
Journal of Inorganic Materials ›› 2019, Vol. 34 ›› Issue (5): 487-492.DOI: 10.15541/jim20180343
Previous Articles Next Articles
Wei LIU1,2,3,Kai ZHENG2,Dong-Hong WANG1,2,Yi-San LEI1,2( ),Huai-Lin FAN3
),Huai-Lin FAN3
Received:2018-07-26
Revised:2018-10-30
Published:2019-05-20
Online:2019-05-14
Supported by:CLC Number:
Wei LIU, Kai ZHENG, Dong-Hong WANG, Yi-San LEI, Huai-Lin FAN. Co3O4 Nanowire Arrays@Activated Carbon Fiber Composite Materials: Facile Hydrothermal Synthesis and Its Electrochemical Application[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2019, 34(5): 487-492.
| Samples | Stotal /(m2·g-1) | Smicropore /(m2·g-1) | Vtotal /(m3·g-1) | Vmicropore /(m3·g-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Co3O4@ACF-1 | 153 | 80 | 0.21 | 0.03 |
| Co3O4@ACF-2 | 177 | 103 | 0.26 | 0.04 |
| Co3O4@ACF-5 | 32 | - | 0.15 | - |
| p-Co3O4 | 20 | - | 0.07 | - |
| v-ACF | 785 | 693 | 0.43 | 0.33 |
Table 1 Specific surface areas and pore volumes of v-ACF, p-Co3O4 and the Co3O4@ACF composites
| Samples | Stotal /(m2·g-1) | Smicropore /(m2·g-1) | Vtotal /(m3·g-1) | Vmicropore /(m3·g-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Co3O4@ACF-1 | 153 | 80 | 0.21 | 0.03 |
| Co3O4@ACF-2 | 177 | 103 | 0.26 | 0.04 |
| Co3O4@ACF-5 | 32 | - | 0.15 | - |
