
Journal of Inorganic Materials ›› 2018, Vol. 33 ›› Issue (12): 1337-1342.DOI: 10.15541/jim20180180
• RESEARCH PAPER • Previous Articles Next Articles
FAN Wen, WU Li-Min
Received:2018-04-25
Published:2018-12-20
Online:2018-11-27
About author:FAN Wen. E-mail: 12110300010@fudan.edu.cn
Supported by:CLC Number:
FAN Wen, WU Li-Min. Controllable Preparation of Nano-TiO2 Lens by Silicon Oil Two-step Dehydration Method[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2018, 33(12): 1337-1342.
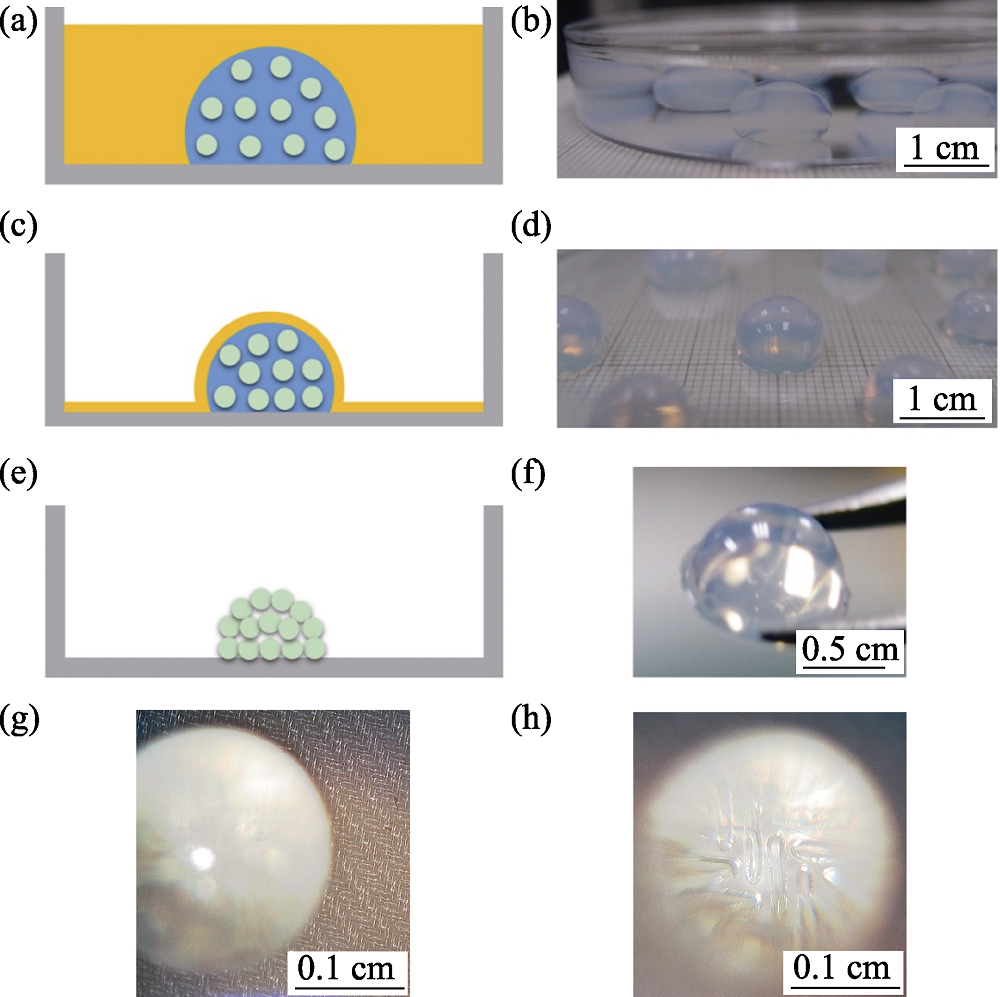
Fig. 1 Schematic diagrams of the assembly of 15 nm TiO2 nanoparticles into a hemispherical lens by silicone oil two-step dehydration method (a, c, e) and corresponding photographs (b, d, f), optical microscopy image focused on the surface of a filter cloth(g), and optical microscopy image focused on the magnified image produced by a TiO2 lens (h)

Fig. 3 Photograph of an aqueous dispersion of 5 nm Au nanoparticles (a), mixed droplets of 5 nm Au nanoparticles and 15 nm TiO2 nanoparticles suspended in silicone oil (b), and assembled TiO2/Au composite lenses (c)
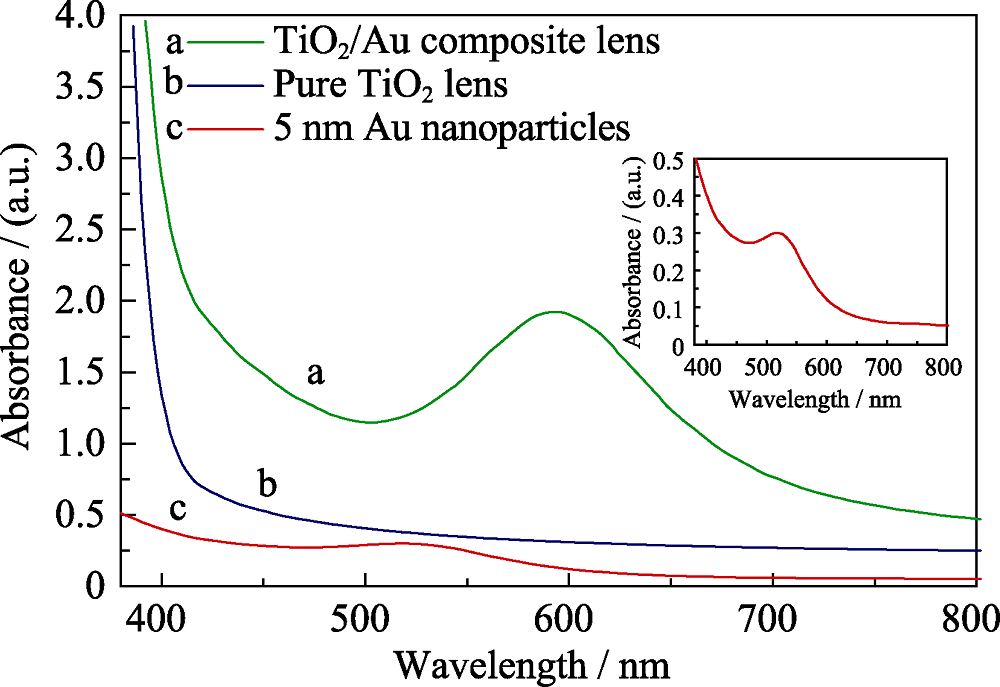
Fig. 4 Absorption spectra of an aqueous dispersion of 5 nm Au nanoparticles, a pure TiO2 lens and a TiO2/Au composite lens with inset showing the single absorption spectrum of an aqueous dispersion of 5 nm Au nanoparticles
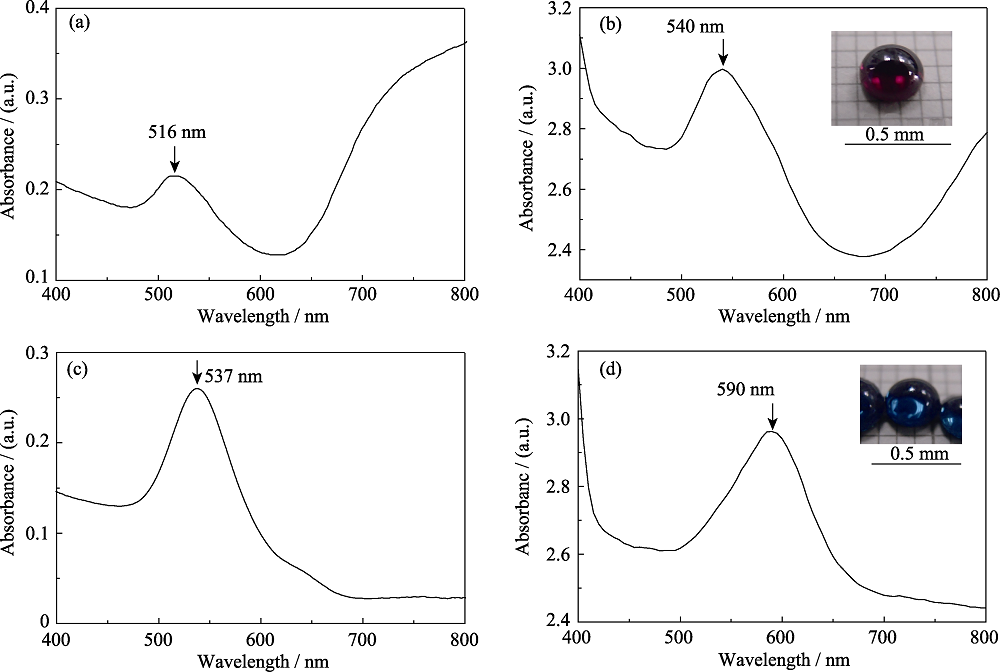
Fig. 5 Absorption spectra of (a) an aqueous dispersion of Au nanorods with an aspect ratio of 3.6, (b) a TiO2/Au nanorods composite lens, (c) an aqueous dispersion of Au nanocubes with a side length of 30 nm, and (d) a TiO2/Au nanocubes composite lensInsets in (b, d) displaying photographs of the corresponding composite lenses, respectively
| [1] | BARNES W L, DEREUX A, EBBESEN T W.Surface plasmon subwavelength optics.Nature, 2003, 424(6950): 824-830. |
| [2] | KHORASANINEJAD M, CHEN W T, DEVLIN R C,et al. Metalenses at visible wavelengths: diffraction-limited focusing and subwavelength resolution imaging. Science, 2016, 352(6290): 1190-1194. |
| [3] | ZHANG N, HAN C, XU Y J,et al. Near-field dielectric scattering promotes optical absorption by platinum nanoparticles. Nature Photonics, 2016, 10(7): 473-482. |
| [4] | GONZÁLEZ-TUDELA A, HUNG C L, CHANG D E,et al. Subwavelength vacuum lattices and atom-atom interactions in two-dimensional photonic crystals. Nature Photonics, 2015, 9(5): 320-325. |
