
Journal of Inorganic Materials ›› 2018, Vol. 33 ›› Issue (5): 475-482.DOI: 10.15541/jim20170330
Special Issue: 离子电池材料
• REVIEW • Next Articles
TAN Yi1,2, XUE Bing1,2
Received:2017-07-06
Revised:2017-08-22
Published:2018-05-20
Online:2018-04-26
CLC Number:
TAN Yi, XUE Bing. Research Progress on Lithium Titanate as Anode Material in Lithium-ion Battery[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2018, 33(5): 475-482.
| Ion | Radius /nm | Doping content molar ratio | Size/nm | Initial discharge capacity/(mAh.g-1) | Cycle performance/ (mAh.g-1) | Method | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cation doping in the Li sites(radius 0.076 nm) | |||||||
| Mg2+ | 0.0720 | 0.20 | 100-200 | 190.0(1C)a | 179.0(1C, 100)b; 150.0(5C, 100) | Solid state reaction | [30] |
| Ca2+ | 0.1000 | 0.10 | 1000-2000 | 169.7(0.5C) | 162.4(1C, 100); 148.8(5C, 100) | Solid state reaction | [31] |
| Sc3+ | 0.0745 | 0.05 | 200 | 174.0(1C); 94.0(40C) | 94.0(40C, 50) | Sol-Gel | [32] |
| Cu2+ | 0.0730 | 0.05 | 200-600 | 158.0(0.1C) | 143.8(0.1C, 150) | Sol-Gel | [33] |
| La3+ | 0.1032 | 0.06 | 24.5 | 169.0(0.1C) | 153.4(1C, 10); 146.9(5C, 10) | Liquid method | [34] |
| Cation doping in the Ti sites (radiusTi3+0.067 nm, Ti4+0.0605 nm) | |||||||
| Al3+ | 0.0535 | 0.15 | 50-200 | 216.0(1C); 163.0(10C) | 180.0(5C, 50); 160.0(10C, 50) | Cellulose-assisted glycine-nitratecombustion | [35] |
| Zr4+ | 0.0720 | 0.03 | 200 | 165.0(5C); 152.0(10C) | 142.0(5C, 200); 127.0(10C, 200) | Liquid method | [36] |
| Ce4+ | 0.0870 | 0.10 | <1000 | 190.0(0.2C); 40.0(2C) | 140.0(2C, 100) | Solid state reaction | [37] |
| Ta5+ | 0.0640 | 0.05 | 500-1000 | 193.0(0.2C) | 132.0(5C, 100) | Solid state reaction | [38] |
| Anions doping in the O site (radius 0.14 nm) | |||||||
| Cl- | 0.181 | 0.2 | 3-8 μm | 148.7(0.5C) | 133.8(0.5C, 50) | Solid state reaction | [39] |
| 120.7(2C) | |||||||
| Br- | 0.196 | 0.3 | 1-2 μm | 174.0(0.2C) | 138.0(10C, 100); 104.0(210C,100) | Solid state reaction | [40] |
Table 1 Summary of representative LTO doped with various cations/anions in the Li, Ti and O sites
| Ion | Radius /nm | Doping content molar ratio | Size/nm | Initial discharge capacity/(mAh.g-1) | Cycle performance/ (mAh.g-1) | Method | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cation doping in the Li sites(radius 0.076 nm) | |||||||
| Mg2+ | 0.0720 | 0.20 | 100-200 | 190.0(1C)a | 179.0(1C, 100)b; 150.0(5C, 100) | Solid state reaction | [30] |
| Ca2+ | 0.1000 | 0.10 | 1000-2000 | 169.7(0.5C) | 162.4(1C, 100); 148.8(5C, 100) | Solid state reaction | [31] |
| Sc3+ | 0.0745 | 0.05 | 200 | 174.0(1C); 94.0(40C) | 94.0(40C, 50) | Sol-Gel | [32] |
| Cu2+ | 0.0730 | 0.05 | 200-600 | 158.0(0.1C) | 143.8(0.1C, 150) | Sol-Gel | [33] |
| La3+ | 0.1032 | 0.06 | 24.5 | 169.0(0.1C) | 153.4(1C, 10); 146.9(5C, 10) | Liquid method | [34] |
