无机材料学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 40 ›› Issue (5): 504-510.DOI: 10.15541/jim20240457 CSTR: 32189.14.jim20240457
所属专题: 【结构材料】陶瓷基复合材料(202512)
收稿日期:2024-11-01
修回日期:2024-12-19
出版日期:2025-05-20
网络出版日期:2024-12-27
通讯作者:
邱海鹏, 研究员. E-mail: hpqiu07@163.com作者简介:陈 义(1992-), 男, 工程师. E-mail: chenyi28@iccas.ac.cn
基金资助:
CHEN Yi( ), QIU Haipeng(
), QIU Haipeng( ), CHEN Mingwei, XU Hao, CUI Heng
), CHEN Mingwei, XU Hao, CUI Heng
Received:2024-11-01
Revised:2024-12-19
Published:2025-05-20
Online:2024-12-27
Contact:
QIU Haipeng, professor. E-mail: hpqiu07@163.comAbout author:CHEN Yi (1992-), male, engineer. E-mail: chenyi28@iccas.ac.cn
Supported by:摘要:
SiC/SiC复合材料已成为高超音速飞行器和高推重比航空发动机的核心热结构材料之一。设计含硼陶瓷前驱体结构及组分, 利用其作为前驱体浸渍裂解(PIP)工艺的浸渍剂, 并将一定量的自愈合组元引入基体, 是提升SiC/SiC复合材料抗氧化性能的技术途径之一。本研究采用硼烷吡啶或硼烷三乙胺作为硼源, 与固态聚碳硅烷(PCS)二甲苯溶液复配, 制备得到硼改性PCS溶液。以此作为PIP工艺浸渍剂, 分别制备了不同基体硼改性SiC/PyC(热解碳)/SiC复合材料, 并研究了硼改性PCS衍生陶瓷的理化性质以及基体硼改性前后SiC/PyC/SiC复合材料的物理及力学性能。研究结果表明, 适量的硼烷吡啶及硼烷三乙胺作为硼源加入固态PCS溶液中, 可在其衍生陶瓷中有效引入硼异质元素。与未改性PCS相比, 硼改性PCS(BP-1和BP-2)的陶瓷产率更高, 衍生陶瓷均呈半结晶β-SiC结构, 其中硼异质元素引入量分别为1.7%和2.2%(质量分数)。与未改性复合材料相比, 基体改性SiC/SiC复合材料密度、显气孔率以及断裂韧性等变化不大, 但弯曲模量从116 GPa提升至132 GPa。另外, 单独采用硼烷吡啶作为硼源所制备的改性复合材料弯曲强度为658 MPa, 与未改性复合材料弯曲强度(643 MPa)相近且离散系数更低。这些结果为基体硼改性SiC/SiC复合材料的制备及高性能SiC/SiC复合材料热端部件的研制提供了重要参考。
中图分类号:
陈义, 邱海鹏, 陈明伟, 徐昊, 崔恒. SiC/SiC复合材料基体硼改性方法及其力学性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(5): 504-510.
CHEN Yi, QIU Haipeng, CHEN Mingwei, XU Hao, CUI Heng. SiC/SiC Composite: Matrix Boron Modification and Mechanical Properties[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(5): 504-510.
