无机材料学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 40 ›› Issue (5): 457-465.DOI: 10.15541/jim20240413 CSTR: 32189.14.jim20240413
安然1( ), 林锶1, 郭世刚2, 张冲2, 祝顺2, 韩颖超1(
), 林锶1, 郭世刚2, 张冲2, 祝顺2, 韩颖超1( )
)
收稿日期:2024-09-18
修回日期:2024-12-08
出版日期:2025-05-20
网络出版日期:2024-12-27
通讯作者:
韩颖超, 研究员. E-mail: hanyingchao@whut.edu.cn作者简介:安 然(2000-), 男, 硕士研究生. E-mail: ar17864218908@163.com
基金资助:
AN Ran1( ), LIN Si1, GUO Shigang2, ZHANG Chong2, ZHU Shun2, HAN Yingchao1(
), LIN Si1, GUO Shigang2, ZHANG Chong2, ZHU Shun2, HAN Yingchao1( )
)
Received:2024-09-18
Revised:2024-12-08
Published:2025-05-20
Online:2024-12-27
Contact:
HAN Yingchao, professor. E-mail: hanyingchao@whut.edu.cnAbout author:AN Ran (2000-), male, Master candidate. E-mail: ar17864218908@163.com
Supported by:摘要:
纳米羟基磷灰石(nHAP)兼具生物相容性及环境友好性, 经铁掺杂改性后, 有望作为一种新型紫外(UV)吸收材料。本研究采用共沉淀法和水热法制备了铁掺杂纳米羟基磷灰石(Fe-nHAP), 通过调节反应时间、温度和铁掺杂比探究了制备工艺对UV吸收性能的影响。结果表明, 随着温度从37 ℃升高至150 ℃, 或将反应时间从0.5 h延长至3 h, 材料结晶度及UV吸收峰值均有一定程度的提升, 表明Fe-nHAP的UV吸收性能与结晶度具有正关联。此外, Fe-nHAP的UV吸收性能还与铁掺杂比密切相关。随着铁掺杂摩尔比从0增至10%, Fe-nHAP的UV吸收性能逐渐增强, 最大吸收值从0.03增至1.35, 这归因于铁掺杂引起材料能带结构变化, 进而使其光学带隙缩小。然而, 高掺杂比导致材料结晶度过低, 使得UV吸收性能提升效果减弱。安全性评价表明铁掺杂摩尔比为7%的Fe-nHAP未表现出细胞毒性、光毒性及皮肤刺激性。综上, Fe-nHAP具备较强的UV吸收性能, 加之良好的生物安全性, 有望成为一种新型UV吸收材料。
中图分类号:
安然, 林锶, 郭世刚, 张冲, 祝顺, 韩颖超. 铁掺杂纳米羟基磷灰石的制备及紫外吸收性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(5): 457-465.
AN Ran, LIN Si, GUO Shigang, ZHANG Chong, ZHU Shun, HAN Yingchao. Iron-doped Nano-hydroxyapatite: Preparation and Ultraviolet Absorption Performance[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(5): 457-465.
| T/℃ | a-axis/Å | c-axis/Å | Volume/Å3 | Crystallinity/% | D(002)/nm | D(310)/nm |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 37 | 9.39411 | 6.80010 | 525.23 | 19.56 | 43.50 | 20.11 |
| 60 | 9.39522 | 6.80268 | 525.54 | 21.25 | 49.66 | 20.30 |
| 80 | 9.39580 | 6.82520 | 525.46 | 25.56 | 54.33 | 20.33 |
| 100 | 9.39954 | 6.84554 | 526.65 | 30.77 | 57.28 | 21.05 |
| 150 | 9.40185 | 6.86230 | 526.90 | 32.00 | 61.50 | 25.49 |
