
Journal of Inorganic Materials ›› 2016, Vol. 31 ›› Issue (5): 473-478.DOI: 10.15541/jim20150508
• Orginal Article • Previous Articles Next Articles
WU Xuan-Rong1, YANG Qiao-Zhen1, ZHAO Yong-Xiang1, LU Yan-Luo2
Received:2015-10-19
Revised:2015-12-02
Published:2016-05-20
Online:2016-04-25
About author:WU Xuan-Rong. E-mail:15135143242@163.com
CLC Number:
WU Xuan-Rong, YANG Qiao-Zhen, ZHAO Yong-Xiang, LU Yan-Luo. Hydrothermal/Solvothermal Synthesis and Photocatalytic Performance of ZnS Microspheres[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2016, 31(5): 473-478.
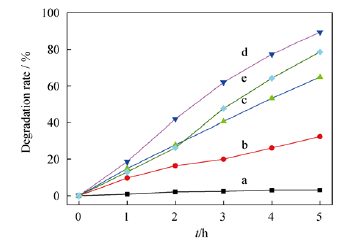
Fig. 5 Phenol photocatalytic degradation performance of as-synthesized ZnS in different solvent systems (a) (CH2OH)2, 0 W; (b) 300 W; (c) (CH2OH)2, 300 W; (d) (CH2OH)2-H2O, 300 W ; (e) H2O, 300 W
| [1] | MURUGANANDHAM M, AMUTHA R, SILLANPAA M.Reagents for ZnS hierarchical and non-hierarchical porous self- assembly.Appl. Mater. Inter., 2010, 2(7): 1817-1823. |
| [2] | WANG Z, QIAN X F, LI Y, et al.Large-scale synthesis of tube-like ZnS and cable-like ZnS-ZnO arrays: preparation through the sulfuration conversion from ZnO arrays via a simple chemical solution route. J. Solid State Chem., 2005, 178(5): 1589-1594. |
| [3] | JIANG L, SUN Y Y, CHEN H, et al.Synthesis and characterizations of flower-like ZnS and ZnS: Cu2+ nanostructures.Mater. Lett., 2014, 131(12): 82-85. |
| [4] | LIU Y, HU J C, NGO C, et al.Gram-scale wet chemical synthesis of wurtzite-8H nanoporous ZnS spheres with high photocatalytic activity.Appl. Catal. B-Environ., 2011, 106(1): 212-219. |
| [5] | YUE G H, YAN P X, YAN D, et al.Hydrothermal synthesis of single-crystal ZnS nanowires.Appl. Phys. A-Mater., 2006, 84(4): 409-412. |
| [6] | PARK J Y, CHOI D Y, HWANG K Y, et al.Synthesis of ZnS microspheres by template-free hydrothermal method for photocatalytic reaction.J. Nanosci. Nanotechno., 2015, 15(7): 5224-5227. |
| [7] | RANA R K, ZHANG L, YU J C, et al.Mesoporous structures from supramolecular assembly of in situ generated ZnS nanoparticles.Langmuir, 2003, 19(14): 5904-5911. |
| [8] | REN G Q, LIN Z, GILBERT B, et al.Evolution of ZnS nanostructure morphology under interfacial free-energy control.Chem. Mater., 2008, 20(7): 2438-2443. |
| [9] | YU X X, YU J G, CHENG B, et al.One-pot template-free synthesis of monodisperse zinc sulfide hollow spheres and their photocatalytic properties.Chem. Eur. J., 2009, 15(27): 6731-6739. |
| [10] | YU C L, YANG K, XIE Y, et al.Novel hollow Pt-ZnO nanocomposite microspheres with hierarchical structure and enhanced photocatalytic activity and stability.Nanoscale, 2013, 5(5): 2142-2151. |
| [11] | YU C L, CAO F F, LI X, et al.Hydrothermal synthesis and characterization of novel PbWO4 microspheres with hierarchical nanostructures and enhanced photocatalytic performance in dye degradation. Chem. Eng. J., 2013, 219(3): 86-95. |
| [12] | YU C L, YU J C, CHAN M.Sonochemical fabrication of fluorinated mesoporous titanium dioxide microspheres.J. Solid State Chem., 2009, 182(5): 1061-1069. |
| [13] | MURUGANANDHAM M, AMUTHA R, REPO E, et al.Controlled mesoporous self-assembly of ZnS microsphere for photocatalytic degradation of methyl orange dye.J. Photoch. Photobio. A, 2010, 216(2): 133-141. |
| [14] | HU C G, ZHANG Z W, LIU H, et al.Direct synthesis and structure characterization of ultrafine CeO2 Nanoparticles.Nanotechnology, 2006, 17(24): 5983-5987. |
| [15] | LI XIN, YU CHANG-LIN, FAN QI-ZHE, et al.Solvothermal preparation spherical ZnS nano-photocatalyst and its photocatalytic activity.Nonferr. Metal. Sci. Eng., 2012, 3(3): 21-26. |
| [16] | SHI F F, CHEN L L, XING C S, et al.ZnS microsphere/g-C3N4 nanocomposite photocatalyst with greatly enhanced visible light performance for hydrogen evolution: synthesis and synergistic mechanism study.RSC Adv., 2014, 4(107): 62223-62229. |
| [17] | NAVANEETHAN M, ARCHANA J, NISHA K D, et al.Temperature dependence of morphology, structural and optical properties of ZnS nanostructures synthesized by wet chemical route.J. Alloys Compd., 2010, 506(1): 249-252. |
| [18] | ZHANG QIN-FENG, HUANG JIAN-FENG, CAO LI-YUN, et al.Preparation and morphology controlling of monodisperse CdS nanospheres by microwave hydrothermal process.Chinese J. Inorg. Chem., 2013, 29(2): 271-276. |
| [19] | DONG F F, GUO Y, ZHANG J, et al.Size-controllable hydrothermal synthesis of ZnS nanospheres and the application in photocatalytic degradation of organic dyes.Mater. Lett., 2013, 97(1): 59-63. |
