
Journal of Inorganic Materials ›› 2018, Vol. 33 ›› Issue (6): 623-628.DOI: 10.15541/jim20170361
• Orginal Article • Previous Articles Next Articles
SONG Jing-Jing1, CHEN Bo1, LIN Kai-Li2
Received:2017-08-07
Revised:2017-09-06
Published:2018-06-20
Online:2018-05-24
About author:SONG Jing-Jing. E-mail: 809078682@qq.com
Supported by:CLC Number:
SONG Jing-Jing, CHEN Bo, LIN Kai-Li. Core-shell Structured Hydroxyapatite/Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticle: Preparation and Application in Drug Delivery[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2018, 33(6): 623-628.
| Samples | Vp/(cm3·g-1) | SBET/(m2·g-1) | Dp/nm | Shell thickness/nm |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HAp | 1.024 | 69.7 | 1.689 | — |
| HAp@mSiO2-1 | 0.608 | 653.4 | 1.929 | 9.59 |
| HAp@mSiO2-2 | 0.591 | 666.6 | 2.188 | 10.01 |
| HAp@mSiO2-3 | 0.467 | 714.1 | 2.450 | 12.97 |
Table 1 Pore size, specific surface area, and shell thickness for kernel HAp and different HAp@mSiO2 samples
| Samples | Vp/(cm3·g-1) | SBET/(m2·g-1) | Dp/nm | Shell thickness/nm |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HAp | 1.024 | 69.7 | 1.689 | — |
| HAp@mSiO2-1 | 0.608 | 653.4 | 1.929 | 9.59 |
| HAp@mSiO2-2 | 0.591 | 666.6 | 2.188 | 10.01 |
| HAp@mSiO2-3 | 0.467 | 714.1 | 2.450 | 12.97 |
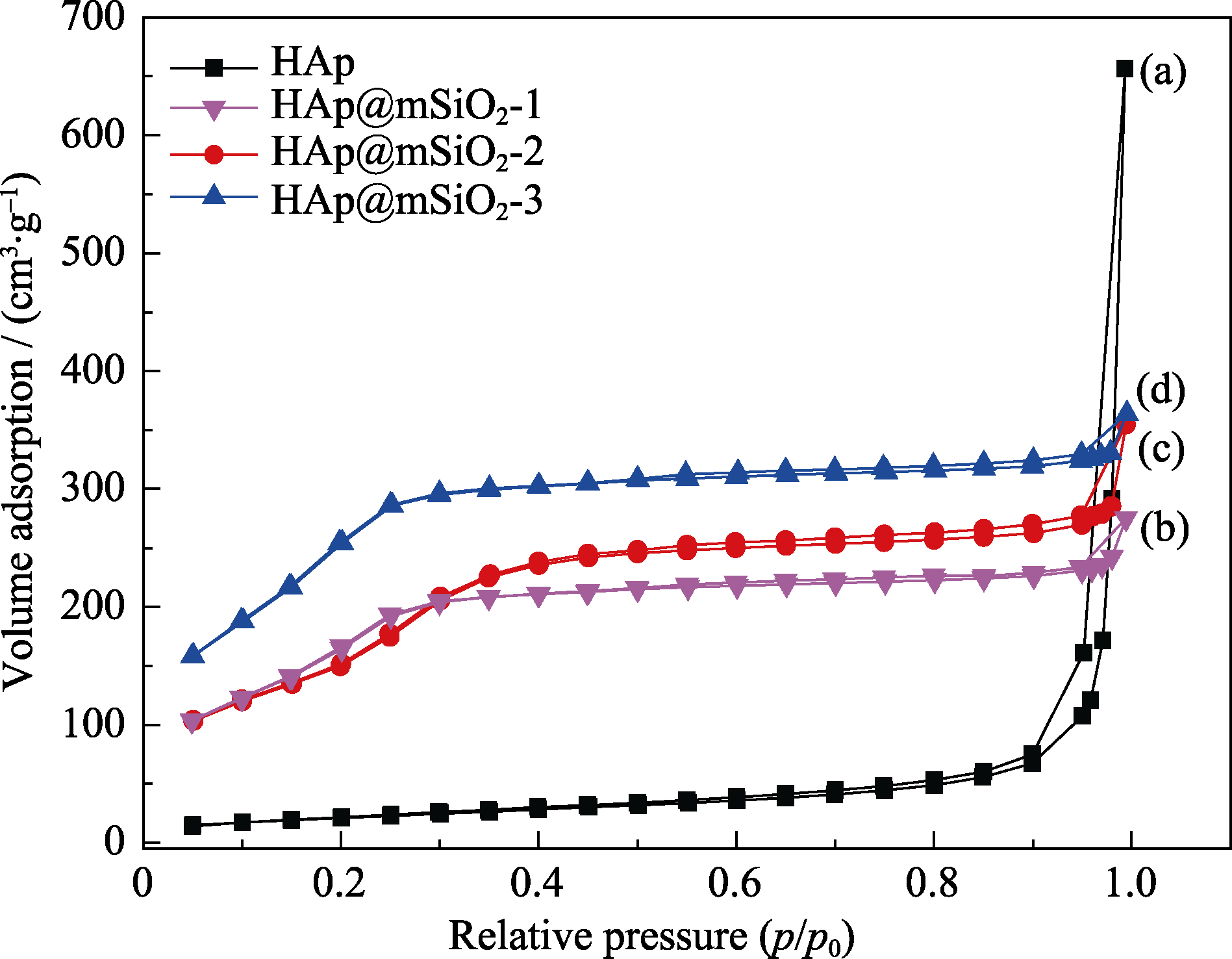
Fig. 5 N2 adsorption/desorption isotherms for core HAp and HAp@mSiO2 with different shell thicknesses(a) HAp; (b) HAp@mSiO2-1; (c) HAp@mSiO2-2; (d) HAp@mSiO2-3
| [1] | JAE YUN-KIM, JI EUN-LEE, JIN WOO-LEE,et al. Magnetic fluorescent delivery vehicle using uniform mesoporous silica spheres embedded with monodisperse magnetic and semiconductor nanocrystals. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2006, 128(3): 688-689. |
| [2] | LIANG ZHI-JIAN, ANDREI SUSHA, FRANK CARUSO.Gold nanoparticle-based core-shell and hollow spheres and ordered assemblies thereof. Chemistry of Materials, 2003, 15(16): 3176-3183. |
| [3] | ZHANG KAI, ZHENG LIN-LI, ZHANG XUE-HAI,et al. Silica- PMMA core-shell and hollow nanospheres. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 2006, 277(1): 145-150. |
| [4] | ZHOU JUAN, CHEN MIN, QIAO XIAO-GUANG,et al. Facile preparation pethod of SiO2/PS/TiO2 multilayer core-shell hybrid microspheres. Langmuir, 2006, 22(24): 10175-10179. |
| [5] | CAI WEI-QUAN, YU JIA-GUO, CHENG BEI,et al. Synthesis of boehmite hollow core/shell and hollow microspheres via sodium tartrate-mediated phase transformation and their enhanced adsorption performance in water treatment. The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2009, 113(33): 14739-14746. |
| [6] | CHEN YU, CHEN HANG-RONG, ZENG DE-PING,et al. Core/shell structured hollow mesoporous nanocapsules: a potential platform for simultaneous cell imaging and anticancer drug delivery. ACS Nano, 2010, 4(10): 6001-6013. |
