无机材料学报 ›› 2023, Vol. 38 ›› Issue (10): 1183-1192.DOI: 10.15541/jim20230013 CSTR: 32189.14.10.15541/jim20230013
所属专题: 【制备方法】3D打印(202506)
吴东江1( ), 赵紫渊1, 于学鑫1, 马广义1, 由竹琳2, 任冠辉3,4, 牛方勇1(
), 赵紫渊1, 于学鑫1, 马广义1, 由竹琳2, 任冠辉3,4, 牛方勇1( )
)
收稿日期:2023-01-09
修回日期:2023-03-06
出版日期:2023-10-20
网络出版日期:2023-03-09
通讯作者:
牛方勇, 副教授. E-mail: niufangyong@dlut.edu.cn作者简介:吴东江(1964-), 男, 教授. E-mail: djwudut@dlut.edu.cn
基金资助:
WU Dongjiang1( ), ZHAO Ziyuan1, YU Xuexin1, MA Guangyi1, YOU Zhulin2, REN Guanhui3,4, NIU Fangyong1(
), ZHAO Ziyuan1, YU Xuexin1, MA Guangyi1, YOU Zhulin2, REN Guanhui3,4, NIU Fangyong1( )
)
Received:2023-01-09
Revised:2023-03-06
Published:2023-10-20
Online:2023-03-09
Contact:
NIU Fangyong, associate professor. E-mail: niufangyong@dlut.edu.cnAbout author:WU Dongjiang (1964-), male, professor. E-mail: djwudut@dlut.edu.cn
Supported by:摘要:
Al2O3-TiCp(AT)复相陶瓷材料以其优异的综合力学性能而被广泛用作金属切削刀具材料。针对AT材料传统烧结方法在能耗及周期方面的局限, 本工作利用激光定向能量沉积技术开展了AT复相陶瓷材料直接增材制造的研究, 系统探讨了不同TiCp比例对复相陶瓷材料微观结构和力学性能的影响。结果表明TiCp颗粒均匀分布在成型样件的基体中, 掺杂TiCp细化了Al2O3晶粒。同时, 由于TiCp与Al2O3基体的热膨胀失配引起裂纹出现偏转、贯穿颗粒等现象, 消耗了裂纹扩展能量, 进而有效抑制了AT材料直接增材过程中的裂纹扩展行为。掺杂TiCp颗粒对熔池形成冲击, 在一定程度上加快了气体的逸出速率, 进而提高了材料的相对密度。但TiCp含量过高将加剧其与Al2O3基体在高温时的化学反应, 生成的气体使复合材料中出现较大气孔并降低了材料部分力学性能。TiCp质量分数为30%的复合材料的相对密度达到96.64%、平均显微硬度达到21.07 GPa和断裂韧性达到4.29 MPa·m1/2。
中图分类号:
吴东江, 赵紫渊, 于学鑫, 马广义, 由竹琳, 任冠辉, 牛方勇. Al2O3-TiCp复相陶瓷激光定向能量沉积直接增材制造[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(10): 1183-1192.
WU Dongjiang, ZHAO Ziyuan, YU Xuexin, MA Guangyi, YOU Zhulin, REN Guanhui, NIU Fangyong. Direct Additive Manufacturing of Al2O3-TiCp Composite Ceramics by Laser Directed Energy Deposition[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(10): 1183-1192.
