无机材料学报 ›› 2020, Vol. 35 ›› Issue (3): 293-300.DOI: 10.15541/jim20190381 CSTR: 32189.14.10.15541/jim20190381
所属专题: 2020年环境材料论文精选(二)重金属元素去除
董丽佳1,郭筱洁2,李雪1,陈朝贵1,金阳1( ),AHMED Alsaedi3,TASAWAr Hayat3,4,赵轻舟5,盛国栋6(
),AHMED Alsaedi3,TASAWAr Hayat3,4,赵轻舟5,盛国栋6( )
)
收稿日期:2019-07-24
修回日期:2019-09-11
出版日期:2020-03-20
网络出版日期:2019-09-20
作者简介:董丽佳(1984-), 女, 博士. E-mail: Donglijia@126.com
DONG Lijia1,GUO Xiaojie2,LI Xue1,CHEN Chaogui1,JIN Yang1( ),AHMED Alsaedi3,TASAWAR Hayat3,4,ZHAO Qingzhou5,SHENG Guodong6(
),AHMED Alsaedi3,TASAWAR Hayat3,4,ZHAO Qingzhou5,SHENG Guodong6( )
)
Received:2019-07-24
Revised:2019-09-11
Published:2020-03-20
Online:2019-09-20
About author:DONG Lijia(1984-), female, PhD. E-mail: Donglijia@126.com
Supported by:摘要:
本研究结合静态实验和X射线吸收精细结构谱学(EXAFS)评估了硫化钼纳米片对重金属Cd(II)的吸附行为和微观机制。结果表明: Cd(II)在硫化钼纳米片上的吸附受溶液pH、反应时间和温度的显著影响, 但不受离子强度的影响。在pH 3.3~9.6范围内, pH升高显著促进了硫化钼对Cd(II)的吸附量, 但不改变吸收速率、吸附等温线和热力学。二级动力学模型能更好地拟合该吸附平衡, 且内表面颗粒扩散模型显示了吸附过程中的三个典型阶段。等温线和热力学分析说明Cd(II)在硫化钼上的吸附是异质性的、自发的、吸热的和不可逆的过程。EXAFS光谱学分析揭示了该吸附存在两种类型: 在较低的pH(3.56, 6.48)条件下, 内表面络合以Cd-S配位键为主; 在较高的pH(9.57)条件下, 出现Cd(OH)2沉淀, 且配位键以Cd-O和Cd-Cd的形式存在。这些研究结果对于评估重金属离子和硫化钼纳米片在分子水平上的作用机理提供了新的视野。
中图分类号:
董丽佳, 郭筱洁, 李雪, 陈朝贵, 金阳, AHMED Alsaedi, TASAWAr Hayat, 赵轻舟, 盛国栋. 不同pH条件下硫化钼纳米片吸附Cd(II)的微观机制研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2020, 35(3): 293-300.
DONG Lijia, GUO Xiaojie, LI Xue, CHEN Chaogui, JIN Yang, AHMED Alsaedi, TASAWAR Hayat, ZHAO Qingzhou, SHENG Guodong. Microscopic Insights into pH-dependent Adsorption of Cd(II) on Molybdenum Disulfide Nanosheets[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2020, 35(3): 293-300.
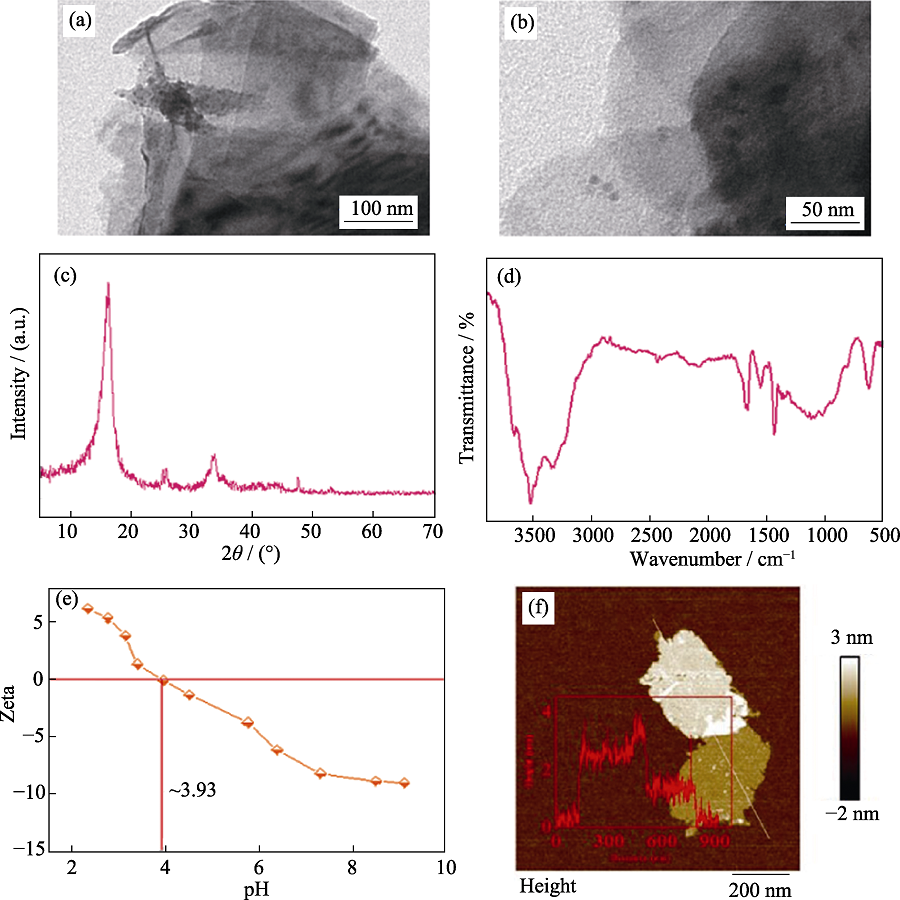
Fig. S1 SEM image (a), TEM image (b), XRD pattern (c), FT-IR spectrum (d), Zeta potentials (e), and height cross-section profile (inset) and corresponding AFM image (f) of MoS2 samples
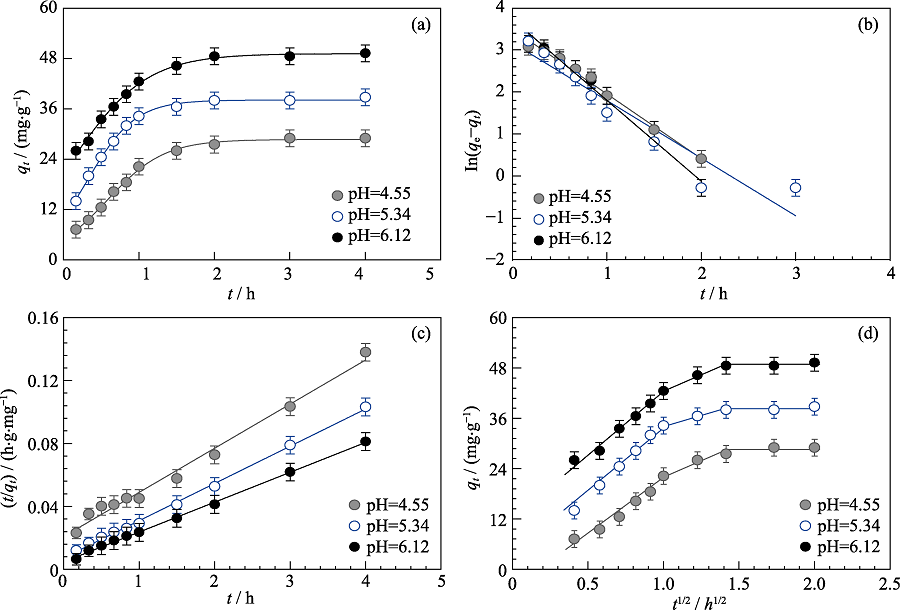
Fig. 3 Cd(II) adsorption on MoS2 nanosheets as a function of contact time (a) and the fitting of pseudo-first-order kinetic model (b), pseudo-second-order kinetic model (c) and intra-particle diffusion model (d) at different pH Cd(II) initial concentration=10 mg/L, m/V=0.15 g/L, I=0.01 mol/L NaNO3, T=293 K
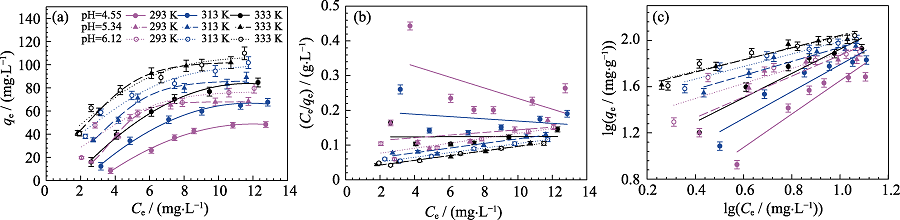
Fig. S2 Adsorption isotherms (a) and fitting results of Langmuir (b) and Freundlich (c) sorption isotherms of Cd(II) sorption on MoS2 at different temperatures and different pH Cd(II) initial concentration=10 mg/L, m/V=0.15 g/L, I = 0.01 mol/L NaNO3
