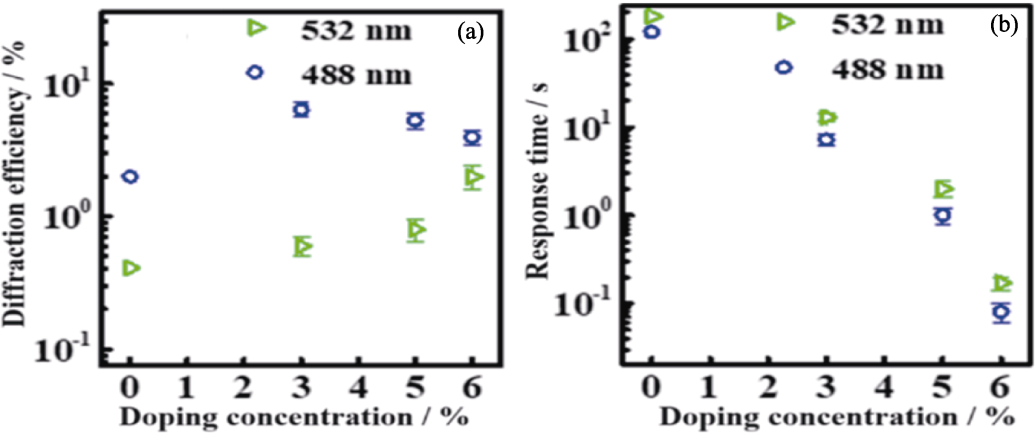
图4 CLN和LN:V, Mg晶体在532和488 nm处的光折变性能[70]
Fig. 4 Photorefractive properties of CLN and LN:V, Mg crystals measured at the wavelength of 532 and 488 nm[70] (a) Diffraction efficiency; (b) Response time
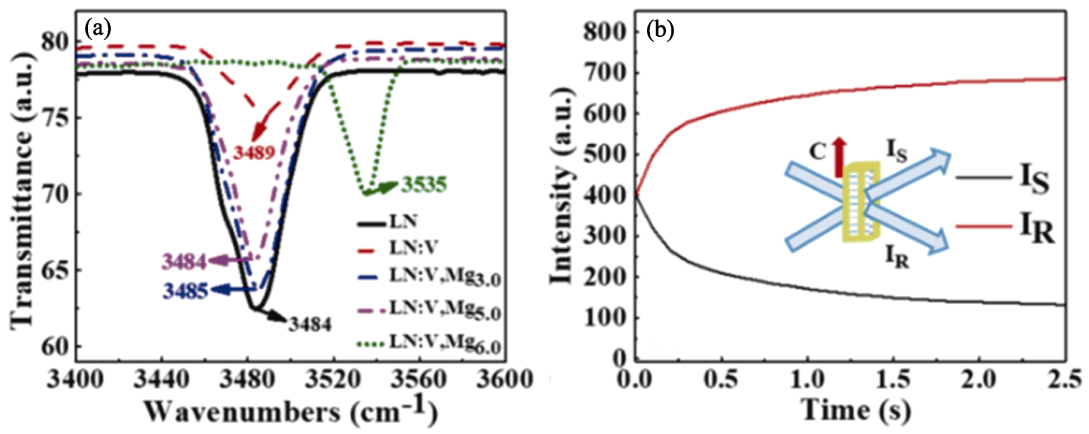
图5 CLN、LN:V和LN:Mg, V晶体的OH-吸收光谱图和双光束耦合的光能量传递曲线[70]
Fig. 5 OH− absorption spectra and light energy transfer curves for two-beam coupling of CLN, LN:V and LN:Mg, V crystals[70] (a) OH− absorption spectra; (b) Light energy transfer curves
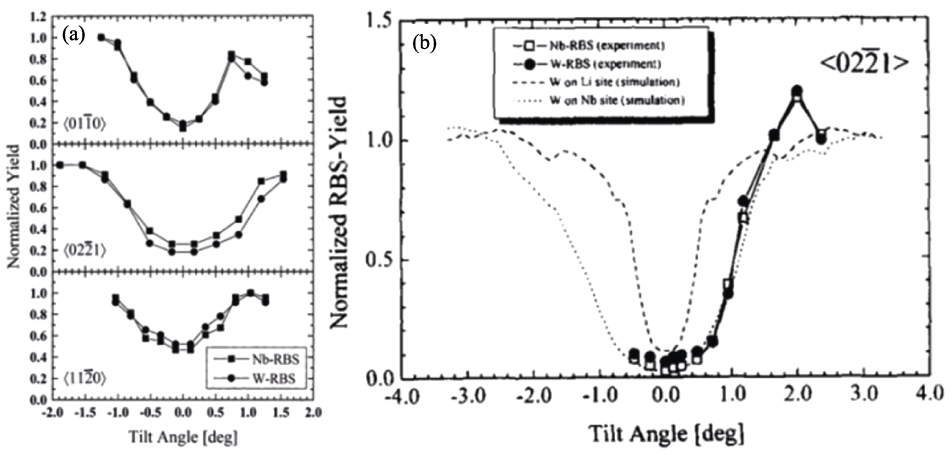
图6 沿<$01\overline{1}0$>、<$02\overline{2}1$>、<$11\overline{2}0$>方向对Nb和W的RBS角度扫描结果与<$02\overline{2}1$>方向Nb离子和W离子占位计算机模拟[73-74]
Fig. 6 Angular scans for Nb- and W-RBS along the <$01\overline{1}0$>, <$02\overline{2}1$>, <$11\overline{2}0$> axial directions, and computer simulation of the occupancy of Nb and W ions in the direction of <$02\overline{2}1$>[73-74] (a) Angular scans; (b) Occupancy simulation
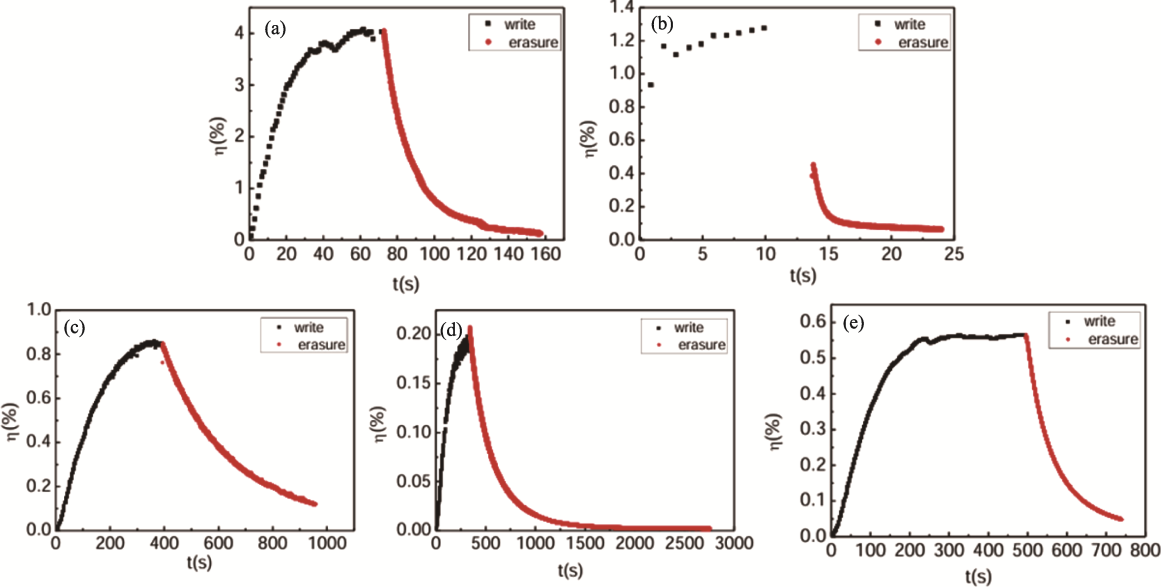
图7 波长532 nm下CLN:W的衍射效率与时间的关系[76]
Fig. 7 Time dependence of diffraction efficiency of CLN:W crystals measured at the wavelength of 532 nm[76] (a) CLN:W0.5in; (b) CLN:W2.0in; (c) CLN:W0.5out; (d) CLN:W2.0out; (e) CLN:W3.0in
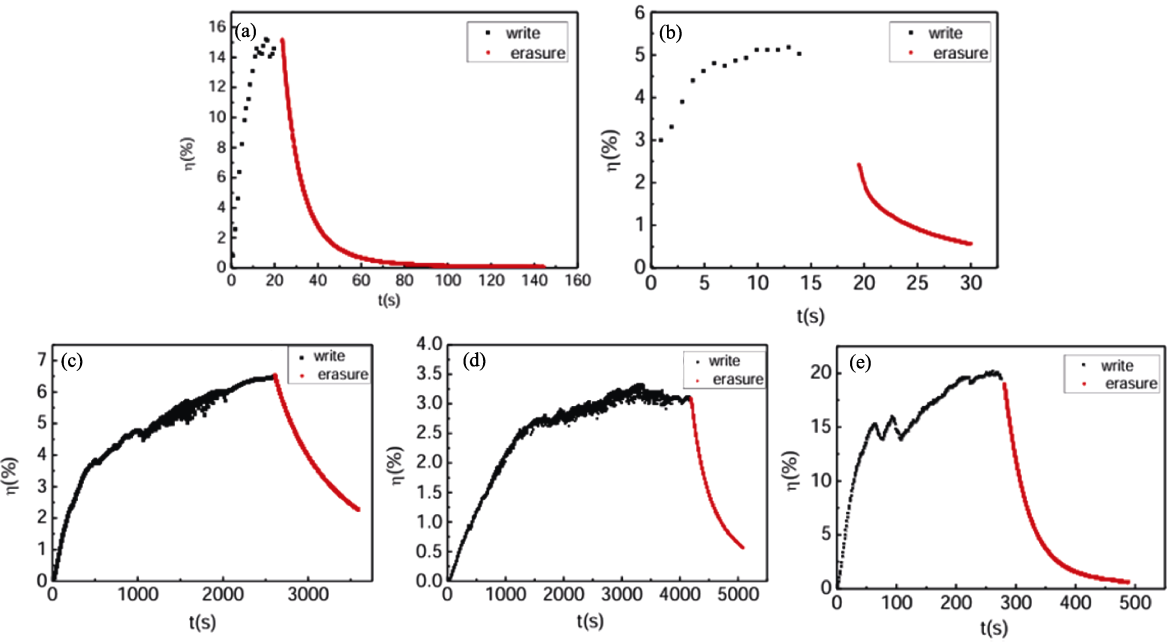
图8 波长488 nm下CLN:W的衍射效率与时间的关系[76]
Fig. 8 Time dependence of diffraction efficiency of CLN:W crystals measured at the wavelength of 488 nm[76] (a) CLN:W0.5in; (b) CLN:W2.0in; (c) CLN:W0.5out; (d) CLN:W2.0out; (e) CLN:W3.0in
