
Journal of Inorganic Materials ›› 2026, Vol. 41 ›› Issue (2): 262-272.DOI: 10.15541/jim20250113
• RESEARCH LETTER • Previous Articles
LI Hao1,2( ), QI Yuan1,2, GAO Xiangdong2(
), QI Yuan1,2, GAO Xiangdong2( ), ZHANG Xingxing2, WANG Jinmin1(
), ZHANG Xingxing2, WANG Jinmin1( )
)
Received:2025-03-18
Revised:2025-04-21
Published:2026-02-20
Online:2025-04-27
Contact:
GAO Xiangdong, professor. E-mail: xdgao@mail.sic.ac.cn;About author:LI Hao (1997-), male, Master candidate. E-mail: 769718909@qq.com
CLC Number:
LI Hao, QI Yuan, GAO Xiangdong, ZHANG Xingxing, WANG Jinmin. High Temperature Resistant Calcium-doped Silica Aerogels with Enhanced Thermal Insulation via Sol-Gel Hydrothermal Route[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2026, 41(2): 262-272.
| Sample | Ca/Si molar ratio | Temperature/℃ | pH* |
|---|---|---|---|
| PSA | 0 | - | - |
| HPSA | 0 | 180 | 5-6 |
| CSA-0.4 | 0.4 | - | 5-6 |
| HCSA-0.4 | 0.4 | 120 | 5-6 |
| 0.4 | 140 | 5-6 | |
| 0.4 | 160 | 5-6 | |
| 0.4 | 180 | 5-6 | |
| 0.4 | 200 | 5-6 | |
| HCSA-0.6 | 0.6 | 180 | 5-6 |
| HCSA-0.8 | 0.8 | 180 | 5-6 |
| HCSA-1.0 | 1.0 | 180 | 5-6 |
| 1.0 | 180 | 7-8 | |
| 1.0 | 180 | 9-10 | |
| 1.0 | 180 | 12-13 | |
| HCSA-1.2 | 1.2 | 180 | 5-6 |
| HCSA-1.5 | 1.5 | 180 | 5-6 |