表1 不同反应温度(T)制备的Fe-nHAP的晶格参数、晶胞体积、结晶度和晶粒尺寸
Table 1 Lattice parameters, volumes, crystallinities, and grain sizes of Fe-nHAP prepared under different temperatures (T)
| T/℃ | a-axis/Å | c-axis/Å | Volume/Å3 | Crystallinity/% | D(002)/nm | D(310)/nm |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 37 | 9.39411 | 6.80010 | 525.23 | 19.56 | 43.50 | 20.11 |
| 60 | 9.39522 | 6.80268 | 525.54 | 21.25 | 49.66 | 20.30 |
| 80 | 9.39580 | 6.82520 | 525.46 | 25.56 | 54.33 | 20.33 |
| 100 | 9.39954 | 6.84554 | 526.65 | 30.77 | 57.28 | 21.05 |
| 150 | 9.40185 | 6.86230 | 526.90 | 32.00 | 61.50 | 25.49 |
| Time/h | a-axis/Å | c-axis/Å | Volume/Å3 | Crystallinity/% | D(002)/nm | D(310)/nm |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.5 | 9.32063 | 6.77150 | 525.11 | 16.77 | 46.72 | 23.05 |
| 1 | 9.32145 | 6.79534 | 525.45 | 20.70 | 49.52 | 23.21 |
| 3 | 9.32498 | 6.82841 | 526.55 | 32.13 | 61.08 | 25.44 |
| 5 | 9.32705 | 6.83254 | 526.73 | 33.06 | 62.01 | 25.54 |
表2 不同反应时间制备的Fe-nHAP的晶格参数、晶胞体积、结晶度和晶粒尺寸
Table 2 Lattice parameters, volumes, crystallinities, and grain sizes of Fe-nHAP prepared for different time
| Time/h | a-axis/Å | c-axis/Å | Volume/Å3 | Crystallinity/% | D(002)/nm | D(310)/nm |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.5 | 9.32063 | 6.77150 | 525.11 | 16.77 | 46.72 | 23.05 |
| 1 | 9.32145 | 6.79534 | 525.45 | 20.70 | 49.52 | 23.21 |
| 3 | 9.32498 | 6.82841 | 526.55 | 32.13 | 61.08 | 25.44 |
| 5 | 9.32705 | 6.83254 | 526.73 | 33.06 | 62.01 | 25.54 |
| Sample | a-axis/Å | c-axis/Å | Volume/Å3 | Crystallinity/% | D(002)/nm | D(310)/nm |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| nHAP | 9.33129 | 6.70756 | 527.13 | 43.92 | 70.79 | 31.45 |
| 0.3%Fe-nHAP | 9.33089 | 6.70422 | 526.85 | 38.71 | 65.22 | 26.68 |
| 1%Fe-nHAP | 9.32652 | 6.70033 | 526.21 | 32.04 | 61.12 | 25.44 |
| 3%Fe-nHAP | 9.32421 | 6.69054 | 526.06 | 32.10 | 60.46 | 25.29 |
| 7%Fe-nHAP | 9.32056 | 6.68135 | 525.98 | 30.36 | 56.23 | 25.10 |