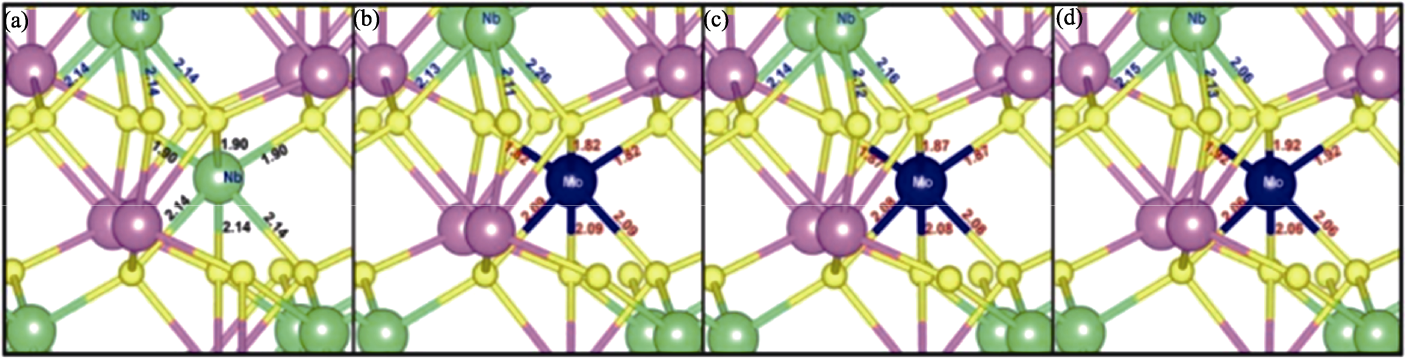
图12 (a)原始和(b) MoNb+、(c) MoNb0、(d) MoNb−点缺陷的晶格畸变[78]
Fig. 12 Local lattice distortion of (a) pristine and (b) MoNb+, (c) MoNb0, (d) MoNb− point defects[78]
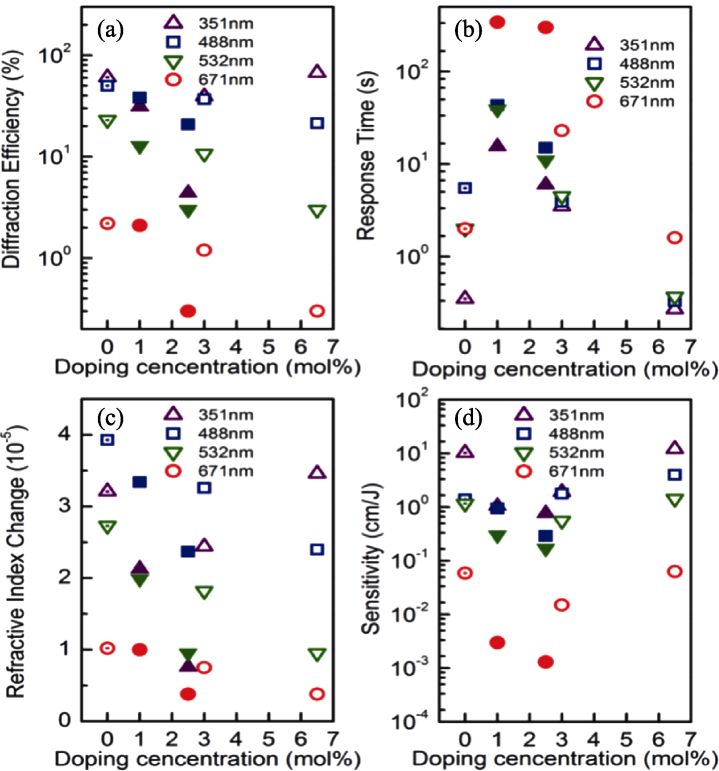
图13 掺杂不同浓度LN:Mo, Mg和LN:Mo, Zr晶体的紫外至可见波段的光折变性能[80]
Fig. 13 Photorefractive properties of LN:Mo, Mg and LN:Mo, Zr with different concentrations from UV to the visible bands[80] (a) Diffraction efficiency; (b) Response time; (c) Refractive index change; (d) Sensitivity
| Crystal | Doping element/% | Diffraction efficiency/% | Response time/s | Ref. | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mo2O3 | MgO | ZnO | In2O3 | ZrO2 | HfO2 | ||||
| LN:Mo | 0.5 | - | - | - | - | - | 28.50 | 5.50 | [ |
| LN:Mo, Mg | 0.5 | 6.5 | - | - | - | - | 60.00 | 0.35 | [ |
| LN:Mo, Zn | 0.5 | - | 7.2 | - | - | - | 17.72 | 0.65 | [ |
| LN:Mo, In | 0.5 | - | - | 3 | - | - | 28.90 | 0.76 | [ |
| LN:Mo, Zr | 0.5 | - | - | - | 2.5 | - | 20.80 | 15.00 | [ |
| LN:Mo, Hf | 0.5 | - | - | - | - | 3.5 | 46.07 | 0.90 | [ |
表1 钼离子与抗光折变离子双掺LN晶体的光折变性能[77,80 -83]
Table 1 Photorefractive properties of Mo ions and photorefraction resistant ions co-doped LN crystals[77,80 -83]
| Crystal | Doping element/% | Diffraction efficiency/% | Response time/s | Ref. | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mo2O3 | MgO | ZnO | In2O3 | ZrO2 | HfO2 | ||||