Table 1 Experimental parameters of the aerogel powders
| Sample | Ca/Si molar ratio | Temperature/℃ | pH* |
|---|---|---|---|
| PSA | 0 | - | - |
| HPSA | 0 | 180 | 5-6 |
| CSA-0.4 | 0.4 | - | 5-6 |
| HCSA-0.4 | 0.4 | 120 | 5-6 |
| 0.4 | 140 | 5-6 | |
| 0.4 | 160 | 5-6 | |
| 0.4 | 180 | 5-6 | |
| 0.4 | 200 | 5-6 | |
| HCSA-0.6 | 0.6 | 180 | 5-6 |
| HCSA-0.8 | 0.8 | 180 | 5-6 |
| HCSA-1.0 | 1.0 | 180 | 5-6 |
| 1.0 | 180 | 7-8 | |
| 1.0 | 180 | 9-10 | |
| 1.0 | 180 | 12-13 | |
| HCSA-1.2 | 1.2 | 180 | 5-6 |
| HCSA-1.5 | 1.5 | 180 | 5-6 |
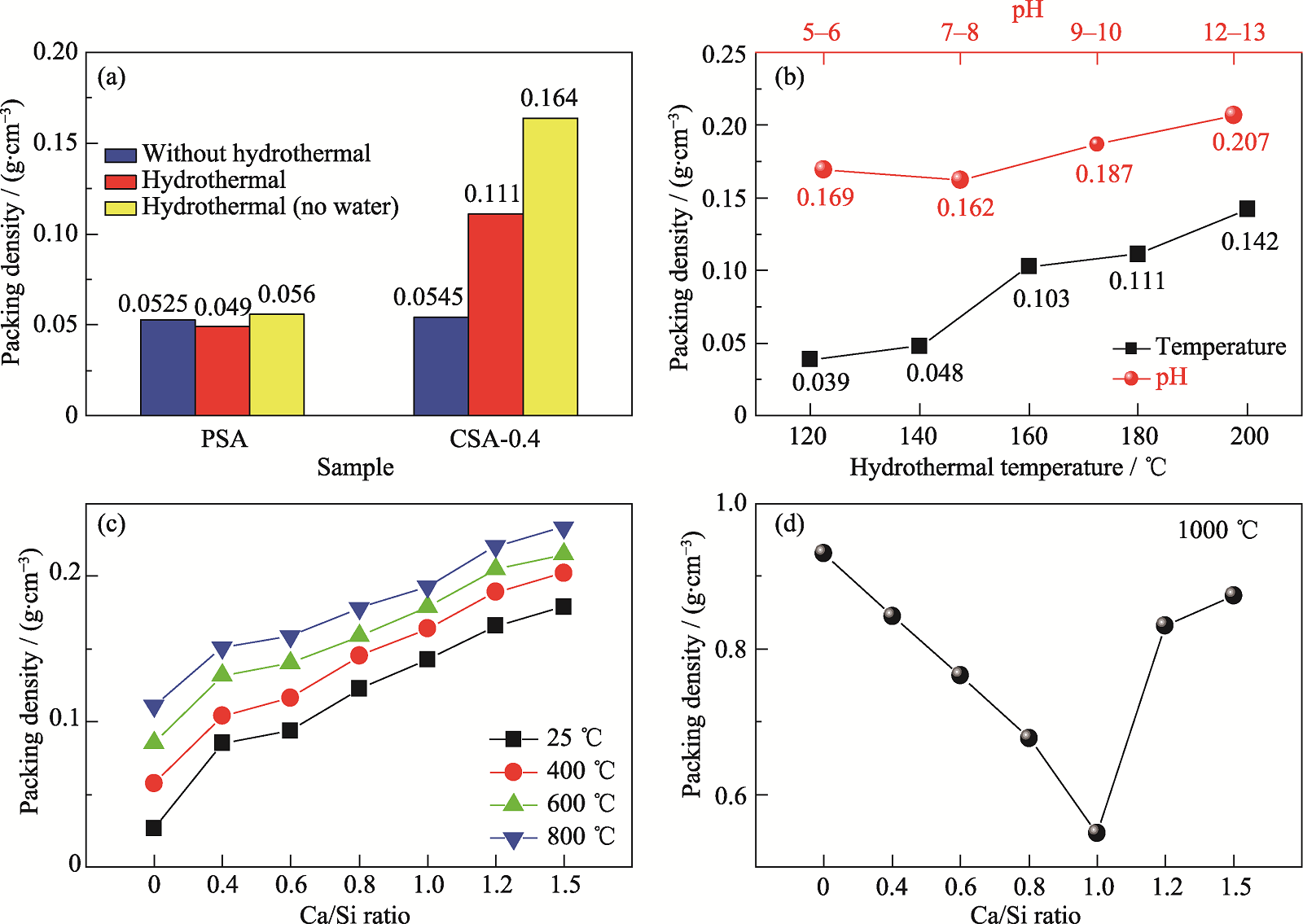