| [7] | GE JIAN-PING, HU YONG-XING, YIN YA-DONG.Highly tunable superparamagnetic colloidal photonic crystals. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2007, 119(39): 7572-7575. |
| [8] | HUANG XIAO-QING, TANG SHAO-HENG, LIU BI-JU,et al. Enhancing the photothermal stability of plasmonic metal nanoplates by a core-shell architecture. Advanced Materials, 2011, 23(30): 3420-3425. |
| [9] | CHAUDHURI GHOSH RAJIB, PARIA SANTANU.Core/shell nanoparticles: classes, properties, synthesis mechanisms, characterization, and applications.Chemical Reviews, 2012, 112(4): 2373-2433. |
| [10] | LIN KAI-LI, PAN JIA-YONG, CHEN YI-WEI,et al. Study the adsorption of phenol from aqueous solution on hydroxyapatite nanopowders. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2009, 161(1): 231-240. |
| [11] | ZHI WEI, SHI FENG, LI JING-YU,et al. Surface microstructure on hydroxyapatite spherules and its regulation on stem cells. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2017, 32(3): 319-325. |
| [12] | ZHU YU-FANG, ZHU MIN, XIN CHEN,et al. Hydroxyapatite whisker-reinforced composite scaffolds through 3D printing for bone repair. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2017, 32(8): 837-844. |
| [13] | CHEN W, LIU Y, COURTNEY H,et al. In vitro anti-bacterial and biological properties of magnetron co-sputtered silver-containing hydroxyapatite coating. Biomaterials, 2006, 27(32): 5512-5517. |
| [14] | SUN HAO, SU FANG-ZHENG, NI JI,et al. Gold supported on hydroxyapatite as a versatile multifunctional catalyst for the direct tandem synthesis of imines and oximes. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2009, 48(24): 4390-4393. |
| [15] | LIN KAI-LI, CHEN LEI, LIU PEI-YI,et al. Hollow magnetic hydroxyapatite microspheres with hierarchically mesoporous microstructure for pH-responsive drug delivery. CrystEngComm, 2013, 15(15): 2999-3008. |
| [16] | ZHU KAI-PING, SUN JING, YE SONG, et al. A novel hollow hydroxyapatite microspheres/chitosan composite drug carrier for controlled release. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2016, 31(4): 434-442. |
| [17] | LAI CHENG-YU, TREWYN B G, JEFTINIJA D M,et al. A mesoporous silica nanosphere-based carrier system with chemically removable CdS nanoparticle caps for stimuli-responsive controlled release of neurotransmitters and drug molecules. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2003, 125(15): 4451-4459. |
| [18] | SHI JIAN-LIN, ZHANG LIN-XIA.Nanocomposites from ordered mesoporous materials.Journal of Materials Chemistry, 2004, 14(5): 795-806. |
| [19] | YU CHENG-ZHOU, FAN JIE, TIAN BO-ZHI,et al. Morphology development of mesoporous materials: a colloidal phase separation mechanism. Chemistry of Materials, 2004, 16(5): 889-898. |
