无机材料学报 ›› 2023, Vol. 38 ›› Issue (8): 910-916.DOI: 10.15541/jim20220775 CSTR: 32189.14.10.15541/jim20220775
所属专题: 【结构材料】核用陶瓷(202506)
刘建1,2( ), 王凌坤1,2, 许保亮1,2, 赵倩1,2, 王耀萱1,2, 丁艺1,2, 张胜泰1,2,3(
), 王凌坤1,2, 许保亮1,2, 赵倩1,2, 王耀萱1,2, 丁艺1,2, 张胜泰1,2,3( ), 段涛1,2(
), 段涛1,2( )
)
收稿日期:2022-12-28
修回日期:2023-02-22
出版日期:2023-08-20
网络出版日期:2023-03-17
通讯作者:
段 涛, 教授. E-mail: duant@ustc.edu.cn; 张胜泰, 助教. E-mail: 1045477738@qq.com作者简介:刘 建(1995-), 男, 硕士研究生. E-mail: 1977812990@qq.com
基金资助:
LIU Jian1,2( ), WANG Lingkun1,2, XU Baoliang1,2, ZHAO Qian1,2, WANG Yaoxuan1,2, DING Yi1,2, ZHANG Shengtai1,2,3(
), WANG Lingkun1,2, XU Baoliang1,2, ZHAO Qian1,2, WANG Yaoxuan1,2, DING Yi1,2, ZHANG Shengtai1,2,3( ), DUAN Tao1,2(
), DUAN Tao1,2( )
)
Received:2022-12-28
Revised:2023-02-22
Published:2023-08-20
Online:2023-03-17
Contact:
DUAN Tao, professor. E-mail: duant@ustc.edu.cn; ZHANG Shengtai, assistant.E-mail: 1045477738@qq.comAbout author:LIU Jian(1995-), male, Master candidate. E-mail: 1977812990@qq.com
Supported by:摘要:
相较于传统固相烧结方法, 熔盐在较低的温度下提供了快速的传质和成核过程, 可合成用于固化高放废物(HLW)的陶瓷固化体。本工作采用熔盐法(MSS)在不同烧结温度(1100、1200、1300、1400、1500 ℃)和不同烧结时间(3、6、9、12、15 h)下制备了掺Nd的锆石(ZrSiO4)陶瓷(Zr1-xNdxSiO4-x/2 (0≤x≤0.1)), 并采用静态浸出试验(PCT)研究掺Nd的ZrSiO4陶瓷在模拟地质处置环境下的化学稳定性。在熔盐与氧化物最佳摩尔比为10 : 1、烧结温度为1200 ℃、烧结时间为6 h的较温和条件下, 利用熔盐法成功合成了Zr1-xNdxSiO4-x/2, 可将Nd在ZrSiO4中的固溶摩尔分数提高到8%, 结果显示MSS法能够降低陶瓷合成温度, 缩短合成时间, 提高固溶量。ZrSiO4陶瓷对三价锕系核素的固化机理为晶格固化。浸出实验结果显示, Nd的归一化浸出率(LRNd)低至~10-5 g·m-2·d-1。浸出前后ZrSiO4陶瓷未发生物相演变, 展现出较好的结构稳定性。浸出模型显示Nd浸出归因于陶瓷表面层发生溶解。研究结果表明, MSS法是一种高效的合成陶瓷固化体的手段。
中图分类号:
刘建, 王凌坤, 许保亮, 赵倩, 王耀萱, 丁艺, 张胜泰, 段涛. 熔盐法低温合成掺钕ZrSiO4陶瓷的物相演变和化学稳定性[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(8): 910-916.
LIU Jian, WANG Lingkun, XU Baoliang, ZHAO Qian, WANG Yaoxuan, DING Yi, ZHANG Shengtai, DUAN Tao. Nd-doped ZrSiO4 Ceramics: Synthesis in Molten Salt at Low Temperature, Phase Evolution and Chemical Stability[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(8): 910-916.