| p-Co3O4 | 20 | - | 0.07 | - |
| v-ACF | 785 | 693 | 0.43 | 0.33 |
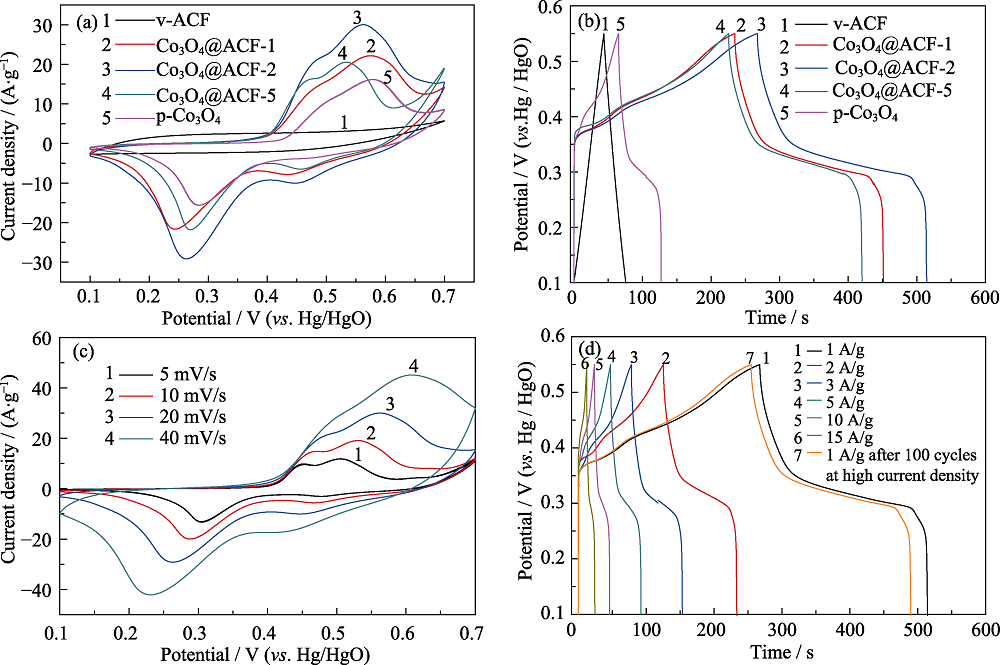
Fig. 5 (a) CV curves of different samples at a scan rate of 20 mV/s; (b) Galvanostatic charge/discharge curves of different samples at 1 A/g; (c) CV curves of Co3O4@ACF-2 at different scan rates; (d) GCD curves of Co3O4@ACF-2 at various current densities
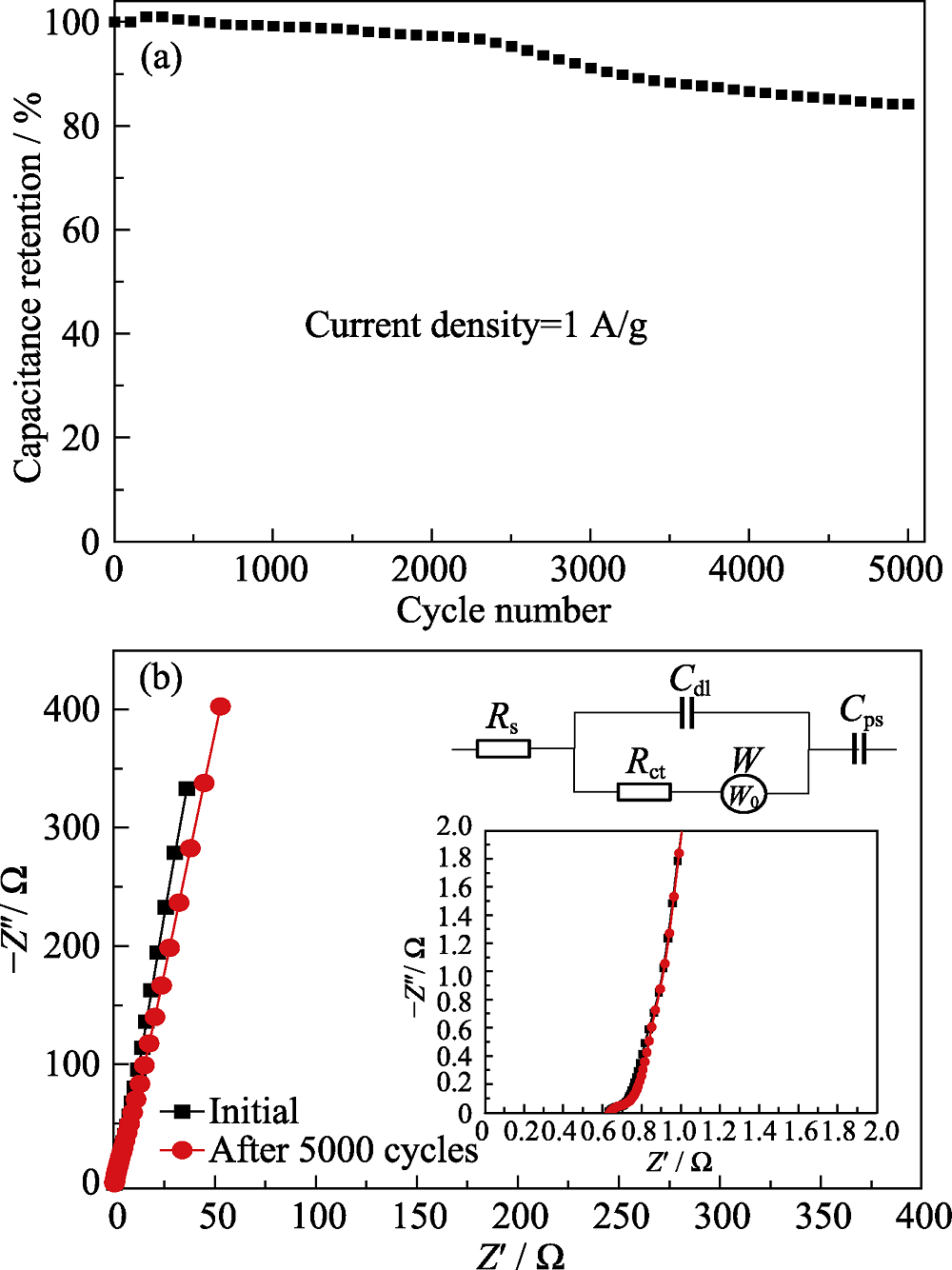
Fig. 7 (a) Cycling stability of the Co3O4@ACF-2 at a density of 1 A/g for 5000 cycles; (b) Nyquist plots of the Co3O4@ACF-2 before and after 5000 cycles with inserts showing magnified plots and equivalent circuit
| [1] | SIMON P, GOGOTSI A Y . Materials for electrochemical capacitors. Nature Materials, 2008,7(11):845-854. |
| [2] | CHEN S M . Recent advancements in electrode materials for the high-performance electrochemical supercapacitors: a review. Internatonal Journal of Electrochemical Science, 2014,9(8):4072-4085. |
| [3] | WANG G, ZHANG L, ZHANG J . A review of electrode materials for electrochemical supercapacitors. Chemical Society Reviews, 2012,41(2):797-828. |
| [4] |
DYATKIN B, PRESSER V, HEON M , et al. Development of a green supercapacitor composed entirely of environmentally friendly materials. ChemSusChem, 2013,6(12):2269-2280.