| Entry | Impregnating agent type | Composite label |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | PCS 50% xylene solution | C0 |
| 2 | BP-1 solution | C1 |
| 3 | BP-2 solution | C2 |
表1 SiC/SiC复合材料编号及其浸渍剂类型
Table 1 SiC/SiC composite numbers and their impregnating agent types
| Entry | Impregnating agent type | Composite label |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | PCS 50% xylene solution | C0 |
| 2 | BP-1 solution | C1 |
| 3 | BP-2 solution | C2 |
| Entry | Precursor type | Ceramic yield/% |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | PCS 50% xylene solution | 68 |
| 2 | BP-1 solution | 79 |
| 3 | BP-2 solution | 81 |
| 4 | Borane pyridine | 49 |
| 5 | Borane pyridine 10% xylene solution | 18 |
表2 陶瓷前驱体类型及其管式炉裂解转化陶瓷产率
Table 2 Types of ceramic precursor and their tube furnace ceramic yields
| Entry | Precursor type | Ceramic yield/% |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | PCS 50% xylene solution | 68 |
| 2 | BP-1 solution | 79 |
| 3 | BP-2 solution | 81 |
| 4 | Borane pyridine | 49 |
| 5 | Borane pyridine 10% xylene solution | 18 |
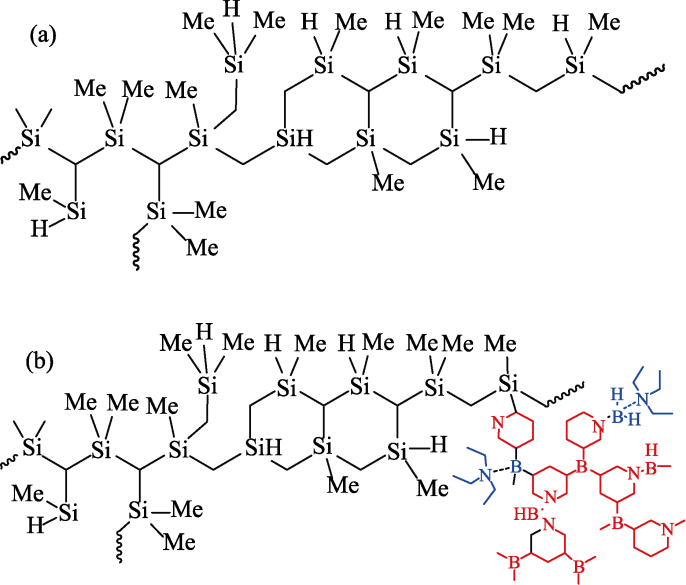
图2 典型PCS分子结构(a)及其与硼烷吡啶、硼烷三乙胺可能的交联网络示意图(b)
Fig. 2 Typical PCS molecular structure (a) and its possible crosslinked network with borane pyridine and borane triethylamine (b)
| Entry | Precursor type | O/% | C/% | Si/% | B/% | N/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | PCS | 1.1 | 39.9 | 59.0 | 0 | 0 |
| 2 | BP-1 | 1.5 | 42.1 | 53.3 | 1.7 | 1.4 |
| 3 | BP-2 | 1.2 | 32.8 | 61.0 | 2.2 | 2.8 |
表3 陶瓷前驱体类型及其衍生陶瓷元素含量(质量分数)
Table 3 Types of ceramic precursor and element contents (in mass) of derived ceramic
| Entry | Precursor type | O/% | C/% | Si/% | B/% | N/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | PCS | 1.1 | 39.9 | 59.0 | 0 | 0 |
| 2 | BP-1 | 1.5 | 42.1 | 53.3 | 1.7 | 1.4 |
| 3 | BP-2 | 1.2 | 32.8 | 61.0 | 2.2 | 2.8 |
| Entry | SiC/SiC composite | Density/ (g·cm-3) | Porosity/% |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | C0 | 2.37±0.01 | 7.80±0.72 |
| 2 | C1 | 2.35±0.02 | 8.40±1.02 |
| 3 | C2 | 2.38±0.03 | 6.27±0.88 |
表4 SiC/SiC复合材料的表观密度及显气孔率
Table 4 Apparent density and porosity of SiC/SiC composites
| Entry | SiC/SiC composite | Density/ (g·cm-3) | Porosity/% |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | C0 | 2.37±0.01 | 7.80±0.72 |
| 2 | C1 | 2.35±0.02 | 8.40±1.02 |
| 3 | C2 | 2.38±0.03 | 6.27±0.88 |
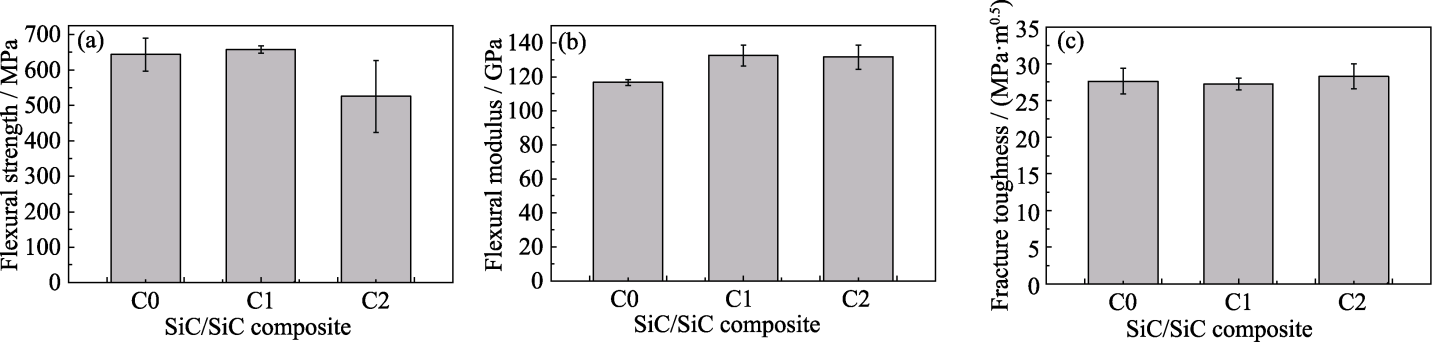
图7 SiC/SiC复合材料C0~C2的室温弯曲强度(a)、弯曲模量(b)及断裂韧性(c)
Fig. 7 (a) Flexural strength, (b) flexural modulus and (c) fracture toughness of SiC/SiC composites C0-C2 at room temperature
