
Journal of Inorganic Materials ›› 2024, Vol. 39 ›› Issue (11): 1212-1220.DOI: 10.15541/jim20240130
Special Issue: 【能源环境】储能电池(202506); 【信息功能】MAX、MXene及其他二维材料(202506); 【能源环境】超级电容器(202409)
• RESEARCH ARTICLE • Previous Articles Next Articles
CHAO Shaofei1( ), XUE Yanhui1, WU Qiong1(
), XUE Yanhui1, WU Qiong1( ), WU Fufa1, MUHAMMAD Sufyan Javed2, ZHANG Wei3
), WU Fufa1, MUHAMMAD Sufyan Javed2, ZHANG Wei3
Received:2024-03-19
Revised:2024-06-18
Published:2024-11-20
Online:2024-07-15
Contact:
WU Qiong, professor. E-mail: wuqiong9918@126.comAbout author:CHAO Shaofei (2000-), male, Master candidate. E-mail: mxenemax@126.com
Supported by:CLC Number:
CHAO Shaofei, XUE Yanhui, WU Qiong, WU Fufa, MUHAMMAD Sufyan Javed, ZHANG Wei. Efficient Potassium Storage through Ti-O-H-O Electron Fast Track of MXene Heterojunction[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(11): 1212-1220.
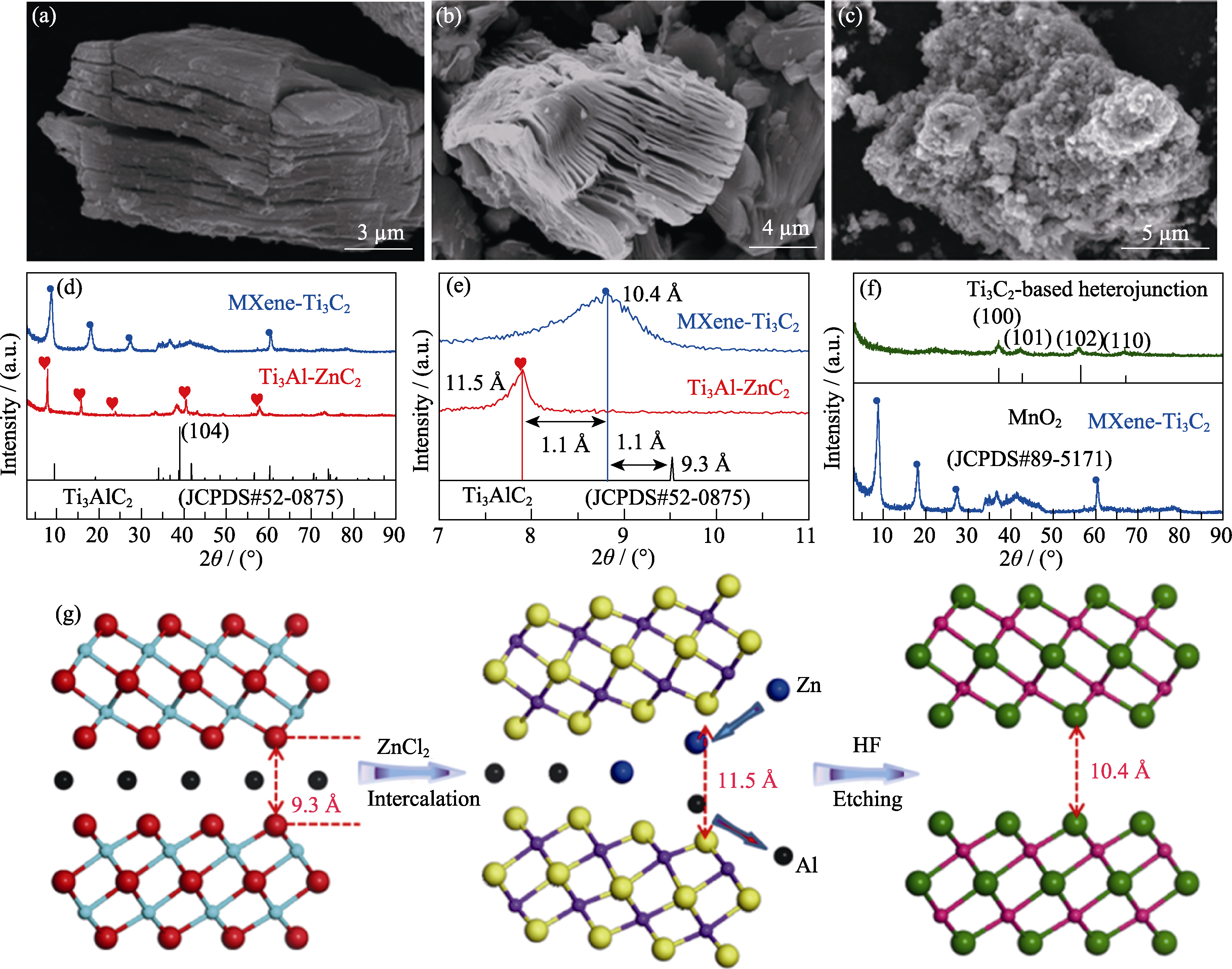
Fig. 1 Structure and morphology characterization of Ti3C2-based heterojunction (a-c) SEM images of (a) Ti3Al-ZnC2, (b) Ti3C2 and (c) Ti3C2-based heterojunction; (d-f) XRD patterns of Ti3Al-ZnC2, Ti3C2 and Ti3C2-based heterojunction; (g) Atomic structure diagram of preparation of Ti3C2 Colorful figures are available on website
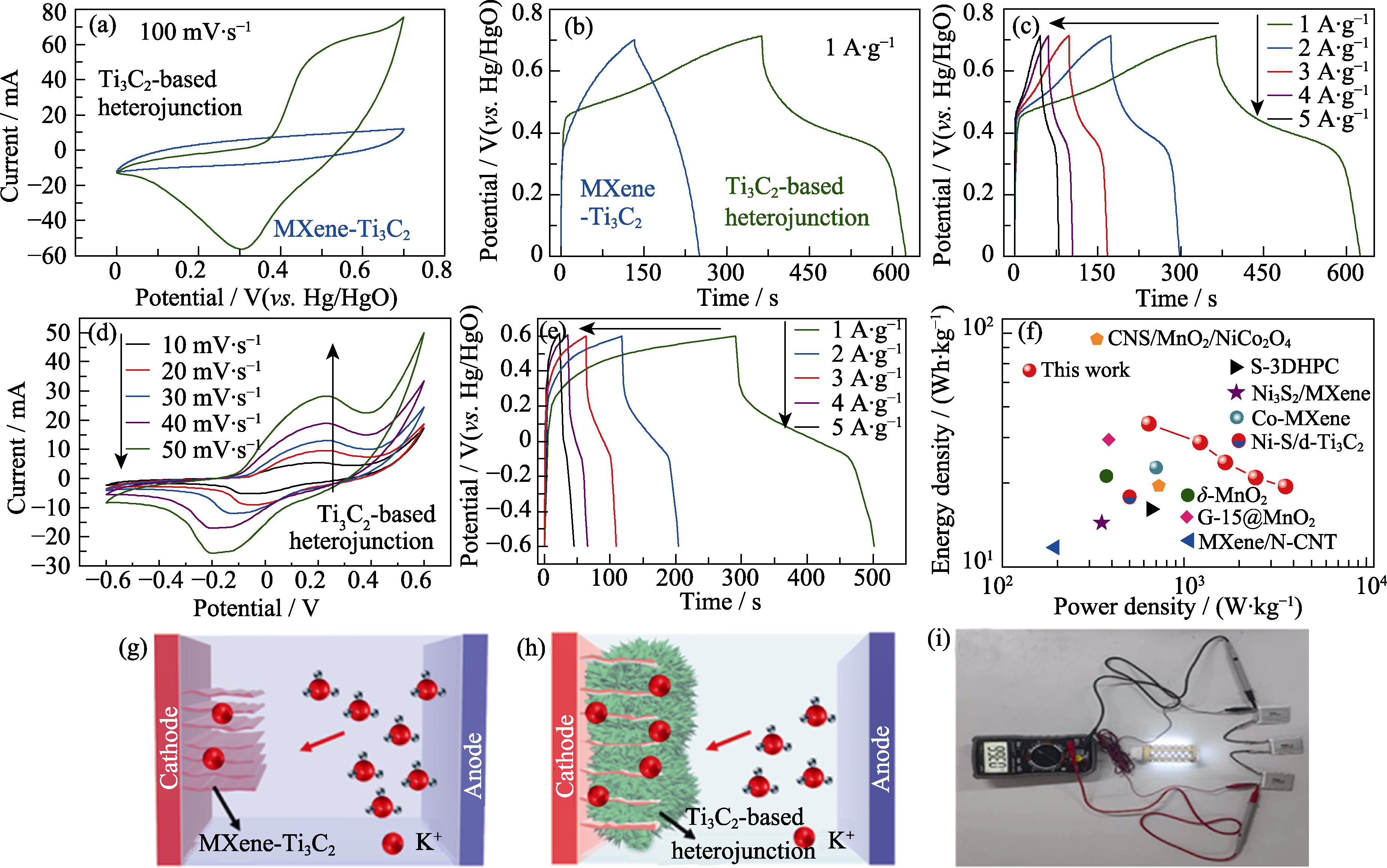
Fig. 3 Electrochemical potassium storage performance tests of Ti3C2-based heterojunction (a) CV curves of Ti3C2 and Ti3C2-based heterojunction in a three-electrode system at a scan rate of 100 mV·s-1; (b) GCD curves of Ti3C2 and Ti3C2-based heterojunction at a current density of 1 A·g-1; (c) GCD curves of Ti3C2-based heterojunction at different current densities; (d) CV curves and (e) GCD curves of Ti3C2-based