无机材料学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 40 ›› Issue (10): 1137-1144.DOI: 10.15541/jim20250030 CSTR: 32189.14.jim20250030
张博1( ), 付一敏1, 陈政1,2, 石澳1, 朱敏1(
), 付一敏1, 陈政1,2, 石澳1, 朱敏1( )
)
收稿日期:2025-01-20
修回日期:2025-02-24
出版日期:2025-10-20
网络出版日期:2025-07-16
通讯作者:
朱 敏, 副研究员. E-mail: mzhu@usst.edu.cn作者简介:张 博(1999-), 男, 硕士研究生. E-mail: 15993162824@163.com
基金资助:
ZHANG Bo1( ), FU Yimin1, CHEN Zheng1,2, SHI Ao1, ZHU Min1(
), FU Yimin1, CHEN Zheng1,2, SHI Ao1, ZHU Min1( )
)
Received:2025-01-20
Revised:2025-02-24
Published:2025-10-20
Online:2025-07-16
Contact:
ZHU Min, associate professor, E-mail: mzhu@usst.edu.cnAbout author:ZHANG Bo (1999-), male, Master candidate. E-mail: 15993162824@163.com
Supported by:摘要:
骨植入材料易感染且具有高发性、迟发性和复发性。然而, 目前常见的抗菌手段通常缺乏选择性, 容易在杀菌的同时对正常组织和细胞造成损害。基于此, 本研究以介孔生物活性玻璃(MBG)为原料, 结合S-NO键的近红外(NIR)光热响应释放NO自由基及Cu2+抗菌性能, 采用氨基化偶联S-亚硝基硫醇(RSNO)制备了MBG-RSNO粉体以供给NO·, 并通过多巴胺聚合及Cu2+螯合合成了PMBG@Cu粉体。将上述两种粉体材料经3D打印得到PMBG@Cu/MBG-RSNO复合抗菌支架。该支架具有NIR光热响应特性, 在808 nm激光脉冲辐照条件下, 支架持续释放的一氧化氮自由基(NO·)含量高达113.71 μg/100 mg MBG-RSNO, 且光热作用将温度升高至约40 ℃, 有利于实现高效灭菌。进一步使用金黄色葡萄球菌(S. aureus)和大肠杆菌(E. coli) 评估复合支架在有/无外部NIR刺激条件下的抗菌效果。实验结果显示, PMBG@Cu/MBG-RSNO复合支架对两种菌种的抗菌效率均达到了99.9%。综上所述, PMBG@Cu/MBG-RSNO复合支架为解决骨植入材料的感染问题并实现骨缺损修复提供了一种潜在的解决方案。
中图分类号:
张博, 付一敏, 陈政, 石澳, 朱敏. 近红外光响应的双相抗菌介孔生物活性玻璃复合支架的制备及抗菌性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(10): 1137-1144.
ZHANG Bo, FU Yimin, CHEN Zheng, SHI Ao, ZHU Min. Near-infrared Responsive Biphasic Antibacterial Mesoporous Bioactive Glass Composite Scaffolds: Preparation and Antibacterial Performance[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(10): 1137-1144.
