
Journal of Inorganic Materials ›› 2021, Vol. 36 ›› Issue (2): 161-167.DOI: 10.15541/jim20200376
Special Issue: 电致变色材料与器件; 功能材料论文精选(2021); 电致变色专栏2021
• TOPLCAL SECTION: Electrochromic Materials and Devices (Contributing Editor: DIAO Xungang, WANG Jinmin) • Previous Articles Next Articles
ZHAO Qi1( ), QIAO Ke1, YAO Yongji1, CHEN Zhang1, CHEN Dongchu2(
), QIAO Ke1, YAO Yongji1, CHEN Zhang1, CHEN Dongchu2( ), GAO Yanfeng1(
), GAO Yanfeng1( )
)
Received:2020-07-06
Revised:2020-10-29
Published:2021-02-20
Online:2020-11-05
Contact:
GAO Yanfeng, professor. E-mail: yfgao@shu.edu.cn;About author:ZHAO Qi(1995–), male, PhD candidate. E-mail: zq0911@shu.edu.cn
Supported by:CLC Number:
ZHAO Qi, QIAO Ke, YAO Yongji, CHEN Zhang, CHEN Dongchu, GAO Yanfeng. High-conductivity Hydrophobic Fumed-SiO2 Composite Gel Electrolyte for High Performance Electrochromic Devices[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(2): 161-167.
| Electrolyte | Ionic conductivity/(mS·cm-1) |
|---|---|
| PMMA/LiClO4/hydrophobic SiO2 (This work) | 5.14 |
| PMMA/LiClO4/hydrophilic SiO2[ | 3.8 |
| P(BMA-St)/hydrophilic SiO2[ | 2.15 |
| PEO/LiCF3SO3/TiO2[ | 0.16 |
| PVDF/LiClO4/palygorskite[ | 0.12 |
| PMMA/LiClO4/[Emim]BF4[ | 2.9 |
| PVB/LiClO4[ | 0.04 |
| PVDF-HFP/LiCF3SO3/ZrO2[ | 1.78 |
| PAN/LiClO4/Li0.33La0.557TiO3[ | 0.0605 |
| Electrolyte | Ionic conductivity/(mS·cm-1) |
|---|---|
| PMMA/LiClO4/hydrophobic SiO2 (This work) | 5.14 |
| PMMA/LiClO4/hydrophilic SiO2[ | 3.8 |
| P(BMA-St)/hydrophilic SiO2[ | 2.15 |
| PEO/LiCF3SO3/TiO2[ | 0.16 |
| PVDF/LiClO4/palygorskite[ | 0.12 |
| PMMA/LiClO4/[Emim]BF4[ | 2.9 |
| PVB/LiClO4[ | 0.04 |
| PVDF-HFP/LiCF3SO3/ZrO2[ | 1.78 |
| PAN/LiClO4/Li0.33La0.557TiO3[ | 0.0605 |
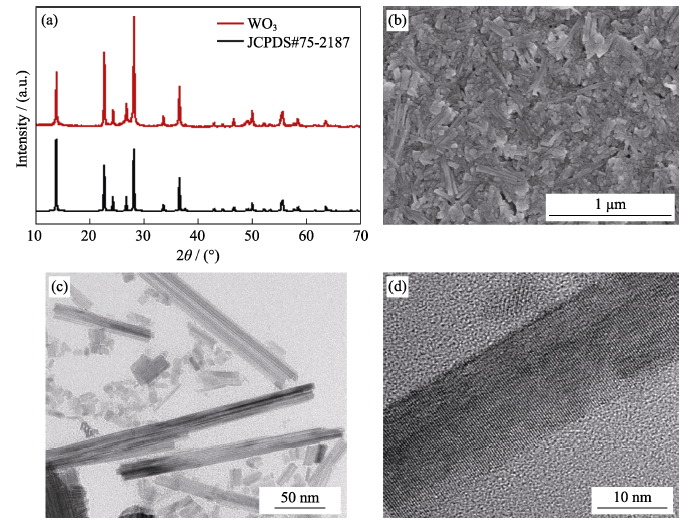
Fig. S4 XRD patterns of the as-prepared WO3(a), SEM image of WO3 films coated on ITO substrates(b), TEM images of WO3 dispersion (c) and typical nanorod (d) with high magnification
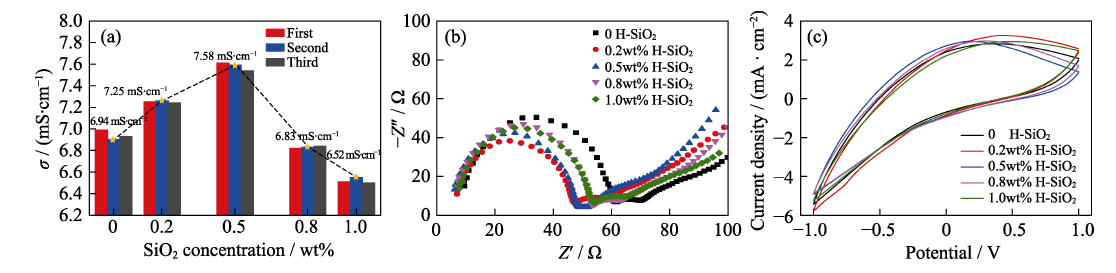
Fig. 4 Ionic conductivity of liquid electrolyte with 0, 0.2wt%, 0.5wt%, 0.8wt%, and 1.0wt% fumed SiO2 (a), and colored state Nyquist plots (b) and CV curves (c) of WO3 films in liquid electrolyte with 0, 0.2wt%, 0.5wt%, 0.8wt% and 1.0wt% fumed SiO2. Scan rate: 100 mV/s
| [1] | PATEL K J, BHATT G G, RAY J R, et al. All-inorganic solid-state electrochromic devices: a review. Journal of Solid State Electrochemistry, 2016,21(2):1-11. |
| [2] | AGNIHOTRYA SA, SEKHON P SS. PMMA based gel electrolyte for EC smart windows. Electrochimica Acta, 1998,44:3121-3126. |
| [3] | LI H, WANG J, SHI Q, et al. Constructing three-dimensional quasi- vertical nanosheet architectures from self-assemble two-dimensional WO3·2H2O for efficient electrochromic devices. Applied Surface Science, 2016,380:281-287. |
