
Journal of Inorganic Materials ›› 2024, Vol. 39 ›› Issue (11): 1221-1227.DOI: 10.15541/jim20240129
Special Issue: 【能源环境】热电材料(202506)
• RESEARCH ARTICLE • Previous Articles Next Articles
ZHANG Zhe1( ), SUN Tingting1, WANG Lianjun1,2(
), SUN Tingting1, WANG Lianjun1,2( ), JIANG Wan1,2,3
), JIANG Wan1,2,3
Received:2024-03-18
Revised:2024-05-12
Published:2024-11-20
Online:2024-06-24
Contact:
WANG Lianjun, professor. E-mail: wanglj@dhu.edu.cnAbout author:ZHANG Zhe (1999-), female, Master candidate. E-mail: 239156115@qq.com
Supported by:CLC Number:
ZHANG Zhe, SUN Tingting, WANG Lianjun, JIANG Wan. Flexible Thermoelectric Films with Different Ag2Se Dimensions: Performance Optimization and Device Integration[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(11): 1221-1227.

Fig. 3 Dispersion and stability of Ag2Se nanopowders with different dimensions in ethanol (a) Photograph of the dispersion after mixing; (b) Photograph of the dispersion after resting for 12 h
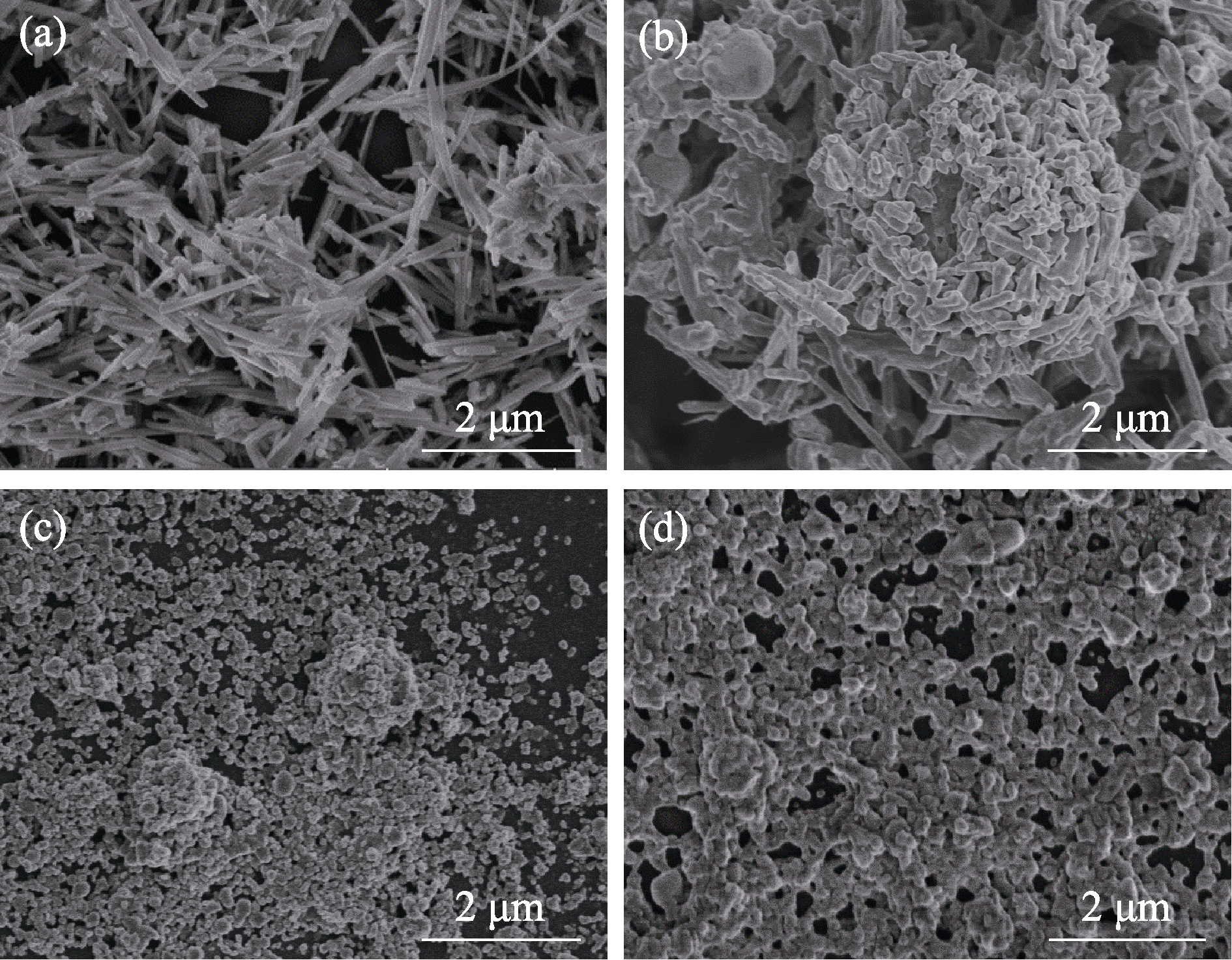
Fig. 4 SEM images of Ag2Se thin films made from nanomaterials with different dimensions (a, c) before and (b, d) after annealing (a, b) Ag2Se NWs-films; (c, d) Ag2Se NPs-films
| Sample | S/(μV·K−1) | σ/(S·cm-1) | PF/(μW·m−1·K−2) | n/cm−3 | μ/(cm2·V−1·s−2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ag2Se NPs-films | -77.9 | 329.0 | 199.6 | 4.8×1018 | 117.5 |
| Ag2Se NWs-films | -76.8 | 139.5 | 82.3 | 4.7×1018 | 81.5 |
Table 1 Room temperature thermoelectric properties of Ag2Se films made from nanomaterials with different dimensions
| Sample | S/(μV·K−1) | σ/(S·cm-1) | PF/(μW·m−1·K−2) | n/cm−3 | μ/(cm2·V−1·s−2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ag2Se NPs-films | -77.9 | 329.0 | 199.6 | 4.8×1018 | 117.5 |
| Ag2Se NWs-films | -76.8 | 139.5 | 82.3 | 4.7×1018 | 81.5 |

Fig. 7 Output performance and bending performance of devices with Ag2Se NPs-films (a) Open-circuit voltage of the device at different ΔT; (b) Output voltage and output power versus current of the device at different ΔT; (c) Variation of the internal resistance (R) of the device with bending cycles; Colorful figures are available on website
| TE legs | PF/(μW·m−1·K−2) | N | Pmax/nW | PDmax/(W·m-2) | ΔT/K | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ag2Se/Nylon | 987.4 | 4 | 460 | 2.3 | 30 | [ |
| Ag2Se/PI | 889.0 | 6 | 800 | 32.0 | 40 | [ |
| Ag2Se/BC | 291.0 | 10 | 280 | 0.05 | 20 | [ |
| Ag2Se/PVDF | 189.0 | 5 | 4.9 | 0.01 | 30 | [ |
| Ag2Se/PI | 199.6 | 4 | 43.7 | 0.54 | 30 | This work |