| Al2O3 | Composition | Al2O3 | SiO2 | Fe2O3 | Na2O | CaO |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Content/% | >99.9 | 0.0041 | 0.0021 | 0.0014 | <0.001 | |
| TiCp | Composition | TiCp | Si/Ca | K/Na | Fe | Al |
| Content/% | >99.1 | <0.01 | <0.005 | <0.09 | <0.01 |
表1 两种原材料粉末的成分及质量分数
Table 1 Composition and mass fraction of two raw materials powder
| Al2O3 | Composition | Al2O3 | SiO2 | Fe2O3 | Na2O | CaO |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Content/% | >99.9 | 0.0041 | 0.0021 | 0.0014 | <0.001 | |
| TiCp | Composition | TiCp | Si/Ca | K/Na | Fe | Al |
| Content/% | >99.1 | <0.01 | <0.005 | <0.09 | <0.01 |
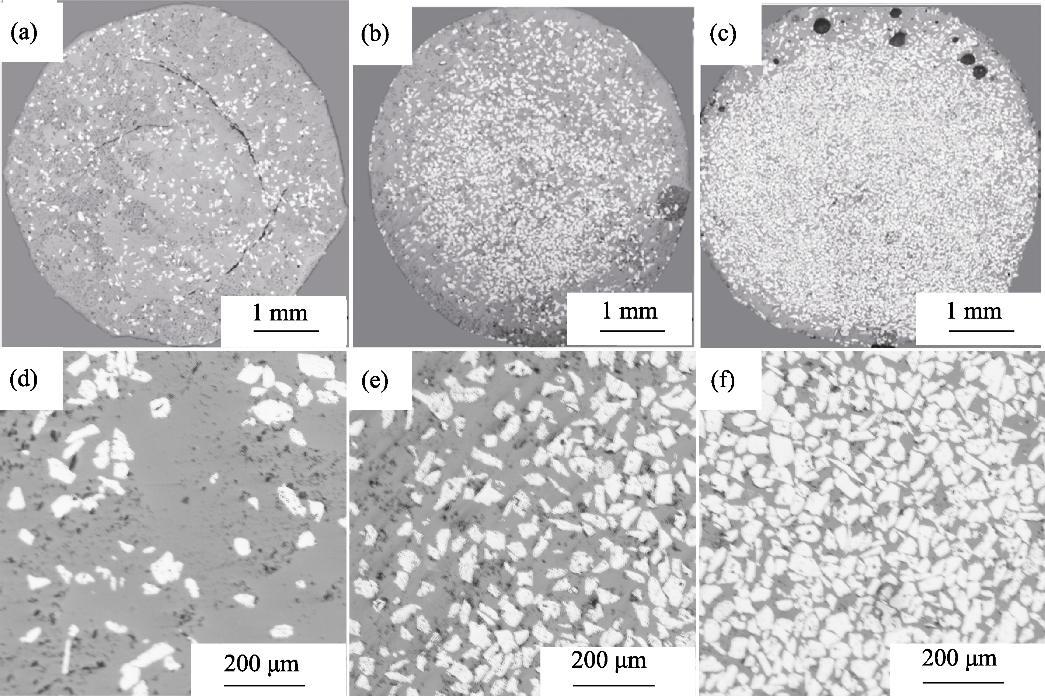
图5 样件横截面全貌以及颗粒分布图
Fig. 5 Full cross-sections and particle distributions of samples (a-c) Full views of (a) AT10, (b) AT30 and (c) AT50;(d-f) Particle distributions of (d) AT10, (e) AT30 and (f) AT50
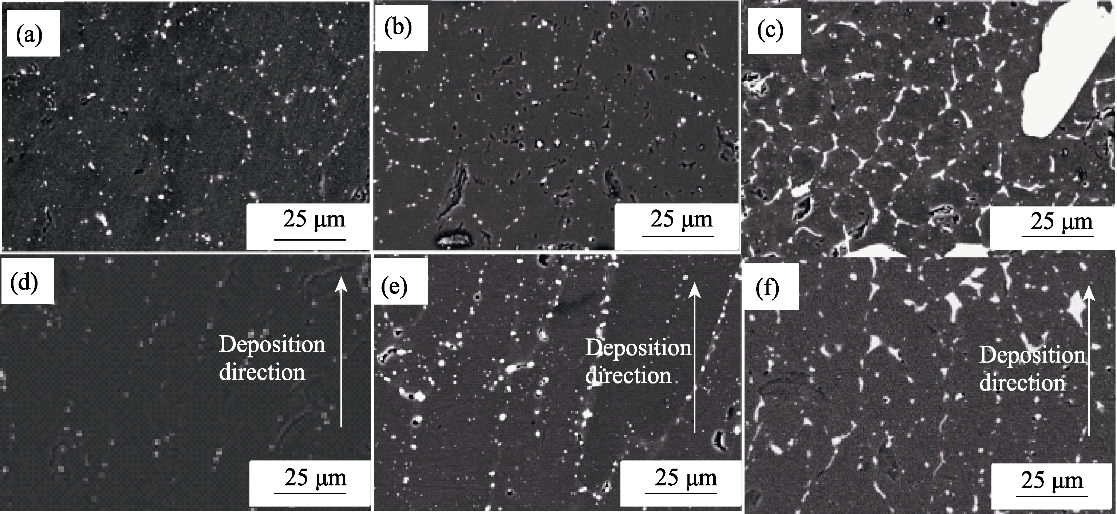
图7 样件微观组织特征