| Cation doping in the Ti sites (radiusTi3+0.067 nm, Ti4+0.0605 nm) | |||||||
| Al3+ | 0.0535 | 0.15 | 50-200 | 216.0(1C); 163.0(10C) | 180.0(5C, 50); 160.0(10C, 50) | Cellulose-assisted glycine-nitratecombustion | [35] |
| Zr4+ | 0.0720 | 0.03 | 200 | 165.0(5C); 152.0(10C) | 142.0(5C, 200); 127.0(10C, 200) | Liquid method | [36] |
| Ce4+ | 0.0870 | 0.10 | <1000 | 190.0(0.2C); 40.0(2C) | 140.0(2C, 100) | Solid state reaction | [37] |
| Ta5+ | 0.0640 | 0.05 | 500-1000 | 193.0(0.2C) | 132.0(5C, 100) | Solid state reaction | [38] |
| Anions doping in the O site (radius 0.14 nm) | |||||||
| Cl- | 0.181 | 0.2 | 3-8 μm | 148.7(0.5C) | 133.8(0.5C, 50) | Solid state reaction | [39] |
| 120.7(2C) | |||||||
| Br- | 0.196 | 0.3 | 1-2 μm | 174.0(0.2C) | 138.0(10C, 100); 104.0(210C,100) | Solid state reaction | [40] |
| Ion | Radius/nm | Doping content molar ratio | Size/ nm | Initial discharge capacity/(mAh.g-1) | Cycle performance/ (mAh.g-1) | Method | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Zn2+ | 0.074 | 0.20 | 1000-2000 | (0-2.5 V) | 216.4(0.5C, 30) | Solid state reaction | [6] |
| 271.6(0.5C)a; 223.0(3C); | 198.0(3C, 100) | ||||||
| 186.0(5C, 200) | |||||||
| 206.0(5C) | |||||||
| Nb5+ | 0.064 | 0.05 | (0-2.5 V) | 231.0(0.12C, 100) | Sol-Gel | [46] | |
| 351.0(0.12C) | |||||||
| Ru4+ | 0.062 | 0.05 | 100-200 | (0.01-2.5 V) | 259.0(3C, 100); 131.0(60C, 100) | Reverse microemulsion method | [47] |
| 274.0(3C) | |||||||
| Bi+3+ | 0.103 | 0.10 | 500-1000 | (0.01-2.5 V) | 203.0(1C, 50) | Solid state reaction | [48] |
| 214.0(1C) |
Table 2 Summary of representative LTO doped with various cations in the Li, Ti and O sites at low potential
| Ion | Radius/nm | Doping content molar ratio | Size/ nm | Initial discharge capacity/(mAh.g-1) | Cycle performance/ (mAh.g-1) | Method | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Zn2+ | 0.074 | 0.20 | 1000-2000 | (0-2.5 V) | 216.4(0.5C, 30) | Solid state reaction | [6] |
| 271.6(0.5C)a; 223.0(3C); | 198.0(3C, 100) | ||||||
| 186.0(5C, 200) | |||||||
| 206.0(5C) | |||||||
| Nb5+ | 0.064 | 0.05 | (0-2.5 V) | 231.0(0.12C, 100) | Sol-Gel | [46] | |
| 351.0(0.12C) | |||||||
| Ru4+ | 0.062 | 0.05 | 100-200 | (0.01-2.5 V) | 259.0(3C, 100); 131.0(60C, 100) | Reverse microemulsion method | [47] |
| 274.0(3C) | |||||||
| Bi+3+ | 0.103 | 0.10 | 500-1000 | (0.01-2.5 V) | 203.0(1C, 50) | Solid state reaction | [48] |
| 214.0(1C) |
| Carbon source | Carbon content/wt% | Thickness/ nm | Initial discharge capacity/(mAh.g-1) | Cycle performance/ (mAh.g-1) | Method | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LPAN+CB | 3.64 | 3-5 | 166.2(10C) | 141.9(10C, 200) | Solid state reaction | [49] |
| PEDOT | 10.00 | 10 | 168.7(1C) | 167.9(1C, 100) | Hydrothermal reaction | [50] |