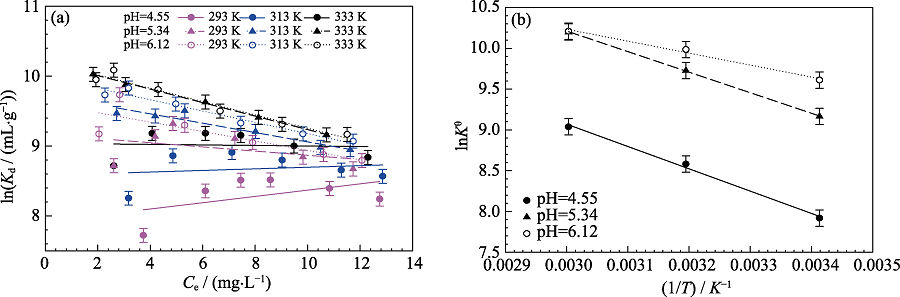
Fig. S3 Linear plots of lnKd versus Ce for Cd(II) at different temperatures and different pH(a), and linear regression plots of lnKθ versus 1/T for Cd(II) sorption on MoS2 at different pH(b) Cd(II) initial concentration=10 mg/L, m/V=0.15 g/L, I=0.01 mol/L NaNO3
| pH | T/K | KF/(mg1-n·Ln∙g-1) | n | R2 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Freundlich equation | 4.55 | 293 | 1.624 | 1.440 | 0.887 |
| 313 | 4.256 | 1.160 | 0.881 | ||
| 333 | 7.461 | 1.052 | 0.904 | ||
| 5.34 | 293 | 9.363 | 0.899 | 0.801 | |
| 313 | 21.627 | 0.603 | 0.907 | ||
| 333 | 32.734 | 0.526 | 0.939 | ||
| 6.12 | 293 | 17.298 | 0.650 | 0.812 | |
| 313 | 28.054 | 0.542 | 0.935 | ||
| 333 | 34.119 | 0.499 | 0.919 | ||
| pH | T/K | qmax /(mg∙g-1) | KL /(L∙mg-1) | R2 | |
| Langmuir equation | 4.55 | 293 | 0.040 | 64.516 | 0.299 |
| 313 | 0.016 | 305.157 | 0.069 | ||
| 333 | 0.001 | 754.717 | 0.017 | ||
| 5.34 | 293 | 0.036 | 262.536 | 0.162 | |
| 313 | 0.132 | 149.276 | 0.918 | ||
| 333 | 0.236 | 147.580 | 0.978 | ||
| 6.12 | 293 | 0.114 | 140.449 | 0.759 | |
| 313 | 0.172 | 152.022 | 0.974 | ||
| 333 | 0.224 | 151.492 | 0.978 |
Table S1 Parameters of Langmuir and Freundlich equations for the sorption of Cd(II) onto MoS2 at different temperatures and different pH
| pH | T/K | KF/(mg1-n·Ln∙g-1) | n | R2 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Freundlich equation | 4.55 | 293 | 1.624 | 1.440 | 0.887 |
| 313 | 4.256 | 1.160 | 0.881 | ||
| 333 | 7.461 | 1.052 | 0.904 | ||
| 5.34 | 293 | 9.363 | 0.899 | 0.801 | |
| 313 | 21.627 | 0.603 | 0.907 | ||
| 333 | 32.734 | 0.526 | 0.939 | ||
| 6.12 | 293 | 17.298 | 0.650 | 0.812 | |
| 313 | 28.054 | 0.542 | 0.935 | ||
| 333 | 34.119 | 0.499 | 0.919 | ||
| pH | T/K | qmax /(mg∙g-1) | KL /(L∙mg-1) | R2 | |
| Langmuir equation | 4.55 | 293 | 0.040 | 64.516 | 0.299 |
| 313 | 0.016 | 305.157 | 0.069 | ||
| 333 | 0.001 | 754.717 | 0.017 | ||
| 5.34 | 293 | 0.036 | 262.536 | 0.162 | |
| 313 | 0.132 | 149.276 | 0.918 | ||
| 333 | 0.236 | 147.580 | 0.978 | ||
| 6.12 | 293 | 0.114 | 140.449 | 0.759 | |
| 313 | 0.172 | 152.022 | 0.974 | ||
| 333 | 0.224 | 151.492 | 0.978 |
| pH | qe/(mg·g-1) | k1/h-1 | R2 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4.55 | 33.023 | 0.059 | 0.9896 | |
| Pseudo-first- order model | 5.34 | 23.903 | 0.053 | 0.9069 |
| 6.12 | 41.777 | 0.074 | 0.9835 | |
| pH | qe/(mg·g-1) | k2/(g·mg-1·h-1) | R2 | |
| 4.55 | 35.638 | 0.038 | 0.9869 | |