Table 2 Comparison of output performance for devices with Ag2Se-based thin films in this work and the literatures
| TE legs | PF/(μW·m−1·K−2) | N | Pmax/nW | PDmax/(W·m-2) | ΔT/K | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ag2Se/Nylon | 987.4 | 4 | 460 | 2.3 | 30 | [ |
| Ag2Se/PI | 889.0 | 6 | 800 | 32.0 | 40 | [ |
| Ag2Se/BC | 291.0 | 10 | 280 | 0.05 | 20 | [ |
| Ag2Se/PVDF | 189.0 | 5 | 4.9 | 0.01 | 30 | [ |
| Ag2Se/PI | 199.6 | 4 | 43.7 | 0.54 | 30 | This work |
| [14] | WU H, SHI X, DUAN J, et al. Advances in Ag2Se-based thermoelectrics from materials to applications. Energy & Environmental Science, 2023, 16(5): 1870. |
| [15] | WANG J, FAN W, YANG J, et al. Tetragonal-orthorhombic-cubic phase transitions in Ag2Se nanocrystals. Chemistry of Materials, 2014, 26(19): 5647. |
| [16] | LIN S, GUO L, WANG X, et al. Revealing the promising near-room-temperature thermoelectric performance in Ag2Se single crystals. Journal of Materiomics, 2023, 9(4): 754. |
| [17] | DING Y, QIU Y, CAI K, et al. High performance n-type Ag2Se film on Nylon membrane for flexible thermoelectric power generator. Nature Communications, 2019, 10: 841. |
| [18] | LI X, LU Y, CAI K, et al. Exceptional power factor of flexible Ag/Ag2Se thermoelectric composite films. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2022, 434: 134739. |
| [19] | YAN L, QI R, CHEN M, et al. Microstructurally tailored thin β-Ag2Se films towards commercial flexible thermoelectrics. Advanced Materials, 2022, 34(7): 2104786. |
| [20] | WANG Z, LIU Y, LI J, et al. High-performance Ag2Se film by a template method for flexible thermoelectric generator. Materials Today Physics, 2023, 36: 101147. |
| [21] |
ZHANG K, ZHENG Q, WANG L, et al. Preparation and characterization of Ag2Se-based ink used for inkjet printing. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(10): 1109.
DOI |
| [22] | KOCZKUR K M, MOURDIKOUDIS S, POLAVARAPU L, et al. Polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP) in nanoparticle synthesis. Dalton Transactions, 2015, 44(41): 17883. |
| [23] | JIANG C, WEI P, DING Y, et al. Ultrahigh performance polyvinylpyrrolidone/Ag2Se composite thermoelectric film for flexible energy harvesting. Nano Energy, 2021, 80: 105488. |
| [24] | LIU Y, LU Y, WANG Z, et al. High performance Ag2Se films by a one-pot method for a flexible thermoelectric generator. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2022, 10(48): 25644. |