DOI URL PMID |
| [5] |
FAN H, SHEN W . Gelatin-based microporous carbon nanosheets as high performance supercapacitor electrodes. ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering, 2016,4(3):1328-1337.
DOI URL |
| [6] | TIAN X D, LI X, YANG T , et al. Recent advances on synthesis and supercapacitor application of binary metal oxide. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2017,32(5):461-468. |
| [7] |
WANG C F, LU S, CHEN H L , et al. One-pot synthesis and application in asymmetric supercapacitors of Mn3O4@RGO nanocomposites. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2016,31(6):581-587.
DOI URL |
| [8] |
WANG C W, WANG Y, GRASER J , et al. Solution-based carbohydrate synthesis of individual solid hollow and porous carbon nanospheres using spray pyrolysis. ACS Nano, 2013,7(12):11156-11165.
DOI URL PMID |
| [9] |
LI M, ZHANG Y Q, YANG L L , et al. Hollow melamine resin- based carbon spheres/graphene composite with excellent performance for supercapacitors. Electrochimica Acta, 2015,166:310-319.
DOI URL |
| [10] | DENG D, KIM B S, GOPIRAMAN M , et al. Needle-like MnO2/activated carbon nanocomposites derived from human hair as versatile electrode materials for supercapacitors. RSC Advances, 2015,5(99):81492-81498. |
| [11] |
NAVEEN A N, MANIMARAN P, SELLADURAI S . Cobalt oxide (Co3O4)/graphene nanosheets (GNS) composite prepared by novel route for supercapacitor application. Journal of Materials Science: Materials in Electronics, 2015,26(11):8988-9000.
DOI URL |
| [12] |
HE G Y, LI J H, CHEN H Q , et al. Hydrothermal preparation of Co3O4@graphene nanocomposite for supercapacitor with enhanced capacitive performance. Materials Letters, 2012,82:61-63.
DOI URL |
| [13] |
DENG M G, WANG R Q, FENG Y H . Effect of petroleum coke expanding by HNO3 on the performance of supercapacitor based on the activated carbon. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2014,29(3):1-8.
DOI URL |
| [14] |
WANG R, SUI Y W, HUANG S F , et al. High-performance flexible all-solid-state asymmetric supercapacitors from nanostructured electrodes prepared by oxidation-assisted dealloying protocol. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2018,331:527-535.
DOI URL |
| [15] |
ZHOU X, CHEN Q, WANG A Q , et al. Bamboo-like composites of V2O5/polyindole and activated carbon cloth as electrodes for all-solid-state flexible asymmetric supercapacitors. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2016,8(6):3776-3783.
DOI URL PMID |
| [16] | COTTINEAU T, TOUPIN M, DELAHAYE T , et al. Nanostructured transition metal oxides for aqueous hybrid electrochemical supercapacitors. Applied Physics A-Materials Science & Processing, 2006,82(4):599-606. |
| [17] |
ZHANG C M, XIE L J, SONG W , et al. Electrochemical performance of asymmetric supercapacitor based on Co3O4/AC materials. Journal of Electroanalytical Chemistry, 2013,706(1):1-6.
DOI URL |
| [18] |
XIA X H, TU J P, MAI Y J , et al. Self-supported hydrothermal synthesized hollow Co3O4 nanowire arrays with high supercapacitor capacitance. Journal of Materials Chemistry, 2011,21(25):9319-9325.
DOI URL |
| [19] |
XIE L J, SU F Y, XIE L F , et al. Self-assembled 3D graphene- based aerogel with Co3O4 nanoparticles as high-performance asymmetric supercapacitor electrode. ChemSusChem, 2015,8(17):2917-2926.
DOI URL PMID |
| [20] |
KUMAR N, YU Y C, LU Y H , et al. Fabrication of carbon nanotube/cobalt oxide nanocomposites via electrophoretic deposition for supercapacitor electrodes. Journal of Materials Science, 2016,51(5):2320-2329.
DOI URL |
| [21] | ZHU P, CAI T, HAN G Y , et al. Preparation and electrochemical performance of PPy/GO-RuO2 film electrode for micro- supercapacitor. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2015,30(5):505-510. |
| [22] |
WANG K, ZHAO N, LEI S , et al. Promising biomass-based activated carbons derived from willow catkins for high performance supercapacitors. Electrochimica Acta, 2015,166:1-11.