heterojunction in a double electrode system; (f) Ragone plot of energy density and power density[37⇓⇓⇓⇓⇓⇓-44]; (g, h) Schematic diagrams of two hybrid supercapacitors; (i) Practical application of Ti3C2-based heterojunction hybrid supercapacitors Colorful figures are available on website
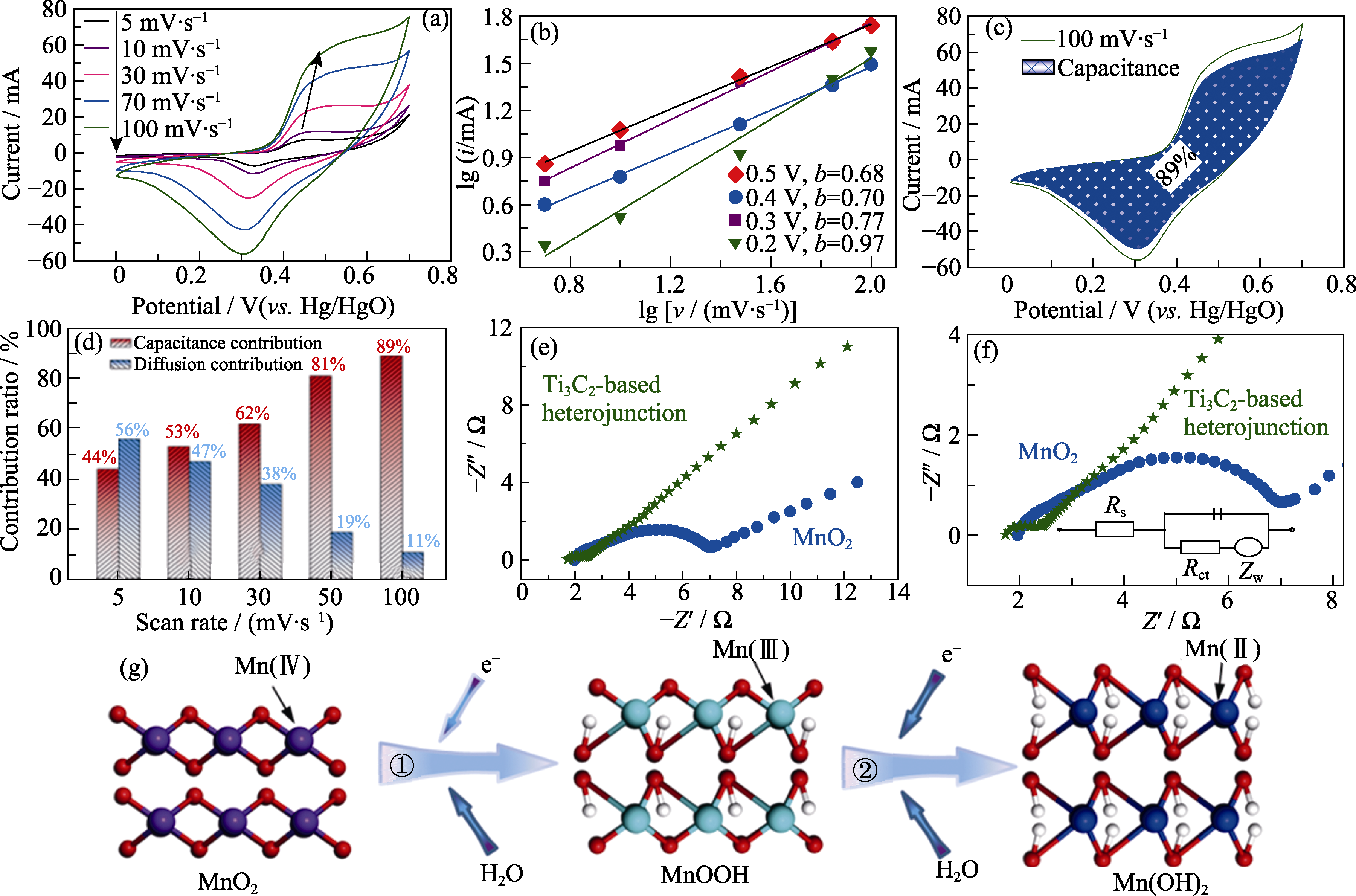
Fig. 4 Dynamic analysis and energy storage mechanism of Ti3C2-based heterojunction (a) CV curves of Ti3C2-based heterojunction at different scanning rates; (b) Relationship between the peak current and the scanning rate at a specific potential; (c) Pseudocapacitance ratio diagram of Ti3C2-based heterojunction at 100 mV·s-1; (d) Pseudocapacitance ratio of Ti3C2-based heterojunction at different scanning rates; (e) EIS plots of Ti3C2-based heterojunction and MnO2; (f) Magnified plots of a region in (e) with inset showing corresponding