| Sucrose | 8.60 | 2-4 | 156.7(40C); 142.1(60C); 132.8(80C) | 114.2(40C, 200); 98.1(60C, 200) 82.7(80C, 200) | One-step liquid process | [51] |
| Citric acid | 1.32 | 2-3 | 165.7(1C); 161.7(5C); 153.9(10C); 147.9(20C) | 144.9(20C, 50) | Sol-Gel | [52] |
| Glucose | 8.96 | 8 | 170.9(0.5C) | 155.6(1C, 100) | Hydrothermal-solid state reaction | [53] |
Table 3 The effects of the carbon source, carbon content, thickness, and graphitization on the electrochemical performance of the carbon coated Li4Ti5O12
| Carbon source | Carbon content/wt% | Thickness/ nm | Initial discharge capacity/(mAh.g-1) | Cycle performance/ (mAh.g-1) | Method | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LPAN+CB | 3.64 | 3-5 | 166.2(10C) | 141.9(10C, 200) | Solid state reaction | [49] |
| PEDOT | 10.00 | 10 | 168.7(1C) | 167.9(1C, 100) | Hydrothermal reaction | [50] |
| Sucrose | 8.60 | 2-4 | 156.7(40C); 142.1(60C); 132.8(80C) | 114.2(40C, 200); 98.1(60C, 200) 82.7(80C, 200) | One-step liquid process | [51] |
| Citric acid | 1.32 | 2-3 | 165.7(1C); 161.7(5C); 153.9(10C); 147.9(20C) | 144.9(20C, 50) | Sol-Gel | [52] |
| Glucose | 8.96 | 8 | 170.9(0.5C) | 155.6(1C, 100) | Hydrothermal-solid state reaction | [53] |
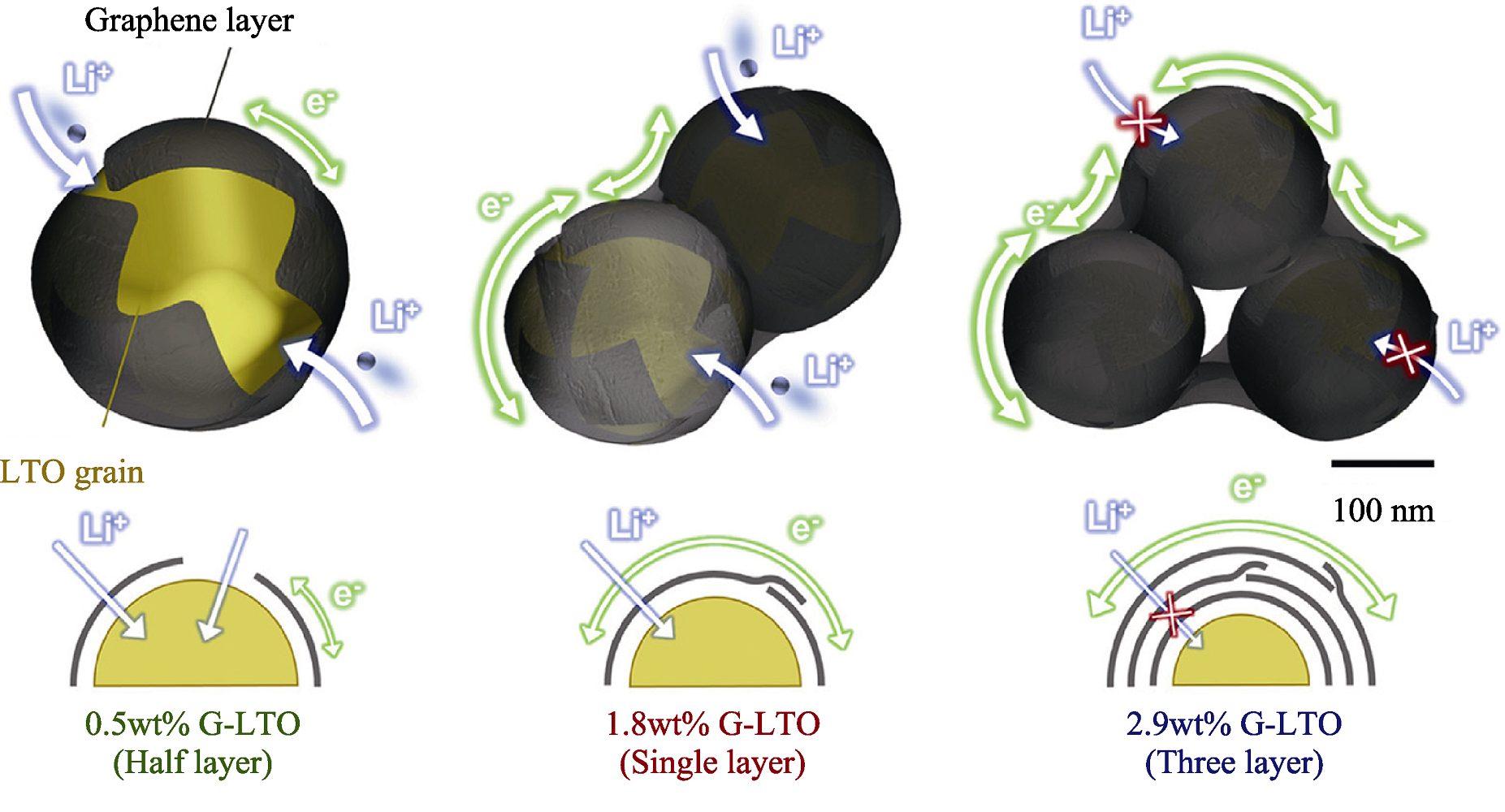
Fig. 5 Schematic illustration representing the electron conduction Li+ and Li+ transport according to the number of graphene layers on the LTO surface[57]
| [1] | LI Z Y, DING F X, ZHAO Y G,et al. Synthesis and electrochemical performance of Li4Ti5O12 submicrospheres coated with TiN as anode materials for lithium-ion battery. Ceram. Int., 2016, 42(14): 15464-15470. |
| [2] | HUI Y N, CAO L Y, XU Z W,et al. In situ synthesis of core-shell Li4Ti5O12@polyaniline composites with enhanced rate performance for lithium-ion battery anodes. J. Mater. Sci. Techno., 2016, 33(3): 231-238. |
| [3] | CHEN S, XIN Y L, ZHOU Y Y,et al. Self-supported Li4Ti5O12 nanosheet arrays for lithium ion batteries with excellent rate capability and ultralong cycle life. Energy Environ. Sci., 2014, 7(6): 1924-1930. |
| [4] | YI T F, YANG S Y, XIE Y.Recent advances of Li4Ti5O12 as a promising next generation anode material for high power lithium- ion batteries.J. Mater. Chem. A, 2015, 3(11): 5750-5777. |
| [5] | BORGHOLS W J H, WAGEMAKER M, LAFONT U,et al. Size effects in the Li4+xTi5O12 spinel. J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2009, 131(49): 17786-17792. |
| [6] | YI T F, LIU H P, ZHU Y R,et al. Improving the high rate performance of Li4Ti5O12 through divalent zinc substitution. J. Power Sources, 2012, 215: 258-265. |
| [7] | WIKENING M, IWANIAK W, HEINE J,et al. Microscopic Li self-diffusion parameters in the lithiated anode material Li4+xTi5O12(0 < or = x < or = 3) measured by 7Li solid state NMR. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2007, 9(47): 6199-6202. |