| 10%Fe-nHAP | 9.32001 | 6.68045 | 525.73 | 27.77 | 55.28 | 25.12 |
表3 不同Fe掺杂比的Fe-nHAP的晶格参数、晶胞体积、结晶度和晶粒尺寸
Table 3 Lattice parameters, volumes, crystallinities, and grain sizes of Fe-nHAP with Fe doped at different molar ratios
| Sample | a-axis/Å | c-axis/Å | Volume/Å3 | Crystallinity/% | D(002)/nm | D(310)/nm |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| nHAP | 9.33129 | 6.70756 | 527.13 | 43.92 | 70.79 | 31.45 |
| 0.3%Fe-nHAP | 9.33089 | 6.70422 | 526.85 | 38.71 | 65.22 | 26.68 |
| 1%Fe-nHAP | 9.32652 | 6.70033 | 526.21 | 32.04 | 61.12 | 25.44 |
| 3%Fe-nHAP | 9.32421 | 6.69054 | 526.06 | 32.10 | 60.46 | 25.29 |
| 7%Fe-nHAP | 9.32056 | 6.68135 | 525.98 | 30.36 | 56.23 | 25.10 |
| 10%Fe-nHAP | 9.32001 | 6.68045 | 525.73 | 27.77 | 55.28 | 25.12 |
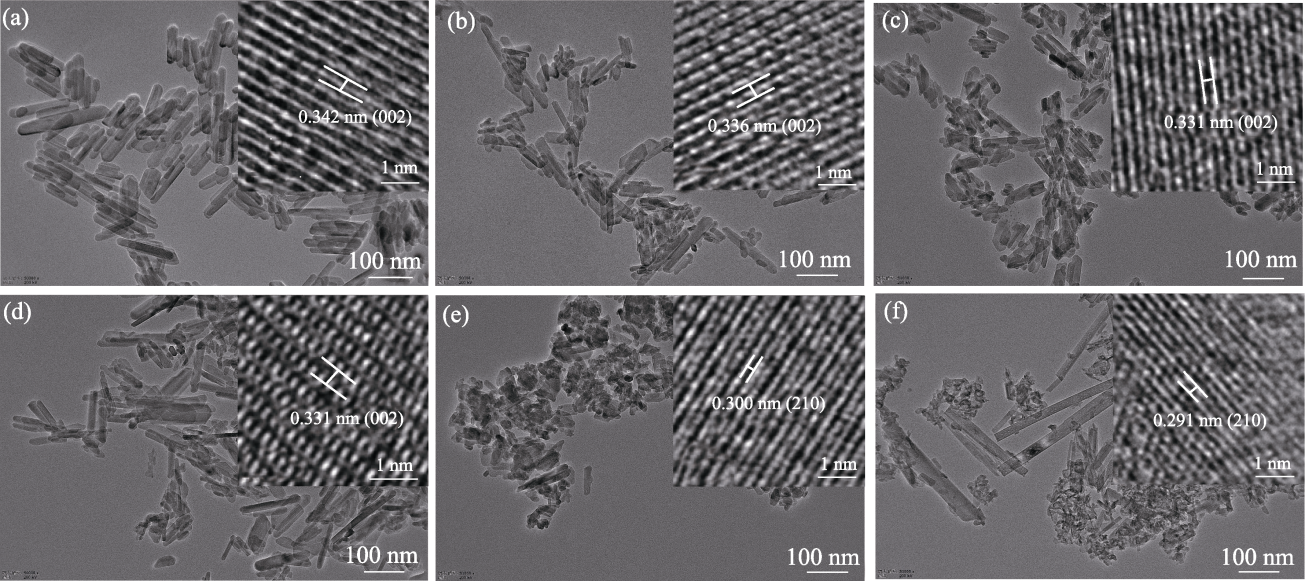
图3 Fe-nHAP(150 ℃、3 h、0~10%Fe)的TEM照片(插图为高分辨TEM(HRTEM)照片)
Fig. 3 TEM images of Fe-nHAP (150 ℃, 3 h, 0-10%Fe) with insets showing corresponding HRTEM images (a) nHAP; (b) 0.3%Fe-nHAP; (c) 1%Fe-nHAP; (d) 3%Fe-nHAP; (e) 7%Fe-nHAP; (f) 10%Fe-nHAP
| Element | nHAP | 0.3%Fe-nHAP | 1%Fe-nHAP | 3%Fe-nHAP | 7%Fe-nHAP | 10%Fe-nHAP |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ca | 37.11176 | 38.84537 | 38.44196 | 37.46884 | 34.68688 | 32.83218 |
| P | 17.12133 | 18.47263 | 18.33874 | 18.44668 | 18.06182 | 17.50755 |
| Fe | 0.00589 | 0.22444 | 0.69487 | 2.04870 | 4.65011 | 6.35854 |
表4 Fe-nHAP(150 ℃、3 h、0~10%Fe)元素占比(%, 质量分数)
Table 4 Elemental composition (%, mass fraction) of Fe-nHAP (150 ℃, 3 h, 0-10%Fe)
| Element | nHAP | 0.3%Fe-nHAP | 1%Fe-nHAP | 3%Fe-nHAP | 7%Fe-nHAP | 10%Fe-nHAP |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ca | 37.11176 | 38.84537 | 38.44196 | 37.46884 | 34.68688 | 32.83218 |
| P | 17.12133 | 18.47263 | 18.33874 | 18.44668 | 18.06182 | 17.50755 |
| Fe | 0.00589 | 0.22444 | 0.69487 | 2.04870 | 4.65011 | 6.35854 |
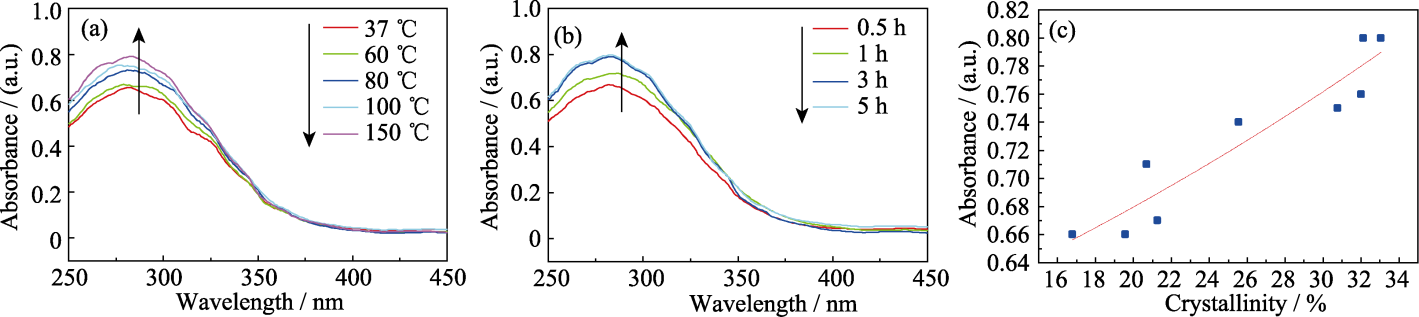
图4 (a)不同反应温度制备的1%Fe-nHAP的UV吸收性能; (b)不同反应时间制备的1%Fe-nHAP的UV吸收性能; (c) 1%Fe-nHAP结晶度与UV吸收性能的关系