equivalent circuit; (g) Schematic diagram of mechanism of pseudocapacitance changed with Mn valence Colorful figures are available on website
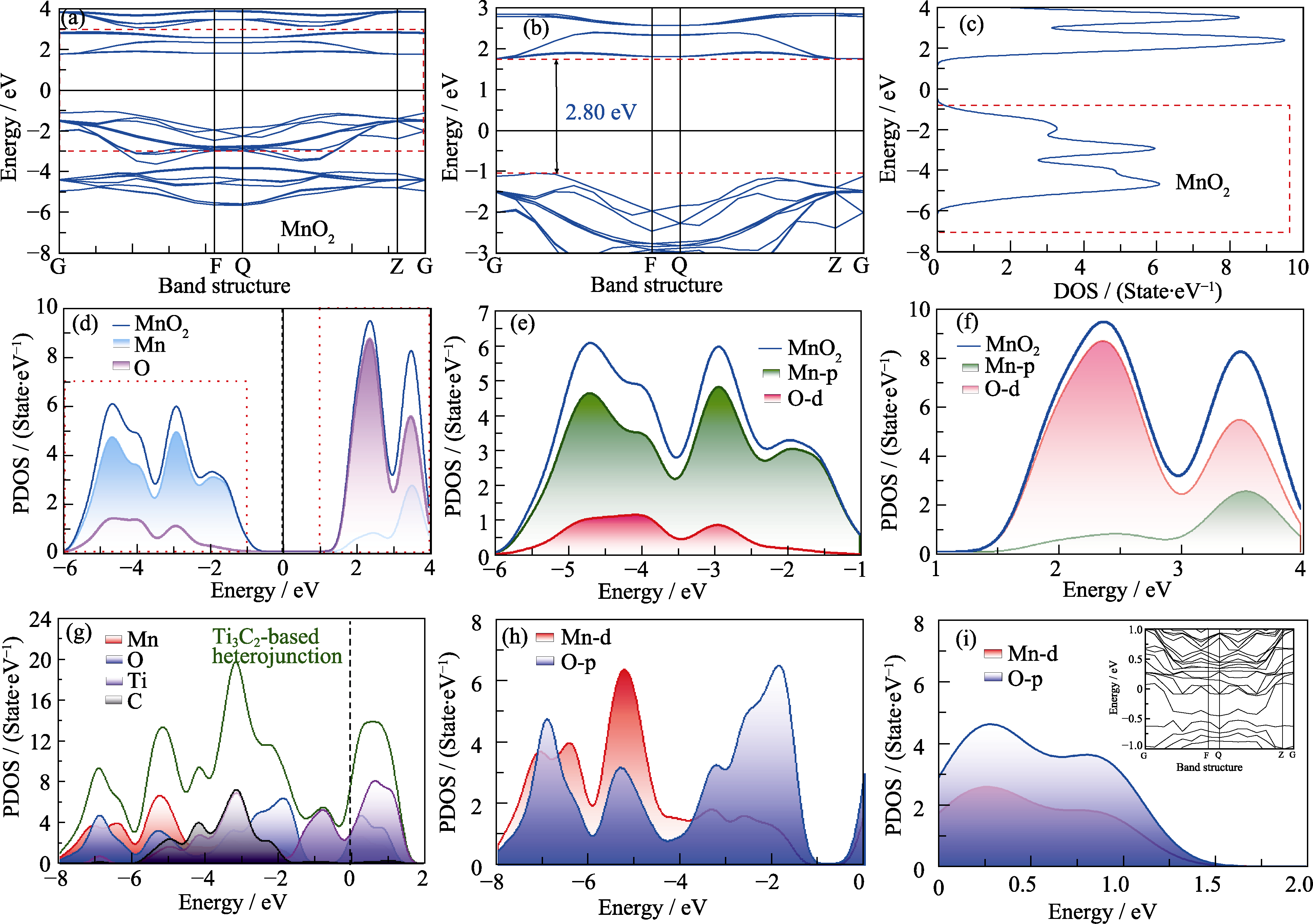
Fig. 6 Electron band structure and state density diagrams of Ti3C2-based heterojunction (a, b) Band structure diagrams of MnO2; (c) DOS diagram of MnO2; (d) PDOS diagrams of Mn and O atoms in MnO2; (e, f) PDOS diagrams of the distribution of electron orbitals of Mn and O atoms in valence and conduction bands; (g) PDOS diagram of each atom in Ti3C2-based heterojunction; (h) PDOS diagrams of Mn and O atoms in valence band of Ti3C2-based heterojunction; (i) PDOS diagrams of Mn and O atoms in conduction band of Ti3C2-based heterojunction with inset showing the band structure diagram of Ti3C2-based heterojunction Colorful figures are available on website