| [4] | GROCE F, APPETECCHI G B, PERSI L, et al. Nanocomposite polymer electrolytes for lithium batteries. Nature, 1998,394:456. |
| [5] | AZIZ S B, WOO T J, KADIR M F Z,, et al. A conceptual review on polymer electrolytes and ion transport models. Journal of Science: Advanced Materials and Devices, 2018,3:1-17. |
| [6] | TAO C, GAO M, YIN B, et al. A promising TPU/PEO blend polymer electrolyte for all-solid-state lithium ion batteries. Electrochimica Acta, 2017,257:31-39. |
| [7] | JUNG H R, JU D H, LEE W J, et al. Electrospun hydrophilic fumed silica/polyacrylonitrile nanofiber-based composite electrolyte membranes. Electrochimica Acta, 2009,54:3630-3637. |
| [8] | KUPPU S V, JEYARAMAN A R, GURUVIAH P K, et al. Preparation and characterizations of PMMA-PVDF based polymer composite electrolyte materials for dye sensitized solar cell. Current Applied Physics, 2018,18:619-625. |
| [9] | ZHAI W, ZHU H, WANG L, et al. Study of PVDF-HFP/PMMA blended micro-porous gel polymer electrolyte incorporating ionic liquid [BMIM] BF4 for lithium ion batteries. Electrochimica Acta, 2014,133:623-630. |
| [10] | VIGNAROOBAN K, DISSANAYAKE M A K L, ALBINSSON I, et al. Effect of TiO2 nano-filler and EC plasticizer on electrical and thermal properties of poly(ethylene oxide)(PEO) based solid polymer electrolytes. Solid State Ionics, 2014,266:25-28. |
| [11] | VIJAYAKUMAR G, KARTHICK S N, SATHIYA PRIYA A R, et al. Effect of nanoscale CeO2 on PVDF-HFP-based nanocomposite porous polymer electrolytes for Li-ion batteries. Journal of Solid State Electrochemistry, 2007,12:1135-1141. |
| [12] | CROCE F, SCROSATI B, MARIOTTO G. Electrochemical and spectroscopic study of the transport properties of composite polymer electrolytes. Chem. Mater., 1992,4:1134-1136. |
| [13] | YAO P, ZHU B, ZHAI H, et al. PVDF/palygorskite nanowire composite electrolyte for 4 V rechargeable lithium batteries with high energy density. Nano Letters, 2018,18:6113-6120. |
| [14] | AHMAD S, AHMAD S, AGNIHOTRY S A. Nanocomposite electrolytes with fumed silica in poly(methyl methacrylate): thermal, rheological and conductivity studies. Journal of Power Sources, 2005,140:151-156. |
| [15] | JITJAICHAM M, KUSUKTHAM B. Spinning of poly(ethylene terephthalate) fiber composites incorporated with fumed silica. Silicon, 2017,10:575-583. |
| [16] | WANG J, KHOO E, LEE PS, et al. Synthesis, assembly, and electrochromic properties of uniform crystalline WO3 nanorods. J. Phys. Chem. C, 2008,112:14306-14312. |
| [17] | ZHAO Q, FANG Y, QIAO K, et al. Printing of WO3/ITO nanocomposite electrochromic smart windows. Solar Energy Materials and Solar Cells, 2019,194:95-102. |