| [20] | ZHONG J H, ZHANG Y, HU C Q, et al.Supercritical solvothermal preparation of a ZnxCd1-xS visible photocatalyst with enhanced activity.J. Mater. Chem. A, 2014, 2(46): 19641-19647. |
| [21] | TANG Y F, LIU X L, MA C C, et al.Enhanced photocatalytic degradation of tetracycline antibiotics by reduced graphene oxide- CdS/ZnS heterostructure photocatalysts.New J. Chem., 2015, 39(1): 5150-5160. |
| [22] | LONG M, CAI W, CAI J, et al.Efficient photocatalytic degradation of phenol over Co3O4/BiVO4 composite under visible light irradiation.J. Phys. Chem. B, 2006, 110(41): 20211-20216. |
| [23] | SHEN Y J, LEI L C, ZHANG X W, et al.Effect of various gases and chemical catalysts on phenol degradation pathways by pulsed electrical discharges.J. Hazard. Mater., 2008, 150(3): 713-722. |
| [1] | ZHOU Houlin, SONG Zhiqing, TIAN Guo, GAO Xingsen. Effects of Growth Conditions on the Formation of Self-assembly Grown Topological Domain in BiFeO3 Nanoislands [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(6): 667-674. |
| [2] | FAN Xiaoxuan, ZHENG Yonggui, XU Lirong, YAO Zimin, CAO Shuo, WANG Kexin, WANG Jiwei. Organic Pollutant Fenton Degradation Driven by Self-activated Afterglow from Oxygen-vacancy-rich LiYScGeO4: Bi3+ Long Afterglow Phosphor [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(5): 481-488. |
| [3] | JIA Xianghua, ZHANG Huixia, LIU Yanfeng, ZUO Guihong. Cu2O/Cu Hollow Spherical Heterojunction Photocatalysts Prepared by Wet Chemical Approach [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(4): 397-404. |
| [4] | MA Binbin, ZHONG Wanling, HAN Jian, CHEN Liangyu, SUN Jingjing, LEI Caixia. ZIF-8/TiO2 Composite Mesocrystals: Preparation and Photocatalytic Activity [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(8): 937-944. |
| [5] | CAO Qingqing, CHEN Xiangyu, WU Jianhao, WANG Xiaozhuo, WANG Yixuan, WANG Yuhan, LI Chunyan, RU Fei, LI Lan, CHEN Zhi. Visible-light Photodegradation of Tetracycline Hydrochloride on Self-sensitive Carbon-nitride Microspheres Enhanced by SiO2 [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(7): 787-792. |
| [6] | WANG Zhaoyang, QIN Peng, JIANG Yin, FENG Xiaobo, YANG Peizhi, HUANG Fuqiang. Sandwich Structured Ru@TiO2 Composite for Efficient Photocatalytic Tetracycline Degradation [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(4): 383-389. |
| [7] | WU Lin, HU Minglei, WANG Liping, HUANG Shaomeng, ZHOU Xiangyuan. Preparation of TiHAP@g-C3N4 Heterojunction and Photocatalytic Degradation of Methyl Orange [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(5): 503-510. |
| [8] | ZHANG Xiangsong, LIU Yetong, WANG Yongying, WU Zirui, LIU Zhenzhong, LI Yi, YANG Juan. Self-assembled Platinum-iridium Alloy Aerogels and Their Efficient Electrocatalytic Ammonia Oxidation Performance [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(5): 511-520. |
| [9] | LING Jie, ZHOU Anning, WANG Wenzhen, JIA Xinyu, MA Mengdan. Effect of Cu/Mg Ratio on CO2 Adsorption Performance of Cu/Mg-MOF-74 [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(12): 1379-1386. |
| [10] | SUN Chen, ZHAO Kunfeng, YI Zhiguo. Research Progress in Catalytic Total Oxidation of Methane [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(11): 1245-1256. |
| [11] | MA Xinquan, LI Xibao, CHEN Zhi, FENG Zhijun, HUANG Juntong. BiOBr/ZnMoO4 Step-scheme Heterojunction: Construction and Photocatalytic Degradation Properties [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(1): 62-70. |
| [12] | CHEN Hanxiang, ZHOU Min, MO Zhao, YI Jianjian, LI Huaming, XU Hui. 0D/2D CoN/g-C3N4 Composites: Structure and Photocatalytic Performance for Hydrogen Production [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(9): 1001-1008. |
| [13] | XUE Hongyun, WANG Congyu, MAHMOOD Asad, YU Jiajun, WANG Yan, XIE Xiaofeng, SUN Jing. Two-dimensional g-C3N4 Compositing with Ag-TiO2 as Deactivation Resistant Photocatalyst for Degradation of Gaseous Acetaldehyde [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(8): 865-872. |
| [14] | CHI Congcong, QU Panpan, REN Chaonan, XU Xin, BAI Feifei, ZHANG Danjie. Preparation of SiO2@Ag@SiO2@TiO2 Core-shell Structure and Its Photocatalytic Degradation Property [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(7): 750-756. |
| [15] | WANG Xiaojun, XU Wen, LIU Runlu, PAN Hui, ZHU Shenmin. Preparation and Properties of Ag@C3N4 Photocatalyst Supported by Hydrogel [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(7): 731-740. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||