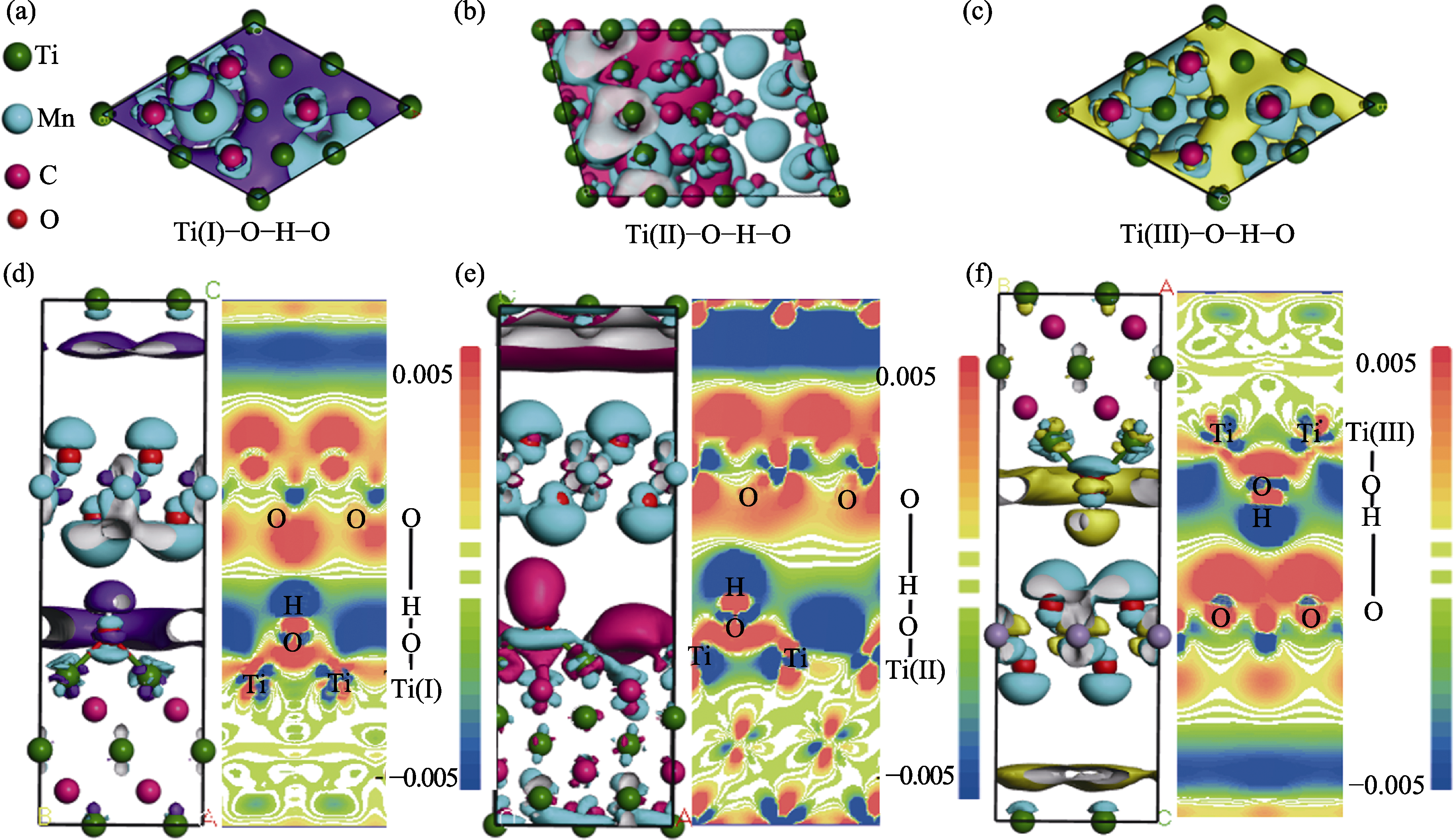
Fig. 7 Differential charge density diagrams of Ti3C2-based heterojunction (a-c) 3D top views of differential charge density diagrams of three heterojunctions; (d-f) 3D differential charge density and 2D differential charge density section diagrams of (d) Ti(I), (e) Ti(Ⅱ) and (f) Ti(Ⅲ) connected heterojunction with MnO2 Colorful figures are available on website
| [1] | WU Q, XUE Y, CHAO S, et al. Moiré superlattice MXene nanosheets constructed from twisted hexagon-Ti3AlC2 by microwave-assisted Lewis molten salt etching: implications for structural stability in electrochemical energy storage. ACS Applied Nano Materials, 2022, 6(1): 677. |
| [2] |
LI S, CHEN J, XIONG J, et al. Encapsulation of MnS nanocrystals into N, S-co-doped carbon as anode material for full cell sodium-ion capacitors. Nano-Micro Letters, 2020, 12: 34.