| [5] | ROGER T, VEZZOLI S, BOLDUC E, ,et al. Coherent perfect absorption in deeply subwavelength films in the single-photon regime. Nature Communications, 2015, 6: 7031-1-5. |
| [6] | FAN W, YAN B, WANG Z, ,et al. Three-dimensional all-dielectric metamaterial solid immersion lens for subwavelength imaging at visible frequencies. Science Advances, 2016, 2(8): e1600901-1-9. |
| [7] | NAQSHBANDI M, CANNING J, GIBSON B C, ,et al. Room temperature self-assembly of mixed nanoparticles into photonic structures. Nature Communications, 2012, 3: 1188-1-7. |
| [8] | HUANG M C Y, ZHOU Y, CHANG-HASNAIN C J. A surface- emitting laser incorporating a high-index-contrast subwavelength grating.Nature Photonics, 2007, 1(2): 119-122. |
| [9] | ZHOU L, TAN Y, WANG J,et al. 3D self-assembly of aluminium nanoparticles for plasmon-enhanced solar desalination. Nature Photonics, 2016, 10(6): 393-398. |
| [10] | GALISTEO-LÓPEZ J F, IBISATE M, SAPIENZA R,et al. Self-assembled photonic structures. Advanced Materials, 2011, 23(1): 30-69. |
| [11] | VON FREYMANN G, KITAEV V, LOTSCH B V,et al. Bottom- up assembly of photonic crystals. Chemical Society Reviews, 2013, 42(7): 2528-2554. |
| [12] | XU L, MA W, WANG L,et al. Nanoparticle assemblies: dimensional transformation of nanomaterials and scalability. Chemical Society Reviews, 2013, 42(7): 3114-3126. |
| [13] | LIU Y, ZHANG X.Metamaterials: a new frontier of science and technology.Chemical Society Reviews, 2011, 40(5): 2494-2507. |
| [14] | SOUKOULIS C M, WEGENER M.Past achievements and future challenges in the development of three-dimensional photonic metamaterials.Nature Photonics, 2011, 5(9): 523-530. |
| [15] | CHOI M, LEE S H, KIM Y,et al. A terahertz metamaterial with unnaturally high refractive index. Nature, 2011, 470(7334): 369-373. |
| [16] | KUZNETSOV A I, MIROSHNICHENKO A E, FU Y H, ,et al. Magnetic light. Scientific Reports, 2012, 2: 492-1-6. |
| [17] | FU Y H, KUZNETSOV A I, MIROSHNICHENKO A E, et al. Directional visible light scattering by silicon nanoparticles. Nature Communications, 2013, 4: 1527-1-6. |
| [18] | JAHANI S, JACOB Z.All-dielectric metamaterials.Nature Nanotechnology, 2016, 11(1): 23-26. |
| [19] | LIU A J, NAGEL S R.Nonlinear dynamics: Jamming is not just cool any more.Nature, 1998, 396(6706): 21-22. |