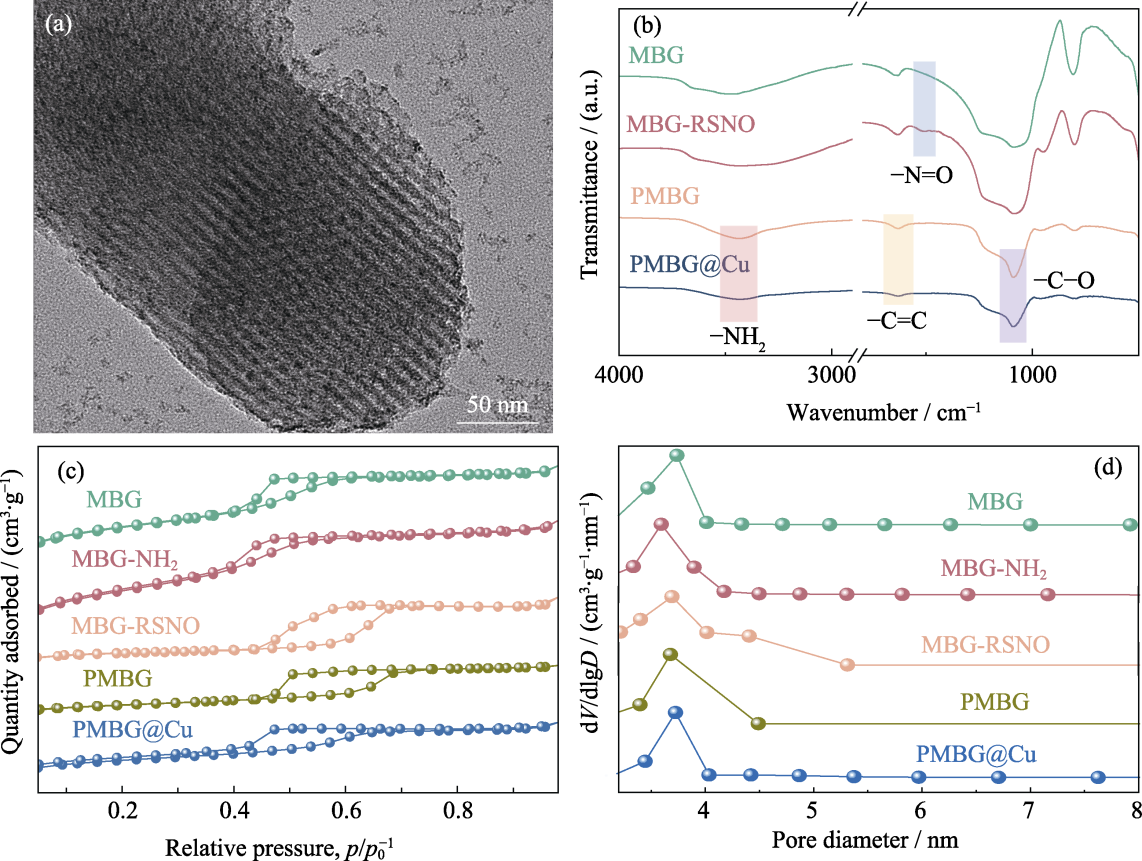
图2 MBG及其改性粉体的理化性能表征
Fig. 2 Physicochemical properties of MBG and modified powders (a) TEM image of MBG; (b) FT-IR spectra; (c) N2 adsorption-desorption isotherm curves; (d) Pore size distributions
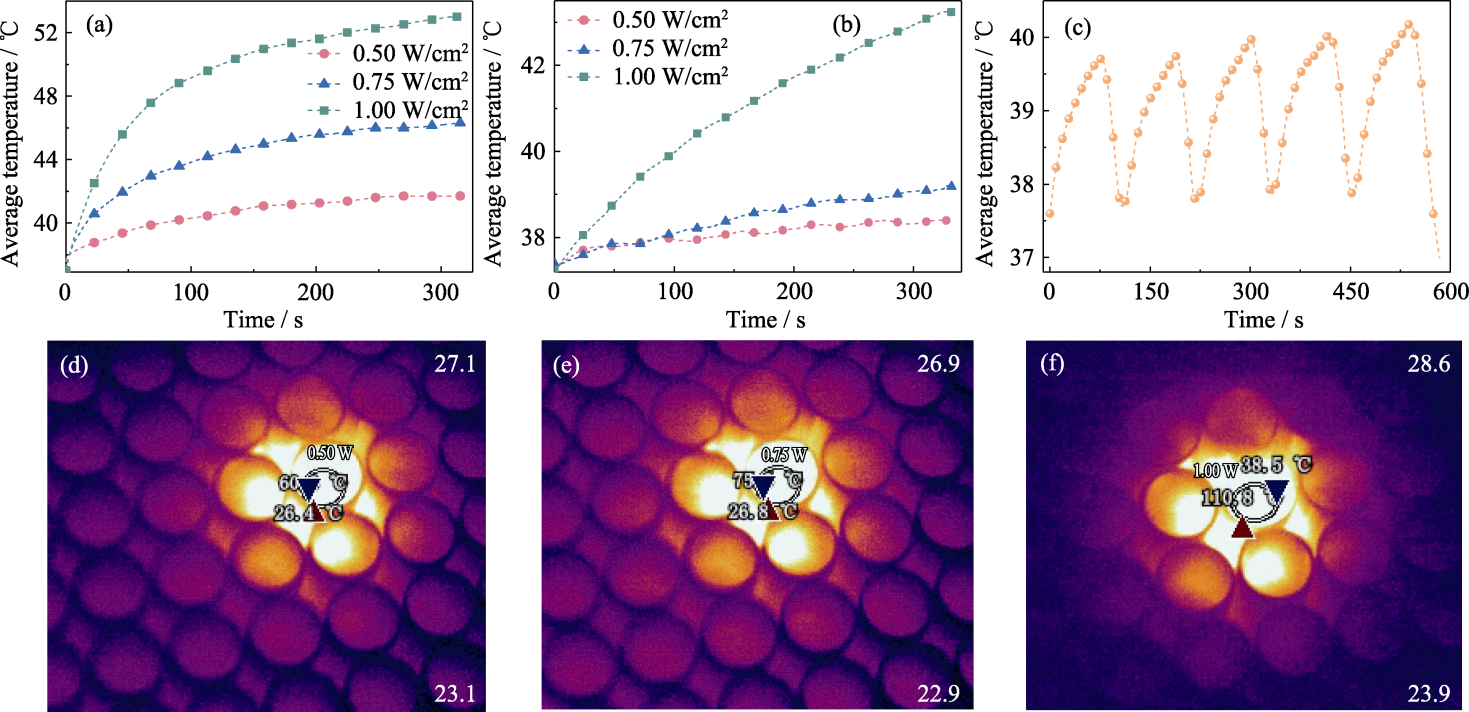
图4 PMBG@Cu/MBG-RSNO复合支架的光热响应性能
Fig. 4 Photothermal response performance of PMBG@Cu/MBG-RSNO composite scaffold (a, b) Photothermal curves in (a) dry state environment and (b) wet state environment; (c) Photothermal cycling curves under 1.00 W/cm2 laser irradiation in dry state environment; (d-f) Thermal images under dry state environment at power densities of (d) 0.50, (e) 0.75 and (f) 1.00 W/cm2
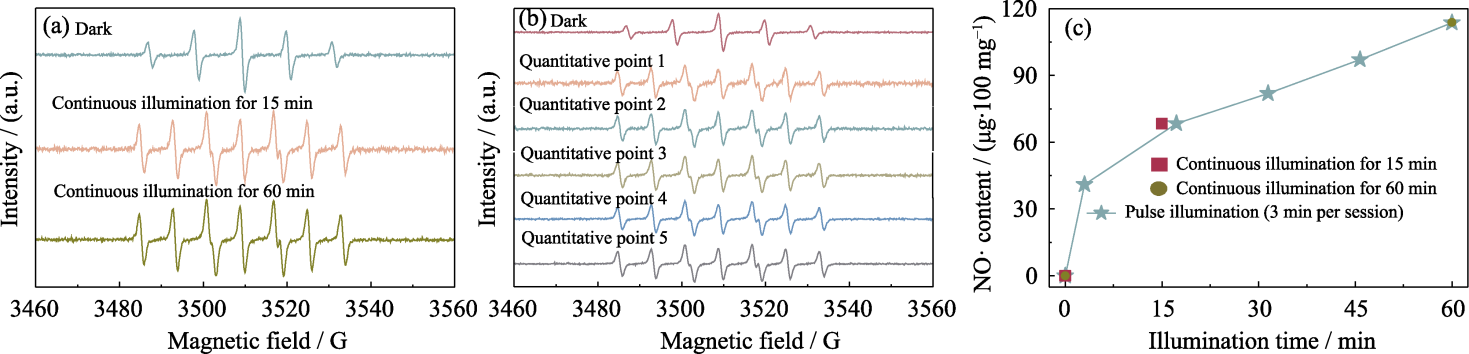
图5 PMBG@Cu/MBG-RSNO复合支架释放NO·的性能分析
Fig. 5 Analysis of NO· release from PMBG@Cu/MBG-RSNO composite scaffold (a) EPR spectra under continuous illumination for 15 and 60 min; (b) EPR spectra with a cumulative total illumination time of 15 min within 60 min under pulsed illumination; (c) Released content of NO·
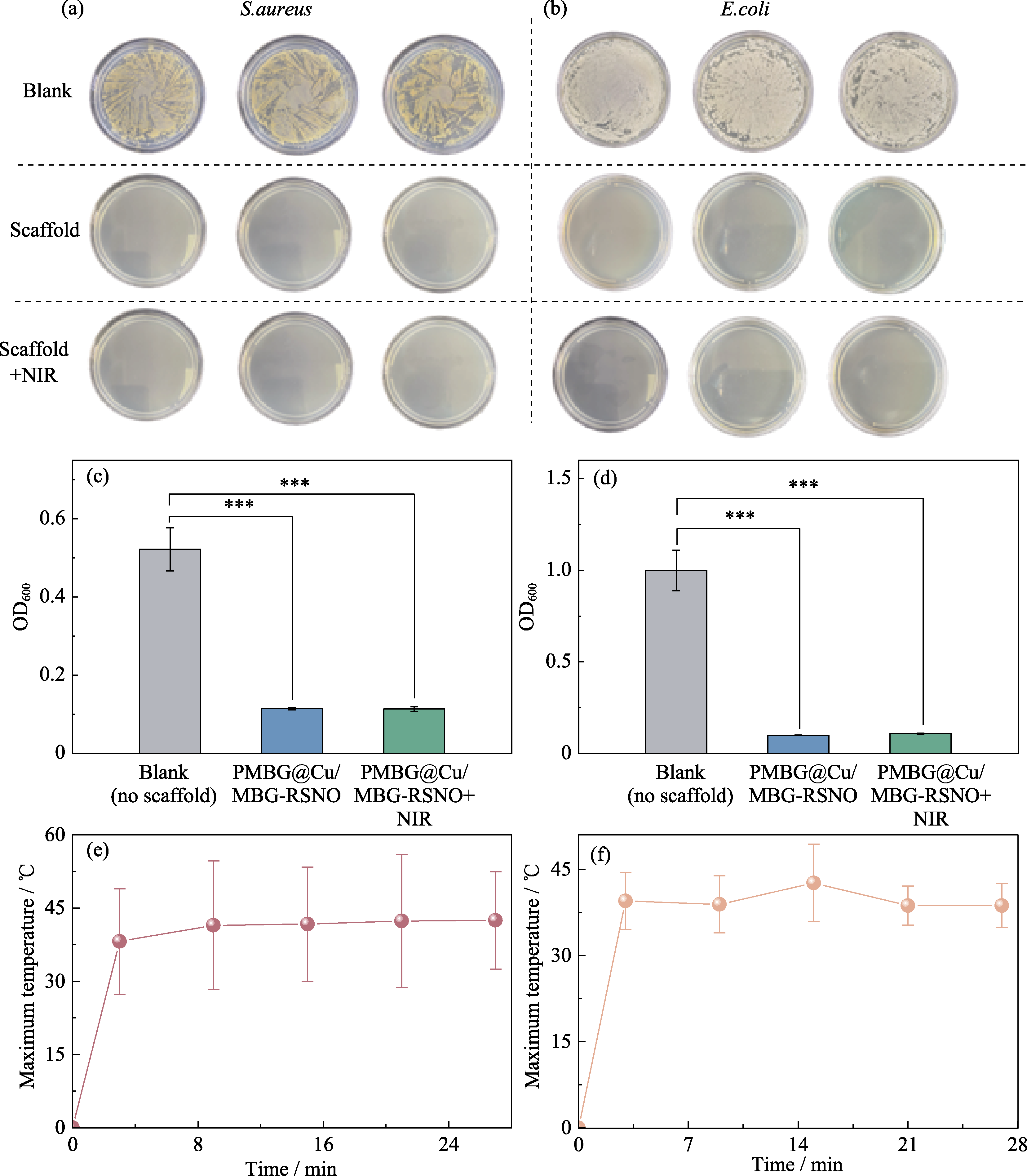