DOI PMID |
| [3] | XU Z, WU M, CHEN Z, et al. Direct structure-performance comparison of all-carbon potassium and sodium ion capacitors. Advanced Science, 2019, 6(12): 1802272. |
| [4] | LIANG J, RAWAL A, YU M, et al. Low-potential solid-solid interfacial charging on layered polyaniline anode for high voltage pseudocapacitive intercalation Li-ion supercapacitors. Nano Energy, 2023, 105: 108010. |
| [5] | TANG H, YAO J, ZHU Y. Recent developments and future prospects for zinc-ion hybrid capacitors: a review. Advanced Energy Materials, 2021, 11(14): 2003994. |
| [6] | LI T, ZHAO H, LI C, et al. Recent progress and prospects in anode materials for potassium-ion capacitors. New Carbon Materials, 2021, 36(2): 253. |
| [7] | CUI Y, ZHAO L, LI B, et al. Tailored MoS2 bilayer grafted onto N/S-doped carbon for ultra-stable potassium-ion capacitor. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2022, 450: 137815. |
| [8] | ANASORI B, LUKATSKAVA M R, GOGOTSI Y. 2D metal carbides and nitrides (MXenes) for energy storage. Nature Reviews Materials, 2017, 2: 16098. |
| [9] | LUKATSKAVA M R, KOTA S, LIN Z, et al. Ultra-high-rate pseudocapacitive energy storage in two-dimensional transition metal carbides. Nature Energy, 2017, 2(8): 17105. |
| [10] | WAN S, LI X, CHEN Y, et al. Ultrastrong MXene films via the synergy of intercalating small flakes and interfacial bridging. Nature Communications, 2022, 13: 7340. |
| [11] | MENG Y, ZENG P, YANG X Y, et al. Simultaneously achieving enhanced water adsorption and rapid adsorbed hydroxyl transfer toward MXene-based materials for highly efficient alkaline electrocatalytic hydrogen evolution. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2023, 466: 143372. |
| [12] | LIU L, ZSCHIESCHE H, ANTONIETTI M, et al. Tuning the surface chemistry of MXene to improve energy storage: example of nitrification by salt melt. Advanced Energy Materials, 2023, 13(2): 2202709. |
| [13] | LI L, CHENG Q F. Recent advances in the high performance MXenes nanocomposites. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(2): 153. |
| [14] | WANG X, LI N, YIN J, et al. Interface interaction-mediated design of tough and conductive MXene-composited polymer hydrogel with high stretchability and low hysteresis for high-performance multiple sensing. Science China Materials, 2023, 66(1): 272. |
| [15] | PAN Z, JIANG Y, YANG P, et al. In situ growth of layered bimetallic ZnCo hydroxide nanosheets for high-performance all-solid-state pseudocapacitor. ACS Nano, 2018, 12(3): 2968. |
| [16] | LI K, LI J, ZHU Q, et al. Three-dimensional MXenes for supercapacitors: a review. Small Methods, 2022, 6(4): 2101537. |
| [17] |
LU M, HAN W, LI H, et al. There is plenty of space in the MXene layers: the confinement and fillings. Journal of Energy Chemistry, 2020, 48: 344.
DOI |
| [18] | LUO J, WANG C, WANG H, et al. Pillared MXene with ultralarge interlayer spacing as a stable matrix for high performance sodium metal anodes. Advanced Functional Materials, 2019, 29(3): 1805946. |
| [19] | ZHAO J, WEN J, XIAO J, et al. Nb2CTx MXene: high capacity and ultra-long cycle capability for lithium-ion battery by regulation of functional groups. Journal of Energy Chemistry, 2021, 53: 387. |
| [20] | TIAN Y, QUE W, LUO Y, et al. Surface nitrogen-modified 2D titanium carbide (MXene) with high energy density for aqueous supercapacitor applications. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2019, 7(10): 5416. |
| [21] | ZOU Z, WANG Q, ZHU K, et al. Ultrathin-walled Bi2S3 nanoroll/MXene composite toward high capacity and fast lithium storage. Small, 2022, 18(13): 2106673. |
| [22] | CHEN J, REN Y, ZHANG H, et al. Ni-Co-Fe layered double hydroxide coated on Ti3C2 MXene for high-performance asymmetric supercapacitor. Applied Surface Science, 2021, 562: 150116. |
| [23] | TANG H, CHEN W, LI N, et al. Layered MnO2 nanodots as high-rate and stable cathode materials for aqueous zinc-ion storage. Energy Storage Materials, 2022, 48: 335. |
| [24] | HAN M, YAO J, HUANG J, et al. Synergistic chemical and electrochemical strategy for high-performance Zn//MnO2 batteries. Chinese Chemical Letters, 2023, 34(2): 107493. |
| [25] | WANG J, GUO W, LIU Z, et al. Engineering of self-aggregation- resistant MnO2 heterostructure with a built-in field for enhanced high-mass-loading energy storage. Advanced Energy Materials, 2023, 13(20): 2300224. |