图2 不同烧结温度(1100、1200、1300、1400、1500 ℃)下MSS法合成的ZrSiO4的XRD图谱
Fig. 2 XRD patterns of ZrSiO4 synthesized by MSS at different temperatures (1100, 1200, 1300, 1400, and 1500 ℃)

图3 1200 ℃不同烧结时间(3, 6, 9, 12, 15 h)MSS法合成ZrSiO4的XRD图谱
Fig. 3 XRD patterns of ZrSiO4 synthesized by MSS at 1200 ℃ for different time (3, 6, 9, 12, and 15 h)
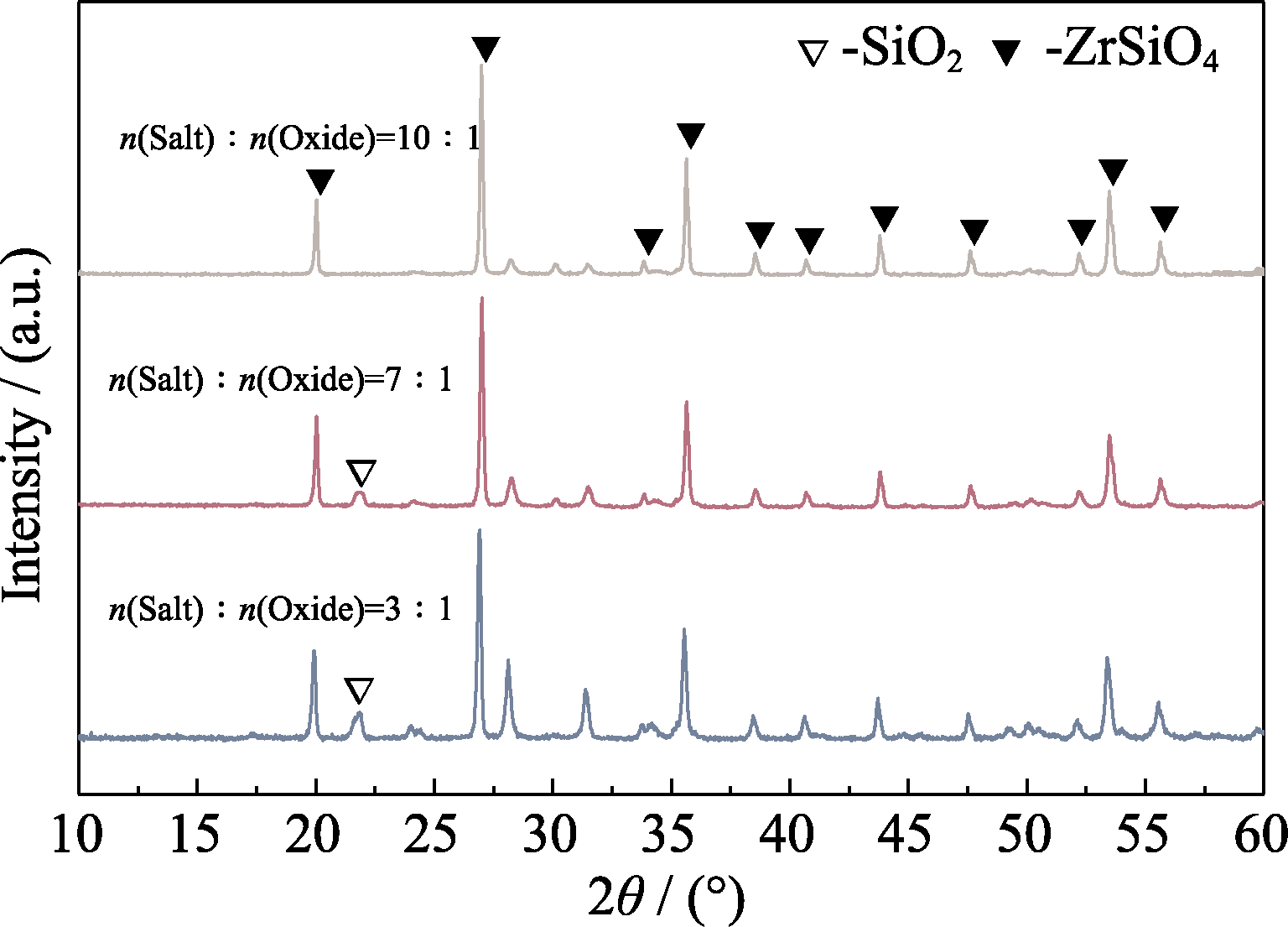
图4 MSS法在不同熔盐与氧化物摩尔比下合成ZrSiO4的XRD图谱(1200 ℃/6 h)