| LN:Mo | 0.5 | - | - | - | - | - | 28.50 | 5.50 | [ |
| LN:Mo, Mg | 0.5 | 6.5 | - | - | - | - | 60.00 | 0.35 | [ |
| LN:Mo, Zn | 0.5 | - | 7.2 | - | - | - | 17.72 | 0.65 | [ |
| LN:Mo, In | 0.5 | - | - | 3 | - | - | 28.90 | 0.76 | [ |
| LN:Mo, Zr | 0.5 | - | - | - | 2.5 | - | 20.80 | 15.00 | [ |
| LN:Mo, Hf | 0.5 | - | - | - | - | 3.5 | 46.07 | 0.90 | [ |
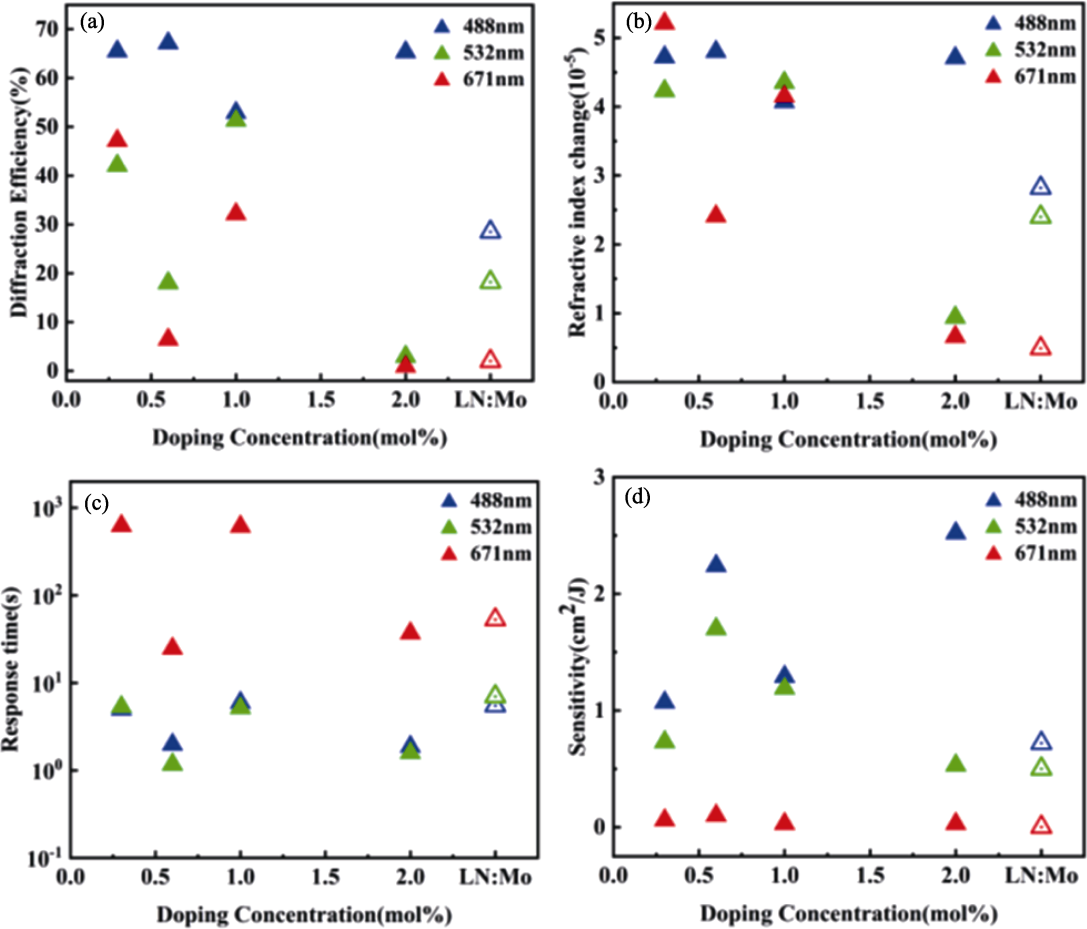
图16 掺杂不同浓度LN:U晶体在可见波段的光折变性能[94]
Fig. 16 Photorefractive properties of LN:U with different concentrations in the visible band[94] (a) Diffraction efficiency; (b) Refractive index change; (c) Response time; (d) Sensitivity
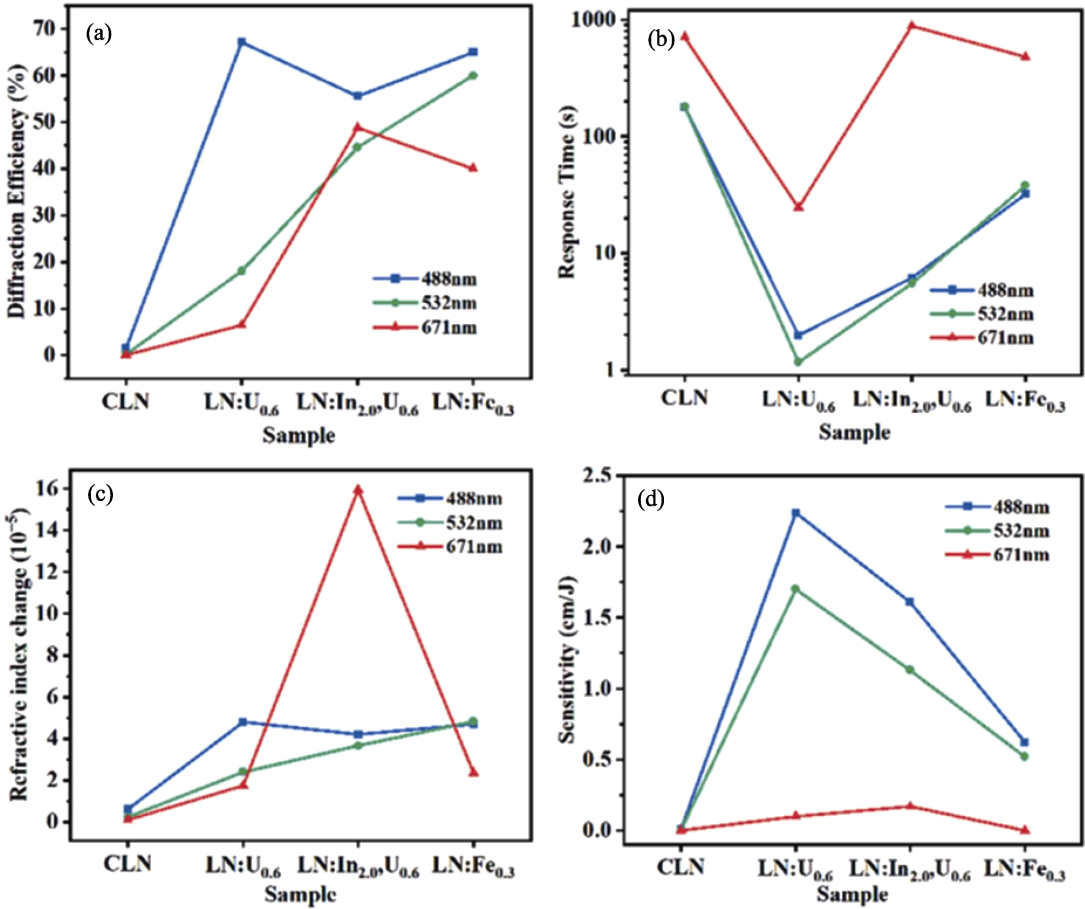
图17 CLN、LN:U0.6、LN:U0.6, In2.0、LN:Fe0.3的光折变性能数据[95]
Fig. 17 Photorefractive parameters of CLN, LN:U0.6, LN:U0.6, In2.0, and LN:Fe0.3[95] (a) Diffraction efficiency; (b) Response time; (c) Refractive index change; (d) Sensitivity
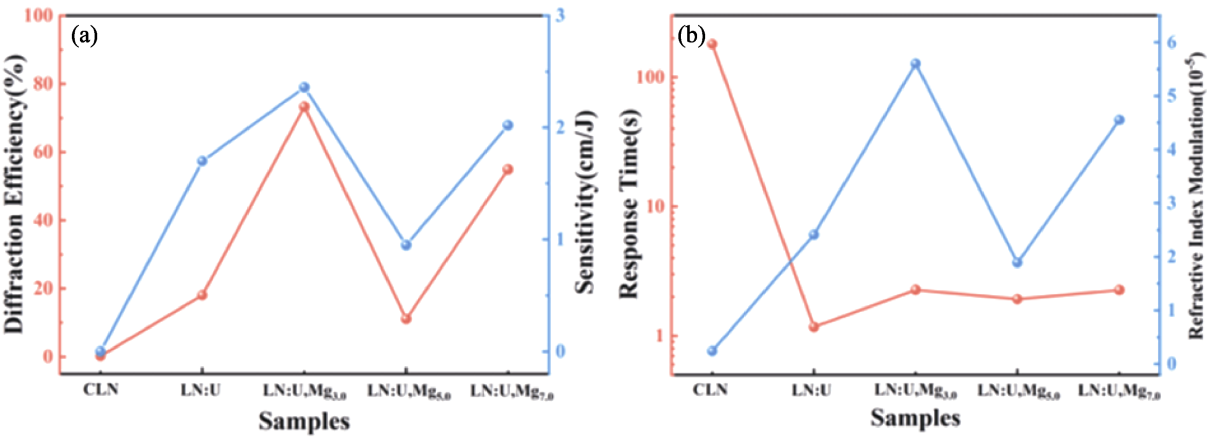
图18 不同掺杂浓度LN:U, Mg晶体的光折变性能[96]
Fig. 18 Photorefractive properties of LN:U, Mg with different concentrations[96] (a) Diffraction efficiency and sensitivity; (b) Response time and refractive index modulation
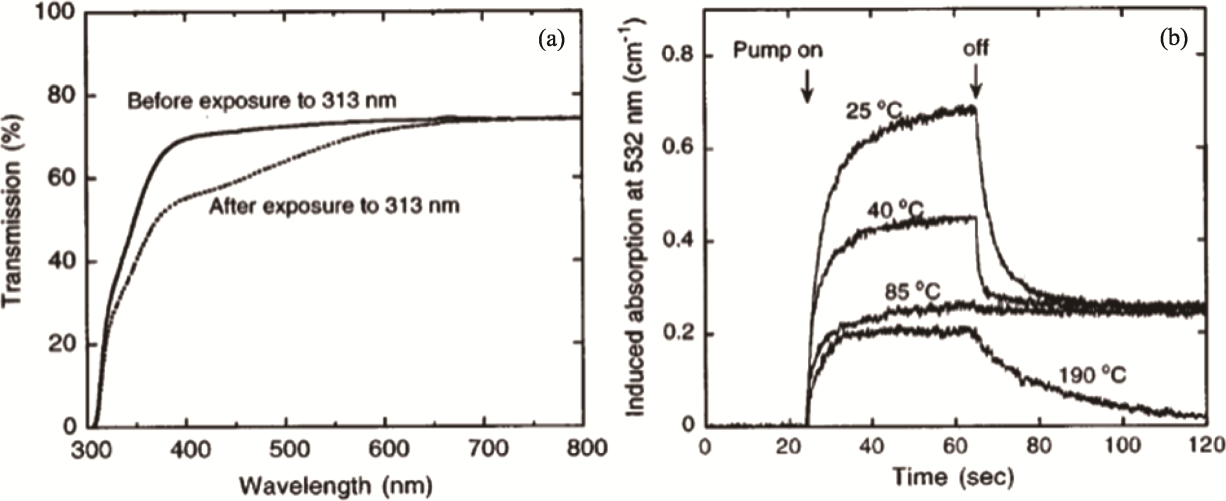
图19 313 nm紫外照射下LN:Tb透射光谱及其诱导吸收随时间的变化[104]
Fig. 19 Transmission spectra of LN:Tb under UV irradiation and temporal evolution of 313 nm induced absorption[104] (a) Transmission spectra; (b) Induced absorbance
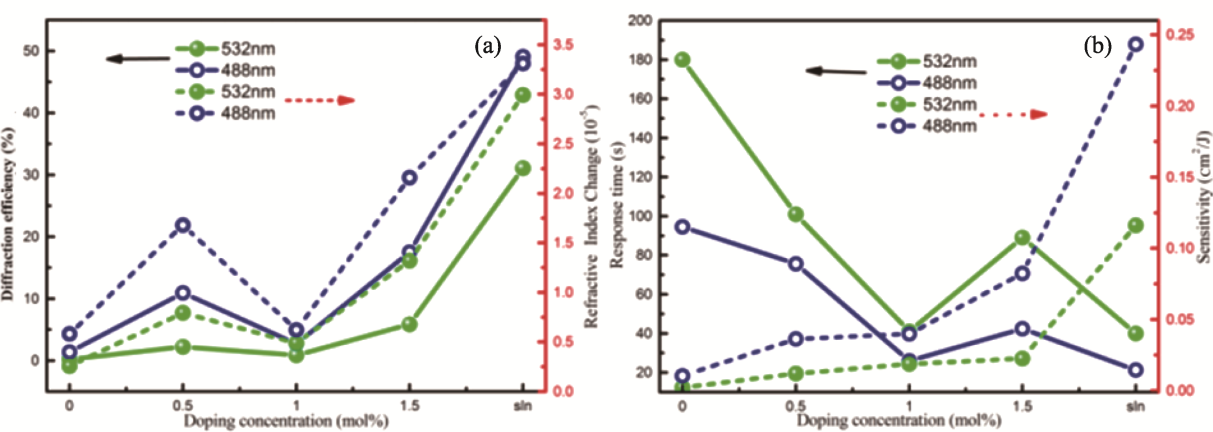