| [25] | HOU S, LIU Y, YIN L, et al. High performance wearable thermoelectric generators using Ag2Se films with large carrier mobility. Nano Energy, 2021, 87: 106223. |
| [26] | LIU Y, LI J, WANG Z, et al. High thermoelectric performance of flexible Ag/Ag2Se composite film on nylon for low-grade energy harvesting. Journal of Materials Science & Technology, 2024, 179: 79. |
| [27] | ZANG J, MA Y, ZHAO Y, et al. Effect of post-annealing treatment on the thermoelectric properties of Ag2Se flexible thin film prepared by magnetron sputtering method. Results in Physics, 2023, 45: 106222. |
| [28] | LIU Y, ZHANG Q, HUANG A, et al. Fully inkjet-printed Ag2Se flexible thermoelectric devices for sustainable power generation. Nature Communications, 2024, 15: 2141. |
| [29] | LI Y, LOU Q, YANG J, et al. Exceptionally high power factor Ag2Se/Se/polypyrrole composite films for flexible thermoelectric generators. Advanced Functional Materials, 2022, 32(7): 2106902. |
| [30] | ZHU J, LI F, ZHAO L, et al. Study on the structure and thermoelectric performance of SnSe cubic phase stabilized by AgBiSe2 alloying. Journal of Liaocheng University (Natural Science Edition), 2023, 36(4): 59. |
| [31] | PALAPORN D, MONGKOLTHANARUK W, TANUSILP S, et al. A simple method for fabricating flexible thermoelectric nanocomposites based on bacterial cellulose nanofiber and Ag2Se. Applied Physics Letters, 2022, 120(7): 3901. |
| [32] | ZHOU H, ZHANG Z, SUN C, et al. Biomimetic approach to facilitate the high filler content in free-standing and flexible thermoelectric polymer composite films based on PVDF and Ag2Se nanowires. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2020, 12(46): 51506. |
| [1] | SUN T, WANG L, JIANG W. Pushing thermoelectric generators toward energy harvesting from the human body: challenges and strategies. Materials Today, 2022, 57: 121. |
| [2] | ZHANG Z, SUN T, WANG L, et al. Research progress on n-type carbon nanotube-based thermoelectric materials. Journal of Liaocheng University (Natural Science Edition), 2023, 36(3): 29. |
| [3] | WANG Y, YANG L, SHI X L, et al. Flexible thermoelectric materials and generators: challenges and innovations. Advanced Materials, 2019, 31(29): 1807916. |
| [4] | WANG S, JIANG M, WANG L, et al. n-Type Pb-free AgBiSe2 based thermoelectric materials with stable cubic phase structure. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(7): 807. |
| [5] | HU Z, FU Y, JIANG M, et al. Thermal stability of Nb/Mg3SbBi interface. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(8): 931. |
