
Journal of Inorganic Materials ›› 2019, Vol. 34 ›› Issue (9): 925-932.DOI: 10.15541/jim20180497
Special Issue: 药物载体与防护材料
• RESEARCH PAPER • Previous Articles Next Articles
XIAO Wen-Qian,ZHANG Jing,LI Ke-Jiang,ZOU Xin-Yu,CAI Yu-Dong,LI Bo( ),LIU Xue(
),LIU Xue( ),LIAO Xiao-Ling
),LIAO Xiao-Ling
Received:2018-10-18
Revised:2018-12-24
Published:2019-09-20
Online:2019-05-29
Supported by:CLC Number:
XIAO Wen-Qian,ZHANG Jing,LI Ke-Jiang,ZOU Xin-Yu,CAI Yu-Dong,LI Bo,LIU Xue,LIAO Xiao-Ling. Litchi-like Superparamagnetic Hydroxyapatite Microspheres with Hierarchically Mesoporous Microspheres[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2019, 34(9): 925-932.
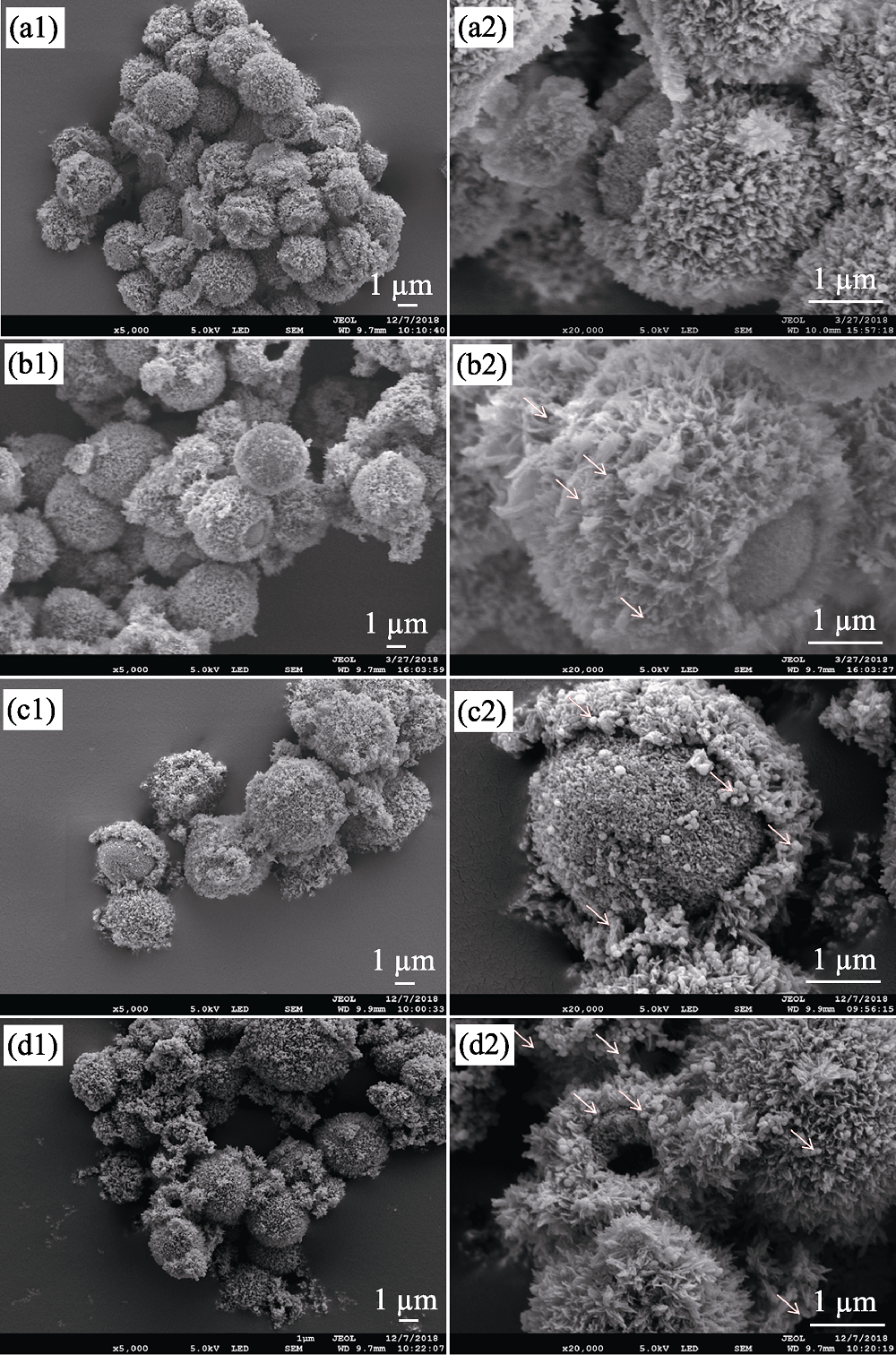

Fig. 1 SEM images of superparamagnetic CaCO3@HA/Fe3O4 microspheres with different Fe3O4 component. Note: S0 (a1, a2), S1 (b1, b2), S2 (c1, c2), S3 (d1, d2)
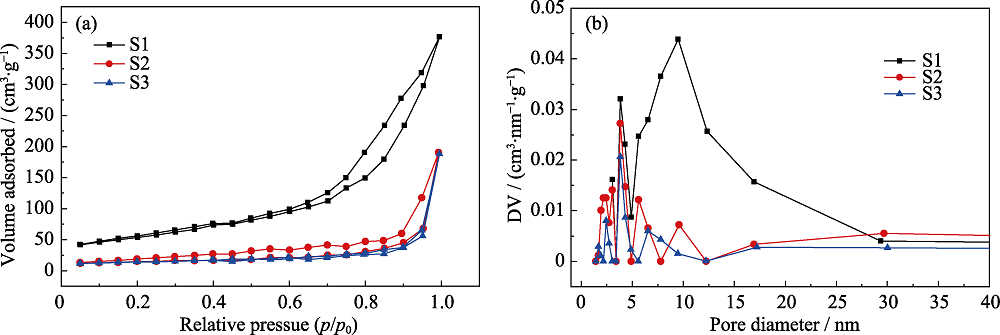
Fig. 5 Typical nitrogen isothermal adsorption curves (a) and mesopore distribution (b) analysis of CaCO3@HA/Fe3O4 microspheres with different Fe3O4 content
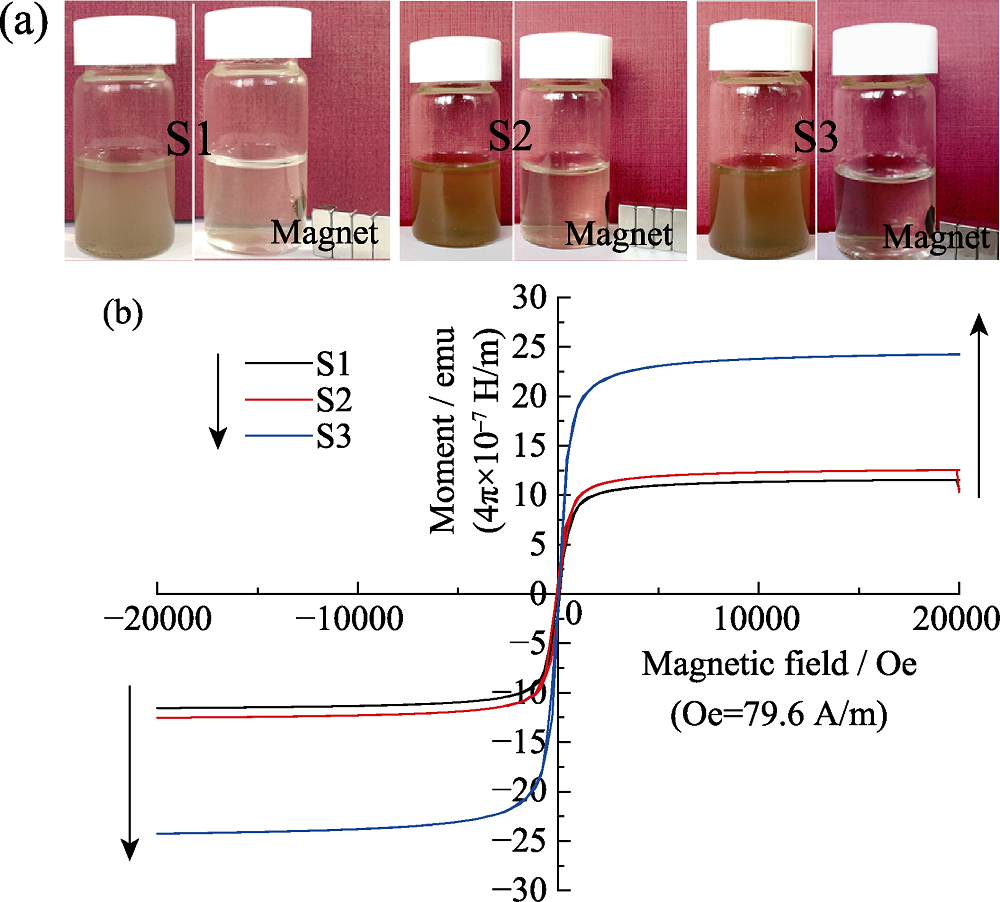
Fig. 7 Digital photographs (a) of the litchi-like CaCO3@HA/Fe3O4 magnetic HA microspheres in aqueous suspension and (b) magnetization of different samples as a function of the applied field measured at 300 K
| Sample | Fe3O4 content/wt% | SBET /(m2·g-1) | DLA /(mg·g-1) | DLE/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| S1 | 16.08 | 196.481 | 96.88 | 96.88 |
| S2 | 17.69 | 50.749 | 96.14 | 96.14 |
| S3 | 37.98 | 46.623 | 97.96 | 97.96 |
Table 1 Fe3O4 content, specific surface area (SBET), drug loading amount (DLA) and drug loading efficiency (DLE) of CaCO3@HA/Fe3O4 microspheres
| Sample | Fe3O4 content/wt% | SBET /(m2·g-1) | DLA /(mg·g-1) | DLE/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| S1 | 16.08 | 196.481 | 96.88 | 96.88 |
| S2 | 17.69 | 50.749 | 96.14 | 96.14 |
| S3 | 37.98 | 46.623 | 97.96 | 97.96 |
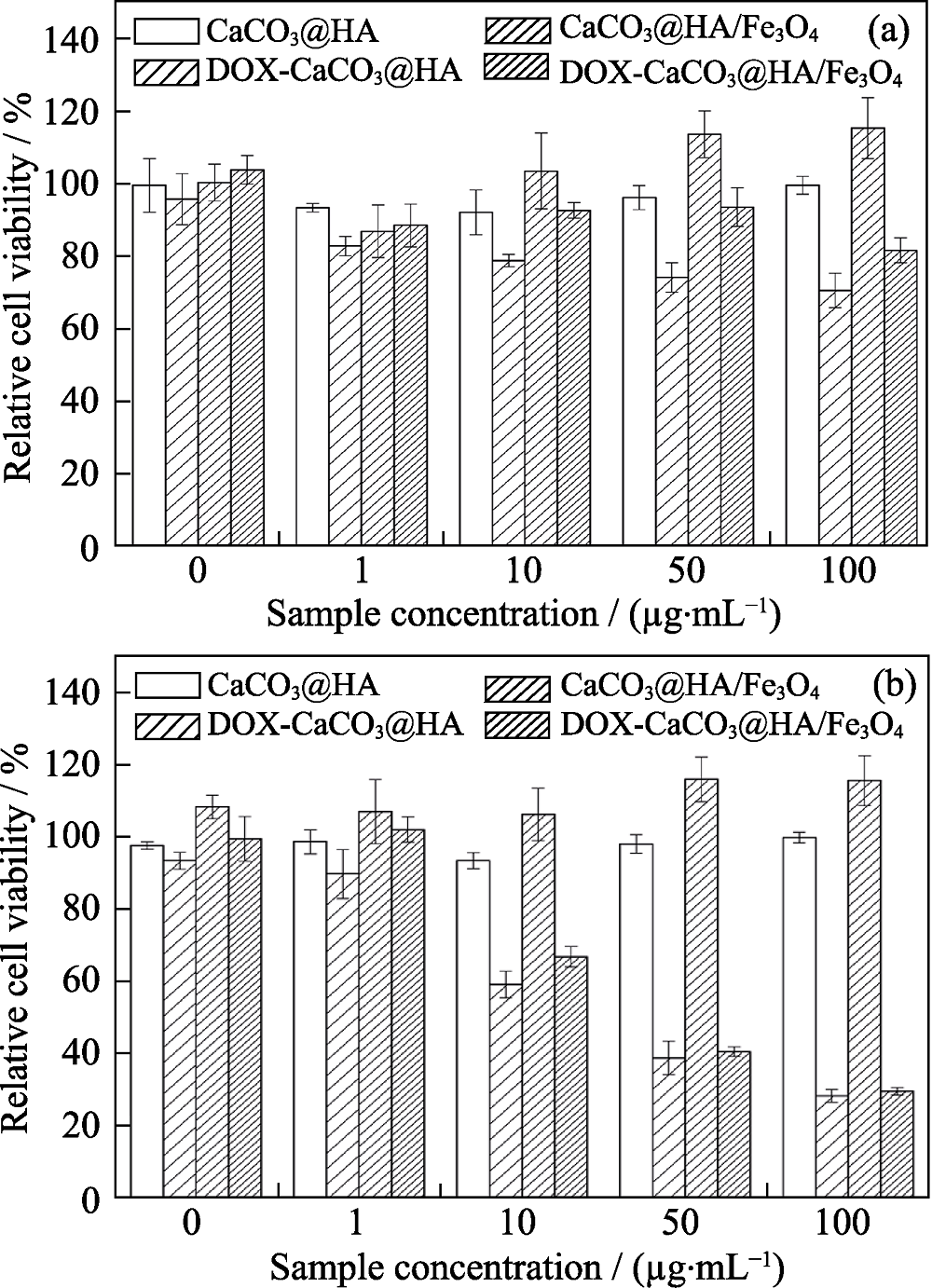