| [8] | YANG S, WANG Q F, LU M W, et al. Synthesis of graphitized carbon, nanodiamond and graphene supported Li4Ti5O12 and comparison of their electrochemical performance as anodes for lithium ion batteries. Appl. Surf. Sci., 2016, 389: 428-437. |
| [9] | ZHU G N, WANG Y G, XIA Y Y.Ti-based compounds as anode materials for Li-ion batteries.Energy Environ. Sci., 2012, 5(5): 6652-6667. |
| [10] | Yang L Y, LI H Z, LIU J,et al. Effects of TiO2 phase on the performance of Li4Ti5O12 anode for lithium-ion batteries. J. Alloys Compd., 2016, 689: 812-819. |
| [11] | MA J, WANG C, WROBLEWSKI S.Kinetic characteristics of mixed conductive electrodes for lithium ion batteries.J. Power Sources, 2007, 164(2): 849-856. |
| [12] | TAKAMI N, HOSHINA K, INAGAKI H.Lithium diffusion in Li4/3Ti5/3O4 particles during insertion and extraction.J. Electrochem. Soc., 2011, 158(6): A725-A730. |
| [13] | LIU W, ZHANG J, WANG Q,et al. The effects of Li2CO3 particle size on the properties of lithium titanate as anode material for lithium-ion batteries. Ionics, 2014, 20(11): 1553-1560. |
| [14] | CHEN C, SPEARS M, WONDRE F, et al. Crystal growth and superconductivity of LiTi2O4 and Li1+1/3Ti2-1/3O4.J. Cryst. Growth, 2003, 250(1/2): 139-145. |
| [15] | GUERFI A, SEVIGNY S, LAGACE M,et al. Nano-particle Li4Ti5O12 spinel as electrode for electrochemical generators. J. Power Sources, 2003, 119(121): 88-94. |
| [16] | MICHALSKA M, KRAJEWSKI M, ZIOLKOWSKA D,et al. Influence of milling time in solid-state synthesis on structure, morphology and electrochemical properties of Li4Ti5O12 of spinel structure. Powder Technol., 2014, 266(6): 372-377. |
| [17] | SENNA M, FAVIAN M, KAVAN L,et al. Electrochemical properties of spinel Li4Ti5O12 nanoparticles prepared via a low-temperature solid route. J. Solid State Electrochem., 2016, 20(10): 2673-2683. |
| [18] | HAN S W, JEONG J, YOON D H.Effects of high-energy milling on the solid-state synthesis of pure nano-sized Li4Ti5O12 for high power lithium battery applications.Appl. Phys. A, 2014, 114(3): 925-930. |
| [19] | WANG Y Q, ZHAO J, QU J,et al. Investigation into the surface chemistry of Li4Ti5O12 nanoparticles for lithium ion batteries. Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2016, 8(39): 26008-26012. |
| [20] | QIU C X, YUAN Z Z, LIU L,et al. Sol-Gel preparation and electrochemical properties of La-doped Li4Ti5O12 anode material for lithium-ion battery. J. Solid State Electrochem., 2013, 17(3): 841-847. |
| [21] | MOHAMMADI M R, FRAY D J.Low temperature nanostructured lithium titanates: controlling the phase composition, crystal structure and surface area.J. Sol-Gel Sci. Techn., 2010, 55(1): 19-35. |
| [22] | LIU G Y, ZHANG R X, BAO K Y,et al. Synthesis of nano- Li4Ti5O12 anode material for lithium ion batteries by a biphasic interfacial reaction route. Ceram. Int., 2016, 42(9): 11468-11472. |