| [6] | SHI X L, ZOU J, CHEN Z G. Advanced thermoelectric design: from materials and structures to devices. Chemical Reviews, 2020, 120(15): 7399. |
| [7] |
PETSAGKOURAKIS I, TYBRANDT K, CRISPIN X, et al. Thermoelectric materials and applications for energy harvesting power generation. Science and Technology of Advanced Materials, 2018, 19(1): 836.
DOI PMID |
| [8] | BLACKBURN J L, FERGUSON A J, CHO C, et al. Carbon- nanotube-based thermoelectric materials and devices. Advanced Materials, 2018, 30(11): 1704386. |
| [9] | WANG C, XIA K, WANG H, et al. Advanced carbon for flexible and wearable electronics. Advanced Materials, 2019, 31(9): 1801072. |
| [10] | YANG J, PU Y, YU H, et al. A cross-plane design for wearable thermoelectric generators with high stretchability and output performance. Small, 2023, 19(45): 2304529. |
| [11] |
SUN T, ZHOU B, ZHENG Q, et al. Stretchable fabric generates electric power from woven thermoelectric fibers. Nature Communications, 2020, 11: 572.
DOI PMID |
| [12] | YANG S, LI Y, DENG L, et al. Flexible thermoelectric generator and energy management electronics powered by body heat. Microsystems & Nanoengineering, 2023, 9(1): 106. |
| [13] | LIU Y, LI Y, WU M, et al. Nanoengineering approach toward high power factor Ag2Se/Se composite films for flexible thermoelectric generators. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2023, 15(30): 36587. |
| [1] | MIAO Xin, YAN Shiqiang, WEI Jindou, WU Chao, FAN Wenhao, CHEN Shaoping. Interface Layer of Te-based Thermoelectric Device: Abnormal Growth and Interface Stability [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(8): 903-910. |
| [2] | HUA Siheng, YANG Dongwang, TANG Hao, YUAN Xiong, ZHAN Ruoyu, XU Zhuoming, LYU Jianan, XIAO Yani, YAN Yonggao, TANG Xinfeng. Effect of Surface Treatment of n-type Bi2Te3-based Materials on the Properties of Thermoelectric Units [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(2): 163-169. |
| [3] | Peng LI, Xiao-Lei NIE, Ye TIAN, Wen-Bing FANG, Ping WEI, Wan-Ting ZHU, Zhi-Gang SUN, Qing-Jie ZHANG, Wen-Yu ZHAO. Fabrication and Planar Cooling Performance of Flexible Bi0.5Sb1.5Te3/epoxy Composite Thermoelectric Films [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2019, 34(6): 679-684. |
| [4] | HU Xiao-Kai, ZHANG Shuang-Meng, ZHAO Fu, LIU Yong, LIU Wei-Shu. Thermoelectric Device: Contact Interface and Interface Materials [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2019, 34(3): 269-278. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||