无机材料学报 ›› 2022, Vol. 37 ›› Issue (3): 241-254.DOI: 10.15541/jim20210590 CSTR: 32189.14.10.15541/jim20210590
所属专题: 2022年度中国知网高下载论文
曹继伟1,2( ), 王沛1,2, 刘志远1,2, 刘长勇1,2, 吴甲民3,4(
), 王沛1,2, 刘志远1,2, 刘长勇1,2, 吴甲民3,4( ), 陈张伟1,2(
), 陈张伟1,2( )
)
收稿日期:2021-09-26
修回日期:2021-10-18
出版日期:2022-03-20
网络出版日期:2021-11-01
通讯作者:
吴甲民, 副教授. E-mail: jiaminwu@hust.edu.cn; 陈张伟, 教授. E-mail: chen@szu.edu.cn
作者简介:曹继伟(1989-), 男, 博士. E-mail: caojiwei@szu.edu.cn
基金资助:
CAO Jiwei1,2( ), WANG Pei1,2, LIU Zhiyuan1,2, LIU Changyong1,2, WU Jiamin3,4(
), WANG Pei1,2, LIU Zhiyuan1,2, LIU Changyong1,2, WU Jiamin3,4( ), CHEN Zhangwei1,2(
), CHEN Zhangwei1,2( )
)
Received:2021-09-26
Revised:2021-10-18
Published:2022-03-20
Online:2021-11-01
Contact:
WU Jiamin, associate professor. E-mail: jiaminwu@hust.edu.cn; CHEN Zhangwei, professor. E-mail: chen@szu.edu.cn
About author:CAO Jiwei (1989-), male, PhD. E-mail: caojiwei@szu.edu.cn
Supported by:摘要:
陶瓷以其优异的热物理化学性能在航空航天、能源、环保以及生物医疗等领域具有极大的应用潜力。随着这些领域相关技术的快速发展, 其核心零件部件外形结构设计日益复杂、内部组织逐步走向定制化、梯度化。陶瓷具有硬度高、脆性大等特点, 较难通过传统的加工成形方法实现异形结构零件的制造, 最终限制了陶瓷材料的工程应用范围。激光增材制造技术作为一种快速发展的增材制造技术, 在复杂精密陶瓷零部件的制造中具有显著优势: 无模、精度高、响应快以及周期短, 同时能够实现陶瓷零件组织结构灵活调配, 有望解决上述异形结构陶瓷零件成形问题。本文综述了多种基于粉末成形的激光增材制造陶瓷技术: 基于粉末床熔融的激光选区烧结和激光选区熔化; 基于定向能量沉积的激光近净成形技术。主要讨论了各类激光增材陶瓷技术的成形原理与特点, 综述了激光选区烧结技术中陶瓷坯体后处理致密化工艺以及激光选区熔化和激光近净成形技术这两种技术中所打印陶瓷坯体基体裂纹开裂行为分析及其控制方法的研究进展, 对比分析了激光选区烧结、激光选区熔化以及激光近净成形技术在成形陶瓷零件的技术特征, 最后展望了激光增材制造陶瓷技术的未来发展趋势。
中图分类号:
曹继伟, 王沛, 刘志远, 刘长勇, 吴甲民, 陈张伟. 基于粉末成形的激光增材制造陶瓷技术研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(3): 241-254.