图20 不同掺杂浓度LN:Bi晶体的光折变性能[106]
Fig. 20 Photorefractive properties of LN:Bi with different concentrations[106] (a) Diffraction efficiency and refractive index change; (b) Response time and sensitivity
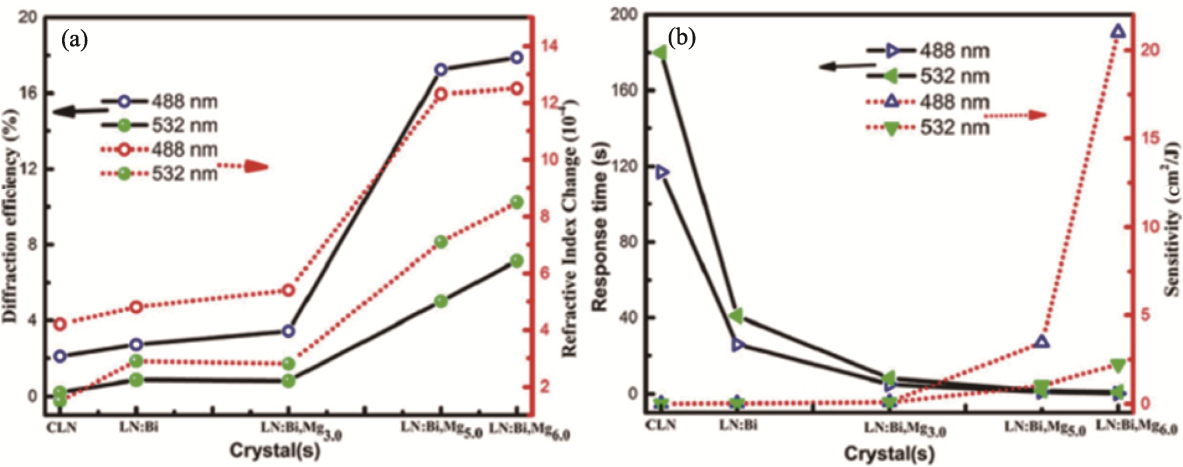
图21 LN:Bi、CLN和不同镁掺杂浓度LN:Bi, Mg晶体的光折变性能[107]
Fig. 21 Photorefractive properties of LN:Bi, CLN, and LN:Bi, Mg with different Mg concentrations[107] (a) Diffraction efficiency and refractive index change; (b) Response time and sensitivity
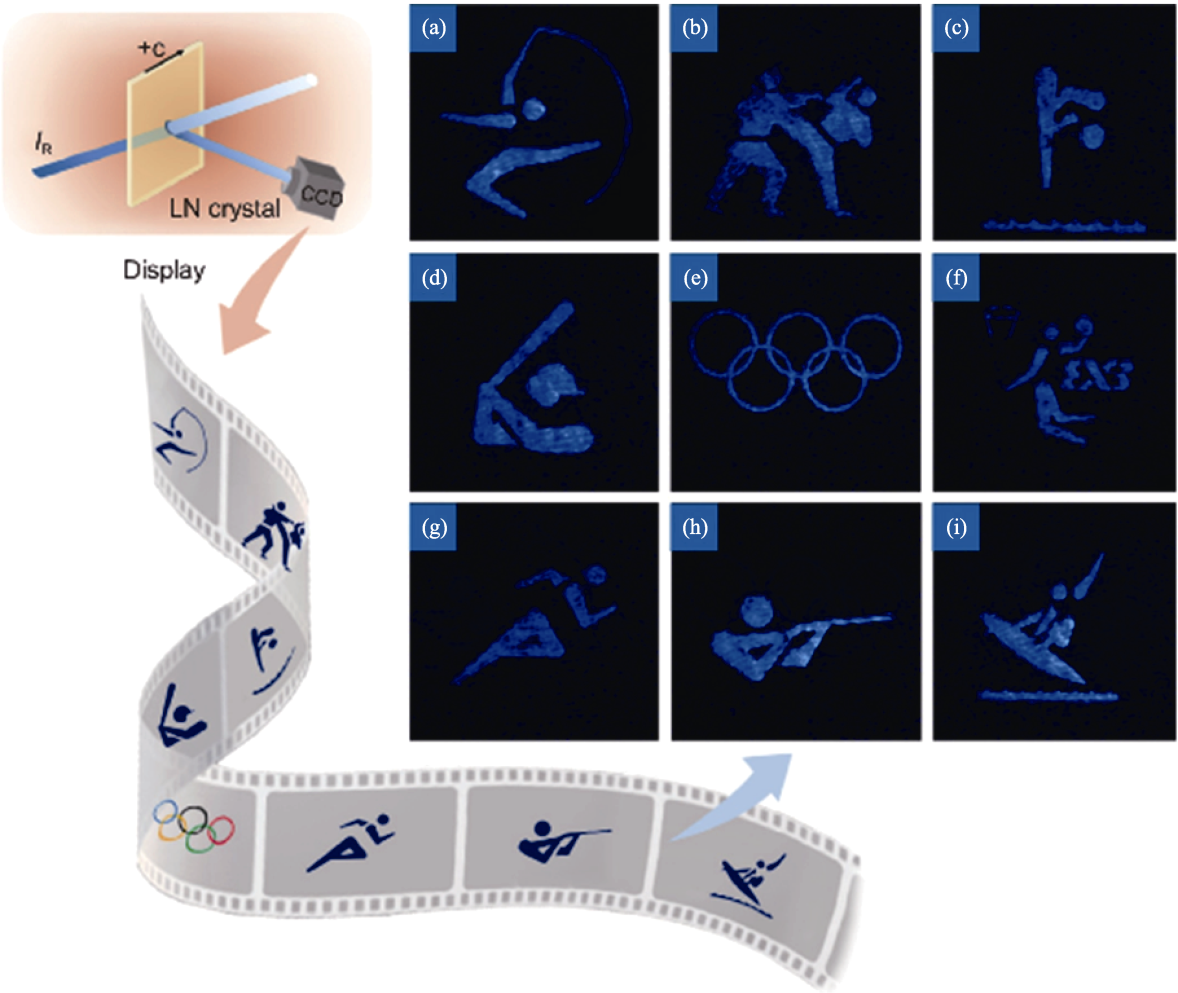
图22 60 Hz全息显示图像[109]
Fig. 22 Holographic images during display (at 60 Hz)[109] (a) Rhythmic gymnastics; (b) Karate kumite; (c) Diving; (d) Baseball; (e) Olympic rings; (f) Basketball; (g) Athletics; (h) Shooting; (i) Surfing
| [1] | KONG Y F, BO F, WANG W W, et al. Recent progress in lithium niobate: optical damage, defect simulation, and on-chip devices. Advance Materials, 2020, 32(3): 1806452. |
| [2] | PAN B C, LIU H X, HUANG Y S, et al. Perspective on lithium- niobate-on-insulator photonics utilizing the electro-optic and acousto-optic effects. ACS Photonics, 2023, 10(7): 2078. |
| [3] | WU Q, JI W, YIN R, et al. Reconfigurable AWGR based on LNOI with a tunable central wavelength and bandwidth used in elastic optical networking. Applied Optics, 2023, 62(25): 6631. |
| [4] | IQBAL M S B, BERRY J, GHOSH K. Study of pure Ni, NiO, and mixture of Ni-NiO thin films on piezoelectric lithium niobate substrate by pulsed laser deposition. Thin Solid Films, 2023, 781: 140002. |