Fig. 9 CCK-8 assay of HaCaT (a) and HN6 tumor cells (b) co-cultured with unloaded or DOX-loaded litchi-like magnetic HA microspheres and litchi-like HA microspheres for 24 h
| [1] | WANG H, LEEUWENBURGH SC, LI Y , et al. The use of micro- and nanospheres as functional components for bone tissue regeneration. Tissue Engineering Part B Reviews, 2012,18(1):24-39. |
| [2] | FAN J B, HUANG C, JIANG L , et al. Nanoporous microspheres: from controllable synthesis to healthcare applications. Journal of Materials Chemistry B, 2013,1(17):2222-2235. |
| [3] | PARK J H, PÉREZ R A, JIN G Z, , et al. Microcarriers designed for cell culture and tissue engineering of bone. Tissue Engineering Part B Reviews, 2013,19(2):172-190. |
| [4] | LIU J, QIAO S Z, CHEN J S , et al. Yolk/shell nanoparticles: new platforms for nanoreactors, drug delivery and lithium-ion batteries. ChemInform, 2011,47(47):12578-12591. |
| [5] | MAHMOUDI M, SANT S, WANG B , et al. Superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles (SPIONs): development, surface modification and applications in chemotherapy. Advanced Drug Delivery Reviews, 2011,63(1/2):24-46. |
| [6] | KIM D H, LI W, CHEN J , et al. Multimodal Imaging of nanocomposite microspheres for transcatheter intra-arterial drug delivery to liver tumors. Scientific Reports, 2016,6:29653. |
| [7] | LIU Y, YANG F, YUAN C , et al. Magnetic nanoliposomes as in situ microbubble bombers for multimodality image-guided cancer theranostics. ACS Nano, 2017,11(2):1509-1519. |
| [8] | PARK J, AN K, HWANG Y , et al. Ultra-large-scale syntheses of monodisperse nanocrystals. Nature Materials, 2004,3(12):891-895. |
| [9] | CHEN Y, CHEN H, GUO L , et al. Hollow/rattle-type mesoporous nanostructures by a structural difference-based selective etching strategy. ACS Nano, 2010,4(1):529-539. |
| [10] | WANG Y, WANG F, CHEN B , et al. Facile one-pot synthesis of yolk-shell superparamagnetic nanocomposites via ternary phase separations. Chemical Communications, 2011,47(37):10350-10352. |
| [11] | LATTUADA M, HATTON TA . Synthesis, properties and applications of Janus nanoparticles. Nano Today, 2011,6(3):286-308. |