CAO Jiwei, WANG Pei, LIU Zhiyuan, LIU Changyong, WU Jiamin, CHEN Zhangwei. Research Progress on Powder-based Laser Additive Manufacturing Technology of Ceramics[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(3): 241-254.
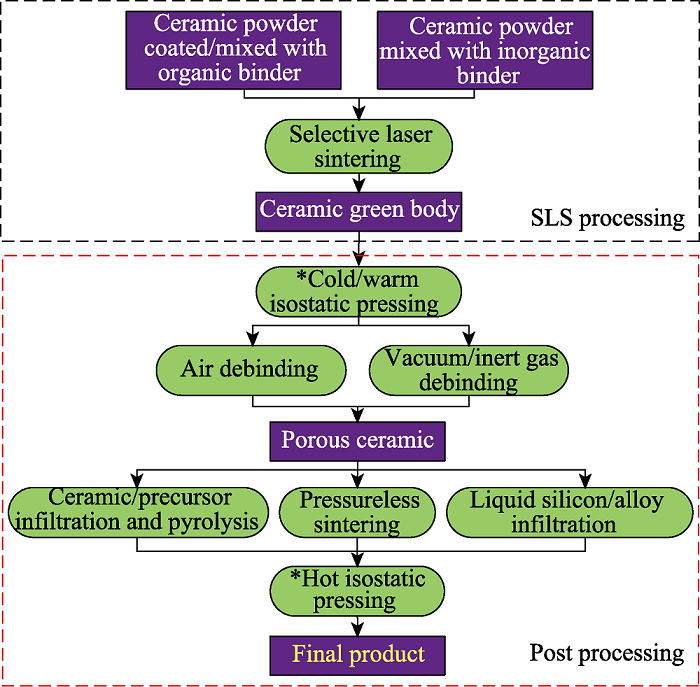
图2 陶瓷零件SLS工艺流程及其它后处理工艺[1]
Fig. 2 Process of SLS and its post-treatment process for ceramic[1] The process marked with asterisk * is optional. SLS: Selective laser sintering

图3 SLS结合等静压制备ZrO2陶瓷零件及其微观形貌[28]
Fig. 3 ZrO2 ceramic parts and their morphologies prepared by SLS combined with isostatic pressing[28] (a, d) ZrO2 ceramic green bodies and their morphologies printed by SLS; (b) Warm isostatic pressure equipment; (c, e) ZrO2 ceramics and their microstructures after warm isostatic pressing sintering. SLS: Selective laser sintering; WIP: Warm isostatic pressing

图4 SiC陶瓷及其复合材料零件SLS制备过程[33,36-37]
Fig. 4 Preparation process of SiC ceramics and its composite parts by SLS[33,36-37] (a-d) Reaction sintering of Cf/SiC ceramic matrix composites by SLS technology; (e-h) SLS preparation process of SiC/SiC ceramics PF: Phenolic resin; Cf: Carbon fiber; SLS: Selective laser sintering; LSI: Liquid silicon infiltration; PIP: Precusor infiltration pyrolysis
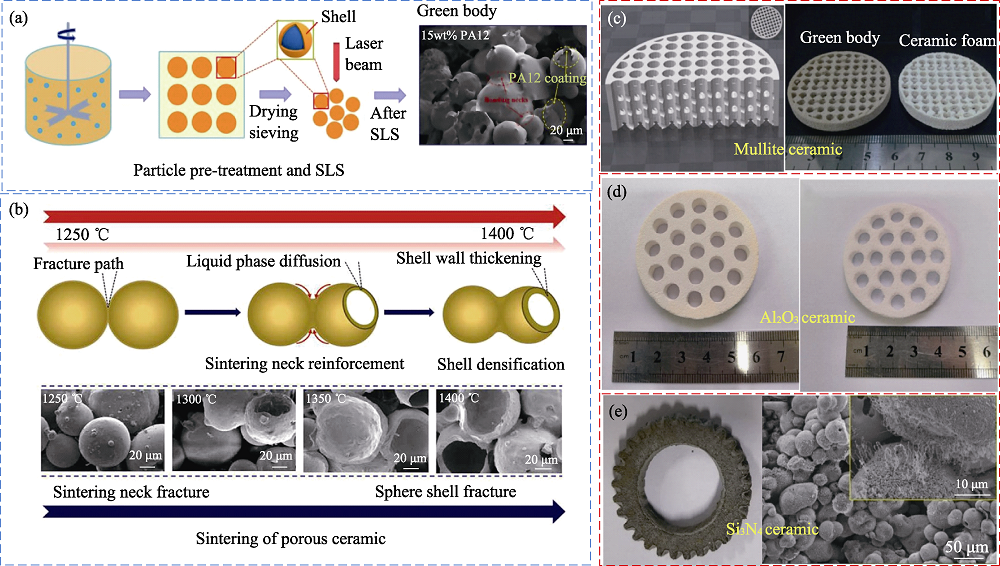
图5 多孔陶瓷SLS制备方法[38,39,40,41]
Fig. 5 Methods of porous ceramic by SLS technology[38,39,40,41] (a) Pre-treatment of ceramic particles and SLS; (b) Sintering of porous ceramic;(c) Porous mullite ceramic; (d) Porous Al2O3 ceramic; (e) Porous Si3N4 ceramic; SLS: Selective laser sintering

图6 SLS打印的多孔陶瓷在生物医学上的应用