Fig. 7 Microstructures of the sample (a-c) Cross-sectional images of (a) AT10, (b) AT30 and (c) AT50; (d-f) Longitudinal section images of (d) AT10, (e) AT30 and (f)AT50
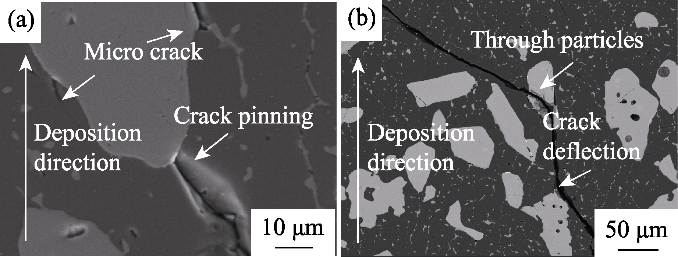
图11 TiCp颗粒对裂纹扩展的偏转和阻碍作用
Fig. 11 Deflection and obstruction effects of TiC particles on crack growth (a) Pinning and micro crack; (b) Through particles and crack deflection
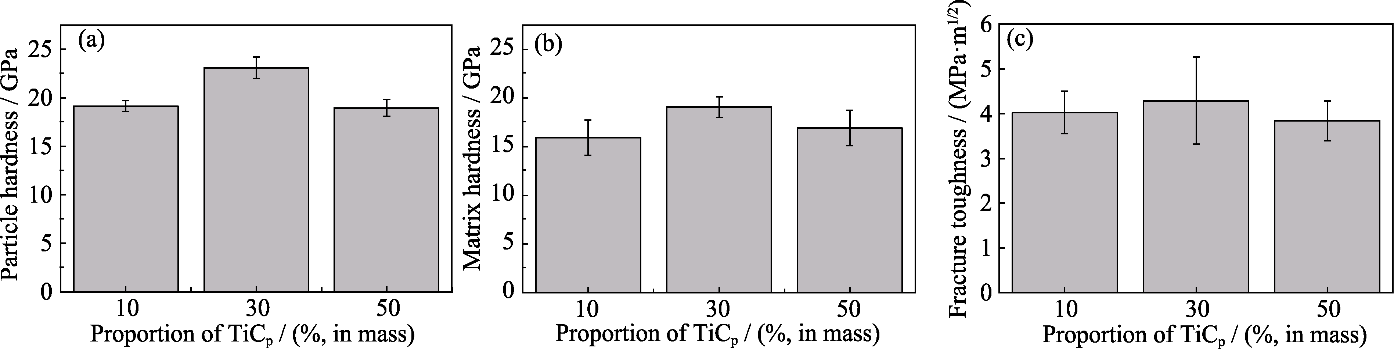
图13 不同比例AT样件的力学性能
Fig. 13 Mechanical properties of AT-samples of different proportions (a) Microhardness of particles; (b) Matrix microhardness; (c) Fracture toughness
| [1] | 申仲琳, 苏海军, 刘海方, 等. 超高温氧化物陶瓷激光增材制造技术与缺陷控制研究进展. 复合材料学报, 2021, 38(3): 668. |
| [2] |
GOLDSTEIN A, SINGURINDI A. Al2O3/TiC based metal cutting tools by microwave sintering followed by hot isostatic pressing. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2010, 83(6): 1530.
DOI URL |
| [3] | 赵喆, 龚江宏, 苗赫濯, 等. TiC颗粒弥散Al2O3复合材料的阻力曲线行为. 硅酸盐学报, 2000, 28(4): 371. |
| [4] |
EVANS A G, CANNON R M. Toughening of brittle solids by martensitic transformations. Acta Metallurgica, 1986, 34(5): 761.