Fig. 4 XRD patterns of ZrSiO4 synthesized by MSS with different molar ratios of molten salt to oxide (1200 ℃/6 h)
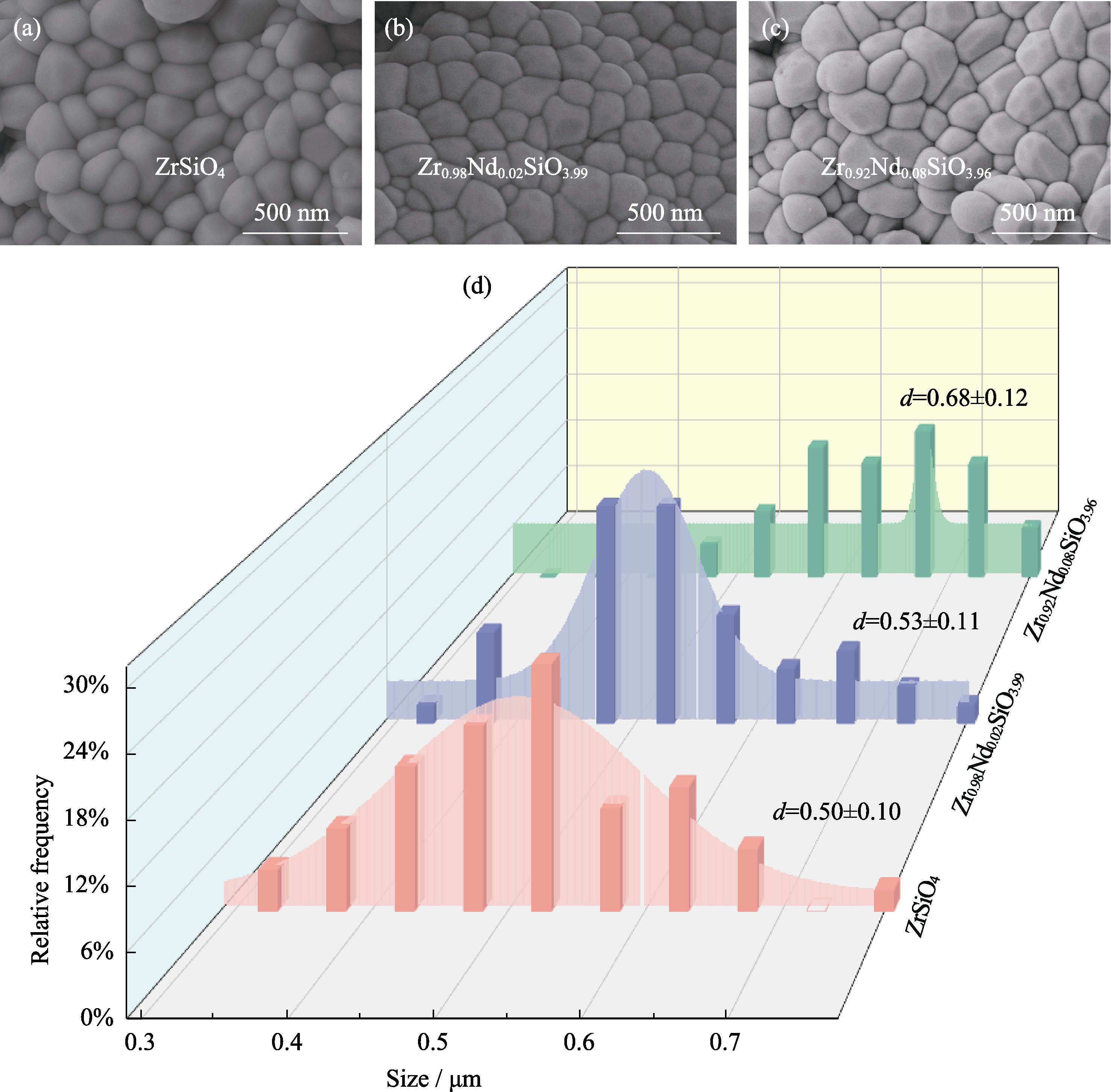
图8 Zr1-xNdxSiO4-x/2的微观形貌及其粒度分布
Fig. 8 Micromorphologies and correponding particle size distributions of Zr1-xNdxSiO4-x/2 (a) ZrSiO4; (b) Zr0.98Nd0.02SiO3.99; (c)Zr0.92Nd0.08SiO3.96; (d) Correponding particle size distribution
| [1] |
HIPPEL F V, EWING R, GARWIN R, et al. Nuclear proliferation: time to bury plutonium. Nature, 2012, 485(7397): 167.