DOI URL |
| [23] | FENG C, ZHANG J F, HE Y , et al. Sub-3 nm Co3O4 nanofilms with enhanced supercapacitor properties. ACS Nano, 2015,9(2):1730-1739. |
| [24] | MA L, ZHOU H, SHEN X , et al. Facile synthesis of Co3O4 porous nanosheets/reduced graphene oxide composites and their excellent supercapacitor performance. RSC Advanced, 2014,4(95):53180-53187. |
| [1] | YANG Endong, LI Baole, ZHANG Ke, TAN Lu, LOU Yongbing. ZnCo2O4-ZnO@C@CoS Core-shell Composite: Preparation and Application in Supercapacitors [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(5): 485-493. |
| [2] | CHAO Shaofei, XUE Yanhui, WU Qiong, WU Fufa, MUHAMMAD Sufyan Javed, ZHANG Wei. Efficient Potassium Storage through Ti-O-H-O Electron Fast Track of MXene Heterojunction [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(11): 1212-1220. |
| [3] | LI Yuejun, CAO Tieping, SUN Dawei. Bi4O5Br2/CeO2 Composite with S-scheme Heterojunction: Construction and CO2 Reduction Performance [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(8): 963-970. |
| [4] | DING Ling, JIANG Rui, TANG Zilong, YANG Yunqiong. MXene: Nanoengineering and Application as Electrode Materials for Supercapacitors [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(6): 619-633. |
| [5] | NIU Haibin, HUANG Jiahui, LI Qianwen, MA Dongyun, WANG Jinmin. Directly Hydrothermal Growth and Electrochromic Properties of Porous NiMoO4 Nanosheet Films [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(12): 1427-1433. |
| [6] | YAO Yishuai, GUO Ruihua, AN Shengli, ZHANG Jieyu, CHOU Kuochih, ZHANG Guofang, HUANG Yarong, PAN Gaofei. In-situ Loaded Pt-Co High Index Facets Catalysts: Preparation and Electrocatalytic Performance [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(1): 71-78. |
| [7] | ZHANG Xian, ZHANG Ce, JIANG Wenjun, FENG Deqiang, YAO Wei. Synthesis, Electronic Structure and Visible Light Photocatalytic Performance of Quaternary BiMnVO5 [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(1): 58-64. |
| [8] | SUN Peng, ZHANG Shaoning, BI Hui, DONG Wujie, HUANG Fuqiang. Tuning Nitrogen Species and Content in Carbon Materials through Constructing Variable Structures for Supercapacitors [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(7): 766-772. |
| [9] | LIU Fangfang, CHUAN Xiuyun, YANG Yang, LI Aijun. Influence of N/S Co-doping on Electrochemical Property of Brucite Template Carbon Nanotubes [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(7): 711-717. |
| [10] | WANG Yiliang, AI Yunlong, YANG Shuwei, LIANG Bingliang, ZHENG Zhenhuan, OUYANG Sheng, HE Wen, CHEN Weihua, LIU Changhong, ZHANG Jianjun, LIU Zhiyong. Facile Synthesis and Supercapacitor Performance of M3O4(M=FeCoCrMnMg) High Entropy Oxide Powders [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(4): 425-430. |
| [11] | XIAO Yumin, Li Bin, QIN Lizhao, LIN Hua, LI Qing, LIAO Bin. Efficient Preparation of CuGeO3 with Controllable Morphology Using CuCl2 as Copper Source [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(1): 69-74. |
| [12] | WANG Juhan,WEN Xiong,LIU Chengchao,ZHANG Yuhua,ZHAO Yanxi,LI Jinlin. Preparation and Fischer-Tropsch Synthesis Performance of Hierarchical Co/Al-SiO2 Catalyst [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2020, 35(9): 999-1004. |
| [13] | LI Zehui,TAN Meijuan,ZHENG Yuanhao,LUO Yuyang,JING Qiushi,JIANG Jingkun,LI Mingjie. Application of Conductive Metal Organic Frameworks in Supercapacitors [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2020, 35(7): 769-780. |
| [14] | CHEN Jun,MA Pei-Hua,ZHANG Cheng,Laurent RUHLMANN,LYU Yao-Kang. Preparation and Electrochemical Property of New Multifunctional Inorganic/Organic Composite Film [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2020, 35(2): 217-223. |
| [15] | FEI Mingjie, ZHANG Renping, ZHU Guisheng, YU Zhaozhe, YAN Dongliang. Preparation and Pseudocapacitive Properties of Phosphate Ion-doped MnFe2O4 [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2020, 35(10): 1137-1141. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||