
Journal of Inorganic Materials ›› 2015, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (8): 872-876.DOI: 10.15541/jim20140501
• Orginal Article • Previous Articles Next Articles
XING Zhi-Bo, LI Jing-Feng
Received:2014-09-30
Revised:2014-12-30
Published:2015-08-20
Online:2015-07-21
About author:XING Zhi-Bo. E-mail: seaflyx@foxmail.com
CLC Number:
XING Zhi-Bo, LI Jing-Feng. Powder Metallurgic Synthesis of Mid-temperature Lead-free AgSn18SbTe20 Thermoelectric Materials and Processing Influence on Thermoelectric Performance[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2015, 30(8): 872-876.
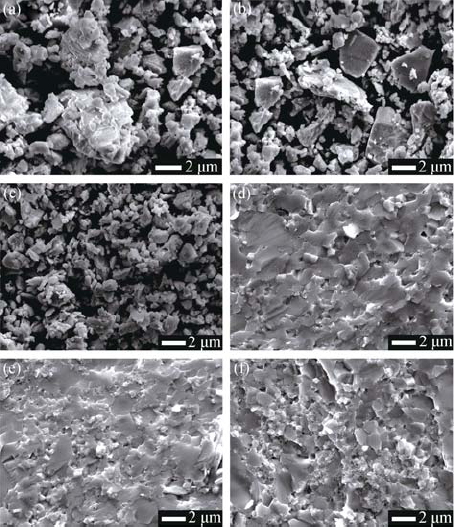
Fig. 2 SEM images of powders milled for different time and bulks sintered at different temperatures after milled for 12 h (a) 4 h; (b) 8 h; (c) 12 h; (d) 12 h-803 K; (e) 12 h-773 K; (f) 12 h-743 K
| Milling time/h | 4 | 8 | 12 | 16 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Density/ (g·cm-3) | 6.15 | 6.19 | 6.17 | 6.21 |
| Sintering temperature/K | 743 | 773 | 803 | |
| Density/ (g·cm-3) | 6.17 | 6.21 | 6.28 | |
Table 1 Density carrier concentrationcarrier concentrationcarrier concentrationcarrier concentrationcarrier concentrationof bulks sintered at 743 K with different milling times and of bulks sintered at different temperatures milled for 12 h
| Milling time/h | 4 | 8 | 12 | 16 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Density/ (g·cm-3) | 6.15 | 6.19 | 6.17 | 6.21 |
| Sintering temperature/K | 743 | 773 | 803 | |
| Density/ (g·cm-3) | 6.17 | 6.21 | 6.28 | |
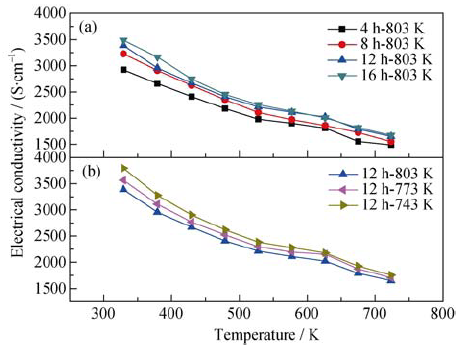
Fig. 3 Temperature dependence of the electrical conductivities carrier concentrationcarrier concentrationcarrier concentrationcarrier concentrationcarrier concentrationof bulks sintered at 803 K with different milling time (a) and sintered at different temperatures after milled for 12 h (b)

Fig. 4 Temperature dependence of the Seebeck coefficient of bulks sintered at 803 K with different milling time (a) and sintered at different temperatures after milled for 12 h (b)
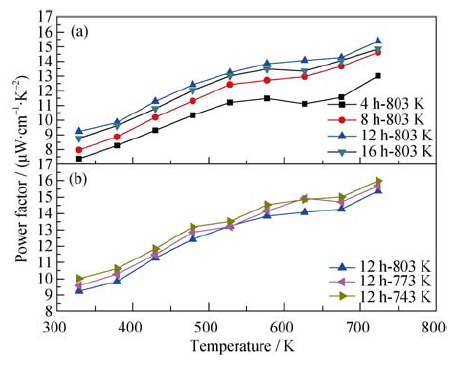
Fig. 5 Temperature dependence of the power factor of bulks sintered at 803 K with different milling time (a) and sintered at different temperatures after milled at 12 h (b)

Fig. 7 Temperature dependence of ZT value of bulks sintered at 803 K with different milling time (a) and sintered at different temperatures after milled for 12 h (b)
| [1] | POUDEL B, HAO Q, MA Y, et al.High-thermoelectric performance of nanostructured bismuth antimony telluride bulk alloys.Science, 2008, 320(5876): 634-638. |
| [2] | HEREMANS J P, JOVOVIC V, TOBERER E S, et al.Enhancement of thermoelectric efficiency in PbTe by distortion of the electronic density of states.Science, 2008, 321(5888): 554-557. |
| [3] | VENKATASUBRAMANIAN R, SIIVOLA E, COLPITTS T, et al.Thin-film thermoelectric devices with high room-temperature figures of merit.Nature, 2001, 413(6856): 597-602. |
| [4] | DRESSELHAUS M S, CHEN G, TANG M Y, et al.New directions for low-dimensional thermoelectric materials.Adv. Mater., 2007, 19(8): 1043-1053. |
| [5] | ZHAN B, LAN J L, LIU Y C, et al.Research progress of oxides thermoelectric materials.Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2014, 29(3): 237-244. |
| [6] | WANG L, LU Q M, ZHANG X, et al.Effect of spinning and milling time on thermoelectric properties of the p-type (Bi0.25Sb0.75)2Te3 alloy.Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2010, 25(6): 588-592. |
| [7] | HSU K F, LOO S, GUO F, et al.Cubic AgPbmSbTe2+m: bulk thermoelectric materials with high figure of merit.Science, 2004, 303(5659): 818-821. |
| [8] | POUDEU P F P, D’ANGELO J, DOWNEY A D, et al. High thermoelectric figure of merit and nanostructuring in bulk p-type Na1-xPbmSbyTem+2.Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2006, 118(23): 3835-3839. |
| [9] | ANDROULAKIS J, HSU K F, PCIONEK R, et al, Nanostructuring and high thermoelectric efficiency in p-Type Ag(Pb1 - ySny)mSbTe2 + m.Adv. Mater., 2006, 18(9): 1170-1173. |
| [10] | KOSUGA A, KUROSAKI K, MUTA H, et al, Thermoelectric properties of p-type (AgSbTe2)x(Pb0.5Sn0.5Te)1 - x (x = 0.05, 0.09, 0.2).J. Alloys Compd., 2006, 416(1/2): 218-221. |