| [1] | 成来飞. 陶瓷基复合材料强韧化与应用基础. 北京: 化学工业出版社, 2019. |
| [2] | 邹豪, 王宇, 刘刚, 等. 碳化硅纤维增韧碳化硅陶瓷基复合材料的发展现状及其在航空发动机上的应用. 航空制造技术, 2017(15): 76. |
| [3] | 张立同. 纤维增韧碳化硅陶瓷复合材料:模拟、表征与设计. 北京: 化学工业出版社, 2009. |
| [4] | NASLAIN R R. SiC-matrix composites: nonbrittle ceramics for thermo-structural application. International Journal of Applied Ceramic Technology, 2005, 2(2): 75. |
| [5] | DARZENS S, FARIZY G, VICENS J, et al. High temperature ceramic matrix composites. Hoboken: John Wiley & Sons, Inc., 2001: 211- 217. |
| [6] | KOTANI M, KOHYAMA A, OKAMURA K, et al. Fabrication of high performance SiC/SiC composite by polymer impregnation and pyrolysis method//USTUNDAG E, FISCHMAN G. 23rd Annual Conference on Composites, Advanced Ceramics, Materials, and Structures: B:Ceramic Engineering and Science Proceedings. Hoboken: John Wiley & Sons, Icn., 1999: 309-316. |
| [7] | GOUJARD S R, VANDENBULCKE L, REY J, et al. Process for the manufacture of a refractory composite material protected against corrosion: US5246736A. 1993-09-21. |
| [8] | LAMOUROUX F, BERTRAND S, PAILLER R, et al. A multilayer ceramic matrix for oxidation resistant carbon fibers-reinforced CMCs. Key Engineering Materials, 1999, 164/165: 365. |
| [9] | LAMOUROUX F, BERTRAND S, PAILLER R, et al. Oxidation- resistant carbon-fiber-reinforced ceramic-matrix composites. Composites Science and Technology, 1999, 59(7): 1073. |
| [10] | RUGGLES-WRENN M B, POPE M T, ZENS T W. Creep behavior in interlaminar shear of a Hi-NicalonTM/SiC-B4C composite at 1200 ℃ in air and in steam. Materials Science and Engineering: A, 2014, 610: 279. |
| [11] | 张立同, 成来飞, 徐永东, 等. 自愈合碳化硅陶瓷基复合材料研究及应用进展. 航空材料学报, 2006, 26(3): 226. |
| [12] | CHEN M, QIU H, ZHANG Q, et al. Influence of precursor concentration on the densification efficiency and properties of SiC/SiC composites. International Journal of Applied Ceramic Technology, 2022, 19(6): 3238. |
| [13] | CHEN Y, CHEN M, XIE W, et al. Influence of polycarbosilane composition on the properties of SiC/SiC composite fabricated by precursor infiltration and pyrolysis process. International Journal of Applied Ceramic Technology, 2024, 21(5): 3237. |
| [14] | HU J, LIU C, YE F, et al. A review on high-performance SiCf/SiC composites prepared by PIP process. Journal of Materials Research and Technology, 2024, 33: 7216. |
| [15] | SONG C, YE F, CHENG L, et al. Long-term ceramic matrix composite for aeroengine. Journal of Advanced Ceramics, 2022, 11(9): 1343. |
| [16] | 张立同, 成来飞. 自愈合陶瓷基复合材料制备与应用基础. 北京: 化学工业出版社, 2015. |