| [5] | TORRY M, RANDALL B W, WATARU N. Auger electron spectroscopy mapping of lithium niobate ferroelectric domains with nano-scale resolution. Optical Material Express, 2023, 13(1): 119. |
| [6] | MEFFAN C, IJIMA T, BANERJEE A, et al. Non-linear processing with a surface acoustic wave reservoir computer. Microsystem Technologies, 2023, 29(8): 1197. |
| [7] | SÁNCHEZ-DENA O, FIERRO-RUIZ C D, VILLALOBOS- MENDOZA S D, et al. Lithium niobate single crystals and powders reviewed-part I. Crystals, 2020, 10(11): 973. |
| [8] | WANG C, ZHANG M, CHEN X, et al. Integrated lithium niobate electro-optic modulators operating at CMOS-compatible voltages. Nature, 2018, 562(7725): 101. |
| [9] | ZHANG Y C, LI S B, XU J J, et al. Conductive domain wall and its applications in lithium niobate. Journal of Synthetic Crystals, 2024, 53(3): 395. |
| [10] | ZHANG M, BUSCAINO B, WANG C, et al. Broadband electro- optic frequency comb generation in a lithium niobate microring resonator. Nature, 2019, 568(7752): 373. |
| [11] | ZHOU J X, LIANG Y T, LIU Z X, et al. On-chip integrated waveguide amplifiers on erbium-doped thin-film lithium niobate on insulator. Laser & Photonics Reviews, 2021, 15(8): 2100030. |
| [12] |
LI M X, LING J W, HE Y, et al. Lithium niobate photonic-crystal electro-optic modulator. Nature Communications, 2020, 11: 4123.