| [12] | XIA L Y, ZHANG M Q, YUAN C E , et al. A facile heteroaggregate- template route to hollow magnetic mesoporous spheres with tunable shell structures. Journal of Materials Chemistry, 2011,21(25):9020-9026. |
| [13] | GUO Y P, LONG T, TANG S , et al. Hydrothermal fabrication of magnetic mesoporous carbonated hydroxyapatite microspheres: biocompatibility, osteoinductivity, drug delivery property and bactericidal property. Journal of Materials Chemistry B, 2014,2(19):2899-2909. |
| [14] | LIN K, CHEN L, LIU P , et al. Hollow magnetic hydroxyapatite microspheres with hierarchically mesoporous microstructure for pH- responsive drug delivery. CrystEngComm, 2013,15(15):2999-3008. |
| [15] | QI C, LIN J, FU LH , et al. Calcium-based biomaterials for diagnosis, treatment, and theranostics. Chemical Society Reviews, 2017,47(2):357-403. |
| [16] | HONG Y, FAN H, LI B , et al. Fabrication, biological effects, and medical applications of calcium phosphate nanoceramics. Materials Science and Engineering: R, 2010,70(3-6):225-242. |
| [17] | YUAN H, FERNANDES H, HABIBOVIC P , et al. Osteoinductive ceramics as a synthetic alternative to autologous bone grafting. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 2010,107(31):13614-13619. |
| [18] | QIAO W, LAN X, TSOI J K H , et al. Biomimetic hollow mesoporous hydroxyapatite microsphere with controlled morphology, entrapment efficiency and degradability for cancer therapy. RSC Adv., 2017,7(71):44788-44798. |
| [19] | LI R, CHEN K, LI G , et al. Structure design and fabrication of porous hydroxyapatite microspheres for cell delivery. Journal of Molecular Structure, 2016,1120:34-41. |
| [20] | WU H C, WANG T W, BOHN M C , et al. Novel magnetic hydroxyapatite nanoparticles as non-viral vectors for the glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor gene. Advanced Functional Materials, 2010,20(1):67-77. |