Fig. 2 Packing densities of different samples (a) PSA and CSA-0.4 under different hydrothermal conditions; (b) HCSA-0.4 at different hydrothermal temperatures and HCSA-1.0 at different hydrothermal pH; (c, d) HCSA sintered at different temperatures for 2 h
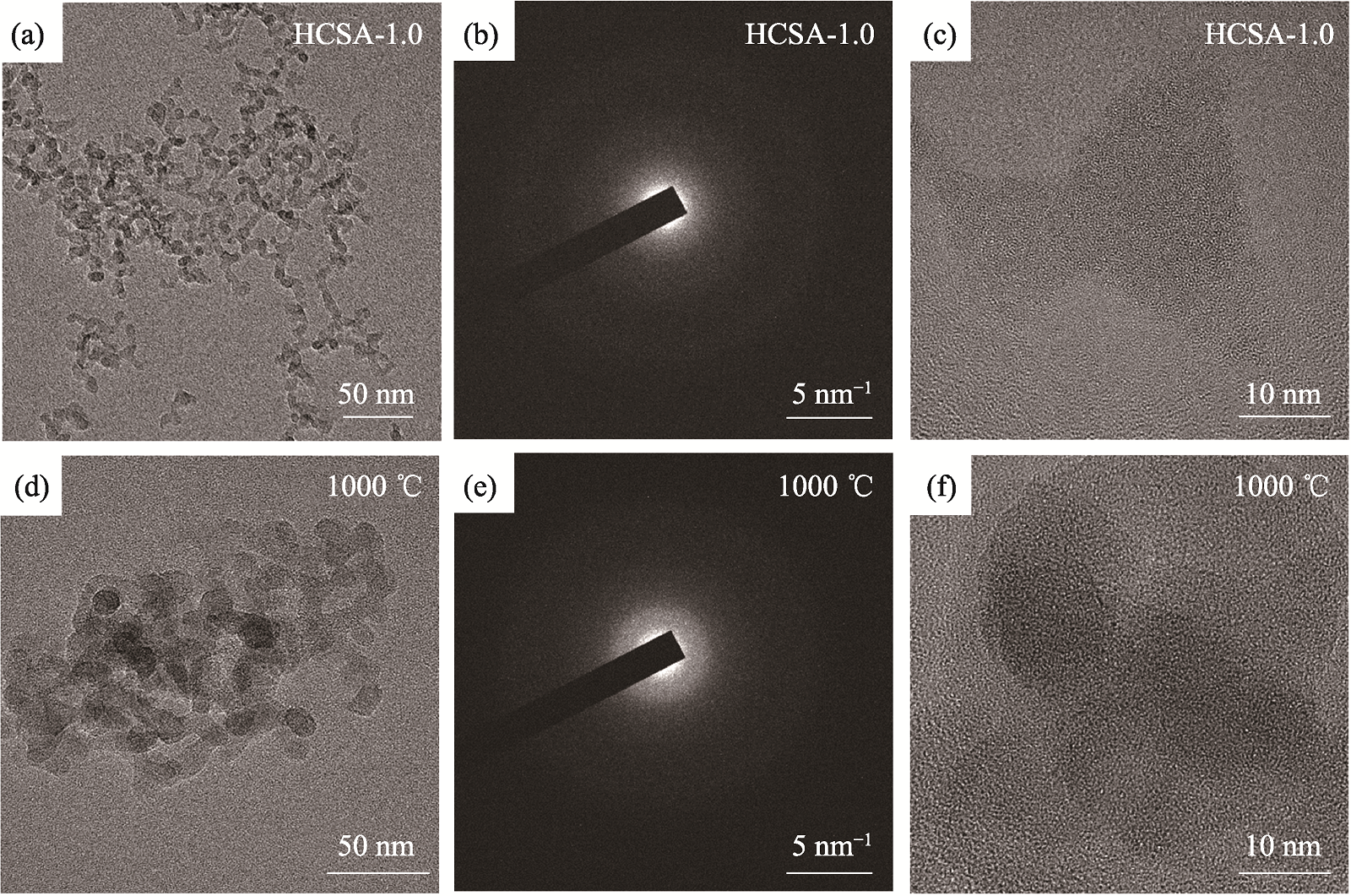
Fig. 5 (a) TEM image, (b) SAED pattern and (c) HRTEM image of the as-prepared HCSA-1.0; (d) TEM image, (e) SAED pattern and (f) HRTEM image of HCSA-1.0 sintered at 1000 ℃ for 2 h
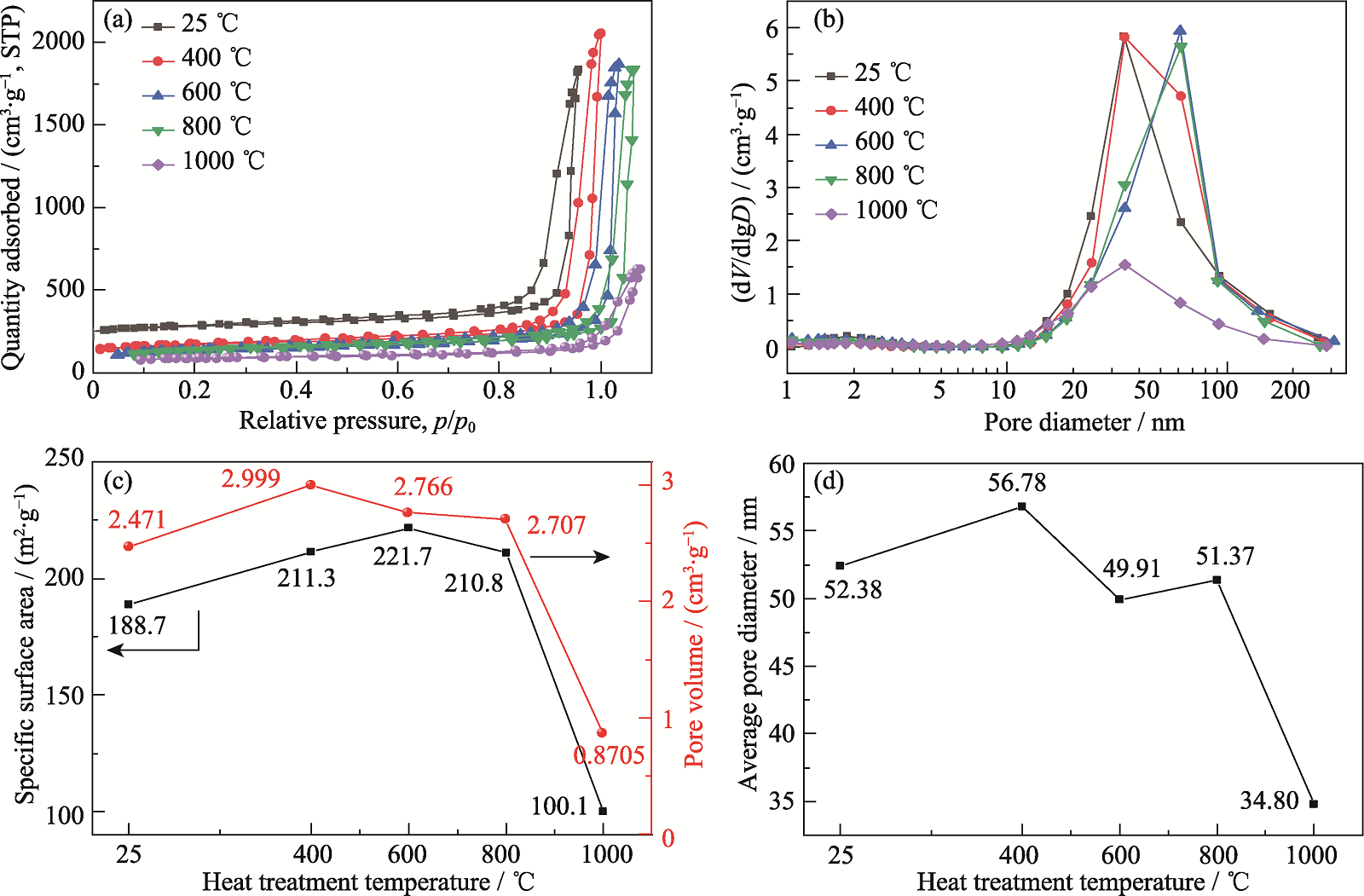
Fig. 6 Pore structure of HCSA-1.0 sintered at different temperatures (a) Adsorption-desorption isotherms; (b) Pore size distributions (evaluated from desorption isotherm); (c) Specific surface area and pore volume; (d) Average pore size