| [18] | EL-FATTAH M A, El SAEED A. M,et al. Chemical interaction of different sized fumed silica with epoxy via ultrasonication for improved coating. Progress in Organic Coatings, 2019,129:1-9. |
| [19] | PUGUAN J M C, CHUNG W J, KIM H, et al. Ion-conductive and transparent PVdF-HFP/silane-functionalized ZrO2 nanocomposite electrolyte for electrochromic applications. Electrochimica Acta, 2016,196:236-244. |
| [20] | SAIKIA D, WU C G, FANG J, et al. Organic-inorganic hybrid polymer electrolytes based on polyether diamine, alkoxysilane, and trichlorotriazine: synthesis, characterization, and electrochemical applications. Journal of Power Sources, 2014,269(10):651-660. |
| [21] | TANG Q, LI H, YUE Y, et al. 1-Ethyl-3-methylimidazolium tetrafluoroborate-doped high ionic conductivity gel electrolytes with reduced anodic reaction potentials for electrochromic devices. Materials & Design, 2017,118:279-285. |
| [22] | LEONES R, SABADINI R C, SENTANIN F C, et al. Polymer electrolytes for electrochromic devices through solvent casting and Sol-Gel routes. Solar Energy Materials & Solar Cells, 2017,169:98-106. |
| [23] | ZHANG F, DONG G, LIU J, et al. Polyvinyl butyral-based gel polymer electrolyte films for solid-state laminated electrochromic devices. Ionics, 2017,23:1879-1888. |
| [24] | RAGHAVAN S R, RILEY M W, FEDKIW P S, et al. Composite polymer electrolytes based on poly(ethylene glycol) and hydrophobic fumed silica: dynamic rheology and microstructure. Chemistry of Materials, 1998,10(1):244-251. |
| [25] | ŠURCA VUK A, JOVANOVSKI V, POLLET-VILLARD A, et al. Imidazolium-based ionic liquid derivatives for application in electrochromic devices. Solar Energy Materials and Solar Cells, 2008,92(2):126-135. |
| [26] | BAE J, KIM H, MOON H C, et al. Low-voltage, simple WO3-based electrochromic devices by directly incorporating an anodic species into the electrolyte. Journal of Materials Chemistry C, 2016,46(4):10887-10892. |
| [27] | CUI J, ZHOU Z, JIA M, et al. Solid polymer electrolytes with flexible framework of SiO2 nanofibers for highly safe solid lithium batteries. Polymers, 2020,12:1324. |
| [1] | WU Xiangquan, TENG Jiachen, JI Xiangxu, HAO Yubo, ZHANG Zhongming, XU Chunjie. Textured Porous Al2O3-SiO2 Composite Ceramic Platelet-sphere Slurry: Characteristics and Simulation of Light Intensity Distribution [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(7): 769-778. |
| [2] | SHEN Bin, ZHANG Xu, XIONG Huai, LI Haiyuan, XIE Xinglong. Preparation and Optical Properties of Sol-Gel SiO2 Antireflective Films [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(5): 525-530. |
| [3] | ZHEN Mingshuo, LIU Xiaoran, FAN Xiangqian, ZHANG Wenping, YAN Dongdong, LIU Lei, LI Chen. Electrochromic Intelligent Visual Humidity Indication System [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(4): 432-440. |