DOI PMID |
| [13] | BRODERICK N G R, BRATFALEAN R T, MONRO T M, et al. Temperature and wavelength tuning of second-, third-, and fourth- harmonic generation in a two-dimensional hexagonally poled nonlinear crystal. Journal of the Optical Society of America B-Optical Physics, 2002, 19(9): 2263. |
| [14] | BURROUS L. Now entering, lithium niobate valley. (2017-12-21) [2024-09-24]. https://otd.harvard.edu/news/now-entering-lithium-niobate-valley. |
| [15] | SARAVI S, PERTSCH T, SETZPFANDT F. Lithium niobate on insulator: an emerging platform for integrated quantum photonics. Advanced Optical Materials, 2021, 9(22): 2100789. |
| [16] | YU Y, YU Z J, WANG L, et al. Ultralow-loss etchless lithium niobate integrated photonics at near-visible wavelengths. Advanced Optical Materials, 2021, 9(19): 2100060. |
| [17] | WEI D Z, WANG C W, WANG H J, et al. Experimental demonstration of a three-dimensional lithium niobate nonlinear photonic crystal. Nature Photonics, 2018, 12(10): 596. |
| [18] | OSBORNE I S. An active platform for integrated optics. Science, 2019, 364(6439): 448. |
| [19] |
GAEENI M R, BAKOUEI A, GHAMSARI M S. Highly stable colloidal lithium niobate nanocrystals with strong violet and blue emission. Inorganic Chemistry, 2022, 61(32): 12886.
DOI PMID |
| [20] | QIAN Y Z, ZHANG Y C, XU J J, et al. Domain-wall p-n junction in lithium niobate thin film on an insulator. Physical Review Applied, 2022, 17(4): 04011. |
| [21] | JIA D, LUO Q, YANG C, et al. High-efficiency edge couplers enabled by vertically tapering on lithium-niobate photonic chips. Applied Physics Letters, 2023, 123(26): 263502. |
| [22] | BOES A, CHANG L, LANGROCK C, et al. Lithium niobate photonics: unlocking the electromagnetic spectrum. Science, 2023, 379(6627): 4396. |
| [23] | BORODINA I A, ZAITSEV B D, ALSOWAIDI A K M, et al. A biological sensor based on the acoustic slot mode using microbial cells for the determination of ampicillin. Acoustical Physics, 2022, 68(6): 537. |
| [24] | CHEN K F, ZHU Y Z, LIU Z H, et al. State of the art in crystallization of LiNbO3 and their applications. Molecules, 2021, 26(22): 7044. |
| [25] | ZHANG T, HE J, HU S Q, et al. Current progress of integrated lithium niobate photonic device technology. Piezoelectrics and Acoustooptics, 2020, 42(6): 837. |
| [26] | CHENG Y. Thin film lithium niobate electro-optic devices and ultralarge-scale photonic integration (invited). Chinese Journal of Lasers, 2024, 51(1): 0119001. |
| [27] | XIONG X, CAO Q T, XIAO Y F. Thin-film lithium niobate photonic integrated devices: advances and oppotunities. Acta Physica Sinica, 2023, 72(23): 234201. |
| [28] | BOES A, CORCORAN B, CHANG L, et al. Status and potential of lithium niobate on insulator (LNOI) for photonic integrated circuits. Laser & Photonic Reviews, 2018, 12(4): 1700256. |
| [29] | CHENG G X, LIU L. High-performance electro-optical modulator based on thin-film lithium niobate (invited). Acta Optica Sinica, 2024, 44(15): 1513001. |
| [30] | ZHU H D, XUE H, XIE X L, et al. Memorable sounds of optics and photonics in 2022. Science & Technology Review, 2023, 41(1): 30. |
| [31] | POP F, HERRERA B, RINALDI M, et al. Lithium niobate piezoelectric micromachined ultrasonic transducers for high data- rate intrabody communication. Nature Communications, 2022, 13: 1782. |
| [32] | QIN Y Y, XUE X M, SHI L, et al. Design of ultra-compact thin-film lithium niobate edge coupler based on micro-nano structure. Journal of Optics, 2024, 26(6): 065803. |
| [33] | WANG M, CHEN Y X, ZHANG S P, et al. Perspectives of thin-film lithium niobate and electro-optic polymers for high-performance electro-optic modulation. Journal of Materials Chemistry C, 2023, 11(33): 11107. |
| [34] | ZHANG R, YANG C, HAO Z Z, et al. Integrated lithium niobate single-mode lasers by the Vernier effect. Science China Physics, Mechanics & Astronomy, 2021, 64(9): 294216. |
| [35] | JIN H, LIU F M, XU P, et al. On-chip generation and manipulation of entangled photons based on reconfigurable lithium-niobate waveguide circuits. Physical Review Letters, 2014, 113(10): 103601. |
| [36] | 夏思宇. 紧扣自主创新勇攀产业“塔尖”. 南京日报, 2024-06-29(A03). |
| [37] | 晶正科技. 2013全国压电和声波理论及器件技术研讨会论文集. 2013全国压电和声波理论及器件技术研讨会, 长沙, 2013: 1. |
| [38] | 上海新硅聚合半导体有限公司. 功能薄膜异质衬底结构及其制备方法、电子元器件: CN118748146A. 2024-10-08. |
| [39] | ZHONG H Z, ZHENG Y, SUN J C, et al. Gigahertz-rate- switchable wavefront shaping through integration of metasurfaces with photonic integrated circuit. Advanced Photonics, 2024, 6(1): 016005. |
| [40] |
THOMASCHEWSKI M, ZENIN V A, WOLFF C, et al. Plasmonic monolithic lithium niobate directional coupler switches. Nature Communications, 2020, 11: 748.
DOI PMID |
| [41] | ASHKIN A, BOYD G D, DZIEDZIC J M, et al. Optical-induced refractive index inhomogeneities in LiNbO3 and LiTaO3. Applied Physics Letters, 1966, 9(1): 72. |
| [42] |
JIANG H W, LUO R, LIANG H X, et al. Fast response of photorefraction in lithium niobate microresonators. Optics Letters, 2017, 42 (17): 3267.
DOI PMID |
| [43] | LU J J, SURYA J B, LIU X W, et al. Periodically poled thin-film lithium niobate microring resonators with a second-harmonic generation efficiency of 250,000%/W. Optica, 2019, 6(12): 1455. |
| [44] |
XU Y T, SAYEM A A, ZOU C L, et al. Photorefraction-induced Bragg scattering in cryogenic lithium niobate ring resonators. Optics Letters, 2021, 46(2): 432.
DOI PMID |
| [45] | ZHENG D H, ZHANG Y Q, WANG S L, et al. Photorefractive effect of lithium niobate crystals. Journal of Synthetic Crystals, 2022, 51(9/10): 1626. |
| [46] |
HOU J K, XUE B Y, MA R X, et al. UV-enhanced photorefractive response rate in a thin-film lithium niobate microdisk. Optics Letters, 2024, 49(12): 3456.