Fig. 4 (a) UV absorption performance of 1%Fe-nHAP prepared under different temperatures; (b) UV absorption performance of 1%Fe-nHAP prepared for different time; (c) Relationship between crystallinity and UV absorption performance of 1%Fe-nHAP
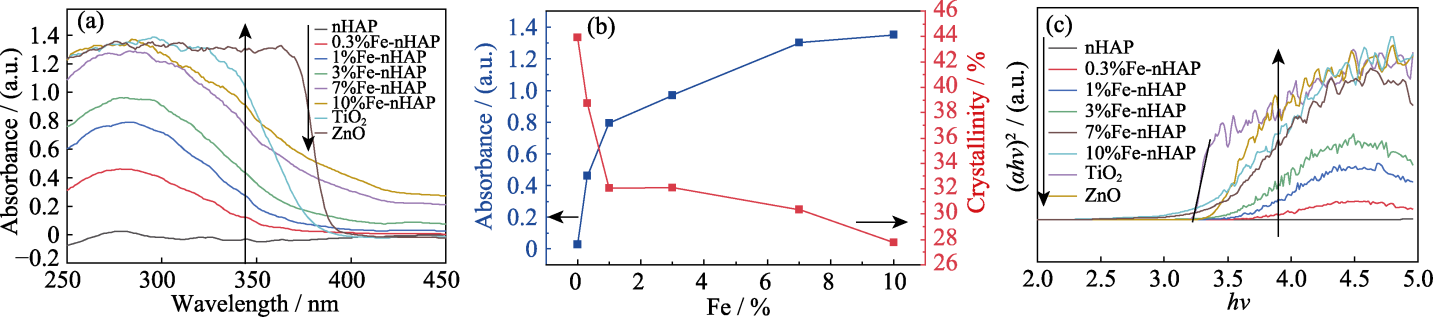
图5 (a)不同材料的UV吸收性能; (b)不同铁掺杂比对Fe-nHAP结晶度及UV吸收性能的影响; (c)不同材料的Tauc曲线
Fig. 5 (a) UV absorption performance of different materials; (b) Effect of iron doping ratio on crystallinity and UV absorption performance of Fe-nHAP; (c) Tauc curves of different materials
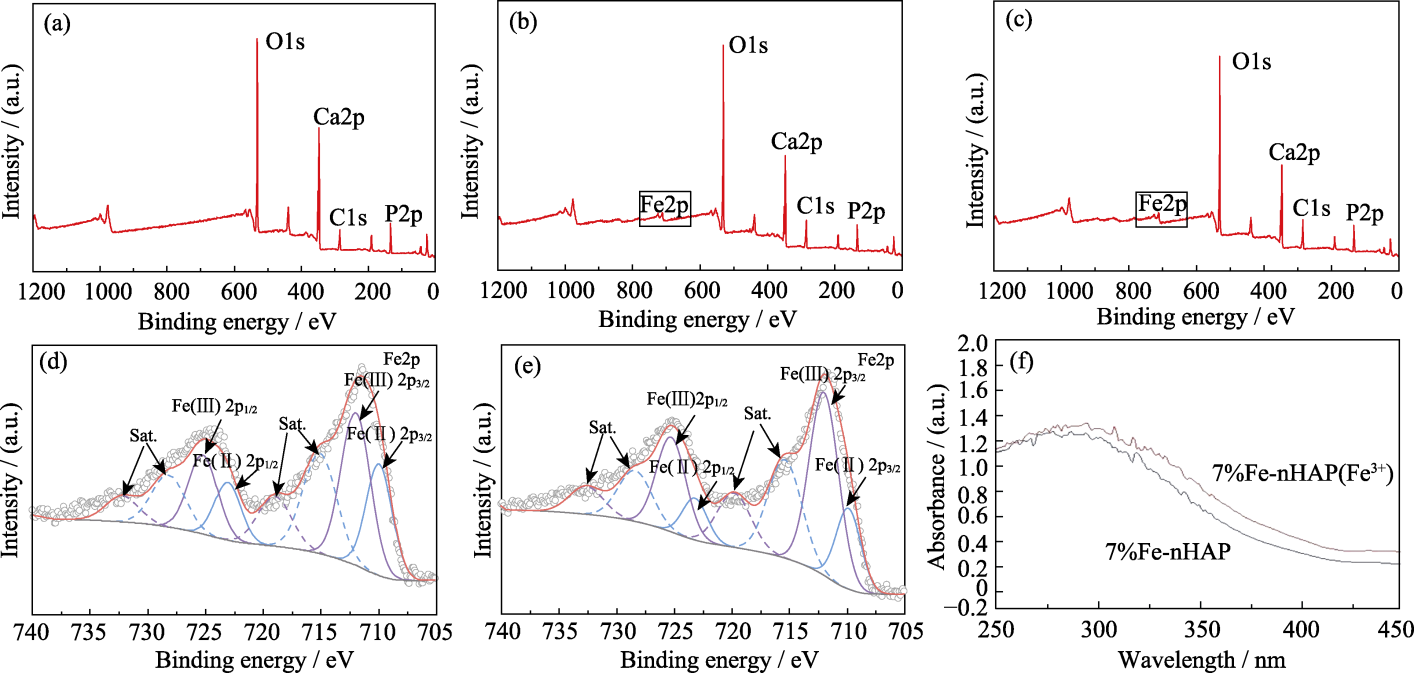
图6 不同材料的XPS谱图以及UV吸收谱图
Fig. 6 XPS spectra and UV absorption spectra of different materials (a) nHAP; (b) 7%Fe-nHAP; (c) 10%Fe-nHAP; (d) Fine Fe2p orbital spectrum of 7%Fe-nHAP; (e) Fine Fe2p orbital spectrum of 10%Fe-nHAP; (f) UV absorption performance of two valence states of Fe in 7%Fe-nHAP
| Test item | Concentration/ (mg·kg-1) | Limit/ (mg·kg-1) |
|---|---|---|
| Hg | 0.002 | 1 |
| Pb | 0.05 | 10 |
| As | 0.01 | 2 |
| Cd | 0.18 | 5 |
| Total colony count | - | 500 |
| Yeasts and molds count | - | 100 |
| T-E. coli | - | 0 |
| Staphylococcus aureus | - | 0 |
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa | - | 0 |
表5 Fe-nHAP的4项重金属和5项菌落数九项测试
Table 5 Test results of Fe-nHAP on 4 heavy metals and 5 microorganisms
| Test item | Concentration/ (mg·kg-1) | Limit/ (mg·kg-1) |
|---|---|---|
| Hg | 0.002 | 1 |
| Pb | 0.05 | 10 |
| As | 0.01 | 2 |
| Cd | 0.18 | 5 |
| Total colony count | - | 500 |
| Yeasts and molds count | - | 100 |
| T-E. coli | - | 0 |
| Staphylococcus aureus | - | 0 |
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa | - | 0 |
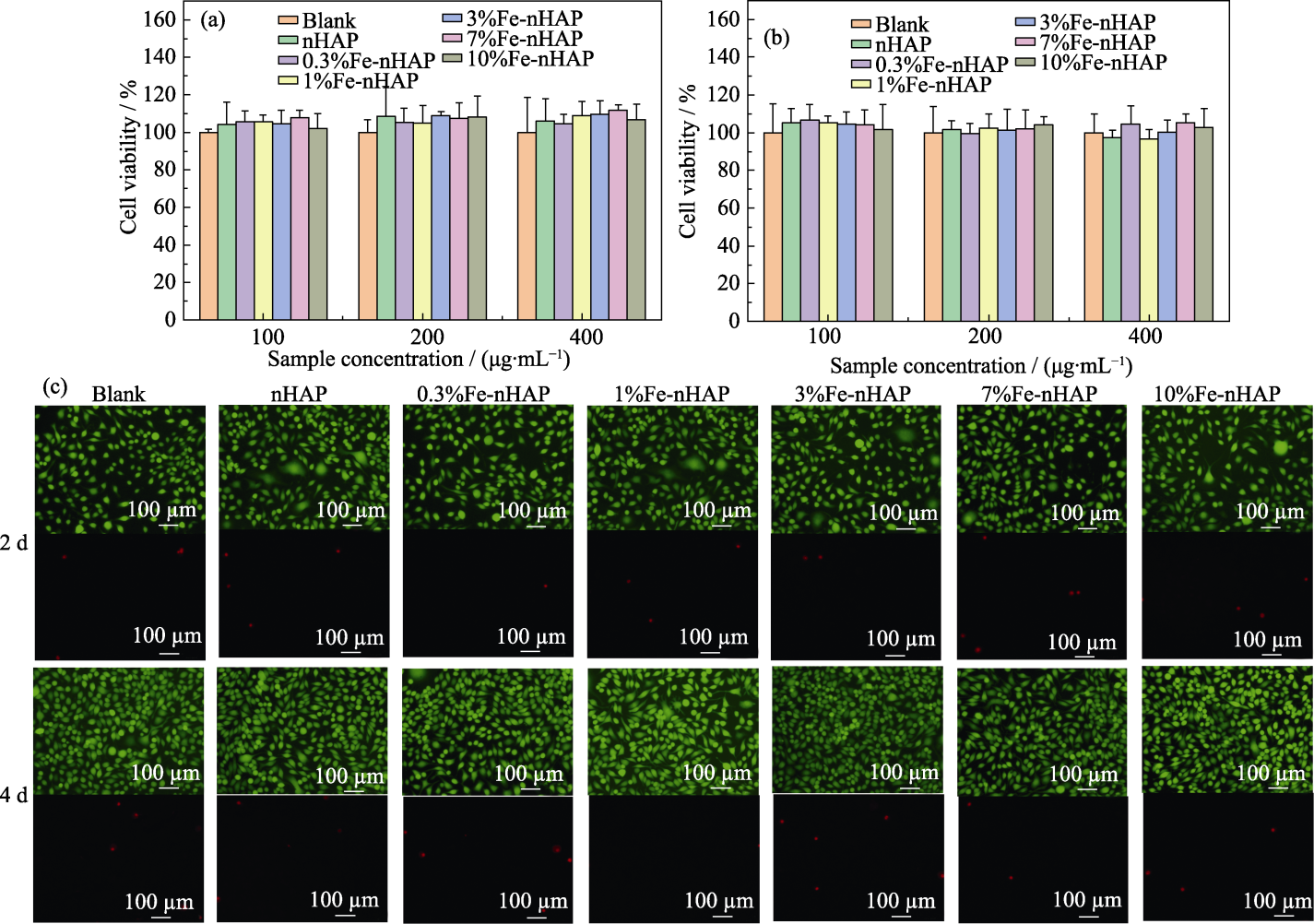
图8 Fe-nHAP(0~10%Fe)的细胞相容性
Fig. 8 Cell compatibilities of Fe-nHAP (0-10%Fe) (a, b) Cell viability after being cultured for (a) 2 and (b) 4 d at different concentrations; (c) Cell dead/live staining after being cultured at a concentration of 200 μg/mL. Colorful figures are available on website