DOI URL |
| [5] |
CAI K F, MCLACHLAN D S, AXEN N, et al. Preparation, microstructures and properties of Al2O3-TiC composites. Ceramics International, 2002, 28(2): 217.
DOI URL |
| [6] |
GEVORKYAN E, RUCKI M, PANCHENKO S, et al. Effect of SiC addition to Al2O3 ceramics used in cutting tools. Materials, 2020, 13(22): 5195.
DOI URL |
| [7] | 程寓, 孙士帅. 一种氧化铝-碳化钛微米复合陶瓷刀具材料及其微波烧结方法. CN104131208A. 2014-11-05. |
| [8] | 高纪明, 陈松年. 氧化铝/碳化钛复合材料的无压烧结. 湖南大学学报:自然科学版, 1996, 23(4): 46. |
| [9] |
XIA T, MUNIR Z, TANG Y, et al. Structure formation in the combustion synthesis of Al2O3/TiC composites. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2000, 83(3): 507.
DOI URL |
| [10] | 苏海军, 王恩缘, 任群, 等. 超高温氧化物共晶复合陶瓷研究进展. 中国材料进展, 2018, 37(6): 437. |
| [11] | 吴甲民. 方兴未艾的陶瓷增材制造. 硅酸盐学报, 2021, 49(09): 1785. |
| [12] | 刘雨, 陈张伟. 陶瓷光固化3D打印技术研究进展. 材料工程, 2020, 48(9): 1. |
| [13] |
WU D, YU X, ZHAO Z. Direct additive manufacturing of TiCp reinforced Al2O3-ZrO2 eutectic functionally graded ceramics by laser directed energy deposition. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2023, 43(6): 2718.
DOI URL |
| [14] |
LIU H, SU H, SHEN Z, et al. Research progress on ultrahigh temperature oxide eutectic ceramics by laser additive manufacturing. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(3): 255.
DOI |
| [15] | WU D, YU C, WANG Q, et al. Synchronous-hammer-forging- assisted laser directed energy deposition additive manufacturing of high-performance 316L samples. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 2022, 307: 117695. |
| [16] | 苏海军, 尉凯晨, 郭伟, 等. 激光快速成形技术新进展及其在高性能材料加工中的应用. 中国有色金属学报, 2013, 23(6): 1567. |
| [17] | 吴甲民, 陈敬炎, 陈安南, 等. 陶瓷零件增材制造技术及在航空航天领域的潜在应用. 航空制造技术, 2017, 11(10): 40. |
| [18] |
WU D, SHI J, NIU F, et al. Direct additive manufacturing of melt growth Al2O3-ZrO2 functionally graded ceramics by laser directed energy deposition. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2022, 42(6): 2957.
DOI URL |
| [19] | HUANG Y, WU D, ZHAO D, et al. Process optimization of melt growth alumina/aluminum titanate composites directed energy deposition: effects of scanning speed. Additive Manufacturing, 2020, 35: 101210. |
| [20] | WU D, ZHAO D, HUANG Y, et al. Shaping quality, microstructure, and mechanical properties of melt-grown mullite ceramics by directed laser deposition. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2021, 871: 159609. |
| [21] | SU H, ZHANG J, LIU L, et al. Rapid growth and formation mechanism of ultrafine structural oxide eutectic ceramics by laser direct forming. Applied Physics Letters, 2011, 99(22): 1174. |
| [22] | ZHAO D, WU D, NIU F, et al. Heat treatment of melt-grown alumina ceramics with trace glass fabricated by laser directed energy deposition. Materials Characterization, 2023, 196: 112639. |
| [23] | HUANG Y, WU D, ZHAO D, et al. Investigation of melt-growth alumina/aluminum titanate composite ceramics prepared by directed energy deposition. International Journal of Extreme Manufacturing, 2021, 3: 035101. |
| [24] |
WEI X, JIN M, YANG H, et al. Advances in 3D printing of magnetic materials: fabrication, properties, and their applications. Journal of Advanced Ceramics, 2022, 11(5): 665.