| [4] | FENG Xingzhe, MA Dongyun, WANG Jinmin. Porous NiMn-LDH Nanosheets Film: Solvothermal Growth and Electrochromic Properties [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(12): 1391-1396. |
| [5] | ZHAO Yawen, QU Fajin, WANG Yanyi, WANG Zhiwen, CHEN Chusheng. Preparation and Properties of Aluminum Silicate Fiber Supported PtTFPP-PDMS Flexible Oxygen Sensing Components [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(10): 1084-1090. |
| [6] | XU Hao, QIAN Wei, HUA Yinqun, YE Yunxia, DAI Fengze, CAI Jie. Effects of Micro Texture Processed by Picosecond Laser on Hydrophobicity of Silicon Carbide [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(8): 923-930. |
| [7] | MA Xiaosen, ZHANG Lichen, LIU Yanchao, WANG Quanhua, ZHENG Jiajun, LI Ruifeng. 13X@SiO2: Synthesis and Toluene Adsorption [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(5): 537-543. |
| [8] | NIU Haibin, HUANG Jiahui, LI Qianwen, MA Dongyun, WANG Jinmin. Directly Hydrothermal Growth and Electrochromic Properties of Porous NiMoO4 Nanosheet Films [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(12): 1427-1433. |
| [9] | SUN Jiawei, WAN Xinyi, YANG Ting, MA Dongyun, WANG Jinmin. Preparation and Electrochromic Properties of Ti2Nb10O29 Films [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(12): 1434-1440. |
| [10] | CHEN Zhang, ZHAO Ruoyi, HAN Shaojie, WANG Huanran, YANG Qun, GAO Yanfeng. Electrochromic WO3 Thin Films: Preparation by Nanocrystalloid Liquid Phase Coating and Performance Optimization [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(11): 1355-1363. |
| [11] | WANG Shiwei. Progress of Spontaneous Coagulation Casting of Ceramic Slurries Based on Hydrophobic Interaction [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(8): 809-820. |
| [12] | HUANG Zhihang, TENG Guanhongwei, TIE Peng, FAN Desong. Electrochromic Property of Perovskite Ceramic Films [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(6): 611-616. |
| [13] | MENG Qing, LI Jiangtao. Hydrophobic BN Powders by Combustion Synthesis and Its Super-hydrophobic Coatings: Preparation and Property [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(10): 1037-1042. |
| [14] | CHEN Xiaomei, CHEN Ying, YUAN Xia. Decomposition of Cyclohexyl Hydroperoxide Catalyzed by Core-shell Material Co3O4@SiO2 [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(1): 65-71. |
| [15] | ZHANG Xiang, LI Wenjie, WANG Lebin, CHEN Xi, ZHAO Jiupeng, LI Yao. Reflective Property of Inorganic Electrochromic Materials [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(5): 451-460. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||