| [26] | DAI Y, ZHANG J, YAN X, et al. Investigating the electrochemical performance of MnO2 polymorphs as cathode materials for aqueous proton batteries. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2023, 471: 144158. |
| [27] | LI X L, ZHU J F, JIAO Y H, et al. Manganese dioxide morphology on electrochemical performance of Ti3C2Tx@MnO2 composites. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2020, 35(1): 119. |
| [28] | TANG Y, ZHENG S, XU Y, et al. Advanced batteries based on manganese dioxide and its composites. Energy Storage Materials, 2018, 12: 284. |
| [29] | WANG J, WANG J G, LIU H, et al. Zinc ion stabilized MnO2 nanospheres for high capacity and long lifespan aqueous zinc-ion batteries. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2019, 7(22): 13727. |
| [30] | JABLONSKIENE J, SIMKUNAITE D, VAICIUNIENE J, et al. Synthesis of carbon-supported MnO2 nanocomposites for supercapacitors application. Crystals, 2021, 11(7): 784. |
| [31] | CLARK S J, SEGALL M D, PICKAD C J, et al. First principles methods using CASTEP. Zeitschrift für Kristallographie - Crystalline Materials, 2005, 220(5/6): 567. |
| [32] | YU M, YANG S, WU C, et al. Machine learning the Hubbard U parameter in DFT+U using Bayesian optimization. npj Computational Materials, 2020, 6: 180. |
| [33] |
LI Y, SHAO H, LIN Z, et al. A general Lewis acidic etching route for preparing MXenes with enhanced electrochemical performance in non-aqueous electrolyte. Nature Materials, 2020, 19(8): 894.
DOI PMID |
| [34] | ZHU X, CAO Z, WANG W, et al. Superior-performance aqueous zinc-ion batteries based on the in situ growth of MnO2 nanosheets on V2CTX MXene. ACS Nano, 2021, 15(2): 2971. |
| [35] | WANG D, GAO Y, LIU Y, et al. Investigation of chloride ion adsorption onto Ti2C MXene monolayers by first-principles calculations. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2017, 5(47): 24720. |
| [36] | XU C, XU B, GU Y, et al. Graphene-based electrodes for electrochemical energy storage. Energy & Environmental Science, 2013, 6(5): 1388. |
| [37] | XI S, CHENG X, GAO X, et al. Simple fabrication of Ti3C2/MnO2 composites as cathode material for high capacity and long cycle lifespan Zn-ion batteries. Energy Technology, 2023, 11(7): 2300122. |
| [38] | WANG Q, YUAN H, ZHANG M, et al. A highly conductive and supercapacitive MXene/N-CNT electrode material derived from a MXene-Co-melamine precursor. ACS Applied Electronic Materials, 2023, 5(5): 2506. |
| [39] | YAN S, WANG Q, LUO S, et al. Coal-based S hybrid self-doped porous carbon for high-performance supercapacitors and potassium- ion batteries. Journal of Power Sources, 2020, 461: 228151. |
| [40] | SI L, XIA Q, LIU K, et al. Hydrothermal synthesis of layered NiS2/Ti3C2Tx composite electrode for supercapacitors. Materials Chemistry and Physics, 2022, 291: 126733. |
| [41] | HONG X, DENG C, WANG X, et al. Carbon nanosheets/MnO2/ NiCo2O4 ternary composite for supercapacitor electrodes. Journal of Energy Storage, 2022, 53: 105086. |
| [42] | KUNWAR J, ACHARYA D, CHHETRI K, et al. Cobalt oxide decorated 2D MXene: a hybrid nanocomposite electrode for high- performance supercapacitor application. Journal of Electroanalytical Chemistry, 2023, 950: 117915. |
| [43] | LUO Y, YANG C, TIAN Y, et al. A long cycle life asymmetric supercapacitor based on advanced nickel-sulfide/titanium carbide (MXene) nanohybrid and MXene electrodes. Journal of Power Sources, 2020, 450: 227694. |
| [44] | ZHANG X, ZHANG F, WEI D, et al. Design and synthesis of K-doped tremella-like δ-MnO2 for high-performance supercapacitor. Journal of Energy Storage, 2023, 72: 108468. |
| [45] | FENG Y, ZHANG M, YAN H, et al. Microwave-assisted efficient exfoliation of MXene and its composite for high-performance supercapacitors. Ceramics International, 2022, 48(7): 9518. |
| [46] | ZHANG Y, CHEN P, WANG Q, et al. High-capacity and kinetically accelerated lithium storage in MoO3 enabled by oxygen vacancies and heterostructure. Advanced Energy Materials, 2021, 11(31): 2101712. |
| [47] | WEN S, LEE J W, YEO I H, et al. The role of cations of the electrolyte for the pseudocapacitive behavior of metal oxide electrodes, MnO2 and RuO2. Electrochimica Acta, 2004, 50(2/3): 849. |
| [48] | SONG L, DUAN Y, ZHANG Y, et al. Promoting defect formation and microwave loss properties in δ-MnO2via Co doping: a first- principles study. Computational Materials Science, 2017, 138: 288. |