| [17] | LUAN X, XU X, ZOU Y, et al. Wet oxidation behavior of SiC/(SiC-SiBCN)x composites prepared by CVI combined with PIOP process. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2019, 102(10): 6239. |
| [18] | CHEN M, QIU H, XIE W, et al. Influence of precursor composition on oxidation behavior of SiBCN multiphase ceramic and oxidation resistance of SiC/SiBCN composites. Journal of the Australian Ceramic Society, 2022, 58(2): 575. |
| [19] | LUAN X, XU X, WANG L, et al. Self-healing enhancing tensile creep of 2D-satin weave SiC/(SiC-SiBCN)x composites in wet oxygen environment. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2020, 40(10): 3509. |
| [20] | CAO F, LI X D, RYU J H, et al. Modification of polycarbosilane by polyborazine as a precursor for oxygen-free SiC fibers. Journal of Materials Chemistry, 2003, 13(8): 1914. |
| [21] | PUERTA A R, REMSEN E E, BRADLEY M G, et al. Synthesis and ceramic conversion reactions of 9-BBN-modified allylhydridopolycarbosilane: a new single-source precursor to boron-modified silicon carbide. Chemistry of Materials, 2003, 15(2): 478. |
| [22] | YU Z, HUANG M, FANG Y, et al. Modification of a liquid polycarbosilane with 9-BBN as a high-ceramic-yield precursor for SiC. Reactive and Functional Polymers, 2010, 70(6): 334. |
| [23] | VIARD A, FONBLANC D, LOPEZ-FERBER D, et al. Polymer derived Si-B-C-N ceramics: 30 years of research. Advanced Engineering Materials, 2018, 20(10): 1800360. |
| [24] | ANAND R, MADHAVI V, LU K. Effect of boron on phase, nanostructure, and thermal stability of polycarbosilane-derived SiC ceramics. Ceramics International, 2024, 50(24): 53701. |
| [25] | BALESTRAT M, DIZ ACOSTA E, HANZEL O, et al. Additive-free low temperature sintering of amorphous SiBC powders derived from boron-modified polycarbosilanes: toward the design of SiC with tunable mechanical, electrical and thermal properties. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2020, 40(7): 2604. |
| [26] | 陶孟, 胡继东, 俸翔, 等. 一种硼改性聚碳硅烷树脂及其制备方法: CN109438712B. 2021-06-11. |
| [27] | 莫高明, 宋育杰, 陈海俊, 等. 一种液态可固化含硼聚碳硅烷及其制备方法: CN110698678A. 2020-01-17. |
| [28] | 裴亚星. 单源聚合物先驱体法制备SiC基超高温纳米复相陶瓷. 厦门: 厦门大学硕士学位论文, 2017. |
| [29] | YU Z, FANG Y, HUANG M, et al. Preparation of a liquid boron-modified polycarbosilane and its ceramic conversion to dense SiC ceramics. Polymers for Advanced Technologies, 2011, 22(12): 2409. |
| [30] | 邵长伟, 王军, 王浩, 等. 一种含硼碳化硅纤维的制备方法: CN104790068A. 2015-07-22. |
| [31] | 董志军, 余汉青, 李轩科, 等. 一种硼掺杂碳化硅纤维及其制备方法: CN108315837A. 2018-07-24. |
| [32] | BILL J, RIEDEL R. Boron carbide nitride derived from amine- boranes. MRS Online Proceedings Library Archive, 1992, 271: 839. |