Fig. 6 Application of porous ceramic by SLS technology in biomedicine (a, b) CC-PLLA porous skull scaffolds and their mechanical properties[43]; (c, d) Porous biological ceramic scaffolds and their micromorphologies[48] SLS: Selective laser sintering
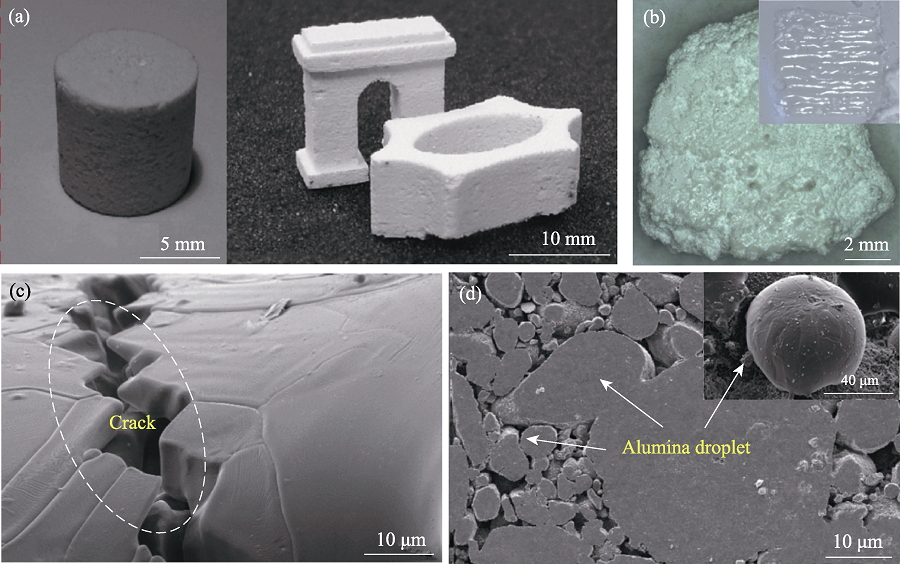
图8 SLM打印的陶瓷及其微观缺陷[51,52]
Fig. 8 Ceramics and their microdefects printed by selective laser melting[51,52] (a) ZrO2 sample; (b, c) Al2O3 samples and cracks; (d) Un-melted alumina balls

图9 SLM陶瓷基体内部闭气孔和表面凹点形成的原因[54]
Fig. 9 Formation of closed pores and pits of ceramic by SLM[54] (a) SLM printing process and Al2O3/GdAlO3/ZrO2 ternary eutectic ceramics; (b) Formation process of the closed pores and pits
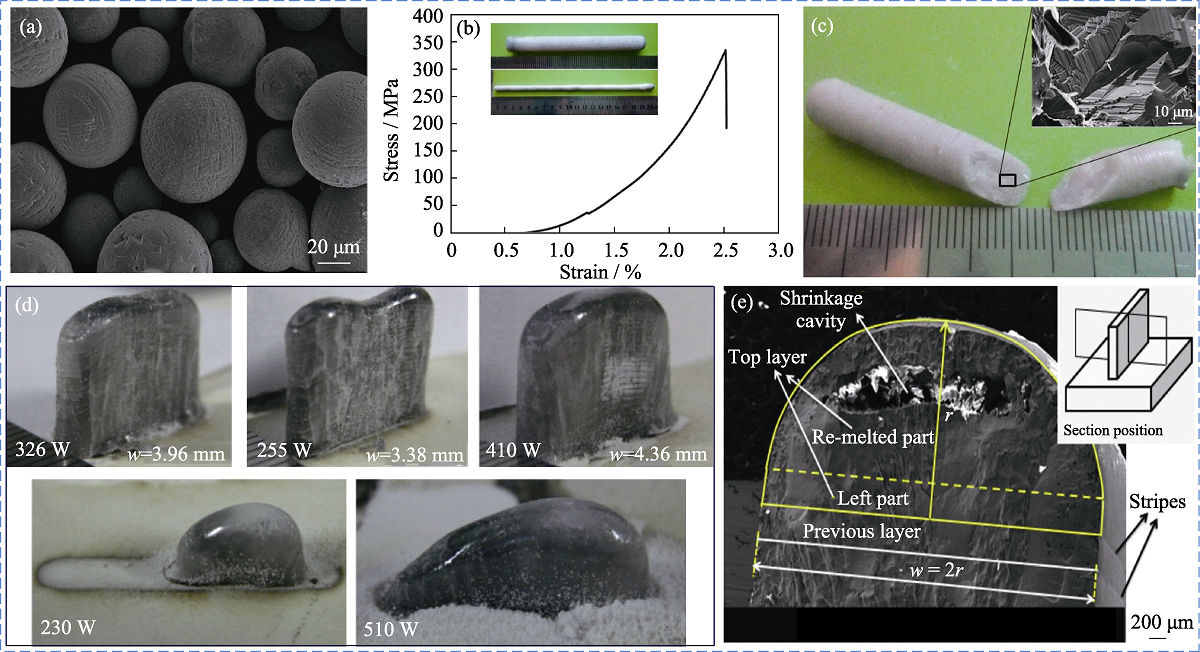
图11 LENS打印的陶瓷试样[62,67]
Fig. 11 Ceramic printed by LENS[62,67] (a) Al2O3 spherical particles; (b, c) Large-sized cylindrical Al2O3 ceramic, stress-strain curve and fracture morphology of Al2O3 ceramic; (d) Single-bead wall part fabricated with different laser power; (e) Typical geometry of the cross-section of a single-bead wall part

图12 Al2O3/GdAlO3/ZrO2共晶陶瓷[70]
Fig. 12 Al2O3/GdAlO3/ZrO2 eutectic ceramics[70] (a) Ceramic shaping process; (b) Eutectic ceramic sample; (c) Annealed eutectic ceramic sample
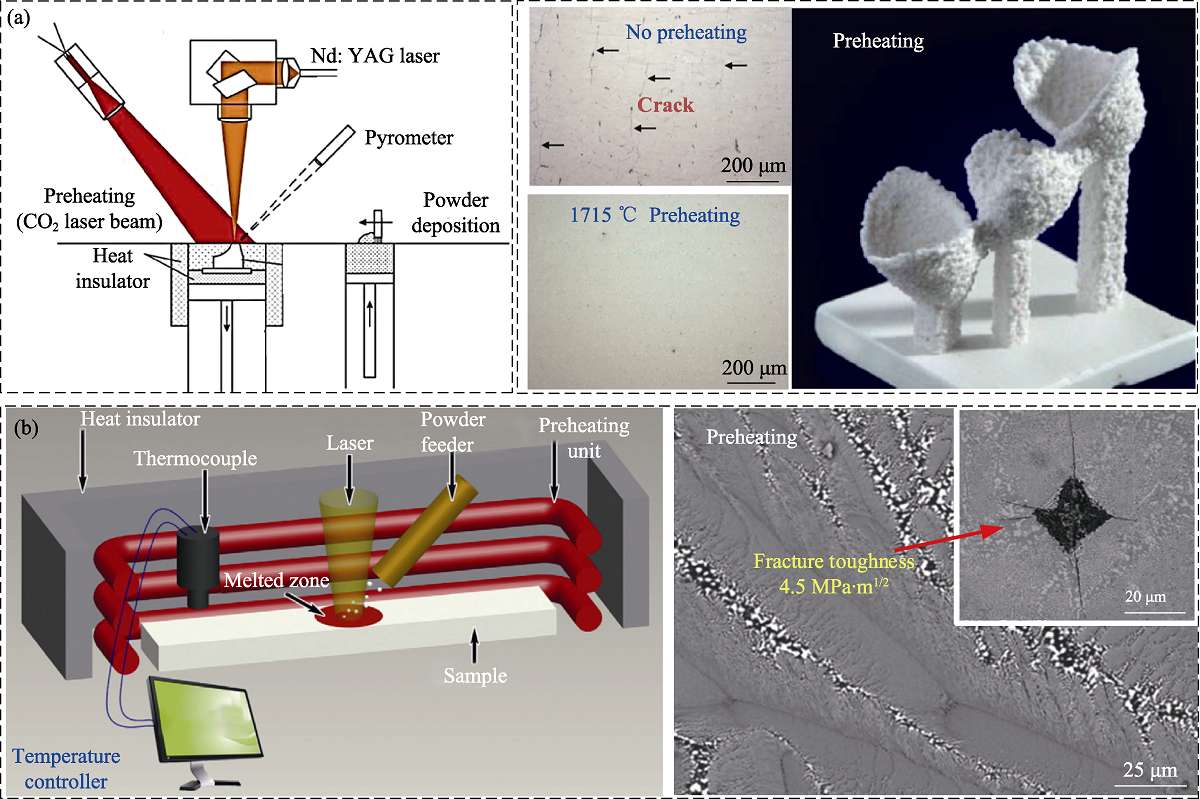
图13 SLM-CO2激光预热方式和LENS-感应预热方式及其制备的陶瓷
Fig. 13 CO2 laser preheating method, induction preheating method and prepared ceramics (a) CO2 laser preheating method and ZrO2/Al2O3 ceramic prepared by SLM[77]; (b) Induction preheating method and ZrO2/Al2O3 ceramic prepared by LENS[75]
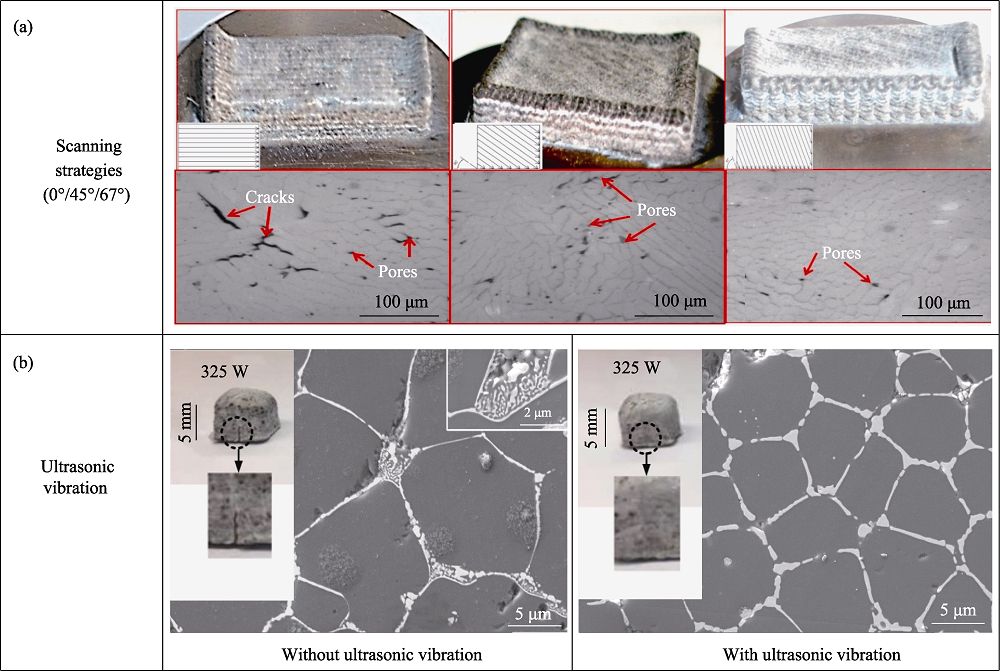
图14 扫描策略和超声振动对裂纹缺陷的影响[63,78]
Fig. 14 Effect of scanning strategy and ultrasonic vibration on the crack defects[63,78] (a) Scanning strategy; (b) Ultrasonic vibration