| [21] | GUO Y P, GUO L H, YAO Y B , et al. Magnetic mesoporous carbonated hydroxyapatite microspheres with hierarchical nanostructure for drug delivery systems. Chemical Communications, 2011,47(44):12215-12217. |
| [22] | HUANG C, ZHOU Y, TANG Z , et al. Synthesis of multifunctional Fe3O4 core/hydroxyapatite shell nanocomposites by biomineralization. Dalton Transactions, 2011,40(18):5026-5031. |
| [23] | BOCK N, RIMINUCCI A, DIONIGI C , et al. A novel route in bone tissue engineering: magnetic biomimetic scaffolds. Acta Biomaterials, 2010,6(3):786-796. |
| [24] | LONG T, GUO YP, TANG S , et al. Emulsion fabrication of magnetic mesoporous carbonated hydroxyapatite microspheres for treatment of bone infection. RSC Advances, 2014,4(23):11816-11825. |
| [25] | INUKAI A, SAKAMOTO N, AONO H , et al. Synthesis and hyperthermia property of hydroxyapatite-ferrite hybrid particles by ultrasonic spray pyrolysis. Journal of Magnetism & Magnetic Materials, 2011,323(7):965-969. |
| [26] | TEO B M, SUH S K, HATTON T A , et al. Sonochemical synthesis of magnetic Janus nanoparticles. Langmuir, 2011,27(1):30-33. |
| [27] | MENG J, ZHANG Y, QI X , et al. Paramagnetic nanofibrous composite films enhance the osteogenic responses of pre-osteoblast cells. Nanoscale, 2010,2(12):2565-2569. |
| [28] | ZHANG Y, WANG H, YAN B , et al. A reusable piezoelectric immunosensor using antibody-adsorbed magnetic nanocomposite. Journal of Immunological Methods, 2008,332(1):103-111. |
| [29] | SAFAVI A, MOMENI S . Highly efficient degradation of azo dyes by palladium/hydroxyapatite/Fe3O4 nanocatalyst. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2012,201(1):125-131. |
| [30] | JIANG X, WANG F, CAI W , et al. Trisodium citrate-assisted synthesis of highly water-dispersible and superparamagnetic mesoporous Fe3O4 hollow microspheres via solvothermal process. Journal of Alloys & Compounds, 2015,636 34-39. |
| [31] | WANG Y, HASSAN MS, GUNAWAN P , et al. Polyelectrolyte mediated formation of hydroxyapatite microspheres of controlled size and hierarchical structure. Journal of Colloid & Interface Science, 2009,339(1):69-77. |