DOI |
| [25] | 刘安丽, 隋长有, 李发智, 等. 陶瓷激光增材制造等离子体特征与成形缺陷的相关性研究. 中国激光, 2020, 47(6): 146. |
| [26] | 中国建筑材料工业协会. 精细陶瓷弯曲强度试验方法: GB/T 6569-2006. 中国标准出版社, 2006. |
| [27] | 龚江宏. 陶瓷材料断裂力学. 北京: 清华大学出版社, 2001: 101- 117. |
| [28] |
VOIGT W. Ueber die beziehung zwischen den beiden elasticitätsconstanten isotroper körper. Annalen Der Physik, 1889, 274(12): 573.
DOI URL |
| [29] |
REUSS A. Berechnung der fleissgrenze von mischkristallen auf grund der plastizitats bedingung für einkrisalle. Zeitschrift für Angewandte Mathematik und Mechanik, 1929, 9(1): 49.
DOI URL |
| [30] |
YUAN P, GU D. Molten pool behaviour and its physical mechanism during selective laser melting of TiC/AlSi10Mg nanocomposites: simulation and experiments. Journal of Physics D: Applied Physics, 2015, 48(3): 035303.
DOI URL |
| [31] |
YUAN P, GU D, DAI D. Particulate migration behavior and its mechanism during selective laser melting of TiC reinforced Al matrix nanocomposites. Materials and Design, 2015, 82(5): 46.
DOI URL |
| [32] |
张进, 黄云涛, 岳新艳, 等. TiC含量对无压烧结TiC-Al2O3导电陶瓷复合材料微观结构与性能的影响. 机械工程材料, 2023, 47(1): 70.
DOI |
| [33] | GOINS P E, FRAZIER W E. A model of grain boundary complexion transitions and grain growth in yttria-doped alumina. Acta Materialia, 2020, 188: 79. |
| [34] | 胡晓清, 曾照强. Al2O3/TiC陶瓷中Al2O3与TiC化学反应抑制的研究. 硅酸盐通报, 1998, 17(5): 45. |
| [35] |
KIM Y W, LEE J G. Pressureless sintering of alumina-titanium carbide composites. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 1989, 72(8): 1333.
DOI URL |
| [36] |
ISHIDA K. Effect of grain size on grain boundary segregation. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 1996, 235(2): 244.
DOI URL |
| [37] |
TERWILLIGER C D, CHIANG Y M. Size-dependent solute segregation and total solubility in ultrafine polycrystals: Ca in TiO2. Acta Metallurgica Et Materialia, 1995, 43(1): 319.
DOI URL |
| [38] | NIU F, WU D, YAN S, et al. Process optimization for suppressing cracks in laser engineered net shaping of Al2O3 ceramics. The Journal of The Minerals, Metals & Materials Society, 2016, 69(3): 557. |
| [39] | LAWN B R, WILSHAW T R. Fracture of brittle solids. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 1975: 47. |
| [40] |
WU D, YU X, ZHAO Z, et al. One-step additive manufacturing of TiCp reinforced Al2O3-ZrO2 eutectic ceramics composites by laser directed energy deposition. Ceramics International, 49(8): 12758.
DOI URL |
| [41] | LANGE F F, Fracture mechanics of ceramics. Ceramurgia International, 1978, 4(3): 142. |
| [42] | GUO J K. The Exploration on new approach of strengthening and toughening of ceramic materials. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 1998, 13(1): 23. |
| [43] | AHSAN M N, BRADLEY R, PINKERTON A J. Microcomputed tomography analysis of intralayer porosity generation in laser direct metal deposition and its causes. Journal of Laser Applications, 2011, 23(2): 807. |
| [44] |
KOBRYN P A, MOORE E H. The effect of laser power and traverse speed on microstructure, porosity, and build height in laser-deposited Ti6A14V. Scripta materialia, 2000. 43(4): 299.
DOI URL |
| [45] |
SUSAN D F, PUSKAR J D, BROOKS J A, et al. Quantitative characterization of porosity in stainless steel LENS powders and deposits. Materials Characterization, 2006. 57(1): 36.
DOI URL |
| [46] |
NIU F, WU D, LU F, et al. Microstructure and macro properties of Al2O3 ceramics prepared by laser engineered net shaping. Ceramics International, 2018, 44(12): 14303.