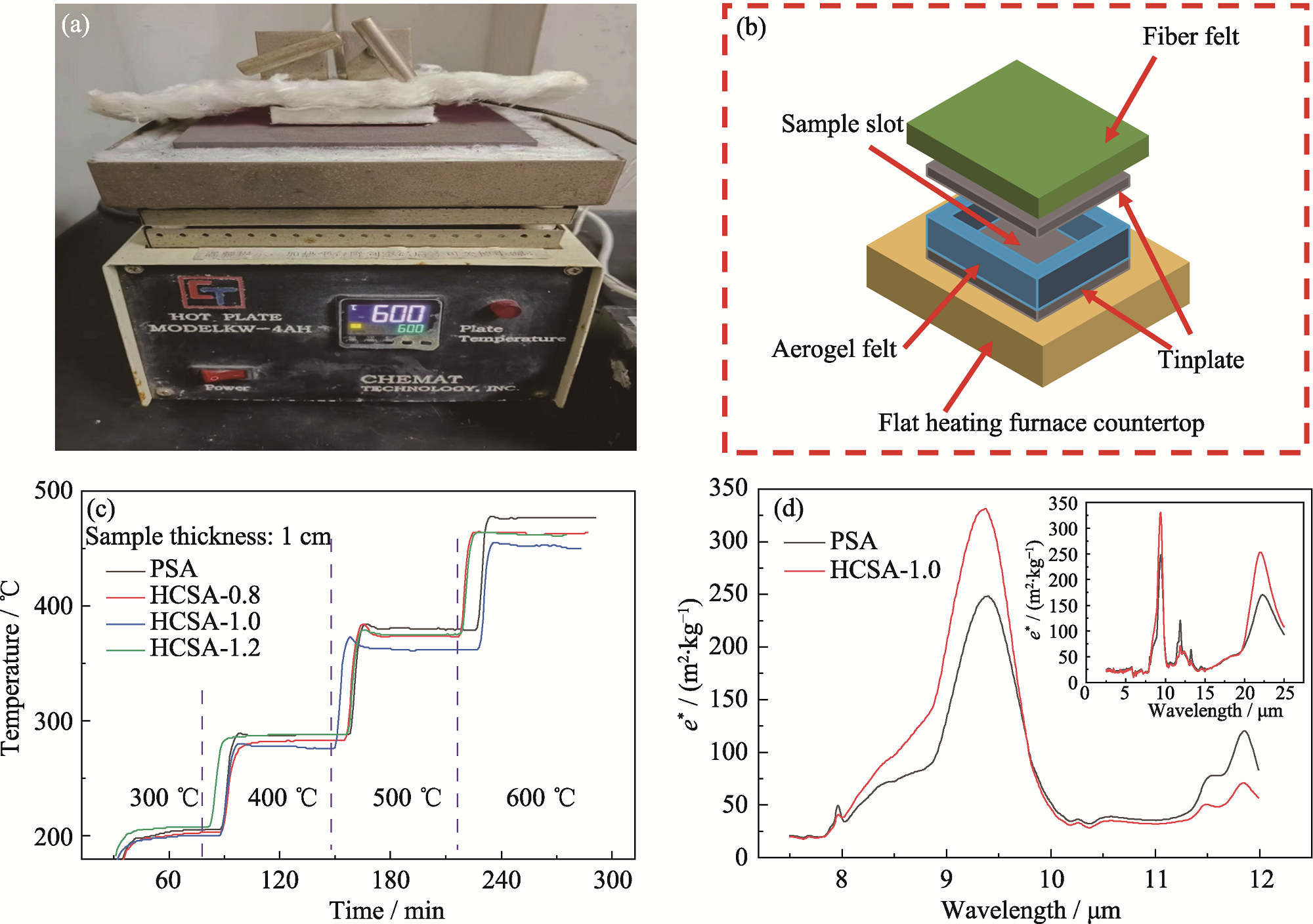
Fig. 9 (a) Flat heating furnace test device; (b) Schematic diagram of a home-made device for measuring thermal insulation properties; (c) Plots of temperature variation of the flat heating furnace test; (d) Specific extinction coefficients of PSA and HCSA-1.0 in infrared band Colorful figures are available on website
| [1] |
AHMAD S, AHMAD S, SHEIKH J N. Silica centered aerogels as advanced functional material and their applications: a review. Journal of Non-Crystalline Solids, 2023, 611: 122322.