| [1] | MATSUMURA Y, ANANTHASWAMY H N. Toxic effects of ultraviolet radiation on the skin. Toxicology and Applied Pharmacology, 2004, 195(3): 298. |
| [2] | ANTONIK D, DENYS B, GÓRA K, et al. Impact of ultraviolet radiation on the skin and the role of photoprotection - the review of the literature. Journal of Education, Health and Sport, 2023, 37(1): 80. |
| [3] | BOSSHARDT O P, GRICHNIK J M. Citrus and melanoma risk: better to consume with dinner? Dermatologic Therapy, 2016, 29(3): 211. |
| [4] | MATTA M K, ZUSTERZEEL R, PILLI N R, et al. Effect of sunscreen application under maximal use conditions on plasma concentration of sunscreen active ingredients: a randomized clinical trial. Journal of the American Medical Association, 2019, 321(21):2082. |
| [5] | ABID A R, MARCINIAK B, PĘDZIŃSKI T, et al. Photo-stability and photo-sensitizing characterization of selected sunscreens’ ingredients. Journal of Photochemistry and Photobiology A: Chemistry, 2017, 332: 241. |
| [6] | VUCKOVIC D, TINOCO A I, LING L, et al. Conversion of oxybenzone sunscreen to phototoxic glucoside conjugates by sea anemones and corals. Science, 2022, 376(6593): 644. |
| [7] | TRAN D T, SALMON R. Potential photocarcinogenic effects of nanoparticle sunscreens: photocarcinogenic and NP sunscreens. Australasian Journal of Dermatology, 2011, 52(1): 1. |
| [8] | CORINALDESI C, MARCELLINI F, NEPOTE E, et al. Impact of inorganic UV filters contained in sunscreen products on tropical stony corals (Acropora spp.). Science of the Total Environment, 2018, 637/638: 1279. |
| [9] | DU X, YUAN X, LIN S, et al. An injectable bone paste of poly (lactic acid)/zinc-doped nano hydroxyapatite composite microspheres for skull repair. Colloids and Surfaces B: Biointerfaces, 2024, 239: 113969. |
| [10] | RAVAL J P, JOSHI P, CHEJARA D R, et al. 3-Fabrication and applications of hydroxyapatite-based nanocomposites coating for bone tissue engineering//INAMUDDIN, ASIRI A M, MOHAMMAD A. Applications of Nanocomposite Materials in Orthopedics. Duxford: Elsevier, 2019: 71- 82. |