DOI |
| [2] |
EWING R C. Nuclear waste forms for actinides. National Academy of Sciences, 1999, 96(7): 3432.
DOI URL |
| [3] |
LI S Y, YANG X Y, LIU J, et al. First-principles calculations and experiments for Ce4+ effects on structure and chemical stabilities of Zr1-xCexSiO4. Journal of Nuclear Materials, 2019, 514: 276.
DOI URL |
| [4] |
Li S Y, LiU J, YANG X Y, et al. Effect of phase evolution and acidity on the chemical stability of Zr1-xNdxSiO4-x/2 ceramics. Ceramics International, 2019, 45(3): 3052.
DOI URL |
| [5] |
RINGWOOD A E, KESSON S E, WARE N G, et al. Immobilisation of high level nuclear reactor wastes in SYNROC. Nature, 1979, 278: 219.
DOI |
| [6] |
ZHANG S T, WANG L K, XU B L, et al. Rapid synthesis of Nd-doped Y3Fe5O12 garnet waste forms by microwave sintering. Ceramics International, 2021, 47(15): 21924.
DOI URL |
| [7] | EWING R C, LUTZE W, WEBER W J. Zircon: a host-phase for the disposal of weapons plutonium. International Journal of Materials Research, 1995, 10(2): 243. |
| [8] |
LU X R, SHU X Y, SHAO D, et al. Radiation stability of Gd2Zr2O7 and Nd2Ce2O7 ceramics as nuclear waste forms. Ceramics International, 2017, 44(1): 760.
DOI URL |
| [9] |
YANG H, TENG Y, REN X, et al. Synthesis and crystalline phase of monazite-type Ce1-xGdxPO4 solid solutions for immobilization of minor actinide curium. Journal of Nuclear Materials, 2014, 444 (1/2/3): 39.
DOI URL |
| [10] |
HANNAH G D, LISA J Z, MAURICIO M, et al. Zirconium stable isotope analysis of zircon by MC-ICP-MS: methods and application to evaluating intra-crystalline zonation in a zircon megacryst. Journal of Analytical Atomic Spectrometry, 2020, 35: 1167.
DOI URL |
| [11] |
WANG X, XUE Z L, ZHOU Z M, et al. Influences of ZrSiO4 doping on microstructure and mechanical properties of Y2SiO5- ZrSiO4 ceramics. Ceramics International, 2021, 48(1): 1277.
DOI URL |
| [12] |
XIONG Y W, LI J J, ZHAO D D, et al. High capacity synergistic immobilization of simulated trivalent actinides by zirconia/zircon multiphase ceramics. Ceramics International, 2023, 49(2): 2472.
DOI URL |
| [13] | YANG X Y, LI S Y, YI Y, et al. Rapid preparation of zirconia/ zircon composites ceramics by microwave method: experiment and first-principle investigation. Progress in Nuclear Energy, 2021, 139: 103839. |
| [14] |
JIANG Z D, XIONG T H, BAI Z M, et al. Effect of Si/Zr molar ratio on the sintering and crystallization behavior of zircon ceramics. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2020, 40(13): 4605.