| Technology | Raw materials | Post-treatment | Dimensional accuracy | Ref. | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PBF | SLS | Al2O3, ZrO2, Si3N4, SiC, Cf/SiC, Si3N4-SiC/SiO2, mullite, porous bio-ceramics such as PA-PEEK, HA-PC, CC-PLLA, etc. | Debinding, isostatic pressing/infiltration pyrolysis, pressureless sintering/reactive sintering | High | [ |
| SLM | Al2O3, ZrO2, ZrO2/Al2O3, MoSi2-Si3N4, ZrB2/ZrC, Al2O3-based eutectic ceramics | None | Low | [ | |
| DED | LENS | Al2O3, ZrO2/Al2O3, Al2O3-based eutectic ceramics | None | Low | [ |
表1 基于粉末成形的激光增材制造陶瓷技术对比
Table 1 Comparation of powder-based laser additive manufacturing technologies of ceramics
| Technology | Raw materials | Post-treatment | Dimensional accuracy | Ref. | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PBF | SLS | Al2O3, ZrO2, Si3N4, SiC, Cf/SiC, Si3N4-SiC/SiO2, mullite, porous bio-ceramics such as PA-PEEK, HA-PC, CC-PLLA, etc. | Debinding, isostatic pressing/infiltration pyrolysis, pressureless sintering/reactive sintering | High | [ |
| SLM | Al2O3, ZrO2, ZrO2/Al2O3, MoSi2-Si3N4, ZrB2/ZrC, Al2O3-based eutectic ceramics | None | Low | [ | |
| DED | LENS | Al2O3, ZrO2/Al2O3, Al2O3-based eutectic ceramics | None | Low | [ |
| [1] |
CHEN Z, LI Z, LI J, et al. 3D printing of ceramics: a review. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2019, 39(4): 661-687.
DOI URL |
| [2] |
RASAKI S A, XIONG D, XIONG S, et al. Photopolymerization- based additive manufacturing of ceramics: a systematic review. Journal of Advanced Ceramics, 2021, 10(3): 442-471.