| [23] | ZHU K X, GAO H Y, HU G X,et al. Scalable synthesis of hierarchical hollow Li4Ti5O12 microspheres assembled by zigzag-like nanosheets for high rate lithium-ion batteries. J. Power Sources, 2017, 340: 263-272. |
| [24] | GUO Q J, LI S Y, WANG H,et al. Molten salt synthesis of nano-sized Li4Ti5O12 doped with Fe2O3 for use as anode material in the lithium ion battery. RSC Adv., 2014. 4(104): 60327-60333. |
| [25] | ZHAO Y G, LI J L, LI Z Y,et al. Pr-modified Li4Ti5O12 nanofibers as an anode material for lithium-ion batteries with outstanding cycling performance and rate performance. Ionics, 2017. 23(3): 597-605. |
| [26] | YANG L H, DONG C D, GUO J.Hybrid microwave synthesis and characterization of the compounds in the Li-Ti-O system.J. Power Sources, 2008, 175(1): 575-580. |
| [27] | LI J, JIN Y L, ZHANG X G,et al. Microwave solid-state synthesis of spinel Li4Ti5O12 nanocrystallites as anode material for lithium- ion batteries. Solid State Ionics, 2007, 178(29/30): 1590-1594. |
| [28] | JIA X L, KAN Y F, ZHU X,et al. Building flexible Li4Ti5O12/CNT lithium-ion battery anodes with superior rate performance and ultralong cycling stability. Nano Energy, 2014, 10: 344-352. |
| [29] | WOLFENSTINE J, ALLEN J L.Electrical conductivity and charge compensation in Ta doped Li4Ti5O12.J. Power Sources, 2008, 180(1): 582-585. |
| [30] | LI F Y, ZHENG M, LI J,et al. Preparation and electrochemical performance of Mg-doped Li4Ti5O12 nanoparticles as anode materials for lithium-ion batteries. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci., 2015, 10(12): 10445-10453. |
| [31] | ZHANG Q Y, ZHANG C L, LI B,et al. Preparation and electrochemical properties of Ca-doped Li4Ti5O12 as anode materials in lithium-ion battery materials for flexible Li-ion batteries. Electrochim. Acta, 2013, 98(16): 146-152. |
| [32] | ZHANG Y Y, ZHANG C M, LIN Y,et al. Influence of Sc3+ doping in B-site on electrochemical performance of Li4Ti5O12 anode materials for lithium-ion battery. J. Power Sources, 2014, 250(3): 50-57. |
| [33] | GE Y Q, JIANG H, FU K,et al. Copper-doped Li4Ti5O12/carbon nanofiber composites as anode for high-performance sodium-ion batteries. J. Power Sources, 2014, 272: 860-865. |
| [34] | BAI Y J, GONG C, QI Y X,et al. Excellent long-term cycling stability of La-doped Li4Ti5O12 anode material at high current rates. J. Mater. Chem., 2012, 22(36): 19054-19060. |
| [35] | CAI R, JIANG S M, YU X,et al. A novel method to enhance rate performance of an Al-doped Li4Ti5O12 electrode by post-synthesis treatment in liquid formaldehyde at room temperature. J. Mater. Chem., 2012, 22(16): 8013-8021. |
| [36] | CHEN Y J, MU D B, HANG R,et al. The Improvement of Discharge Capacity of Zr-doped Lithium Titanate for Lithium Ion Batteries. Matec Web Conf., 2016, 67: 06028. |