DOI URL |
| [2] |
PENG F, JIANG Y, FENG J, et al. Research proggress on alumina aerogel composites for high-temperature thermal insulation. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(7): 673.
DOI |
| [3] | LI F P, CHU J B, QIU H B, et al. Compression resilience mechanism of silica fiber aerogel. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(9): 981. |
| [4] |
LUO Y, XIA S, NIU B, et al. Preparation and high temperature inorganic transformation of flexible silicon aerogel. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(12): 1281.
DOI |
| [5] |
AKHTER F, SOOMRO S A, INGLEZAKIS V J. Silica aerogels; a review of synthesis, applications and fabrication of hybrid composites. Journal of Porous Materials, 2021, 28(5): 1387.
DOI |
| [6] |
LIU Z H, DING Y D, WANG F, et al. Thermal insulation material based on SiO2 aerogel. Construction and Building Materials, 2016, 122: 548.
DOI URL |
| [7] | EL RASSY H, MAURY S, BUISSON P, et al. Hydrophobic silica aerogel-lipase biocatalysts. Journal of Non-Crystalline Solids, 2004, 350: 23. |
| [8] |
RAO A V, HEGDE N D, HIRASHIMA H. Absorption and desorption of organic liquids in elastic superhydrophobic silica aerogels. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2007, 305(1): 124.
PMID |
| [9] |
MALEKI H, DURAES L, GARCIA-GONZALEZ C A, et al. Synthesis and biomedical applications of aerogels: possibilities and challenges. Advances in Colloid and Interface Science, 2016, 236: 1.
DOI PMID |
| [10] | LAMY-MENDES A, PONTINHA A D R, ALVES P, et al. Progress in silica aerogel-containing materials for buildings’ thermal insulation. Construction and Building Materials, 2021, 286: 122815. |
| [11] |
ALMEIDA C M R, GHICA M E, DURÃES L. An overview on alumina-silica-based aerogels. Advances in Colloid and Interface Science, 2020, 282: 102189.
DOI URL |
| [12] |
WALKER R C, POTOCHNIAK A E, HYER A P, et al. Zirconia aerogels for thermal management: review of synthesis, processing, and properties information architecture. Advances in Colloid and Interface Science, 2021, 295: 102464.
DOI URL |
| [13] |
KIM Y N, SHAO G N, JEON S J, et al. Sol-Gel synthesis of sodium silicate and titanium oxychloride based TiO2-SiO2aerogels and their photocatalytic property under UV irradiation. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2013, 231: 502.
DOI URL |
| [14] | GAO S, YANG T, LIU S N, et al. Preparation of high-temperature resistant aluminum-doped silica aerogel from aluminum sol source by ambient pressure drying. Journal of Sol-Gel Science and Technology, 2023, 109(1): 162. |
| [15] |
WU Y, WANG X D, SHEN J. Metal oxide aerogels for high- temperature applications. Journal of Sol-Gel Science and Technology, 2022, 106(2): 360.
DOI |
| [16] |
GAO S, CAO Z Q, LIU K, et al. Preparation of high-temperature resistant aerogels by incorporating aluminum sol into composite silica sources using ambient pressure drying. Polymers, 2024, 16(16): 2296.
DOI URL |
| [17] |
ZHANG X X, GAO X D, DONG Y B, et al. Nanoporous Mg-doped SiO2 nanoparticles with tunable infrared emissivity toward effective radiative cooling coatings. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2023, 940: 168905.