DOI URL |
| [15] | DING Y, JIANG Z D, XIONG T H, et al. Phase and microstructure evolution of 0.2Zr1-xCexO2/Zr1-yCeySiO4 (0≤x+y≤1) ceramics designed to immobilize tetravalent actinides. Journal of Nuclear Materials, 2020, 539: 152318. |
| [16] |
MARTINEZ J M, BIESUZ M, DONG J, et al. Flash sintering of zircon: rapid consolidation of an ultrahigh bandgap ceramic. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2021, 9(1): 374.
DOI URL |
| [17] |
GENTRY R V, SWORSKI T J, MCKOWN H S, et al. Differential lead retention in zircons: implications for nuclear waste containment. Science, 1982, 216(4543): 296.
DOI URL |
| [18] |
WEBER W J. Self-radiation damage and recovery in Pu-doped zircon. Radiation Effects and Defects in Solids, 1991, 115(4): 341.
DOI URL |
| [19] |
DING Y, LU X R, DAN H, et al. Phase evolution and chemical durability of Nd-doped zircon ceramics designed to immobilize trivalent actinides. Ceramics International, 2015, 41(8): 10044.
DOI URL |
| [20] |
DING Y, LU X R, TU H, et al. Phase evolution and microstructure studies on Nd3+ and Ce4+co-doped zircon ceramics. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2015, 35(7): 2153.
DOI URL |
| [21] |
DING Y, JIANG Z D, LI Y J, et al. Low temperature and rapid preparation of zirconia/zircon (ZrO2/ZrSiO4) composite ceramics by a hydrothermal-assisted Sol-Gel process. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2018, 735: 2190.
DOI URL |
| [22] | HU X L, CHEN K, et al., Microwave sintering: new technology for ceramic sintering. China Ceramics, 1995: 222. |
| [23] |
LI J S, FAN J Y, YUAN Y, et al. Effect of oscillatory pressure on the sintering behavior of ZrO2 ceramic. Ceramics International, 2020, 46(9): 13240.
DOI URL |
| [24] |
DING Y, LI Y J, JIANG Z D, et al. Phase Evolution and chemical stability of the Nd2O3-ZrO2-SiO2 system synthesized by a novel hydrothermal-assisted Sol-Gel process. Journal of Nuclear Materials, 2018, 510: 10.
DOI URL |
| [25] |
LI H L, DENG J X, CHEN J J, et al. Topochemical molten salt synthesis for functional perovskite compounds. Chemical Science, 2016, 7(2): 855.
DOI URL |
| [26] |
GEORGE Z C, DEREK J F. Direct electrochemical reduction of titanium dioxide to titanium in molten calcium chloride. Nature, 2000, 407: 361.
DOI |
| [27] | HUANG Z, LI F L, JIAO C P, et al. Molten salt synthesis of La2Zr2O7 ultrafine powders. Ceramics International, 2016, 42(5): 6221. |
| [28] | DASH A, VASSEN R, GUILLON O, et al. Molten salt shielded synthesis of oxidation prone materials in air. Nature Materials, 2019, 18(5): 465. |
| [29] |
Li Y, SHAO H, LIN Z, et al. A general Lewis acidic etching route for preparing MXenes with enhanced electrochemical performance in non-aqueous electrolyte. Nature materials, 2020, 19(4): 894.
DOI |
| [30] |
TAŞ A C. Molten salt synthesis of calcium hydroxyapatite whiskers. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2010, 84(2): 295.
DOI URL |
| [31] |
EINARSRUD M A, GRANDE T. 1D oxide nanostructures from chemical solutions. Chemical Society Reviews, 2014, 43(7): 2187.
DOI URL |
| [32] | DE GROOT G J, VAN DER SLOOT H A. Determination of leaching characteristics of waste materials leading to environmental product certification. ASTM Special Technical Publication, 1992, 2: 149. |
| [33] |
GILBERT, MATTHEW R. Molten salt synthesis of titanate pyrochlore waste-forms. Ceramics International, 2016, 42(4): 5263.
DOI URL |
| [34] |
DING Y, LU X R, DAN H, et al. Phase evolution and chemical durability of Nd-doped zircon ceramics designed to immobilize trivalent actinides. Ceramics International, 2015, 41(8): 10044.