| [20] | FAN W, CHEN M, YANG S, ,et al. Centrifugation-assisted assembly of colloidal silica into crack-free and transferrable films with tunable crystalline structures. Scientific Reports, 2015, 5: 12100-1-10. |
| [21] | YANG X, LIU H, LI L,et al. Review on influence factors of surface plasmon resonance for nobel metal nanoparticles. Journal of Functional Materials, 2010, 2(41): 341-349. |
| [22] | LEONHARDT U.Optical metamaterials: invisibility cup.Nature Photonics, 2007, 1(4): 207-208. |
| [23] | FREESTONE I, MEEKS N, SAX M,et al. The Lycurgus cup-a roman nanotechnology. Gold Bulletin, 2007, 40(4): 270-277. |
| [24] | 邹志宇. 贵金属纳米粒子复合玻璃的制备及光电性能研究. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学博士学位论文, 2009. |
| [25] | ZHANG N, HAN C, XU Y J,et al. Near-field dielectric scattering promotes optical absorption by platinum nanoparticles. Nature Photonics, 2016, 10(7): 473-482. |
| [1] | ZHOU Houlin, SONG Zhiqing, TIAN Guo, GAO Xingsen. Effects of Growth Conditions on the Formation of Self-assembly Grown Topological Domain in BiFeO3 Nanoislands [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(6): 667-674. |
| [2] | LIAN Minli, SU Jiaxin, HUANG Hongyang, JI Yuyin, DENG Haifan, ZHANG Tong, CHEN Chongqi, LI Dalin. Supported Ni Catalysts from Ni-Mg-Al Hydrotalcite-like Compounds:Preparation and Catalytic Performance for Ammonia Decomposition [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(1): 53-60. |
| [3] | YU Man, GAO Rongyao, QIN Yujun, AI Xicheng. Influence of Upconversion Luminescent Nanoparticles on Hysteresis Effect and Ion Migration Kinetics in Perovskite Solar Cells [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(4): 359-366. |
| [4] | WANG Zhaoyang, QIN Peng, JIANG Yin, FENG Xiaobo, YANG Peizhi, HUANG Fuqiang. Sandwich Structured Ru@TiO2 Composite for Efficient Photocatalytic Tetracycline Degradation [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(4): 383-389. |
| [5] | ZHANG Xiangsong, LIU Yetong, WANG Yongying, WU Zirui, LIU Zhenzhong, LI Yi, YANG Juan. Self-assembled Platinum-iridium Alloy Aerogels and Their Efficient Electrocatalytic Ammonia Oxidation Performance [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(5): 511-520. |