| Pseudo-second- order model | 5.34 | 42.230 | 0.078 | 0.9978 |
| 6.12 | 52.659 | 0.077 | 0.9986 | |
| pH | C/(mg·L-1) | ki/(g·mg-1·h-1/2) | R2 | |
| 4.55 | 19.985 | 2.628 | 0.942 | |
| Intra-particle diffusion model | 5.34 | 32.500 | 1.877 | 0.987 |
| 6.12 | 39.759 | 3.004 | 0.980 |
Table 1 Parameters of kinetic models for the adsorption of Cd(II) on MoS2 as a function of pH
| pH | qe/(mg·g-1) | k1/h-1 | R2 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4.55 | 33.023 | 0.059 | 0.9896 | |
| Pseudo-first- order model | 5.34 | 23.903 | 0.053 | 0.9069 |
| 6.12 | 41.777 | 0.074 | 0.9835 | |
| pH | qe/(mg·g-1) | k2/(g·mg-1·h-1) | R2 | |
| 4.55 | 35.638 | 0.038 | 0.9869 | |
| Pseudo-second- order model | 5.34 | 42.230 | 0.078 | 0.9978 |
| 6.12 | 52.659 | 0.077 | 0.9986 | |
| pH | C/(mg·L-1) | ki/(g·mg-1·h-1/2) | R2 | |
| 4.55 | 19.985 | 2.628 | 0.942 | |
| Intra-particle diffusion model | 5.34 | 32.500 | 1.877 | 0.987 |
| 6.12 | 39.759 | 3.004 | 0.980 |
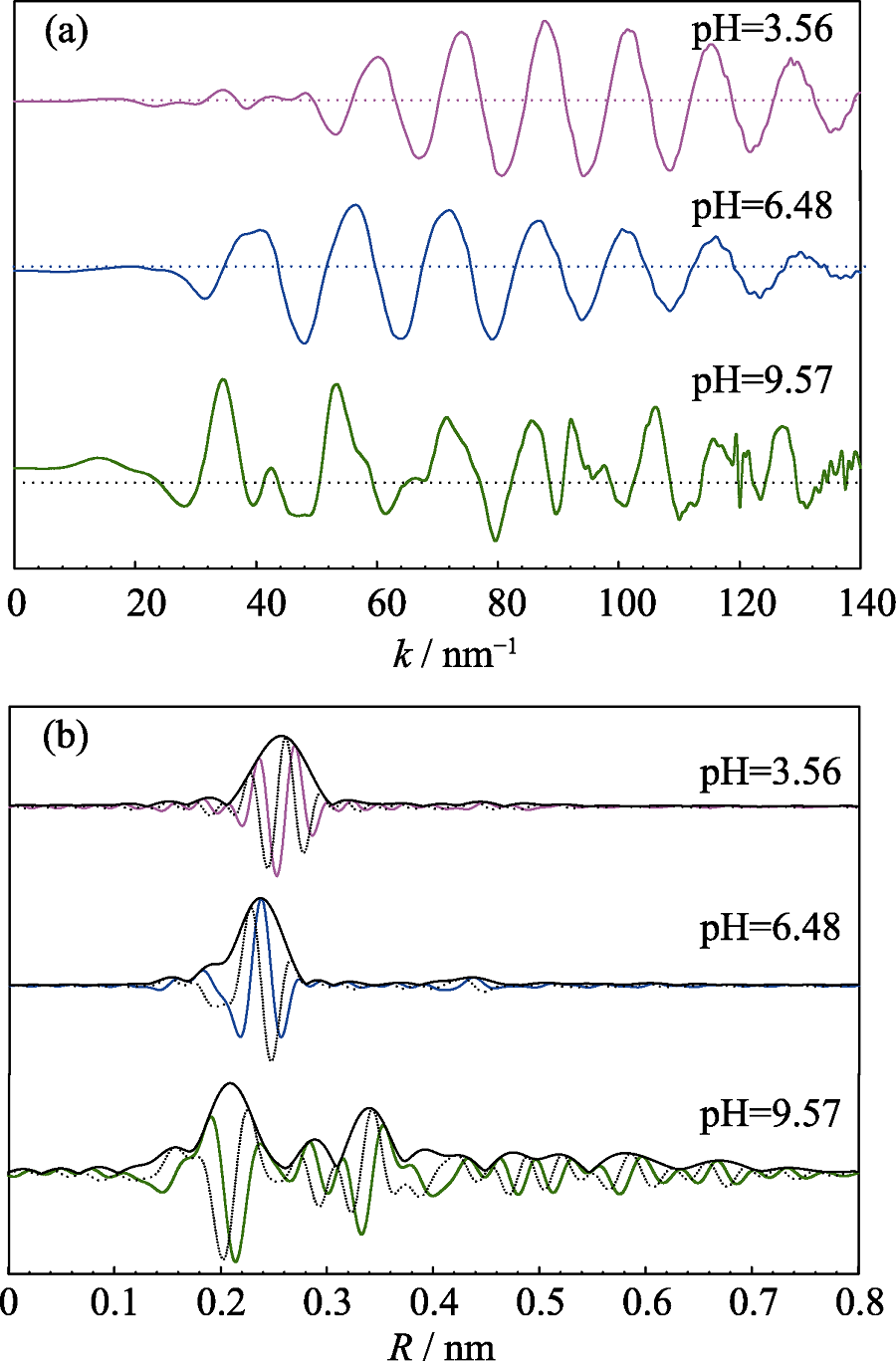
Fig. 4 Normalized, background-subtracted and k3-weighted EXAFS spectra (a) and corresponding RSF magnitudes and imaginary parts (b) of Cd reference samples
| pH | T | ΔGθ/(kJ/mg) | ΔSθ/(J∙mg-1· K-1) | ΔHθ/(kJ∙mg-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4.55 | 293 | -19.291 | 143.66592 | 22.803 |
| 313 | -22.333 | 22.635 | ||
| 333 | -25.022 | 22.818 | ||
| 5.34 | 293 | -22.331 | 147.73978 | 20.957 |
| 313 | -25.312 | 20.930 | ||
| 333 | -28.239 | 20.958 | ||
| 6.12 | 293 | -23.412 | 121.71696 | 12.251 |
| 313 | -25.986 | 12.111 | ||
| 333 | -28.267 | 12.265 |
Table S2 Parameters of thermodynamics for adsorption of Cd(II) onto MoS2 at 3 temperatures and different pH
| pH | T | ΔGθ/(kJ/mg) | ΔSθ/(J∙mg-1· K-1) | ΔHθ/(kJ∙mg-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4.55 | 293 | -19.291 | 143.66592 | 22.803 |
| 313 | -22.333 | 22.635 | ||
| 333 | -25.022 | 22.818 | ||
| 5.34 | 293 | -22.331 | 147.73978 | 20.957 |
| 313 | -25.312 | 20.930 | ||
| 333 | -28.239 | 20.958 | ||
| 6.12 | 293 | -23.412 | 121.71696 | 12.251 |
| 313 | -25.986 | 12.111 | ||
| 333 | -28.267 | 12.265 |
| Sample conditions | shells | R/nm | CN | σ2 /nm2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cd(NO3)2(aq) | Cd-O | 0.233(4) | 6.2(3) | 0.0010(1) |
| Cd(OH)2 | Cd-O | 0.238(2) | 6.1(4) | 0.0014(5) |
| Cd-Cd | 0.359(3) | 5.9(4) | 0.0032(5) | |
| CdS | Cd-S | 0.259(1) | 4.1(3) | 0.0024(2) |
| pH 3.56, sorption | Cd-S | 0.255(2) | 3.9(5) | 0.0027(3) |