| [11] | WANG H, LI JF, NAN C W, et al, High-performance Ag0.8Pb18+xSbTe20 thermoelectric bulk materials fabricated by mechanical alloying and >spark plasma sintering. Appl. Phys. Lett., 2006, 88(9): 0921041-1-3. |
| [12] | ZHOU M, LI JF, KITA T, Nanostructured AgPbmSbTem+2 system bulk materials with enhanced thermoelectric performance.J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130: 4527-4532. |
| [13] | LI Z Y, ZOU M M, LI J F, Comparison of thermoelectric performance of AgPbxSbTe20 (x= 20-22.5) polycrystals fabricated by different methods.J. Alloys Compd., 2013, 549: 319-323. |
| [1] | LI Junsheng, ZENG Liang, LIU Rongjun, WANG Yanfei, WAN Fan, LI Duan. Functional Strontium Tantalum Oxynitride Ceramics: Efficient Synthesis, Densification and Dielectric Performance [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(8): 885-892. |
| [2] | HE Danqi, WEI Mingxu, LIU Ruizhi, TANG Zhixin, ZHAI Pengcheng, ZHAO Wenyu. Heavy-Fermion YbAl3 Materials: One-step Synthesis and Enhanced Thermoelectric Performance [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(5): 577-582. |
| [3] | CHENG Cheng, LI Jianbo, TIAN Zhen, WANG Pengjiang, KANG Huijun, WANG Tongmin. Thermoelectric Property of In2O3/InNbO4 Composites [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(7): 724-730. |
| [4] | WAN Peng, LI Mian, HUANG Qing. Molten Salt Assisted Synthesis of Dy3Si2C2 Coated SiC Powders and Sintering Behavior of SiC Ceramics [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(1): 49-54. |
| [5] | KANG Huijun,ZHANG Xiaoying,WANG Yanxia,LI Jianbo,YANG Xiong,LIU Daquan,YANG Zerong,WANG Tongmin. Effect of Rare-earth Variable-valence Element Eu doping on Thermoelectric Property of BiCuSeO [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2020, 35(9): 1041-1046. |
| [6] | QIU Xiaoxiao,ZHOU Xiying,FU Yuntian,SUN Xiaomeng,WANG Lianjun,JIANG Wan. Influence of Ge1-xInxTe Microstructure on Thermoelectric Properties [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2020, 35(8): 916-922. |
| [7] | ZHAO Zhankui, LI Tao, LU Shuhan, WANG Minggang, ZHANG Jingjing, CHENG Daowen, WU Chen, CHI Yue, WANG Hongli. Magnetic Properties and Resistivity of Soft Magnetic Composites Regulated by SPS Enhanced Interface Reaction Mechanism [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2020, 35(11): 1223-1226. |
| [8] | LI Xin, XI Li-Li, YANG Jiong. First Principles High-throughput Research on Thermoelectric Materials: a Review [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2019, 34(3): 236-246. |
| [9] | LUO Jun, HE Shi-Yang, LI Zhi-Li, LI Yong-Bo, WANG Feng, ZHANG Ji-Ye. Progress on High-throughput Synthesis and Characterization Methods for Thermoelectric Materials [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2019, 34(3): 247-259. |
| [10] | SHEN Jia-Jun, FANG Teng, FU Tie-Zheng, XIN Jia-Zhan, ZHAO Xin-Bing, ZHU Tie-Jun. Lattice Thermal Conductivity in Thermoelectric Materials [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2019, 34(3): 260-268. |
| [11] | YU Guan-Ting, XIN Jia-Zhan, ZHU Tie-Jun, ZHAO Xin-Bing. Thermoelectric Property of Zn-Sb Doped Mg2(Si,Sn) Alloys [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2019, 34(3): 310-314. |
| [12] | WANG Wei, LUO Shi-Jie, XIAN Cong, XIAO Qun, YANG Yang, OU Yun, LIU Yun-Ya, XIE Shu-Hong. Enhanced Thermoelectric Properties of Hydrothermal Synthesized BiCl3/Bi2S3 Composites [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2019, 34(3): 328-334. |
| [13] | ZOU Can-Hui, LONG Ying, ZHENG Xin, ZHANG Jin-Yang, LIN Hua-Tai. Preparation, Microstructure and Property of Ternary Transition Metal Boride Os1-xRuxB2 [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2018, 33(7): 787-792. |
| [14] | WANG Ming-Hui, ZHONG Hong-Bin, FAN Yu-Chi, CHEN Ting. Spark Plasma Sintering of Bioactive Ca2MgSi2O7 Ceramics [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2017, 32(8): 825-830. |
| [15] | LI Xiao-Yu, ZHANG Li, TANG Xin-Feng, ZHANG Qing-Jie. Preparation and Characterization of γ-NaxCoO2 by Sodium Polyacrylate Gel Method [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2017, 32(6): 603-608. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||