| [11] | IBRAHIM M, LABAKI M, GIRAUDON J M, et al. Hydroxyapatite, a multifunctional material for air, water and soil pollution control: a review. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2020, 383: 121139. |
| [12] | LI C Y, DING Z Y, HAN Y C. In vitro antibacterial and osteogenic properties of manganese doped nano hydroxyapatite. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(3): 313. |
| [13] | YIN H R, LIU J, QIAO Y P, et al. Effect of strontium on luminescence properties and substitution site of Eu doped Sr-Ca- hydroxyapatite. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2016, 31(10): 1103. |
| [14] | TAMPIERI A, D’ALESSANDRO T, SANDRI M, et al. Intrinsic magnetism and hyperthermia in bioactive Fe-doped hydroxyapatite. Acta Biomaterialia, 2012, 8(2): 843. |
| [15] | WANG C, YUAN X, KANG H, et al. Structural characterization, photothermal effect and biological properties of La/Ga ion co-doped hydroxyapatite coated with polydopamine. Journal of Industrial and Engineering Chemistry, 2024, 139: 573. |
| [16] | TAO B, LIN C, GUO A, et al. Fabrication of copper ions- substituted hydroxyapatite/polydopamine nanocomposites with high antibacterial and angiogenesis effects for promoting infected wound healing. Journal of Industrial and Engineering Chemistry, 2021, 104: 345. |
| [17] | HE W, XIE Y, XING Q, et al. Sol-Gel synthesis of biocompatible Eu3+/Gd3+ co-doped calcium phosphate nanocrystals for cell bioimaging. Journal of Luminescence, 2017, 192: 902. |
| [18] | WANG Y H, HAO H, LI Y, et al. Selenium-substituted hydroxyapatite nanoparticles and their in vivo antitumor effect on hepatocellular carcinoma. Colloids and Surfaces B: Biointerfaces, 2016, 140: 297. |
| [19] | YASUKAWA A, TAMURA J. Preparation and structure of titanium- cerium-calcium hydroxyapatite particles and their ultraviolet protecting ability. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 2021, 609: 125705. |