| pH 6.48, sorption | Cd-S | 0.257(1) | 3.8(4) | 0.0023(5) |
| pH 9.57, sorption | Cd-O | 0..34(5) | 5.9(6) | 0.0016(3) |
| Cd-Cd | 0.357(3) | 5.6(4) | 0.0037(2) |
Table s3 Structural parameters of Cd(II) reference and sorption samples
| Sample conditions | shells | R/nm | CN | σ2 /nm2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cd(NO3)2(aq) | Cd-O | 0.233(4) | 6.2(3) | 0.0010(1) |
| Cd(OH)2 | Cd-O | 0.238(2) | 6.1(4) | 0.0014(5) |
| Cd-Cd | 0.359(3) | 5.9(4) | 0.0032(5) | |
| CdS | Cd-S | 0.259(1) | 4.1(3) | 0.0024(2) |
| pH 3.56, sorption | Cd-S | 0.255(2) | 3.9(5) | 0.0027(3) |
| pH 6.48, sorption | Cd-S | 0.257(1) | 3.8(4) | 0.0023(5) |
| pH 9.57, sorption | Cd-O | 0..34(5) | 5.9(6) | 0.0016(3) |
| Cd-Cd | 0.357(3) | 5.6(4) | 0.0037(2) |
| [1] | ZENG G, LIU Y, TANG L , et al. Enhancement of Cd(II) adsorption by polyacrylic acid modified magnetic mesoporous carbon. Chem. Eng. J., 2015,259:153-160. |
| [2] | YANG G, TANG L, LEI X , et al. Cd(II) removal from aqueous solution by adsorption on ketoglutaric acid-modified magnetic chitosan. Appl. Surf. Sci., 2014,292:710-716. |
| [3] | LUO L, MA Y B, ZHANG S Z , et al. An inventory of trace element inputs to agricultural soils in China. J. Environ. Manage, 2009,90(8):2524-2530. |
| [4] | KHAN T A, CHAUDHRY S A, ALI I . Equilibrium uptake, isotherm and kinetic studies of Cd(II) adsorption onto iron oxide activated red mud from aqueous solution. J. Mol. Liq., 2015,202:165-175. |
| [5] | AWUAL M R, KHRAISHEH M, ALHARTHI N H , et al. Efficient detection and adsorption of cadmium(II) ions using innovative nano-composite materials. Chem. Eng. J., 2018,343:118-127. |
| [6] | LIAO Q, ZOU D, PAN W , et al. Highly-efficient scavenging of P(V), Cr(VI), Re(VII) anions onto g-C3N4 nanosheets from aqueous solutions as impacted via water chemistry. J. Mol. Liq., 2018,258:275-284. |
| [7] | DONG L, YANG J, MOU Y , et al. Effect of various environmental factors on the adsorption of U(VI) onto biochar derived from rice straw. J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem., 2017,314(1):377-386. |
| [8] | SHENG G D, YANG Q, PENG F , et al. Determination of colloidal pyrolusite, Eu(III) and humic substance interaction: a combined batch and EXAFS approach. Chem. Eng. J., 2014,245:10-16. |
| [9] | YU S J, WANG X X, PANG H W , et al. Boron nitride-based materials for the removal of pollutants from aqueous solutions: a review. Chem. Eng. J., 2018,333:343-360. |