DOI URL |
| [3] |
LU Z, CAO J, SONG Z, et al. Research progress of ceramic matrix composite parts based on additive manufacturing technology. Virtual and Physical Prototyping, 2019, 14(4): 333-348.
DOI URL |
| [4] |
PFEIFFER S, FLORIO K, PUCCIO D, et al. Direct laser additive manufacturing of high performance oxide ceramics: a state-of-the-art review. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2021, 41(13): 6087-6014.
DOI URL |
| [5] | DECKARD C R. Method and Apparatus for Producing Parts by Selective Sintering. U.S. Patent. No.4863538. 1989.09.05. |
| [6] | LAKSHMINARAYAN U, OGRYDIZIAK S, MARCUS H. Selective Laser Sintering of Ceramic Materials. 1990 International Solid Freeform Fabrication Symposium, Austin, 1990: 16-26. |
| [7] | LAKSHMINARAYAN U, MARCUS H. Microstructural and Mechanical Properties of Al2O3/P2O5 and Al2O3/B2O3 Composties Fabricated by Selective Laser Sintering. 1991 International Solid Freeform Fabrication Symposium, Austin, 1991: 205-212. |
| [8] |
CLARE A, CHALKER P, DAVIES S, et al. Selective laser sintering of barium titanate-polymer composite films. Journal of Materials Science, 2008, 43(9): 3197-3202.
DOI URL |
| [9] |
TAN K, CHUA C, LEONG K, et al. Scaffold development using selective laser sintering of polyetheretherketone-hydroxyapatite biocomposite blends. Biomaterials, 2003, 24(18): 3115-3123.
DOI URL |
| [10] |
GAO C, YANG B, HU H, et al. Enhanced sintering ability of biphasic calcium phosphate by polymers used for bone scaffold fabrication. Materials Science and Engineering: C, 2013, 33(7): 3802-3810.
DOI URL |
| [11] |
LEE I. Densification of porous Al2O3-Al4B2O9 ceramic composites fabricated by SLS process. Journal of Materials Science Letters, 1999, 18(19): 1557-1561.
DOI URL |
| [12] | HARLAN N, PARK S M, BOURELL D L, et al. Selective Laser Sintering of Zirconia with Micro-scale Features. 1999 International Solid Freeform Fabrication Symposium, Austin, 1999: 297-302. |
| [13] |
TANG H H. Direct laser fusing to form ceramic parts. Rapid Prototyping Journal, 2002, 8(5): 284-289.
DOI URL |
| [14] |
XIAO K, DALGARNO K, WOOD D, et al. Indirect selective laser sintering of apatite-wollostonite glass-ceramic. Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, Part H: Journal of Engineering in Medicine, 2008, 222(7): 1107-1114.
DOI URL |
| [15] |
LIU J, ZHANG B, YAN C, et al. The effect of processing parameters on characteristics of selective laser sintering dental glass-ceramic powder. Rapid Prototyping Journal, 2010, 16(2): 138-145.
DOI URL |
| [16] | SHI Y S, CHENG D, LIU J H, et al. Al2O3/SiO2 composite ceramic parts by selective laser sintering. Journal of Huazhong University of Science and Technology (Nature Science Edition), 2007, 35(11): 20-23. |
| [17] |
YVES-CHRISTIAN H, JAN W, WILHELM M, et al. Net shaped high performance oxide ceramic parts by selective laser melting. Physics Procedia, 2010, 5: 587-594.
DOI URL |
| [18] | VAIL N K, BALASUBRAMANIAN B, BARLOW J W, et al. A thermal model of polymer degradation during selective laser sintering of polymer coated ceramic powders. Rapid Prototyping Journal, 1996, 2(3): 24-40. |
| [19] |
CHEN A N, WU J M, LIU K, et al. High-performance ceramic parts with complex shape prepared by selective laser sintering: a review. Advances in Applied Ceramics, 2017, 117(2): 100-117.
DOI URL |
| [20] | WU J M, CHEN A N, LIU M Y, et al. Preparation of ceramic materials used for selective laser sintering and related forming methods. Materials China, 2017, 36(Z1): 575-582. |
| [21] |
TANG H H, CHIU M L, YEN H C. Slurry-based selective laser sintering of polymer-coated ceramic powders to fabricate high strength alumina parts. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2011, 31(8): 1383-1388.
DOI URL |
| [22] |
FRIEDEL T, TRAVITZKY N, NIEBLING F, et al. Fabrication of polymer derived ceramic parts by selective laser curing. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2005, 25(2/3): 193-197.
DOI URL |
| [23] | WOHLERT M, BOURELL D. Rapid Prototyping of Mg/SiC Composites by a Combined SLS and Pressureless Infiltration Process. 1996 Solid Freeform Fabrication Symposium, Austin, 1996: 79-88. |
| [24] |
DECKERS J, KRUTH J P, SHAHZAD K, et al. Density improvement of alumina parts produced through selective laser sintering of alumina-polyamide composite powder. CIRP Annals- Manufacturing Technology, 2012, 61(1): 211-214.
DOI URL |
| [25] |
DECKERS J, SHAHZAD K, VLEUGELS J, et al. Isostatic pressing assisted indirect selective laser sintering of alumina components. Rapid Prototyping Journal, 2012, 18(5): 409-419.
DOI URL |
| [26] |
SHAHZAD K, DECKERS J, KRUTH J P, et al. Additive manufacturing of alumina parts by indirect selective laser sintering and post processing. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 2013, 213(9): 1484-1494.
DOI URL |
| [27] |
DECKERS J P, SHAHZAD K, CARDON L, et al. Shaping ceramics through indirect selective laser sintering. Rapid Prototyping Journal, 2016, 22(3): 544-558.