| [32] | BRETCANU O, SPRIANO S, VERNÉ E , et al. The influence of crystallised Fe3O4 on the magnetic properties of coprecipitation- derived ferrimagnetic glass-ceramics. Acta Biomaterials, 2005,1(4):421-429. |
| [33] | YANG Y H, LIU C H, LIANG Y H , et al. Hollow mesoporous hydroxyapatite nanoparticles (hmHANPs) with enhanced drug loading and pH-responsive release properties for intracellular drug delivery. Journal of Materials Chemistry B, 2013,1(19):2447-2450. |
| [1] | AN Ran, LIN Si, GUO Shigang, ZHANG Chong, ZHU Shun, HAN Yingchao. Iron-doped Nano-hydroxyapatite: Preparation and Ultraviolet Absorption Performance [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(5): 457-465. |
| [2] | YANG Endong, LI Baole, ZHANG Ke, TAN Lu, LOU Yongbing. ZnCo2O4-ZnO@C@CoS Core-shell Composite: Preparation and Application in Supercapacitors [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(5): 485-493. |
| [3] | ZHANG Tingting, WANG Fangyuan, LIU Changyou, ZHANG Guorong, LÜ Jiahui, SONG Yuchen, JIE Wanqi. Hydrothermal-sintering Preparation of Cr2+:ZnSe/ZnSe Nanotwins with Core-shell Structure [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(4): 409-415. |
| [4] | LI Chengyu, DING Ziyou, HAN Yingchao. In vitro Antibacterial and Osteogenic Properties of Manganese Doped Nano Hydroxyapatite [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(3): 313-320. |
| [5] | YUE Quanxin, GUO Ruihua, WANG Ruifen, AN Shengli, ZHANG Guofang, GUAN Lili. 3D Core-shell Structured NiMoO4@CoFe-LDH Nanorods: Performance of Efficient Oxygen Evolution Reaction and Overall Water Splitting [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(11): 1254-1264. |
| [6] | WU Rui, ZHANG Minhui, JIN Chenyun, LIN Jian, WANG Deping. Photothermal Core-Shell TiN@Borosilicate Bioglass Nanoparticles: Degradation and Mineralization [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(6): 708-716. |
| [7] | MA Xiaosen, ZHANG Lichen, LIU Yanchao, WANG Quanhua, ZHENG Jiajun, LI Ruifeng. 13X@SiO2: Synthesis and Toluene Adsorption [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(5): 537-543. |