| [10] | YAO W, WANG X, LIANG Y , et al. Synthesis of novel flower-like layered double oxides/carbon dots nanocomposites for U(VI) and 241Am(III) efficient removal: batch and EXAFS studies. Chem. Eng. J., 2018,332:775-786. |
| [11] | WANG J, WANG X X, ZHAO G X , et al. Polyvinylpyrrolidone and polyacrylamide intercalated molybdenum disulfide as adsorbents for enhanced removal of chromium(VI) from aqueous solutions. Chem. Eng. J., 2018,334:569-578. |
| [12] | LIAO Q, ZOU D S, PAN W , et al. Highly efficient capture of Eu(III), La(III), Nd(III), Th(IV) from aqueous solutions using g-C3N4 nanosheets. J. Mol. Liq., 2018,252:351-361. |
| [13] | WANG X X, YU S J, WANG X K . Removal of radionuclides by metal-organic framework-based materials. J. Inorg. Mater., 2019,34(1):17-26. |
| [14] | WANG N, PANG H, YU S , et al. Investigation of adsorption mechanism of layered double hydroxides and their composites on radioactive uranium: a review. Acta Chim. Sinica, 2019,77(2):143-152. |
| [15] | LIU X, MA R, WANG X , et al. Graphene oxide-based materials for efficient removal of heavy metal ions from aqueous solution: a review. Environ. Pollut., 2019,252:62-73. |
| [16] | WANG X X, CHEN L, WANG L , et al. Synthesis of novel nanomaterials and their application in efficient removal of radionuclides. Sci. China Chem., 2019,62(8):933-967. |
| [17] | FENG B, YAO C, CHEN S , et al. Highly efficient and selective recovery of Au(III) from a complex system by molybdenum disulfide nanoflakes. Chem. Eng. J., 2018,350:692-702. |
| [18] | CHEN H J, HUANG J, LEI X L , et al. Adsorption and diffusion of lithium on MoS2 monolayer: the role of strain and concentration. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci., 2013,8:2196-2203. |
| [19] | JIA F, WANG Q, WU J , et al. Two-dimensional molybdenum disulfide as a superb adsorbent for removing Hg+ from water. ACS Sustainable Chem. Eng., 2017,5:7410-7419. |
| [20] | JIA F, ZHANG X, SONG S . AFM study on the adsorption of Hg 2+ on natural molybdenum disulfide in aqueous solutions . Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2017,19:3837-3844. |
| [21] | WANG Z, MI B . Environmental applications of 2D molybdenum disulfide (MoS2) nanosheet. Environ. Sci. Technol., 2017,51:8229-8244. |
| [22] | AI K, RUAN C, SHEN M , et al. MoS2 nanosheets with widened interlayer spacing for high-efficiency removal of mercury in aquatic systems. Adv. Funct. Mater., 2016,26:5542-5549. |