DOI URL |
| [18] |
ZU G Q, SHEN J, ZOU L P, et al. Highly thermally stable zirconia/silica composite aerogels prepared by supercritical deposition. Microporous and Mesoporous Materials, 2017, 238: 90.
DOI URL |
| [19] |
TU F, YU Y X, WANG Y, et al. Preparation of SiO2/Fe2O3 composite aerogels for thermal insulation enhancement. Ceramics International, 2024, 50(2): 2976.
DOI URL |
| [20] |
IKIZLER B K, YAPC E, YÜCEL S, et al. Production and characterization of calcium silica aerogel powder as a food additive. ACS Omega, 2023, 8(12): 11479.
DOI PMID |
| [21] |
ZHU M Y, LI G Y, GONG W B, et al. Calcium-doped boron nitride aerogel enables infrared stealth at high temperature up to 1300 ℃. Nano-Micro Letters, 2021, 14(1): 18.
DOI |
| [22] |
YANG J X, ZHANG Y W, HONG Z L, et al. Preparations of TiO2 nanocrystal coating layers with various morphologies on mullite fibers for infrared opacifier application. Thin Solid Films, 2012, 520(7): 2651.
DOI URL |
| [23] |
FENG J P, CHEN D P, NI W, et al. Study of IR absorption properties of fumed silica-opacifier composites. Journal of Non- Crystalline Solids, 2010, 356(9/10): 480.
DOI URL |
| [24] |
WANG X D, SUN D, DUAN Y Y, et al. Radiative characteristics of opacifier-loaded silica aerogel composites. Journal of Non- Crystalline Solids, 2013, 375: 31.
DOI URL |
| [25] |
WEI G S, LIU Y S, ZHANG X X, et al. Thermal conductivities study on silica aerogel and its composite insulation materials. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2011, 54(11/12): 2355.
DOI URL |
| [26] |
YOU J G, XING H P, XUE J, et al. Preparation of rigid cross- linked PVC foam with excellent thermal insulation through adding high-reflectivity IR opacifier. Composites Science and Technology, 2021, 203: 108566.
DOI URL |
| [27] |
SHI T Q, GAO X D, WU Y Q, et al. Ba/Sn induced high temperature phase and microstructure evolution of silica aerogel via co-precursor Sol-Gel method. Chemical Physics, 2021, 545: 111161.
DOI URL |
| [28] |
YAO J Q, GAO X D, WU Y Q, et al. High-temperature resistant ambient pressure-dried aluminum doped silica aerogel from inorganic silicon and aluminum sources. Ceramics International, 2022, 48(11): 15006.
DOI URL |
| [29] |
SING K S W. Reporting physisorption data for gas/solid systems with special reference to the determination of surface area and porosity. Pure and Applied Chemistry, 1985, 57(4): 603.
DOI URL |
| [30] |
ROUQUEROL J, AVNIR D, FAIRBRIDGE C W, et al. Recommendations for the characterization of porous solids. Pure and Applied Chemistry, 1994, 66(8): 1739.
DOI URL |
| [31] |
BHAGAT S D, RAO A V. Surface chemical modification of TEOS based silica aerogels synthesized by two step (acid-base) Sol-Gel process. Applied Surface Science, 2006, 252(12): 4289.
DOI URL |
| [32] |
BHAGAT S D, KIM Y H, AHN Y S, et al. Rapid synthesis of water-glass based aerogels by in situ surface modification of the hydrogels. Applied Surface Science, 2007, 253(6): 3231.