| [49] | ZHOU Y, ZHOU Z, HU L, et al. A facile approach to tailor electrocatalytic properties of MnO2 through tuning phase transition, surface morphology and band structure. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2022, 438: 135561. |
| [50] | XIAO M X, LI M M, SONG E H, et al. Halogenated Ti3C2 MXene as high capacity electrode material for Li-ion batteries. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(6): 660. |
| [51] | JIN X, SHIN S J, KIM N, et al. Superior role of MXene nanosheet as hybridization matrix over graphene in enhancing interfacial electronic coupling and functionalities of metal oxide. Nano Energy, 2018, 53: 841. |
| [1] | YANG Endong, LI Baole, ZHANG Ke, TAN Lu, LOU Yongbing. ZnCo2O4-ZnO@C@CoS Core-shell Composite: Preparation and Application in Supercapacitors [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(5): 485-493. |
| [2] | DING Ling, JIANG Rui, TANG Zilong, YANG Yunqiong. MXene: Nanoengineering and Application as Electrode Materials for Supercapacitors [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(6): 619-633. |
| [3] | WANG Shiyi, FENG Aihu, LI Xiaoyan, YU Yun. Pb (II) Adsorption Process of Fe3O4 Supported Ti3C2Tx [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(5): 521-528. |
| [4] | SUN Peng, ZHANG Shaoning, BI Hui, DONG Wujie, HUANG Fuqiang. Tuning Nitrogen Species and Content in Carbon Materials through Constructing Variable Structures for Supercapacitors [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(7): 766-772. |
| [5] | LIU Fangfang, CHUAN Xiuyun, YANG Yang, LI Aijun. Influence of N/S Co-doping on Electrochemical Property of Brucite Template Carbon Nanotubes [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(7): 711-717. |
| [6] | WANG Yiliang, AI Yunlong, YANG Shuwei, LIANG Bingliang, ZHENG Zhenhuan, OUYANG Sheng, HE Wen, CHEN Weihua, LIU Changhong, ZHANG Jianjun, LIU Zhiyong. Facile Synthesis and Supercapacitor Performance of M3O4(M=FeCoCrMnMg) High Entropy Oxide Powders [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(4): 425-430. |
| [7] | LI Zehui,TAN Meijuan,ZHENG Yuanhao,LUO Yuyang,JING Qiushi,JIANG Jingkun,LI Mingjie. Application of Conductive Metal Organic Frameworks in Supercapacitors [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2020, 35(7): 769-780. |
| [8] | CHEN Jun,MA Pei-Hua,ZHANG Cheng,Laurent RUHLMANN,LYU Yao-Kang. Preparation and Electrochemical Property of New Multifunctional Inorganic/Organic Composite Film [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2020, 35(2): 217-223. |
| [9] | FEI Mingjie, ZHANG Renping, ZHU Guisheng, YU Zhaozhe, YAN Dongliang. Preparation and Pseudocapacitive Properties of Phosphate Ion-doped MnFe2O4 [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2020, 35(10): 1137-1141. |
| [10] | DING Zhuofeng, YANG Yongqiang, LI Zaijun. Synthesis and Supercapacitor Performance of Histidine-functionalized Carbon Dots/Graphene Aerogel [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2020, 35(10): 1130-1136. |
| [11] | MA Ya-Nan, LIU Yu-Fei, YU Chen-Xu, ZHANG Chuan-Kun, LUO Shi-Jun, GAO Yi-Hua. Monolayer Ti3C2Tx Nanosheets with Different Lateral Dimension: Preparation and Electrochemical Property [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2020, 35(1): 93-98. |
| [12] | LI Teng-Fei, HUANG Lu-Jun, YAN Xu-Dong, LIU Qing-Lei, GU Jia-Jun. Ti3C2Tx/Wood Carbon as High-areal-capacity Electrodes for Supercapacitors [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2020, 35(1): 126-130. |
| [13] | ZHANG Tian-Yu, CUI Cong, CHENG Ren-Fei, HU Min-Min, WANG Xiao-Hui. Fabrication of Planar Porous MXene/Carbon Composite Electrodes by Simultaneous Ammonization/Carbonization [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2020, 35(1): 112-118. |
| [14] | Wei-Jia XU, Da-Ping QIU, Shi-Qiang LIU, Min LI, Ru YANG. Preparation of Cork-derived Porous Activated Carbon for High Performance Supercapacitors [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2019, 34(6): 625-632. |
| [15] | Wei LIU, Kai ZHENG, Dong-Hong WANG, Yi-San LEI, Huai-Lin FAN. Co3O4 Nanowire Arrays@Activated Carbon Fiber Composite Materials: Facile Hydrothermal Synthesis and Its Electrochemical Application [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2019, 34(5): 487-492. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||