| [23] | TONG S, DENG H, WANG L , et al. Multi-functional nanohybrid of ultrathin molybdenum disulfide nanosheets decorated with cerium oxide nanoparticles for preferential uptake of lead (II) ions. Chem. Eng. J., 2018,335:22-31. |
| [24] | LI X, LI Q, LINGHU W , et al. Sorption properties of U(VI) and Th(IV) on two-dimensional molybdenum disulfide (MoS2) nanosheets: effects of pH, ionic strength, contact time, humic acids and temperature. Environ. Technol. Innov., 2018,11:328-338. |
| [25] | WANG Q, YANG L, JIA F , et al. Removal of Cd(II) from water by using nano-scale molybdenum disulphide sheets as adsorbents. J. Mol. Liq., 2018,263:526-533. |
| [26] | ZHI L, ZUO W, CHEN F , et al. 3D MoS2 composition aerogel as chemosensors and adsorbents for colorimetric detection and high- capacity adsorption of Hg2+. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng., 2016,4:3398-3408. |
| [27] | AI K, RUAN C, SHEN M , et al. MoS2 nanosheets with widened interlayer spacing for high-efficiency removal of mercury in aquatic systems. Adv. Funct. Mater., 2016,26:5542-5549. |
| [28] | AGHAGOLI M J, BEYKI M H, SHEMIRANI F . Application of dahlia-like molybdenum disulfide nanosheets for solid phase extraction of Co(II) in vegetable and water samples. Food Chem., 2017,223:8-15. |
| [29] | GAO X, SHENG G D, HUANG Y Y . Mechanism and microstructure of Eu(III) interaction with γ-MnOOH by a combination of batch and high resolution EXAFS investigation. Sci. China Chem., 2013,56:1658-1666. |
| [30] | DONG L, LIAO Q, LINGHU W , et al. Application of EXAFS with a bent crystal analyzer to study the pH-dependent microstructure of Eu(III) onto birnessite. J. Environ. Chem. Eng., 2018,6:842-848. |
| [31] | VASCONCELOS I F, HAACK E A, MAURICE P A , et al. EXAFS analysis of cadmium(II) adsorption to kaolinite. Chem. Geol., 2008,249:237-249. |
| [32] | LIU C, FRENKEL A I, VAIRAVAMURTHY A , et al. Sorption of cadmium on humic acid: mechanistic and kinetic studies with atomic force microscopy and X-ray absorption fine structure spectroscopy. Can. J. Soil Sci., 2001,81:337-348. |
| [33] | SHENG G D, YANG S T, LI Y M , et al. Retention mechanisms and microstructure of Eu(III) on manganese dioxides studied by batch and high resolution EXAFS technique. Radiochim. Acta, 2014,102:155-167. |
| [34] | COLEMAN J N, LOTYA M, O’NEILL A , et al. Two dimensional nanosheets produced by liquid exfoliation of layered materials. Science, 2011,331(6017):568-571. |
| [35] | SPLENDIANI A, SUN L, ZHANG Y , et al. Emerging photoluminescence in monolayer MoS2. Nano Lett., 2010,10:1271-1275. |