图6 PMBG@Cu/MBG-RSNO复合支架的体外抗菌效果及光热温度分析
Fig. 6 In vitro antibacterial effect and photothermal temperature analysis of PMBG@Cu/MBG-RSNO composite scaffold (a, b) Photos of (a) S. aureus group and (b) E. coli group; (c, d) OD values of (c) S. aureus and (d) E. coli under UV-Vis with asterisks indicating statistically significant difference of treatments vs. untreated culture (*** indicates p < 0.001); (e, f) The highest temperature of (e) S. aureus and (f) E. coli under 5 times pulsed illumination by 808 nm laser at a power density of 1.00 W/cm2
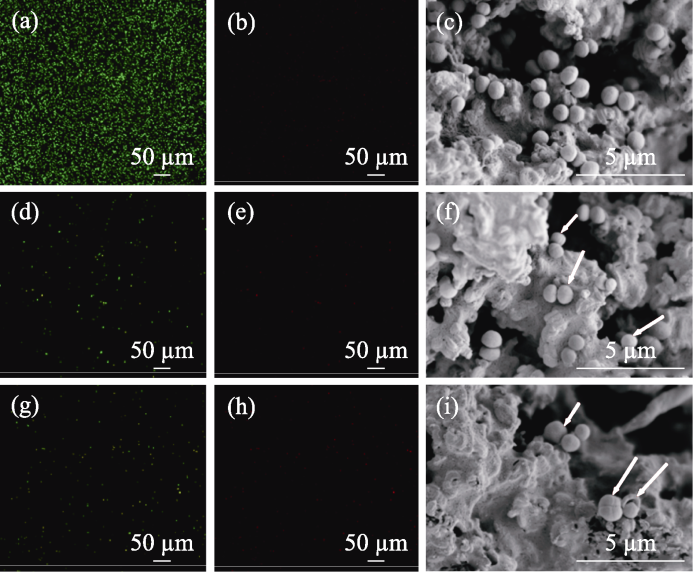
图7 PMBG@Cu/MBG-RSNO复合支架在有/无NIR照射下的抗菌性能及SEM照片
Fig. 7 Antimicrobial properties and SEM images of PMBG@Cu/MBG-RSNO composite scaffold with and without NIR illumination (a, b) Confocal images of (a) SYTO-9 and (b) PI staining for the blank group of S. aureus; (d, e) Confocal images of (d) SYTO-9 and (e) PI staining for PMBG@Cu/MBG-RSNO group of S. aureus; (g, h) Confocal images of (g) SYTO-9 and (h) PI staining for PMBG@Cu/ MBG-RSNO+NIR group of S. aureus; (c, f, i) SEM images of PMBG@Cu/MBG-RSNO composite scaffold with and without NIR illumination