| [8] | LIU Yan, ZHANG Yufan, WANG Ximan, LI Ting, MA Wenting, YANG Fuwei, CHEN Liang, ZHAO Dongyue, YAN Xiaoqin. Consolidation of Fragile Weathered Bone Relics Using Hydroxyapatite Material as Consolidant [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(11): 1345-1354. |
| [9] | CHI Congcong, QU Panpan, REN Chaonan, XU Xin, BAI Feifei, ZHANG Danjie. Preparation of SiO2@Ag@SiO2@TiO2 Core-shell Structure and Its Photocatalytic Degradation Property [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(7): 750-756. |
| [10] | CHEN Yaling, SHU Song, WANG Shaoxin, LI Jianjun. Mn-HAP SCR Catalyst: Preparation and Sulfur Resistance [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(10): 1065-1072. |
| [11] | CHEN Xiaomei, CHEN Ying, YUAN Xia. Decomposition of Cyclohexyl Hydroperoxide Catalyzed by Core-shell Material Co3O4@SiO2 [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(1): 65-71. |
| [12] | ZHU Yutong, TAN Peijie, LIN Hai, ZHU Xiangdong, ZHANG Xingdong. Injectable Hyaluronan/Hydroxyapatite Composite: Preparation, Physicochemical Property and Biocompatibility [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(9): 981-990. |
| [13] | LIN Ziyang, CHANG Yuchen, WU Zhangfan, BAO Rong, LIN Wenqing, WANG Deping. Different Simulated Body Fluid on Mineralization of Borosilicate Bioactive Glass-based Bone Cement [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(7): 745-752. |
| [14] | WU Zhongcao, HUAN Zhiguang, ZHU Yufang, WU Chengtie. 3D Printing and Characterization of Microsphere Hydroxyapatite Scaffolds [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(6): 601-607. |
| [15] | WU Yonghao, LI Xiangfeng, ZHU Xiangdong, ZHANG Xingdong. Construction of Hydroxyapatite Nanoceramics with High Mechanical Strength and Efficiency in Promoting the Spreading and Viability of Osteoblasts [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(5): 552-560. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||