| [20] | QI MEI-LI, QI JIA, XIAO GUI-YONG, et al. Effect of surfactants on the morphology of hydroxyapatite fibers. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2016, 31(4): 726-730. |
| [21] | LIU CONG-YING, GUO JIA, YANG WU-LI,et al. Magnetic mesoporous silica microspheres with thermo-sensitive polymer shell for controlled drug release. Journal of Materials Chemistry, 2009, 19(27): 4764-4770. |
| [22] | SUK BON YOON, KWONNAM SOHN, JEONG YEONY KIM,et al. Fabrication of carbon capsules with hollow macroporous core/mesoporous shell structures. Advanced Materials, 2002, 14(1): 19-21. |
| [23] | LI WEI, ZHAO DONG-YUAN.Extension of the Stöber method to construct mesoporous SiO2 and TiO2 shells for uniform multifunctional core-shell structures.Advanced Materials, 2013, 25(1): 142-149. |
| [24] | AHMED MOHAMED EL-TONI, SHU YIN, TSUGIO SATO. Control of silica shell thickness and microporosity of titania-silica core-shell type nanoparticles to depress the photocatalytic activity of titania.Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2006, 300(1): 123-130. |
| [25] | FOWLER B.Infrared studies of apatites. I. Vibrational assignments for calcium, strontium, and barium hydroxyapatites utilizing isotopic substitution.Inorganic Chemistry, 1974, 13(1): 194-207. |
| [26] | HAO LI-JING, YANG HUI, ZHAO NA-RU,et al. Hydrothermal synthesis of hydroxyapatite fibers precipitated by propionmide. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2013, 28(1): 63-68. |
| [27] | KANG XIAO-JIAO, CHENG ZI-YONG, LI CHUN-XIA,et al. Core-shell structured up-conversion luminescent and mesoporous NaYF4: Yb3+/Er3+@nSiO2@mSiO2 nanospheres as carriers for drug delivery. The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2011, 115(32): 15801-15811. |
| [28] | HIDEO HATA, SHUUYA SAEKI, TATSUO KIMURA,et al. Adsorption of taxol into ordered mesoporous silicas with various pore diameters. Chemistry of Materials, 1999, 11(4): 1110-1119. |
| [29] | ZHAO CHUN-XIA, YU LEI, ANTON P J MIDDELBERG. Magnetic mesoporous silica nanoparticles end-capped with hydroxyapatite for pH-responsive drug release.Journal of Materials Chemistry B, 2013, 1(37): 4828-4833. |
| [1] | AN Ran, LIN Si, GUO Shigang, ZHANG Chong, ZHU Shun, HAN Yingchao. Iron-doped Nano-hydroxyapatite: Preparation and Ultraviolet Absorption Performance [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(5): 457-465. |
| [2] | WANG Yueyue, HUANG Jiahui, KONG Hongxing, LI Huaizhu, YAO Xiaohong. Silver Loaded Radial Mesoporous Silica: Preparation and Application in Dental Resins [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(1): 77-83. |
| [3] | YANG Endong, LI Baole, ZHANG Ke, TAN Lu, LOU Yongbing. ZnCo2O4-ZnO@C@CoS Core-shell Composite: Preparation and Application in Supercapacitors [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(5): 485-493. |