| [37] | ZHOU T P, FENG X Y, GUO X,et al. Solid-state synthesis and electrochemical performance of Ce-doped Li4Ti5O12 anode materials for lithium-ion batteries. Electrochim. Acta, 2015, 174: 369-375. |
| [38] | GUO M, WANG S Q, DING L X,et al. Tantalum-doped lithium titanate with enhanced performance for lithium-ion batteries. J. Power Sources, 2015, 283(25): 372-380. |
| [39] | HUANG Y D, QI Y L, JIA D Z,et al. Synthesis and electrochemical properties of spinel Li4Ti5O12-xClx anode materials for lithium- ion batteries. J. Solid State Electrochem., 2012, 16(5): 2011-2016. |
| [40] | WANG J Q, YANG Z Z, LI W H,et al. Nitridation Br-doped Li4Ti5O12 anode for high rate lithium ion batteries. J. Power Sources, 2014, 266(1): 323-331. |
| [41] | DING K Q, ZHAO J, SUN Y Z,et al. Using potassium ferricyanide as a dopant to prepare K and Fe co-doped Li4Ti5O12. Ceram. Int., 2016, 42(16): 19187-19194. |
| [42] | BAI X, LI W, WEI A J,et al. Preparation and electrochemical properties of Mg2+ and F- co-doped Li4Ti5O12 anode material for use in the lithium-ion batteries materials for flexible Li-ion batteries. Electrochim. Acta, 2016, 222: 1045-1055. |
| [43] | XU P, HUANG X B, REN Y R,et al. Na+ and Zr4+ co-doped Li4Ti5O12 as anode materials with superior electrochemical performance for lithium ion batteries. RSC Adv., 2016, 6(93): 90455-90461. |
| [44] | LONG W M, WANG X Y, YANG S Y,et al. Electrochemical properties of Li4Ti5-2xNixMnxO12 compounds synthesized by Sol-Gel process. Mater. Chem. Phys., 2011, 131(1): 431-435. |
| [45] | SHKROB I A, ZHU Y, MARIN T W,et al. Reduction of carbonate electrolytes and the formation of solid-electrolyte interface (SEI) in lithium-ion batteries. 1. spectroscopic observations of radical intermediates generated in one-electron reduction of carbonates. J. Phys. Chem. C, 2013, 117(38): 19255-19269. |
| [46] | TIAN B B, XIANG H F, ZHANG L,et al. Effect of Nb-doping on electrochemical stability of Li4Ti5O12 discharged to 0 V. J. Solid State Electrochem., 2012, 16(1): 205-211. |
| [47] | WANG W, WANG H L, WANG S B,et al. Ru-doped Li4Ti5O12 anode materials for high rate lithium-ion batteries. J. Power Sources, 2013, 228(11): 244-249. |
| [48] | SUBBURAJ T, PRASANNA K, KIM K J,et al. Structural and electrochemical evaluation of bismuth doped lithium titanium oxides for lithium ion batteries. J. Power Sources, 2015, 280: 23-29. |
| [49] | HUANG P X, TANG S H, PENG H,et al. In-situ synthesis of graphitized-carbon coated Li4Ti5O12/C anode for high-rate lithium ion batteries. Mater. Sci. Forum, 2015, 814: 358-364. |
| [50] | WANG X Y, SHEN L F, LI H S,et al. PEDOT coated Li4Ti5O12 nanorods: soft chemistry approach synthesis and their lithium storage properties. Electrochim. Acta, 2014, 129(16): 283-289. |