DOI PMID |
| [47] | WANG Y, LI M, GAO M Y, et al. Photonic time-delayed reservoir computing based on lithium niobate microring resonators. Physics Optics, DOI: 10.48550/arXiv.2408.13476. |
| [48] | WU J B, YAO S H, XIA Z R, et al. A new crystal growth method for the growth of near-stoichiometric LiNbO3. Journal of the Chinese Ceramic Society, 2008, 36(5): 608. |
| [49] | BYER R L, YOUNG J F., FEIGELSON R S. Growth of high-quality LiNbO3 crystals from the congruent melt. Journal of Applied Physics, 1970, 41(6): 2320. |
| [50] | LERNER P, LEGRAS C, DUMAS J P. Stoechiométrie des monocristaux de métaniobate de lithium. Journal of Crystal Growth, 1968, 3: 231. |
| [51] | IYI N, KITAMURA K, IZUMI F, et al. Comparative study of defect structures in lithium niobate with different compositions. Journal of Solid State Chemistry, 1992, 101(2): 340. |
| [52] | BLUMEL J, BORN E, METZGER T. Solid state NMR study supporting the lithium vacancy defect model in congruent lithium niobate. Journal of Physics and Chemistry of Solids, 1994, 55(7): 589. |
| [53] | KOJIMA S. Composition variation of optical phonon damping in lithium niobate crystals. Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, 1993, 32(9): 4373. |
| [54] | WILKINSON A P, CHEETHAM A K, JARMAN R H. The defect structure of congruently melting lithium niobate. Journal of Applied Physics, 1993, 74(5): 3080. |
| [55] | CHEN K F, LI Y L, PENG C, et al. Microstructure and defect characteristics of lithium niobate with different Li concentrations. Inorganic Chemistry Frontiers, 2021, 8(17): 4006. |
| [56] | HE X K, XUE D F, KITAMURA K. Defects and their control of lithium niobate crystals. Journal of Synthetic Crystals, 2005, 34(5): 884. |
| [57] | PHILLIPS W, AMODEI J J, STAEBLER D L. Optical and holographic storage properties of transition metal doped lithium niobate. RCA Review, 1972, 33: 94. |
| [58] | SIDOROV N V, YANICHEV A A, GABAIN A A, et al. Photorefractive properties of lithium niobate single crystals doped with copper. Journal of Applied Spectroscopy, 2013, 80(2): 226. |
| [59] | YUE X F, ADIBI A, HUDSON T, et al. Role of cerium in lithium niobate for holographic recording. Journal of Applied Physics, 2000, 87(9): 4051. |
| [60] | LIU Y, LIU L, XU L, et al. Experimental study of non-volatile holographic storage in doubly- and triply-doped lithium niobate crystals. Optics Communications, 2000, 181(1/2/3): 47. |
| [61] | ZHANG G Y, XU J J, LIU S M, et al. Study of resistance against photorefractive light-induced scattering in LiNbO3:Fe, Mg crystals. Proceedings of SPIE, 1995, 2529: 14. |
| [62] | KONG Y F, WU S Q, LIU S G, et al. Fast photorefractive response and high sensitivity of Zr and Fe codoped LiNbO3 crystals. Applied Physics Letters, 2008, 92(25): 1064. |
| [63] | SHIN S H, JAVIDI B. Speckle-reduced three-dimensional volume holographic display by use of integral imaging. Applied Optics, 2002, 41(14): 2644. |
| [64] | PAYNE D J, EGDELL R G, WALSH A, et al. Electronic origins of structural distortions in post-transition metal oxides: experimental and theoretical evidence for a revision of the lone pair model. Physical Review Letters, 2006, 96(15): 157403. |
| [65] | LU Z B, WANG H, TAO Y H. WOx nanoparticles coupled with nitrogen-doped porous carbon toward electrocatalytic N2 reduction. Nanoscale, 2023, 15(36): 14847. |
| [66] |
DONG Y F, LIU S G, LI W, et al. Improved ultraviolet photorefractive properties of vanadium-doped lithium niobate crystals. Optics Letters, 2011, 36(10): 1779.
DOI PMID |
| [67] |
DONG Y F, LIU S G, KONG Y F, et al. Fast photorefractive response of vanadium-doped lithium niobate in the visible region. Optics Letters, 2012, 37(11): 1841.
DOI PMID |
| [68] | ARAUJO R M, MATTOS E F D S, MÁRIO E G V, et al. Computer simulation of the incorporation of V2+, V3+, V4+, V5+ and Mo3+, Mo4+, Mo5+, Mo6+ dopants in LiNbO3. Crystals, 2020, 10(6): 457. |
| [69] | FAN Y J, LI L L, LI Y L, et al. Hybrid density functional theory study of vanadium doping in stoichiometric and congruent LiNbO3. Physical Review B, 2019, 99(3): 035147. |
| [70] | SAEED S, ZHENG D H, LIU H D, et al. Rapid response of photorefraction in vanadium and magnesium co-doped lithium niobate. Journal of Physics D-Applied Physics, 2019, 52(40): 5303. |
| [71] | LIU M N, XUE D F, ZHANG S C, et al. Chemical synthesis of stoichiometric lithium niobate powders. Materials Letters, 2005, 59(8/9): 1095. |
| [72] | XUE D F. Structural characteristics of lithium niobate and lithium tantalate crystals. Chemical Research, 2002, 13(4): 1. |
| [73] | KLING A, VALDREZ C, MARQUES J G, et al. Incorporation of tungsten in lithium niobate by diffusion. Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research Section B: Beam Interactions with Materials and Atoms, 2002, 190: 524. |
| [74] | KLING A, MARQUES J G, SOARES J C, et al. Valence effect on the incorporation of tungsten implanted into lithium niobate. Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research Section B: Beam Interactions with Materials and Atoms, 1997, 127(2): 520. |
| [75] | KLING A, MARQUES J G, SILVA M F D, et al. Incorporation of hexavalent impurities into LiNbO3. Radiation Effects and Defects in Solids, 1999, 150: 249. |
| [76] | HUANG M. Study on the tungsten-doped lithium niobate crystals. Tianjin: Nankai University Master’s thesis, 2015. |
| [77] |
TIAN T, KONG Y F, LIU S G, et al. Photorefraction of molybdenum-doped lithium niobate crystals. Optics Letters, 2012, 37(13): 2679.
DOI PMID |
| [78] | WANG W W, LIU H D, ZHENG D H, et al. Interaction between Mo and intrinsic or extrinsic defects of Mo doped LiNbO3 from first-principles calculations. Journal of Physics: Condensed Matter, 2020, 32(25): 2557701. |
| [79] | LI L L, LI L Y, ZHAO X, et al. Abnormal lattice occupation of Mo and related polarons in LiNbO3: hybrid density functional theory investigation. Journal of Materiomics, 2020, 6(1): 183. |
| [80] |
TIAN T, KONG Y F, LIU S G, et al. Fast UV-Vis photorefractive response of Zr and Mg codoped LiNbO3:Mo. Optics Express, 2013, 21(9): 10460.