DOI URL |
| [47] |
FRANCISCO I D, MERINO R I, ORERA V M, et al. Growth of Al2O3/ZrO2(Y2O3) eutectic rods by the laser floating zone technique: effect of the rotation. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2005, 25(8): 1341.
DOI URL |
| [48] |
WU D, HUANG Y, NIU F, et al. Effects of TiO2 doping on microstructure and properties of directed laser deposition alumina/ aluminum titanate composites. Virtual and Physical Prototyping, 2019, 14(4): 371.
DOI URL |
| [49] |
ZHAO D, WU D, SHI J, et al. Microstructure and mechanical properties of melt-grown alumina-mullite/glass composites fabricated by directed laser deposition. Journal of Advanced Ceramics, 2022, 11(1): 75.
DOI |
| [50] | PETCH N J. The cleavage strength of polycrystals. Journal of the Iron and Steel Institute, 1953, 174(1): 25. |
| [51] | HALL E O. The deformation and ageing of mild steel: III discussion of results. Proceedings of the Physical Society of London, 1951, 64(381): 747. |
| [1] | 陈义, 邱海鹏, 陈明伟, 徐昊, 崔恒. SiC/SiC复合材料基体硼改性方法及其力学性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(5): 504-510. |
| [2] | 崔宁, 张玉新, 王鲁杰, 李彤阳, 于源, 汤华国, 乔竹辉. (TiVNbMoW)Cx高熵陶瓷的单相形成过程与碳空位调控[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(5): 511-520. |
| [3] | 李紫薇, 弓伟露, 崔海峰, 叶丽, 韩伟健, 赵彤. 前驱体法制备(Zr, Hf, Nb, Ta, W)C-SiC复相陶瓷及性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(3): 271-280. |
| [4] | 高晨光, 孙晓亮, 陈君, 李达鑫, 陈庆庆, 贾德昌, 周玉. 基于湿法纺丝技术的SiBCN-rGO陶瓷纤维的组织结构、力学和吸波性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(3): 290-296. |
| [5] | 穆浩洁, 张源江, 喻彬, 付秀梅, 周世斌, 李晓东. ZrO2掺杂Y2O3-MgO纳米复相陶瓷的制备及性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(3): 281-289. |
| [6] | 李伟, 许志明, 苟燕子, 尹森虎, 余艺平, 王松. SiC纤维烧结陶瓷的制备及其性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(2): 177-183. |
| [7] | 魏相霞, 张晓飞, 徐凯龙, 陈张伟. 增材制造柔性压电材料的现状与展望[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(9): 965-978. |
| [8] | 范武刚, 曹雄, 周响, 李玲, 赵冠楠, 张兆泉. 8YSZ陶瓷在模拟压水堆水环境中的耐腐蚀性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(7): 803-809. |
| [9] | 陈乾, 苏海军, 姜浩, 申仲琳, 余明辉, 张卓. 超高温氧化物陶瓷激光增材制造及组织性能调控研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(7): 741-753. |
| [10] | 姜灵毅, 庞生洋, 杨超, 张悦, 胡成龙, 汤素芳. C/SiC-BN复合材料的制备及氧化行为[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(7): 779-786. |
| [11] | 王伟明, 王为得, 粟毅, 马青松, 姚冬旭, 曾宇平. 以非氧化物为烧结助剂制备高导热氮化硅陶瓷的研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(6): 634-646. |
| [12] | 孙海洋, 季伟, 王为民, 傅正义. TiB-Ti周期序构复合材料设计、制备及性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(6): 662-670. |
| [13] | 蔡飞燕, 倪德伟, 董绍明. 高熵碳化物超高温陶瓷的研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(6): 591-608. |
| [14] | 刘国昂, 王海龙, 方成, 黄飞龙, 杨欢. B4C含量对(Ti0.25Zr0.25Hf0.25Ta0.25)B2-B4C陶瓷力学性能及抗氧化性能的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(6): 697-706. |
| [15] | 粟毅, 史扬帆, 贾成兰, 迟蓬涛, 高扬, 马青松, 陈思安. 浆料浸渍辅助PIP工艺制备C/HfC-SiC复合材料的微观结构及性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(6): 726-732. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||