| [1] |
SZOSTAKOWSKI B, DEMAIO M. Ideal xenograft or a perfect bone substitute?-A retrospective review and analysis of the historical concept of ivory implants in orthopaedics. International Orthopaedics, 2020, 44(5): 1003.
DOI PMID |
| [2] | NGUYEN T T, JANG Y S, KIM Y K, et al. Osteogenesis-related gene expression and guided bone regeneration of a strontium- doped calcium-phosphate-coated titanium mesh. ACS Biomaterials Science & Engineering, 2019, 5(12): 6715. |
| [3] | PARÉ A, CHARBONNIER B, TOURNIER P, et al. Tailored three-dimensionally printed triply periodic calcium phosphate implants: a preclinical study for craniofacial bone repair. ACS Biomaterials Science & Engineering, 2020, 6(1): 553. |
| [4] | NAIR L S, LAURENCIN C T. Biodegradable polymers as biomaterials. Progress in Polymer Science, 2007, 32(8/9): 762. |
| [5] |
ZHANG L, YANG G, JOHNSON B N, et al. Three-dimensional (3D) printed scaffold and material selection for bone repair. Acta Biomaterialia, 2019, 84: 16.
DOI PMID |
| [6] | JODATI H, YILMAZ B, EVIS Z. A review of bioceramic porous scaffolds for hard tissue applications: effects of structural features. Ceramics International, 2020, 46(10): 15725. |
| [7] | O'BRIEN F J. Biomaterials & scaffolds for tissue engineering. Materials Today, 2011, 14(3): 88. |
| [8] | ZHU Y, KASKEL S. Comparison of the in vitro bioactivity and drug release property of mesoporous bioactive glasses (MBGs) and bioactive glasses (BGs) scaffolds. Microporous and Mesoporous Materials, 2009, 118(1/2/3): 176. |
| [9] | DU X, WEI D, HUANG L, et al. 3D printing of mesoporous bioactive glass/silk fibroin composite scaffolds for bone tissue engineering. Materials Science & Engineering C-Materials for Biological Applications, 2019, 103: 109731. |
| [10] | SHUKLA R, LAVORE F, MAITY S, et al. Teixobactin kills bacteria by a two-pronged attack on the cell envelope. Nature, 2022, 608(7922): 390. |
| [11] |
WORLEY B V, SLOMBERG D L, SCHOENFISCH M H. Nitric oxide-releasing quaternary ammonium-modified poly(amidoamine) dendrimers as dual action antibacterial agents. Bioconjugate Chemistry, 2014, 25(5): 918.