| [6] | YU Yefan, XU Ling, NI Zhongbing, SHI Dongjian, CHEN Mingqing. Prussian Blue Modified Biochar: Preparation and Adsorption of Ammonia Nitrogen from Sewage [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(2): 205-212. |
| [7] | XUE Hongyun, WANG Congyu, MAHMOOD Asad, YU Jiajun, WANG Yan, XIE Xiaofeng, SUN Jing. Two-dimensional g-C3N4 Compositing with Ag-TiO2 as Deactivation Resistant Photocatalyst for Degradation of Gaseous Acetaldehyde [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(8): 865-872. |
| [8] | CHENG Weijie, WANG Minglei, LIN Guoqiang. Composition, Structure and Properties of CrAlN-DLC Hard Composite Films Deposited by Arc Ion Plating [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(7): 764-772. |
| [9] | CHI Congcong, QU Panpan, REN Chaonan, XU Xin, BAI Feifei, ZHANG Danjie. Preparation of SiO2@Ag@SiO2@TiO2 Core-shell Structure and Its Photocatalytic Degradation Property [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(7): 750-756. |
| [10] | WANG Xiaojun, XU Wen, LIU Runlu, PAN Hui, ZHU Shenmin. Preparation and Properties of Ag@C3N4 Photocatalyst Supported by Hydrogel [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(7): 731-740. |
| [11] | SU Dongliang, CUI Jin, ZHAI Pengbo, GUO Xiangxin. Mechanism Study on Garnet-type Li6.4La3Zr1.4Ta0.6O12 Regulating the Solid Electrolyte Interphases of Si/C Anodes [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(7): 802-808. |
| [12] | ZHANG Ye, YAO Dongxu, ZUO Kaihui, XIA Yongfeng, YIN Jinwei, ZENG Yuping. Combustion Synthesis of Si3N4-BN-SiC Composites by in-situ Introduction of BN and SiC [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(5): 574-578. |
| [13] | MA Hui, TAO Jianghui, WANG Yanni, HAN Yu, WANG Yabin, DING Xiuping. Gold Nanoparticles Supported on Silica & Titania Hybrid Mesoporous Spheres and Their Catalytic Performance Regulation [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(4): 404-412. |
| [14] | LI Bangxin, ZHANG Qian, XIAO Jie, XIAO Wenyan, ZHOU Ying. Iron-doping Enhanced Basic Nickel Carbonate for Moisture Resistance and Catalytic Performance of Ozone Decomposition [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(1): 45-50. |
| [15] | CHEN Xiaomei, CHEN Ying, YUAN Xia. Decomposition of Cyclohexyl Hydroperoxide Catalyzed by Core-shell Material Co3O4@SiO2 [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(1): 65-71. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||