| [33] | RIEDEL R, BILL J, PASSING G. A novel carbon material derived from pyridine-borane. Advanced Materials, 1991, 3(11): 551. |
| [34] | BILL J, FRIESS M, RIEDEL R. Conversion of amine-boranes to boron carbide nitride. European journal of Solid State and Inorganic Chemistry, 1992, 29: 195. |
| [35] | 王天一. BCN陶瓷制备工艺优化及微结构调控研究. 天津: 河北工业大学硕士学位论文, 2023. |
| [36] | HE L, ZHANG Z, YANG X, et al. Liquid polycarbosilanes: synthesis and evaluation as precursors for SiC ceramic. Polymer International, 2015, 64(8): 979. |
| [1] | 崔宁, 张玉新, 王鲁杰, 李彤阳, 于源, 汤华国, 乔竹辉. (TiVNbMoW)Cx高熵陶瓷的单相形成过程与碳空位调控[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(5): 511-520. |
| [2] | 穆爽, 马沁, 张禹, 沈旭, 杨金山, 董绍明. Yb2Si2O7改性SiC/SiC复合材料的氧化行为研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(3): 323-328. |
| [3] | 李紫薇, 弓伟露, 崔海峰, 叶丽, 韩伟健, 赵彤. 前驱体法制备(Zr, Hf, Nb, Ta, W)C-SiC复相陶瓷及性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(3): 271-280. |
| [4] | 高晨光, 孙晓亮, 陈君, 李达鑫, 陈庆庆, 贾德昌, 周玉. 基于湿法纺丝技术的SiBCN-rGO陶瓷纤维的组织结构、力学和吸波性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(3): 290-296. |
| [5] | 穆浩洁, 张源江, 喻彬, 付秀梅, 周世斌, 李晓东. ZrO2掺杂Y2O3-MgO纳米复相陶瓷的制备及性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(3): 281-289. |
| [6] | 李伟, 许志明, 苟燕子, 尹森虎, 余艺平, 王松. SiC纤维烧结陶瓷的制备及其性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(2): 177-183. |
| [7] | 范武刚, 曹雄, 周响, 李玲, 赵冠楠, 张兆泉. 8YSZ陶瓷在模拟压水堆水环境中的耐腐蚀性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(7): 803-809. |
| [8] | 王伟明, 王为得, 粟毅, 马青松, 姚冬旭, 曾宇平. 以非氧化物为烧结助剂制备高导热氮化硅陶瓷的研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(6): 634-646. |
| [9] | 孙海洋, 季伟, 王为民, 傅正义. TiB-Ti周期序构复合材料设计、制备及性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(6): 662-670. |
| [10] | 蔡飞燕, 倪德伟, 董绍明. 高熵碳化物超高温陶瓷的研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(6): 591-608. |
| [11] | 刘国昂, 王海龙, 方成, 黄飞龙, 杨欢. B4C含量对(Ti0.25Zr0.25Hf0.25Ta0.25)B2-B4C陶瓷力学性能及抗氧化性能的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(6): 697-706. |
| [12] | 粟毅, 史扬帆, 贾成兰, 迟蓬涛, 高扬, 马青松, 陈思安. 浆料浸渍辅助PIP工艺制备C/HfC-SiC复合材料的微观结构及性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(6): 726-732. |
| [13] | 李雷, 程群峰. 高性能MXenes纳米复合材料研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(2): 153-161. |
| [14] | 刘艳艳, 谢曦, 刘增乾, 张哲峰. MAX相陶瓷增强金属基复合材料: 制备、性能与仿生设计[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(2): 145-152. |
| [15] | 王博, 蔡德龙, 朱启帅, 李达鑫, 杨治华, 段小明, 李雅楠, 王轩, 贾德昌, 周玉. SrAl2Si2O8增强BN陶瓷的力学性能及抗热震性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(10): 1182-1188. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||