| [4] | ZHANG Tingting, WANG Fangyuan, LIU Changyou, ZHANG Guorong, LÜ Jiahui, SONG Yuchen, JIE Wanqi. Hydrothermal-sintering Preparation of Cr2+:ZnSe/ZnSe Nanotwins with Core-shell Structure [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(4): 409-415. |
| [5] | LI Chengyu, DING Ziyou, HAN Yingchao. In vitro Antibacterial and Osteogenic Properties of Manganese Doped Nano Hydroxyapatite [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(3): 313-320. |
| [6] | YUE Quanxin, GUO Ruihua, WANG Ruifen, AN Shengli, ZHANG Guofang, GUAN Lili. 3D Core-shell Structured NiMoO4@CoFe-LDH Nanorods: Performance of Efficient Oxygen Evolution Reaction and Overall Water Splitting [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(11): 1254-1264. |
| [7] | WU Rui, ZHANG Minhui, JIN Chenyun, LIN Jian, WANG Deping. Photothermal Core-Shell TiN@Borosilicate Bioglass Nanoparticles: Degradation and Mineralization [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(6): 708-716. |
| [8] | MA Xiaosen, ZHANG Lichen, LIU Yanchao, WANG Quanhua, ZHENG Jiajun, LI Ruifeng. 13X@SiO2: Synthesis and Toluene Adsorption [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(5): 537-543. |
| [9] | LIU Yan, ZHANG Yufan, WANG Ximan, LI Ting, MA Wenting, YANG Fuwei, CHEN Liang, ZHAO Dongyue, YAN Xiaoqin. Consolidation of Fragile Weathered Bone Relics Using Hydroxyapatite Material as Consolidant [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(11): 1345-1354. |
| [10] | CHI Congcong, QU Panpan, REN Chaonan, XU Xin, BAI Feifei, ZHANG Danjie. Preparation of SiO2@Ag@SiO2@TiO2 Core-shell Structure and Its Photocatalytic Degradation Property [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(7): 750-756. |
| [11] | CHEN Yaling, SHU Song, WANG Shaoxin, LI Jianjun. Mn-HAP SCR Catalyst: Preparation and Sulfur Resistance [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(10): 1065-1072. |
| [12] | CHEN Xiaomei, CHEN Ying, YUAN Xia. Decomposition of Cyclohexyl Hydroperoxide Catalyzed by Core-shell Material Co3O4@SiO2 [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(1): 65-71. |
| [13] | ZHU Yutong, TAN Peijie, LIN Hai, ZHU Xiangdong, ZHANG Xingdong. Injectable Hyaluronan/Hydroxyapatite Composite: Preparation, Physicochemical Property and Biocompatibility [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(9): 981-990. |
| [14] | LIN Ziyang, CHANG Yuchen, WU Zhangfan, BAO Rong, LIN Wenqing, WANG Deping. Different Simulated Body Fluid on Mineralization of Borosilicate Bioactive Glass-based Bone Cement [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(7): 745-752. |
| [15] | WU Zhongcao, HUAN Zhiguang, ZHU Yufang, WU Chengtie. 3D Printing and Characterization of Microsphere Hydroxyapatite Scaffolds [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(6): 601-607. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||