| [20] | DE ARAUJO T S, DE SOUZA S O, MIYAKAWA W, et al. Phosphates nanoparticles doped with zinc and manganese for sunscreens. Materials Chemistry and Physics, 2010, 124(2/3): 1071. |
| [21] | WANG J, NONAMI T, YUBATA K. Syntheses, structures and photophysical properties of iron containing hydroxyapatite prepared by a modified pseudo-body solution. Journal of Materials Science: Materials in Medicine, 2008, 19(7): 2663. |
| [22] | HADAGALLI K, SHENOY S, SHAKYA K R, et al. Effect of Fe3+ substitution on the structural modification and band structure modulated UV absorption of hydroxyapatite. International Journal of Applied Ceramic Technology, 2021, 18(2): 332. |
| [23] | PICCIRILLO C, FERNÁNDEZ-ARIAS M, BOUTINGUIZA M, et al. Increased UV absorption properties of natural hydroxyapatite- based sunscreen through laser ablation modification in liquid. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2019, 102(6): 3163. |
| [24] | PREDOI D, ICONARU S L, CIOBANU S C, et al. Development of iron-doped hydroxyapatite coatings. Coatings, 2021, 11(2): 186. |
| [25] | BALAKRISHNAN S, PADMANABHAN V P, KULANDAIVELU R, et al. Influence of iron doping towards the physicochemical and biological characteristics of hydroxyapatite. Ceramics International, 2021, 47(4): 5061. |
| [26] | PON-ON W, MEEJOO S, TANG I M. Incorporation of iron into nano hydroxyapatite particles synthesized by the microwave process. International Journal of Nanoscience, 2007, 6(1): 9. |
| [27] | KRAMER E R, MOREY A M, STARUCH M, et al. Synthesis and characterization of iron-substituted hydroxyapatite via a simple ion-exchange procedure. Journal of Materials Science, 2013, 48(2): 665. |
| [28] | TEIXEIRA M A C, PICCIRILLO C, TOBALDI D M, et al. Effect of preparation and processing conditions on UV absorbing properties of hydroxyapatite-Fe2O3 sunscreen. Materials Science and Engineering: C, 2017, 71: 141. |