DOI URL |
| [28] |
SHAHZAD K, DECKERS J, ZHANG Z, et al. Additive manufacturing of zirconia parts by indirect selective laser sintering. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2014, 34(1): 81-89.
DOI URL |
| [29] |
WANG K, BAO C, ZHANG C, et al. Preparation of high-strength Si3N4 antenna window using selective laser sintering. Ceramics International, 2021, 47(22): 31277-31285.
DOI URL |
| [30] | SHI Y S, LIU K, HE W T, et al. Densification of alumina components via indirect selective laser sintering combined with isostatic pressing. Applied Laser, 2013(1): 7-12. |
| [31] | DU Y Y, SHI Y S, WEI Q S. Technology and simulation of cold isostatic pressing of selective laser sintered parts. Laser Technology, 2014, 38(1): 96-100. |
| [32] | HE W T, WEI Q S, LIU K, et al. The application of numerical simulation in the SLS/CIP process of alumina ceramics. Materials Science & Technology, 2014, 22(4): 56-60. |
| [33] |
ZHU W, FU H, XU Z, et al. Fabrication and characterization of carbon fiber reinforced SiC ceramic matrix composites based on 3D printing technology. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2018, 38(14): 4604-4613.
DOI URL |
| [34] |
FU H, ZHU W, XU Z, et al. Effect of silicon addition on the microstructure, mechanical and thermal properties of Cf/SiC composite prepared via selective laser sintering. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2019, 792: 1045-1053.
DOI URL |
| [35] |
YU S, ZENG T, PAN X, et al. Fabrication of Si3N4-SiC/SiO2 composites using 3D printing and infiltration processing. Ceramics International, 2021, 47(20): 28218-28225.
DOI URL |
| [36] |
JIN L, ZHANG K, XU T, et al. The fabrication and mechanical properties of SiC/SiC composites prepared by SLS combined with PIP. Ceramics International, 2018, 44(17): 20992-20999.
DOI URL |
| [37] | ZHANG K, ZENG T, XU G, et al. Mechanical properties of SiCp/SiC composite lattice core sandwich panels fabricated by 3D printing combined with precursor impregnation and pyrolysis. Composite Structures, 2020, 240: 12060. |
| [38] |
WEI Z H, CHENG L J, MA Y X, et al. Direct fabrication mechanism of pre-sintered Si3N4 ceramic with ultra-high porosity by laser additive manufacturing. Scripta Materialia, 2019, 173: 91-95.
DOI URL |
| [39] |
CHEN A N, LI M, WU J M, et al. Enhancement mechanism of mechanical performance of highly porous mullite ceramics with bimodal pore structures prepared by selective laser sintering. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2019, 776: 486-494.
DOI URL |
| [40] |
WU J M, LI M, LIU S S, et al. Preparation of porous Al2O3 ceramics with enhanced properties by SLS using Al2O3 poly-hollow microspheres (PHMs) coated with CaSiO3 sintering additive. Ceramics International, 2020, 46(17): 26888-26894.
DOI URL |
| [41] |
CHEN A N, GAO F, LI M, et al. Mullite ceramic foams with controlled pore structures and low thermal conductivity prepared by SLS using core-shell structured polyamide12/FAHSs composites. Ceramics International, 2019, 45(12): 15538-15546.
DOI URL |
| [42] |
SONG X, LI W, SONG P, et al. Selective laser sintering of aliphatic-polycarbonate/hydroxyapatite composite scaffolds for medical applications. The International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 2015, 81(1-4): 15-25.
DOI URL |
| [43] |
GAYER C, RITTER J, BULLEMER M, et al. Development of a solvent-free polylactide/calcium carbonate composite for selective laser sintering of bone tissue engineering scaffolds. Materials Science and Engineering: C, 2019, 101: 660-673.
DOI URL |
| [44] |
CHUNG H, DAS S. Functionally graded Nylon-11/silica nanocomposites produced by selective laser sintering. Materials Science and Engineering: A, 2008, 487(1/2): 251-257.
DOI URL |
| [45] |
LORRISON J, DALGARNO K, WOOD D. Processing of an apatite-mullite glass-ceramic and an hydroxyapatite/phosphate glass composite by selective laser sintering. Journal of Materials Science: Materials in Medicine, 2005, 16(8): 775-781.
DOI URL |
| [46] |
GOODRIDGE R, DALGARNO K, WOOD D. Indirect selective laser sintering of an apatite-mullite glass-ceramic for potential use in bone replacement applications. Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, Part H: Journal of Engineering in Medicine, 2006, 220(1): 57-68.
DOI URL |
| [47] |
GOODRIDGE R D, WOOD D J, OHTSUKI C, et al. Biological evaluation of an apatite-mullite glass-ceramic produced via selective laser sintering. Acta Biomaterialia, 2007, 3(2): 221-231.
DOI URL |
| [48] |
DUAN B, WANG M, ZHOU W Y, et al. Three-dimensional nanocomposite scaffolds fabricated via selective laser sintering for bone tissue engineering. Acta Biomater, 2010, 6(12): 4495-4505.
DOI URL |
| [49] |
SCHLEIFENBAUM H, MEINERS W, WISSENBACH K, et al. Individualized production by means of high power selective laser melting. CIRP Journal of Manufacturing Science and Technology, 2010, 2(3): 161-169.
DOI URL |
| [50] |
MERCELIS P, KRUTH J P. Residual stresses in selective laser sintering and selective laser melting. Rapid Prototyping Journal, 2006, 12(5): 254-265.
DOI URL |
| [51] |
SHISHKOVSKY I, YADROITSEV I, BERTRAND P, et al. Alumina-zirconium ceramics synthesis by selective laser sintering/ melting. Applied Surface Science, 2007, 254(4): 966-970.