DOI URL |
| [35] |
DING Y, JIANG Z D, LI Y J, et al. Effect of alpha-particles irradiation on the phase evolution and chemical stability of Nd- doped zircon ceramics. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2017, 729: 483.
DOI URL |
| [36] |
XUE Q, WANG P, LI J S, et al. Investigation of the leaching behavior of lead in stabilized/solidified waste using a two-year semi-dynamic leaching test. Chemosphere, 2017, 166: 1.
DOI URL |
| [37] |
ALEKSEEVA L, NOKHRIN A, BOLDIN M, et al. Study of the hydrolytic stability of fine-grained ceramics based on Y2.5Nd0.5Al5O12 oxide with a garnet structure under hydrothermal conditions. Materials, 2021, 14: 2125.
DOI URL |
| [1] | 武向权, 滕家琛, 季祥旭, 郝禹博, 张忠明, 徐春杰. 织构化多孔Al2O3-SiO2复合陶瓷片-球混合浆料特性及光强分布仿真[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(7): 769-778. |
| [2] | 邱子豪, 田志林, 郑丽雅, 李斌. Si3N4陶瓷在高温熔盐-水氧环境下的腐蚀行为[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(3): 274-282. |
| [3] | 孙敬伟, 王洪磊, 孙楚函, 周新贵, 纪小宇. 碳源对先驱体转化法制备TaC陶瓷粉体微观结构及性能影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(2): 184-192. |
| [4] | 胡佳军, 王凯, 侯鑫广, 杨婷, 夏鸿雁. 熔盐法合成高导热磷化硼及其热管理性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(9): 933-940. |
| [5] | 罗世淋, 张胜泰, 许保亮, 王凌坤, 段思逸菡, 丁艺, 赵倩, 段涛. YIG陶瓷对三价锕系模拟核素的固化行为研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(7): 757-763. |
| [6] | 杨勇, 郭啸天, 唐杰, 常浩天, 黄政仁, 胡秀兰. 非氧化物陶瓷光固化增材制造研究进展及展望[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(3): 267-277. |
| [7] | 周港怀, 刘耀, 石原, 刘绍军. 活性氧化铝催化剂载体的光固化浆料制备与成型[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(3): 297-302. |
| [8] | 王亚宁, 张玉琪, 宋索成, 陈若梦, 刘亚雄, 段玉岗. 氧化锆陶瓷扫描光固化成形与脱脂烧结工艺研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(3): 303-309. |
| [9] | 朱俊逸, 张成, 罗忠强, 曹继伟, 刘志远, 王沛, 刘长勇, 陈张伟. 脱脂工艺对光固化3D打印堇青石陶瓷性能的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(3): 317-324. |
| [10] | 李乔磊, 顾玥, 于雪华, 张朝威, 邹明科, 梁静静, 李金国. 烧结温度对3D打印硅基陶瓷型芯表面形貌及粗糙度的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(3): 325-332. |
| [11] | 刘国仟, 闫长海, 张可强, 金华, 何汝杰. 立体光刻增材制造中固含量对Al2O3陶瓷性能的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(3): 353-360. |
| [12] | 刘平平, 钟鑫, 张乐, 李红, 牛亚然, 张翔宇, 李其连, 郑学斌. 硅酸镱环境障涂层抗熔盐腐蚀行为与机制研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(12): 1267-1274. |
| [13] | 舒朝琴, 朱敏, 朱钰方. 熔盐法制备含钴氯磷灰石及其抗氧化性能和细胞相容性研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(11): 1225-1235. |
| [14] | 吴爱军, 朱敏, 朱钰方. 含铜硅酸钙纳米棒复合水凝胶用于肿瘤治疗和皮肤伤口愈合性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(11): 1203-1216. |
| [15] | 王烈林, 谢华, 谢宇骐, 胡平涛, 尹雯, 任馨玥, 丁芸. Nd2Zr2O7烧绿石A、B位晶格固化钍的结构演化及化学稳定性研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(10): 1073-1078. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||