| [36] | KUMAR A S K, JIANG S J, WARCHOL J K . Synthesis and characterization of two-dimensional transition metal dichalcogenide magnetic MoS2@Fe3O4 nanoparticles for adsorption of Cr(VI)/Cr(III). ACS Omega, 2017,2:6187-6200. |
| [37] | TAKAMATSU R, ASAKURA K, CHUN W J , et al. EXAFS studies about the sorption of cadmium ions on montmorillonite. Chem. Lett., 2006,35:224-225. |
| [38] | HUANG X, CHEN T, ZOU X , et al. The adsorption of Cd(II) on manganese oxide investigated by batch and modeling techniques. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health, 2017,14(10):1145. |
| [39] | GUECHI E, BEGGAS D . Removal of cadmium (II) from water using fibre fruit lufa as biosorbent. Desalin. Water Treat., 2017,94:181-188. |
| [40] | ABASIYAN S M A, MAHDANINIA G R . Polyvinyl alcohol- based nanocomposite hydrogels containing magnetic laponite RD to remove cadmium. Environ. Sci. Poll. Res., 2018,25:14977-14988. |
| [41] | CORBETT J F . Pseudo first-order kinetics. J. Chem. Educ., 1972,49:663. |
| [42] | HO Y S, MCKAY G . A comparison of chemisorption kinetic models applied to pollutant removal on various sorbents. Process. Saf. Environ., 1998,76:332-340. |
| [43] | GRAAF G H, SCHOLTENS H, STAMHUIS E J , et al. Intra-particle diffusion limitations in low-pressure methanol synthesis. Chem. Eng. Sci., 1990,45:773-783. |
| [44] | HO Y S, MCKAY G . The kinetics of sorption of divalent metal ions onto sphagnum moss peat. Water Rer., 2000,34:735-742. |
| [45] | TEMKIN M J, PYZHEV V . Recent modifications to Langmuir isotherms. Acta Physchim, 1940,12:217-222. |
| [46] | XUE C, QI P S, LIU Y Z . Adsorption of aquatic Cd 2+ using a combination of bacteria and modified carbon fiber . Adsorpt. Sci. Technol., 2017,36:857-871. |
| [47] | GU P, ZHANG S, ZHANG C , et al. Two-dimensional MAX- derived titanate nanostructures for efficient removal of Pb(II). Dalton Trans., 2019,48(6):2100-2107. |
| [48] | CHEN W, LU Z, XIAO B , et al. Enhanced removal of lead ions from aqueous solution by iron oxide nanomaterials with cobalt and nickel doping. J. Clean. Prod., 2019,211:1250-1258. |
| [49] | ZHANG D, NIU H Y, ZHANG X L , et al. Strong adsorption of chlorotetracycline on magnetite nanoparticles. J. Hazard. Mater., 2011,192:1088-1093. |
| [50] | ZHANG H, YU X, CHEN L , et al. Study of 63Ni adsorption on NKF-6 zeolite. J. Environ. Radioact., 2010,101:1061-1069. |
| [51] | BEKCI Z, SEKI Y, YURDAKOC M K . A study of equilibrium and FTIR, SEM/EDS analysis of trimethoprim adsorption onto K10. J. Mol. Struct., 2007,827:67-74. |