DOI URL |
| [52] |
DECKERS J, MEYERS S, KRUTH J P, et al. Direct selective laser sintering/melting of high density alumina powder layers at elevated temperatures. Physics Procedia, 2014, 56 117-124.
DOI URL |
| [53] |
BERTRAND P, BAYLE F, COMBE C, et al. Ceramic components manufacturing by selective laser sintering. Applied Surface Science, 2007, 254(4): 989-992.
DOI URL |
| [54] |
LIU H, SU H, SHEN Z, et al. Effect of scanning speed on the solidification process of Al2O3/GdAlO3/ZrO2 eutectic ceramics in a single track by selective laser melting. Ceramics International, 2019, 45(14): 17252-17257.
DOI URL |
| [55] |
MÜHLER T, GOMES C M, HEINRICH J, et al. Slurry-based additive manufacturing of ceramics. International Journal of Applied Ceramic Technology, 2015, 12(1): 18-25.
DOI URL |
| [56] |
GAHLER A, HEINRICH J G, GUENSTER J. Direct laser sintering of Al2O3-SiO2 dental ceramic components by layer-wise slurry deposition. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2006, 89(10): 3076-3080.
DOI URL |
| [57] | MÜHLER T, GOMES C, ASCHERI M, et al. Slurry-based powder beds for the selective laser sintering of silicate ceramics. J. Ceram. Sci. Technol., 2015, 6(2): 113-118. |
| [58] |
TIAN X, GÜNSTER J, MELCHER J, et al. Process parameters analysis of direct laser sintering and post treatment of porcelain components using Taguchi's method. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2009, 29(10): 1903-1915.
DOI URL |
| [59] |
LI Y, HU Y, CONG W, et al. Additive manufacturing of alumina using laser engineered net shaping: effects of deposition variables. Ceramics International, 2017, 43(10): 7768-7775.
DOI URL |
| [60] |
BALLA V K, BOSE S, BANDYOPADHYAY A. Processing of bulk alumina ceramics using laser engineered net shaping. International Journal of Applied Ceramic Technology, 2008, 5(3): 234-242.
DOI URL |
| [61] | GRIFFITH M, KEICHER D, ATWOOD C, et al. Free Form Fabrication of Metallic Components Using Laser Engineered Net Shaping (LENS). 1996 Solid Freeform Fabrication Symposium, Austin, 1996. |
| [62] |
NIU F, WU D, LU F, et al. Microstructure and macro properties of Al2O3 ceramics prepared by laser engineered net shaping. Ceramics International, 2018, 44(12): 14303-14310.
DOI URL |
| [63] |
HU Y, NING F, CONG W, et al. Ultrasonic vibration-assisted laser engineering net shaping of ZrO2-Al2O3 bulk parts: effects on crack suppression, microstructure, and mechanical properties. Ceramics International, 2018, 44(3): 2752-2760.
DOI URL |
| [64] |
NIU F, WU D, MA G, et al. Nanosized microstructure of Al2O3-ZrO2(Y2O3) eutectics fabricated by laser engineered net shaping. Scripta Materialia, 2015, 95: 39-41.
DOI URL |
| [65] |
NIU F, WU D, MA G, et al. Rapid fabrication of eutectic ceramic structures by laser engineered net shaping. Procedia CIRP, 2016, 42: 91-95.
DOI URL |
| [66] |
YAN S, WU D, MA G, et al. Nano-sized Al2O3-ZrO2 eutectic ceramic structures prepared by ultrasonic-assisted laser engineered net shaping. Materials Letters, 2018, 212: 8-11.
DOI URL |
| [67] |
NIU F, WU D, ZHOU S, et al. Power prediction for laser engineered net shaping of Al2O3 ceramic parts. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2014, 34(15): 3811-3817.
DOI URL |
| [68] |
YAN S, WU D, NIU F, et al. Effect of ultrasonic power on forming quality of nano-sized Al2O3-ZrO2 eutectic ceramic via laser engineered net shaping (LENS). Ceramics International, 2018, 44(1): 1120-1126.
DOI URL |
| [69] |
SU H J, ZHANG J, LIU L, et al. Rapid growth and formation mechanism of ultrafine structural oxide eutectic ceramics by laser direct forming. Applied Physics Letters, 2011, 99(22): 221913.
DOI URL |
| [70] | LIU H, SU H, SHEN Z, et al. Preparation of large-size Al2O3/GdAlO3/ZrO2 ternary eutectic ceramic rod by laser directed energy deposition and its microstructure homogenization mechanism. Journal of Materials Science & Technology, 2021, 85: 218-223. |
| [71] |
LIU H, SU H, SHEN Z, et al. One-step additive manufacturing and microstructure evolution of melt-grown Al2O3/GdAlO3/ZrO2 eutectic ceramics by laser directed energy deposition. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2021, 41(6): 3547-3558.
DOI URL |
| [72] |
WILKES J, HAGEDORN Y C, MEINERS W, et al. Additive manufacturing of ZrO2-Al2O3 ceramic components by selective laser melting. Rapid Prototyping Journal, 2013, 19(1): 51-57.