| [51] | MU D B, CHEN Y J, WU B R,et al. Nano-sized Li4Ti5O12/C anode material with ultrafast charge/discharge capability for lithium ion batteries. J. Alloys Compd., 2016, 671: 157-163. |
| [52] | KUO Y C, LIN J Y.One-pot Sol-Gel synthesis of Li4Ti5O12/C anode materials for high-performance Li-ion batteries.Electrochim. Acta, 2014, 142: 43-50. |
| [53] | GAO L, LIU R J, HU H,et al. Carbon-decorated Li4Ti5O12/rutile TiO2 mesoporous microspheres with nanostructures as high-performance anode materials in lithium-ion batteries. Nanotechnology, 2014, 25(17): 175402-175410. |
| [54] | XUE R, YAN J W, JIANG L,et al. Fabrication of lithium titanate/ graphene composites with high rate capability as electrode materials for hybrid electrochemical super capacitors. Mater. Chem. Phys., 2015, 160: 375-382. |
| [55] | LI R Y, CHEN T Y, SUN B B,et al. Novel lithium titanate-graphene hybrid containing two graphene conductive frameworks for lithium- ion battery with excellent electrochemical performance. Mater. Res. Bull., 2015, 70: 965-975. |
| [56] | YANG X J, ZHENG A B, WANG X L,et al. Graphene nanosheet and carbon layer co-decorated Li4Ti5O12 as high performance anode material for rechargeable lithium-ion batteries. Ceram. Int., 2017, 43(3): 3252-3258. |
| [57] | KIM J, LEE K E, KIM K H,et al. Single-layer graphene-wrapped Li4Ti5O12 anode with superior lithium storage capability. Carbon, 2017, 114: 275-283. |
| [58] | KIM K T, YU C Y, YOON C S,et al. Carbon-coated Li4Ti5O12 nanowires showing high rate capability as an anode material for rechargeable sodium batteries. Nano Energy, 2015, 12: 725-734. |
| [59] | LUO H J, SHEN L F, RUI K,et al. Carbon coated Li4Ti5O12 nanorods as superior anode material for high rate lithium ion batteries. J. Alloys Compd., 2013, 572: 37-42. |
| [60] | LIU J, SONG K, AKEN P A,et al. Self-supported Li4Ti5O12-C nanotube arrays as high-rate and long-life anode materials for flexible Li-ion batteries. Nano Lett., 2014, 14(5): 2597-2603. |
| [1] | WANG Tianyue, WANG Mengying, HUANG Qingjiao, YANG Jiaming, WANG Shunhua, DIAO Xungang. Preparation of Lithium Titanate Thin Film for Electrochromic Smart Window by Sol-Gel Spin Coating Method [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(5): 471-478. |
| [2] | XIA Tian, MENG Xie, LUO Ting, ZHAN Zhongliang. La 3+-substituted Sr2Fe1.5Ni0.1Mo0.4O6-δ as Anodes for Solid Oxide Fuel Cells [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2020, 35(5): 617-622. |
| [3] | ZHENG Shiyou, DONG Fei, PANG Yuepeng, HAN Pan, YANG Junhe. Research Progress on Nanostructured Metal Oxides as Anode Materials for Li-ion Battery [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2020, 35(12): 1295-1306. |
| [4] | GUO Si-Lin, KANG Shuai, LU Wen-Qiang. Ge Nanoparticles in MXene Sheets: One-step Synthesis and Highly Improved Electrochemical Property in Lithium-ion Batteries [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2020, 35(1): 105-111. |