DOI URL |
| [1] | FENG Guanzheng, YANG Jian, ZHOU Du, CHEN Qiming, XU Wentao, ZHOU Youfu. Mechanism for Hydrothermal-carbothermal Synthesis of AlN Nanopowders [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(1): 104-110. |
| [2] | XIAO Wenyan, FU Yan, YANG Shubin, ZHU Jie, CHENG Zhaoyang, WEN Xiaoxu, TANG Jiafan, YU Liang, ZHANG Qian. Seawater Electrolysis Performance of Self-supported Amorphous Ce-FeHPi/NF Electrode [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(12): 1348-1356. |
| [3] | YUE Quanxin, GUO Ruihua, WANG Ruifen, AN Shengli, ZHANG Guofang, GUAN Lili. 3D Core-shell Structured NiMoO4@CoFe-LDH Nanorods: Performance of Efficient Oxygen Evolution Reaction and Overall Water Splitting [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(11): 1254-1264. |
| [4] | XU Zhou, LIU Yuxuan, CHI Junlin, ZHANG Tingting, WANG Shuyue, LI Wei, MA Chunhui, LUO Sha, LIU Shouxin. Horseshoe-shaped Hollow Porous Carbon: Synthesis by Hydrothermal Carbonization with Dual-template and Electrochemical Property [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(8): 954-962. |
| [5] | LI Yuejun, CAO Tieping, SUN Dawei. Bi4O5Br2/CeO2 Composite with S-scheme Heterojunction: Construction and CO2 Reduction Performance [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(8): 963-970. |
| [6] | NIU Haibin, HUANG Jiahui, LI Qianwen, MA Dongyun, WANG Jinmin. Directly Hydrothermal Growth and Electrochromic Properties of Porous NiMoO4 Nanosheet Films [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(12): 1427-1433. |
| [7] | YAO Yishuai, GUO Ruihua, AN Shengli, ZHANG Jieyu, CHOU Kuochih, ZHANG Guofang, HUANG Yarong, PAN Gaofei. In-situ Loaded Pt-Co High Index Facets Catalysts: Preparation and Electrocatalytic Performance [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(1): 71-78. |
| [8] | ZHANG Xian, ZHANG Ce, JIANG Wenjun, FENG Deqiang, YAO Wei. Synthesis, Electronic Structure and Visible Light Photocatalytic Performance of Quaternary BiMnVO5 [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(1): 58-64. |
| [9] | WANG Tingting, SHI Shumei, LIU Chenyuan, ZHU Wancheng, ZHANG Heng. Synthesis of Hierarchical Porous Nickel Phyllosilicate Microspheres as Efficient Adsorbents for Removal of Basic Fuchsin [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(12): 1330-1336. |
| [10] | SONG Keke, HUANG Hao, LU Mengjie, YANG Anchun, WENG Jie, DUAN Ke. Hydrothermal Preparation and Characterization of Zn, Si, Mg, Fe Doped Hydroxyapatite [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(10): 1091-1096. |
| [11] | XIAO Yumin, Li Bin, QIN Lizhao, LIN Hua, LI Qing, LIAO Bin. Efficient Preparation of CuGeO3 with Controllable Morphology Using CuCl2 as Copper Source [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(1): 69-74. |
| [12] | WANG Juhan,WEN Xiong,LIU Chengchao,ZHANG Yuhua,ZHAO Yanxi,LI Jinlin. Preparation and Fischer-Tropsch Synthesis Performance of Hierarchical Co/Al-SiO2 Catalyst [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2020, 35(9): 999-1004. |
| [13] | ZHANG Dongshuo,CAI Hao,GAO Kaiyin,MA Zichuan. Preparation and Visible-light Photocatalytic Degradation on Metronidazole of Zn2SiO4-ZnO-biochar Composites [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2020, 35(8): 923-930. |
| [14] | WANG Zhihu,ZHANG Jumei,BAI Lijing,ZHANG Guojun. Mg(OH)2 Film on Micro-arc Oxidation Ceramic Coating of AZ31 Magnesium Alloy: Preparation and Corrosion Resistance [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2020, 35(6): 709-716. |
| [15] | ZHANG Zhibin, ZHOU Runze, DONG Zhimin, CAO Xiaohong, LIU Yunhai. Adsorption of U(VI)-CO3/Ca-U(VI)-CO3 by Amidoxime-functionalized Hydrothermal Carbon [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2020, 35(3): 352-358. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||