| [52] | GRÄFE M, SINGH B, BALASUBRAMANIAN M . Surface speciation of Cd(II) and Pb(II) on kaolinite by EXAFS spectroscopy. J. Colloid Interf. Sci., 2007,315:21-32. |
| [53] | SHENG G, DONG H, SHEN R , et al. Microscopic insights into the temperature dependent adsorption of Eu(III) onto titanate nanotubes studied by FTIR, XPS, XAFS and batch technique. Chem. Eng. J., 2013,217:486-494. |
| [1] | 穆浩洁, 张源江, 喻彬, 付秀梅, 周世斌, 李晓东. ZrO2掺杂Y2O3-MgO纳米复相陶瓷的制备及性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(3): 281-289. |
| [2] | 范武刚, 曹雄, 周响, 李玲, 赵冠楠, 张兆泉. 8YSZ陶瓷在模拟压水堆水环境中的耐腐蚀性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(7): 803-809. |
| [3] | 姜灵毅, 庞生洋, 杨超, 张悦, 胡成龙, 汤素芳. C/SiC-BN复合材料的制备及氧化行为[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(7): 779-786. |
| [4] | 薛轶凡, 李玮洁, 张中伟, 庞旭, 刘愚. 碳纤维布表面PyC界面相微观结构及均匀性的工艺调控[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(4): 399-408. |
| [5] | 吴爽, 苟燕子, 王永寿, 宋曲之, 张庆雨, 王应德. 高温热处理对国产KD-SA型SiC纤维组成结构与力学性能的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(5): 569-576. |
| [6] | 李建波, 田震, 蒋全伟, 于砺锋, 康慧君, 曹志强, 王同敏. 不同元素掺杂对CaTiO3微观结构及热电性能的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(12): 1396-1404. |
| [7] | 吴东江, 赵紫渊, 于学鑫, 马广义, 由竹琳, 任冠辉, 牛方勇. Al2O3-TiCp复相陶瓷激光定向能量沉积直接增材制造[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(10): 1183-1192. |
| [8] | 洪督, 牛亚然, 李红, 钟鑫, 郑学斌. 等离子喷涂TiC-Graphite复合涂层摩擦磨损性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(6): 643-650. |
| [9] | 吴西士, 朱云洲, 黄庆, 黄政仁. 树脂基多孔碳孔结构对Cf/SiC复合材料连接性能的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(12): 1275-1280. |
| [10] | 黄新友, 刘玉敏, 刘洋, 李晓英, 冯亚刚, 陈肖朴, 陈鹏辉, 刘欣, 谢腾飞, 李江. 醇水共沉淀法制备Yb:YAG透明陶瓷及其性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2021, 36(2): 217-224. |
| [11] | 张俊敏, 陈小武, 廖春景, 郭斐宇, 杨金山, 张翔宇, 董绍明. SiCf/SiC复合材料的RMI制备方法以及微观结构和性能优化[J]. 无机材料学报, 2021, 36(10): 1103-1110. |
| [12] | 朱丹阳, 钱康, 陈肖朴, 胡泽望, 刘欣, 李晓英, 潘裕柏, MIHÓKOVÁ Eva, NIKL Martin, 李江. 热等静压烧结制备细晶粒Ce,Y:SrHfO3闪烁陶瓷[J]. 无机材料学报, 2021, 36(10): 1118-1124. |
| [13] | 吴小军,杨杰,郑蕊,张兆甫,杨毅. 烧蚀型面结构对CVI+HPIC工艺制备针刺C/C喉衬等离子烧蚀性能的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2020, 35(6): 654-660. |
| [14] | 张伟,高鹏,侯成义,李耀刚,张青红,王宏志. 基于ZnO复合材料的芯片式pH和温度传感器[J]. 无机材料学报, 2020, 35(4): 416-422. |
| [15] | 李丽, 郭筱洁, 金阳, 陈朝贵, Abdullah M Asiri, HadiM M arwani, 赵轻舟, 盛国栋. 氮化硼纳米片吸附Cd(II)的动力学和热力学研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2020, 35(3): 284-292. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||