DOI PMID |
| [81] | XUE L Y, LIU H D, ZHENG D H, et al. The photorefractive response of Zn and Mo co-doped LiNbO3 in the visible region. Crystals, 2019, 9(5): 228. |
| [82] | ZHU L, ZHENG D H, LIU H D, et al. Enhanced photorefractive properties of indium co-doped LiNbO3: Mo crystals. Applied Physics Letters, 2019, 8(9): 095316. |
| [83] | ZHU L, ZHENG D H, SAEED S, et al. Photorefractive properties of molybdenum and hafnium co-doped LiNbO3 crystals. Crystals, 2018, 8(8): 322. |
| [84] | TIAN T, KONG Y F, LIU H D, et al. Fabrication of p-type lithium niobate crystals by molybdenum doping and polarization. Journal of Physics: Conference Series, 2017, 867: 012037. |
| [85] | 田甜. p型铌酸锂晶体的制备. 第十七届全国晶体生长与材料学术会议, 哈尔滨, 2015: 2. |
| [86] | PEI Z D, HU Q, KONG Y F, et al. Investigation on p-type lithium niobate crystals. AIP Advances, 2011, 1(3): 032171. |
| [87] | SOHLER W, HU H, RICKEN R, et al. Integrated optical devices in lithium niobate. Optics & Photonics News, 2008, 19(1): 24. |
| [88] | KIENLE F, LIN D, ALAM S U, et al. Green-pumped, picosecond MgO:PPLN optical parametric oscillator. Journal of the Optical Society of America B, 2012, 29(1): 144. |
| [89] | PORWAL N K, KUMAR M, SASTRY M D. Electron paramagnetic resonance studies in photorefractive crystals I: hyperfine interaction and photo induced charge transfer in 235U5+ and 238U5+ doped LiNbO3. Pramana-journal of Physics, 1996, 47(6): 481. |
| [90] | LEWIS W B, HECHT H G, EASTMAN M P. Electron paramagnetic resonance and optical studies of pentavalent uranium. Journal of Cheminformatics, 1973, 4(35): 1634. |
| [91] | BRAVO D, BAUSÁ L E, LÓPEZ F J. EPR and optical study of uranium-doped LiNbO3 single crystals. Radiation Effects and Defects in Solids, 1999, 149: 363. |
| [92] | OKAMOTO E, IKEOM H, MUTO K. Holographic storage in U-doped LiNbO3. Applied Optics, 1975, 14(10): 2453. |
| [93] | TIAN T, YUAN W, LIU W, et al. Crystal growth and spectroscopic properties of uranium dioxide doped LiNbO3 with multiband absorption. Journal of Crystal Growth, 2021, 565(1): 126132. |
| [94] | TIAN T, CHEN Y H, ZHANG J, et al. Photorefraction of uranium-doped lithium niobate crystals at multiple visible wavelengths. CrystEngComm, 2023, 25(8): 1207. |
| [95] | TIAN T, XU W J, FANG C K, et al. The influence of In3+ on the crystal growth and visible band photorefraction of uranium-doped lithium niobate single crystals. Crystals, 2024, 14(4): 380. |
| [96] | TIAN T, WU T F, ZHANG J, et al. Improvement of the photorefractive responsive time and optical damage resistance of LiNbO3 by co-doping with uranium and magnesium. Optical Materials, 2024, 157(2): 116223. |
| [97] | TIAN T, YAN X D, KONG Y F, et al. Improvement in the photorefractive response speed and mechanism of pure congruent lithium niobate crystals by increasing the polarization current. Crystals, 2017, 7(12): 368. |
| [98] | JIN M, WU X J, LI X H, et al. Optical properties of La2Ti2O7 crystal grown by Bridgman method. Jouranal of Synthetic Crystals, 2011, 40(5): 1126. |
| [99] | TIAN T, FENG H W, ZHANG Y, et al. Crystal growth and luminescence properties of Dy3+ and Ge4+ co-doped Bi4Si3O12 single crystals for high power warm white LED. Crystals. 2017, 7(8): 249. |
| [100] | KONG Y F, WEN J K, WANG H F. New doped lithium niobate crystal with high resistance to photorefraction—LiNbO3:In. Applied Physics Letters, 1995, 66(3): 280. |
| [101] | GOROBERTS B S, ENGOYAN S S, SIDORENKO G A. Investigation of uranium and uranium-containing minerals by their luminescence spectra. Soviet Atomic Energy, 1977, 42(3): 196. |
| [102] | PALATNIKOV M N, SIDOROV N V, KADETOVA A V, et al. Concentration threshold in optically nonlinear LiNbO3:Tb crystals. Optics & Laser Technology, 2021, 137: 106821. |
| [103] | SHIN H, LEE S, LEE M. Holographic recording in congruent LiNbO3 co-doped with Tb and Fe. Materials Science Forum, 2004, 449: 981. |
| [104] | LEE M, TAKEKAWA S, FURUKAWA Y, et al. Nonvolatile two-color holographic recording in Tb-doped LiNbO3. Applied Physics Letters, 2000, 76(13): 1653. |
| [105] | TIAN T. Study on the growth and photorefractive characteristics of molybdenum-doped lithium niobate series crystals. Tianjin: Nankai University PhD’s Thesis, 2013. |
| [106] | ZHENG D H, KONG Y F, LIU S G, et al. The photorefractive characteristics of bismuth-oxide doped lithium niobate crystals. AIP Advances, 2015, 5(1): 017132. |
| [107] | ZHENG D H, KONG Y F, LIU S G, et al. The simultaneous enhancement of photorefraction and optical damage resistance in MgO and Bi2O3 co-doped LiNbO3 crystals. Scientific Reports, 2016, 6: 20308. |
| [108] | ZHENG D H, WANG W W, WANG S L, et al. Real-time dynamic holographic display realized by bismuth and magnesium co-doped lithium niobate. Applied Physics Letters, 2019, 114(24): 241903. |
| [109] | WANG S L, SHAN Y D, ZHENG D H, et al. The real-time dynamic holographic display of LN:Bi,Mg crystals and defect-related electron mobility. Opto-Electronic Advances, 2022, 5(12): 210135. |
| [110] | WANG S L, SHAN Y D, WANG W W, et al. Lone-pair electron effect induced a rapid photorefractive response in site-controlled LiNbO3:Bi,M (M=Zn, In, Zr) crystals. Applied Physics Letters, 2021, 118(19): 191902. |
| [111] | ZHENG Y L, CHEN X F. Integrated nonlinear photonics on thin-film lithium niobate: a route to an all-optical information era. Physics, 2024, 53(1): 22. |
| [112] |
WANG L Z, LIU S G, KONG Y F, et al. Increased optical-damage resistance in tin-doped lithium niobate. Optics Letters, 2010, 35(6): 883.
DOI PMID |
| [113] | HOTA P, KAPURIA A, BOSE S, et al. The role of lone-pair electrons on electrocatalytic activity of copper antimony sulfide nanostructures. Materials Chemistry and Physics, 2022, 291(15): 126676. |
| [1] | 范雨竹, 王媛, 王林燕, 向美玲, 鄢雨婷, 黎本慧, 李敏, 文志东, 王海超, 陈永福, 邱会东, 赵波, 周成裕. 氧化石墨烯基吸附材料去除水体中Pb(II): 制备、性能及机理[J]. 无机材料学报, 2026, 41(1): 12-26. |
| [2] | 徐锦涛, 高攀, 何唯一, 蒋圣楠, 潘秀红, 汤美波, 陈锟, 刘学超. 3C-SiC晶体制备研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2026, 41(1): 1-11. |
| [3] | 余升阳, 苏海军, 姜浩, 余明辉, 姚佳彤, 杨培鑫. 激光增材制造超高温氧化物陶瓷孔隙缺陷形成及抑制研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(9): 944-956. |
| [4] | 刘江平, 管鑫, 唐振杰, 朱文杰, 罗永明. 含氮挥发性有机化合物催化氧化的研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(9): 933-943. |
| [5] | 肖晓琳, 王玉祥, 谷佩洋, 朱圳荣, 孙勇. 二维无机材料调控病损皮肤组织再生的研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(8): 860-870. |
| [6] | 马景阁, 吴成铁. 无机生物材料用于毛囊和毛发再生的研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(8): 901-910. |
| [7] | 张洪健, 赵梓壹, 吴成铁. 无机生物材料调控神经细胞功能及神经化组织再生的研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(8): 849-859. |
| [8] | 艾敏慧, 雷波. 微纳米生物活性玻璃: 功能化设计与血管化皮肤再生[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(8): 921-932. |
| [9] | 王宇彤, 常江, 徐合, 吴成铁. 硅酸盐生物陶瓷/玻璃促创面修复的研究进展:作用、机制和应用方式[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(8): 911-920. |
| [10] | 马文平, 韩雅卉, 吴成铁, 吕宏旭. 无机活性材料在类器官研究领域的应用[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(8): 888-900. |
| [11] | 罗晓民, 乔志龙, 刘颍, 杨晨, 常江. 无机生物活性材料调控心肌再生的研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(8): 871-887. |
| [12] | 朱文杰, 唐璐, 陆继长, 刘江平, 罗永明. 钙钛矿型氧化物催化氧化挥发性有机化合物的研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(7): 735-746. |
| [13] | 胡智超, 杨鸿宇, 杨鸿程, 孙成礼, 杨俊, 李恩竹. P-V-L键理论在微波介质陶瓷性能调控中的应用[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(6): 609-626. |
| [14] | 吴琼, 沈炳林, 张茂华, 姚方周, 邢志鹏, 王轲. 铅基织构压电陶瓷研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(6): 563-574. |
| [15] | 张碧辉, 刘小强, 陈湘明. Ruddlesden-Popper结构杂化非常规铁电体的研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(6): 587-608. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||