| [5] | Yi TAN, Kai WANG. Silicon-based Anode Materials Applied in High Specific Energy Lithium-ion Batteries: a Review [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2019, 34(4): 349-357. |
| [6] | HU Xi, LIU Hong-Bo, XIA Xiao-Hong, GU Zhi-Qiang. Polyaniline-carbon Pillared Graphene Composite: Preparation and Electrochemical Performance [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2019, 34(2): 145-151. |
| [7] | LIU Huan-Long, ZHAO Wei, LI Rui-Zhe, HUANG Xie-Yi, TANG Yu-Feng, LI Dong-Mei, HUANG Fu-Qiang. Facile Synthesis of Reduced Graphene Oxide In-situ Wrapped MnTiO3 Nanoparticles for Excellent Lithium Storage [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2018, 33(9): 1022-1028. |
| [8] | QIN Shi-Lin, LI Ji-Cheng, LI Zhao-Hui, HU Zhong-Liang, DING Yan-Huai, LEI Gang-Tie, XIAO Qi-Zhen. Ferric Oxide-reduced Graphene Oxide Composite Material: Synthesis Based on Covalent Binding and Its Lithium-storage Property [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2018, 33(7): 741-748. |
| [9] | YANG Ke, HOU Chao, SONG Xiao-Yan. Synthesis and Property of Novel Li21Si5/Graphene Composites Anode for High Energy Lithium-ion Batteries [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2018, 33(10): 1065-1069. |
| [10] | MENG Xiang-Lu, HUO Han-Yu, GUO Xiang-Xin, DONG Shao-Ming. Influence of Film Thickness on the Electrochemical Performance of α-SiOx Thin-film Anodes [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2018, 33(10): 1141-1146. |
| [11] | YANG Tao, LI Xiao, TIAN Xiao-Dong, SONG Yan, LIU Zhan-Jun, GUO Quan-Gui. Preparation and Electrochemical Performance of Si@C/SiOx as Anode Material for Lithium-ion Batteries [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2017, 32(7): 699-704. |
| [12] | LI Wei, ZHANG Yuan-Jie, WANG Xuan-Peng, NIU Chao-Jiang, AN Qin-You, MAI Li-Qiang. Synthesis and Electrochemical Performance of LiMn0.6Fe0.4PO4/C Cathode for Lithium-ion Batteries [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2017, 32(5): 476-482. |
| [13] | CAI Ya-Ling, LI Ya-Fei, WANG Zeng-Mei, ZHANG Yao, CHEN Jian, GUO Xin-Li. CTAB-assisted Synthesis of MoS2/C Nano-flowers with Improved Electrochemical Performances for Lithium Ion Batteries [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2016, 31(12): 1289-1294. |
| [14] | LIU Jian-Zhe, GUO Peng-Fei. VS2 Nanosheets: A Potential Anode Materiral for Li-ion Batteriers [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2015, 30(12): 1339-1344. |
| [15] | LIU Ya-Di, YUAN Chun, ZHOU Yu-Cun, ZOU Jie, XIN Xian-Shuang, WANG Shao-Rong. Composite Anodes with Ni Impregnated LST-SSZ for Direct Methane Solid Oxide Fuel Cells [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2014, 29(11): 1121-1126. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||