DOI URL |
| [73] | AGGARANGSI P, BEUTH J L. Localized Preheating Approaches for Reducing Residual Stress in Additive Manufacturing. International Solid Freeform Fabrication Symposium, Austin, 2006. |
| [74] | HAGEDORN Y, BALACHANDRAN N, MEINERS W, et al. SLM of Net-shaped High Strength Ceramics: New Opportunities for Producing Dental Restorations. Proceedings of the Solid Freeform Fabrication Symposium, Austin, 2011: 536-546. |
| [75] | LIU Z, SONG K, GAO B, et al. Microstructure and mechanical properties of Al2O3/ZrO2 directionally solidified eutectic ceramic prepared by laser 3D printing. Journal of Materials Science & Technology, 2016, 32(4): 320-325. |
| [76] | WILKES J, HAGEDORN Y C, OCYLOK S, et al. Rapid Manufacturing of Ceramic Parts by Selective Laser Melting. Ceramic Engineering and Science Proceedings, Wiley-Blackwell, United States, 2010. |
| [77] |
WILKES J, HAGEDORN Y C, MEINERS W, et al. Additive manufacturing of ZrO2-Al2O3 ceramic components by selective laser melting. Rapid Prototyping Journal, 2013, 19(1): 51-57.
DOI URL |
| [78] |
MISHRA G K, PAUL C P, RAI A K, et al. Experimental investigation on laser directed energy deposition based additive manufacturing of Al2O3 bulk structures. Ceramics International, 2021, 47(4): 5708-5720.
DOI URL |
| [79] |
MEYERS S, DE LEERSNIJDER L, VLEUGELS J, et al. Direct laser sintering of reaction bonded silicon carbide with low residual silicon content. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2018, 38(11): 3709-3717.
DOI URL |
| [80] | DUBINENKO G E, ZINOVIEV A L, BOLBASOV E N, et al. Preparation of poly(l-lactic acid)/hydroxyapatite composite scaffolds by fused deposit modeling 3D printing. Materials Today: Proceedings, 2020, 22: 228-234. |
| [81] |
MINASYAN T, LIU L, HOLOVENKO Y, et al. Additively manufactured mesostructured MoSi2-Si3N4 ceramic lattice. Ceramics International, 2019, 45(8): 9926-9933.
DOI URL |
| [82] |
HONG M H, MIN B K, LEE D H, et al. Marginal fit of metal-ceramic crowns fabricated by using a casting and two selective laser melting processes before and after ceramic firing. Journal of Prosthetic Dentistry, 2019, 122(5): 475-481.
DOI URL |
| [83] |
KING D, MIDDENDORF J, CISSEL K, et al. Selective laser melting for the preparation of an ultra-high temperature ceramic coating. Ceramics International, 2019, 45(2): 2466-2473.
DOI URL |
| [1] | 朱文杰, 唐璐, 陆继长, 刘江平, 罗永明. 钙钛矿型氧化物催化氧化挥发性有机化合物的研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(7): 735-746. |
| [2] | 余艺平, 肖鹏, 赵长浩, 徐梦迪, 姚立冬, 李伟, 王松. 耐高温层状Ta/Ta0.5Hf0.5C金属陶瓷的高频等离子体风洞烧蚀行为研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(7): 790-798. |
| [3] | 余乐洋阳, 赵芳霞, 张舒心, 徐以祥, 牛亚然, 张振忠, 郑学斌. 感应等离子球化技术制备喷涂用高熵硼化物粉体[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(7): 808-816. |
| [4] | 魏志帆, 陈国清, 祖宇飞, 刘渊, 李明浩, 付雪松, 周文龙. ZrB2-HfSi2复相陶瓷显微组织及其核-周结构形成机制[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(7): 817-825. |
| [5] | 胡智超, 杨鸿宇, 杨鸿程, 孙成礼, 杨俊, 李恩竹. P-V-L键理论在微波介质陶瓷性能调控中的应用[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(6): 609-626. |
| [6] | 何国强, 张恺恒, 王震涛, 包健, 席兆琛, 方振, 王昌昊, 王威, 王鑫, 姜佳沛, 李祥坤, 周迪. Ba(Nd1/2Nb1/2)O3: 一种被低估的K40微波介质陶瓷[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(6): 639-646. |
| [7] | 张家维, 陈宁, 程原, 王博, 朱建国, 金城. Bi4Ti3O12铋层状压电陶瓷的A/B位掺杂及其电学性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(6): 690-696. |
| [8] | 唐莹, 李洁, 相怀成, 方维双, 林慧兴, 杨俊峰, 方亮. Rattling效应: 一种影响微波介质陶瓷谐振频率温度系数的新机制[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(6): 656-666. |
| [9] | 吴琼, 沈炳林, 张茂华, 姚方周, 邢志鹏, 王轲. 铅基织构压电陶瓷研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(6): 563-574. |
| [10] | 张碧辉, 刘小强, 陈湘明. Ruddlesden-Popper结构杂化非常规铁电体的研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(6): 587-608. |
| [11] | 吴杰, 杨帅, 王明文, 李景雷, 李纯纯, 李飞. 铅基织构压电陶瓷的发展历程、现状与挑战[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(6): 575-586. |
| [12] | 周阳阳, 张艳艳, 于子怡, 傅正钱, 许钫钫, 梁瑞虹, 周志勇. 通过Bi3+自掺杂增强CaBi4Ti4O15基陶瓷压电性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(6): 719-728. |
| [13] | 杨燕, 张发强, 马名生, 王墉哲, 欧阳琪, 刘志甫. 基于CuO-TiO2-Nb2O5复合氧化物烧结助剂的ZnAl2O4陶瓷低温烧结研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(6): 711-718. |
| [14] | 黄子鹏, 贾文晓, 李玲霞. (Ti0.5W0.5)5+掺杂MgNb2O6陶瓷的晶体结构与太赫兹介电性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(6): 647-655. |
| [15] | 姜昆, 李乐天, 郑木鹏, 胡永明, 潘勤学, 吴超峰, 王轲. PZT陶瓷的低温烧结研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(6): 627-638. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||