| [29] | 侯清玉, 董红英, 马文, 等. Ga高掺杂对ZnO的最小光学带隙和吸收带边影响的第一性原理研究. 物理学报, 2013, 62(15): 157101. |
| [1] | 李淑芳,赵爽,周潇,李满荣. Zn3-xMnxTeO6的晶体结构与吸收光谱和磁性研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2020, 35(8): 895-901. |
| [2] | 陈希亮, 陈庆华, 庄颖, 颜廷亭. KGM/明胶/nano HAP椎间盘纤维环组织工程支架的制备与研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2018, 33(1): 60-66. |
| [3] | 邵冲云, 许文彬, 刘力挽, 杨秋红, 胡丽丽, 周秦岭, 王世凯. Al3+/Yb3+/P5+掺杂对石英玻璃紫外透过和紫外激发荧光的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2015, 30(12): 1327-1333. |
| [4] | 杜宝中, 唐晓庆, 彭振国, 米海涛. 磺基水杨酸插层Mg/Cu/Zn/Al-LDHs的组装、表征及紫外性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2014, 29(4): 352-356. |
| [5] | 李 健, 韩志军, 魏 延, 牛璐璐, 刘 宇, 路国运, 黄 棣. 纳米羟基磷灰石/壳聚糖复合微球的原位仿生制备及表征[J]. 无机材料学报, 2014, 29(12): 1327-1332. |
| [6] | 蒋立新, 蒋柳云, 马 驰, 韩崇涛, 徐莉娟, 熊成东. 新型改性的n-HA与PLGA复合材料的制备及性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2013, 28(7): 751-756. |
| [7] | 郑雄飞, 翟文杰, 梁迎春, 孙 涛. 低温沉积制造壳聚糖-纳米羟基磷灰石支架[J]. 无机材料学报, 2011, 26(1): 12-16. |
| [8] | 涂小牛, 郑燕青, 陈 辉, 孔海宽, 忻 隽, 曾一明, 施尔畏. 高均匀性高掺镁铌酸锂晶体的生长与表征[J]. 无机材料学报, 2010, 25(12): 1257-1262. |
| [9] | 赵彩霞,张伟德. 载钛(Ⅳ)锌(Ⅱ)纳米羟基磷灰石的制备及抗菌性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2009, 24(6): 1243-1248. |
| [10] | 苏佳灿,李 明,禹宝庆,张春才. 纳米羟基磷灰石/聚己内酯复合生物活性多孔支架研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2009, 24(3): 485-490. |
| [11] | 曾丽平,曹丽云,黄剑锋,郭 申. HA改性短切碳纤维/PMMA生物复合材料力学性能的研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2009, 24(3): 475-479. |
| [12] | 王 江,左 奕,杨维虎,周 钢,张 利,李玉宝. 纳米羟基磷灰石丝素蛋白仿生矿化材料的制备研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2009, 24(2): 264-268. |
| [13] | 廖建国,王学江,左奕,张利,文季秋,李玉宝. 硅烷偶联剂对纳米羟基磷灰石表面改性的研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2008, 23(1): 145-149. |
| [14] | 蒋柳云,李玉宝,张利,王学江. 纳米羟基磷灰石/壳聚糖-羧甲基纤维素复合支架材料的研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2008, 23(1): 135-140. |
| [15] | 赵尹,李春忠,刘秀红. 燃烧合成铁掺杂TiO2纳米晶的染料敏化光催化性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2007, 22(6): 1070-1074. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||