DOI PMID |
| [12] |
CHUG M K, BACHTIAR E, NARWOLD N, et al. Tailoring nitric oxide release with additive manufacturing to create antimicrobial surfaces. Biomaterials Science, 2021, 9(8): 3100.
DOI PMID |
| [13] |
BARRAUD N, HASSETT D J, HWANG S H, et al. Involvement of nitric oxide in biofilm dispersal of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Journal of Bacteriology, 2006, 188(21): 7344.
DOI PMID |
| [14] |
MIYAHARA Y, NAGAYA N, KATAOKA M, et al. Monolayered mesenchymal stem cells repair scarred myocardium after myocardial infarction. Nature Medicine, 2006, 12(4): 459.
DOI PMID |
| [15] | ANJU B S, NAIR N R, RAJPUT J, et al. Role of ancillary ligands in S-nitrosothiol and NO generation from nitrite-thiol interactions at mononuclear zinc(II) sites. Chemical Science, 2024, 15(43): 18000. |
| [16] | DE ALMEIDA H V, BOMEDIANO M P, CATORI D M, et al. Integrating 3D printing of biomaterials with nitric oxide release. Biomaterials Science, 2025, 13(4): 858. |
| [17] | PERRIN-SARRADO C, ZHOU Y, SALGUES V, et al. S-nitrosothiols as potential therapeutics to induce a mobilizable vascular store of nitric oxide to counteract endothelial dysfunction. Biochemical Pharmacology, 2020, 173: 113686. |
| [18] | SHEN Z, ZHENG S, XIAO S, et al. Red-light-mediated photoredox catalysis enables self-reporting nitric oxide release for efficient antibacterial treatment. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2021, 60(37): 20452. |
| [19] | DONG K, JU E, GAO N, et al. Synergistic eradication of antibiotic- resistant bacteria based biofilms in vivo using a NIR-sensitive nanoplatform. Chemical Communications, 2016, 52(30): 5312. |
| [20] | REN L, YANG K, GUO L, et al. Preliminary study of anti-infective function of a copper-bearing stainless steel. Materials Science and Engineering: C, 2012, 32(5): 1204. |
| [21] | WANG S, YANG C, REN L, et al. Study on antibacterial performance of Cu-bearing cobalt-based alloy. Materials Letters, 2014, 129: 88. |
| [22] | KOYANAGI T, SAKAMOTO M, TAKEUCHI Y, et al. Analysis of microbiota associated with peri-implantitis using 16S rRNA gene clone library. Journal of Oral Microbiology, 2010, 2(1): 5104. |
| [23] | CORDEIRO J M, BARÃO V A R, DE AVILA E D, et al. Tailoring Cu2+-loaded electrospun membranes with antibacterial ability for guided bone regeneration. Biomaterials Advances, 2022, 139: 212976. |
| [24] | TAYLOR-EDINBYRD K, LI T, KUMAR R. Effect of chemical structure of S-nitrosothiols on nitric oxide release mediated by the copper sites of a metal organic framework based environment. Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics, 2017, 19(19): 11947. |
| [25] | ZHU M, ZHANG J H, TAO C L, et al. Design of mesoporous bioactive glass/hydroxyapatite composites for controllable co-delivery of chemotherapeutic drugs and proteins. Materials Letters, 2014, 115: 194. |
| [26] | DEKA J R, SONG Y, YANG Y C. The influence of isothermal aging, surfactant and inorganic precursors concentrations on pore size and structural order of mesoporous bioactive glass. Solid State Sciences, 2018, 84: 104. |
| [27] | BRIGHT L M E, GARREN M R S, DOUGLASS M, et al. Synthesis and characterization of nitric oxide-releasing ampicillin as a potential strategy for combatting bacterial biofilm formation. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2023, 15(12): 15185. |
| [28] | LIU Y, ZHANG S, ZHANG X H, et al. Porous PLGA/MBG scaffold enhanced bone regeneration through osteoimmunomodulation. Composites Part B-Engineering, 2024, 272: 16. |
| [29] | HUANG Y, HUANG J, JIANG M, et al. NIR-triggered theranostic Bi2S3 light transducer for on-demand NO release and synergistic gas/photothermal combination therapy of tumors. ACS Applied Bio Materials, 2019, 2(11): 4769. |
| [30] |
WANG Y, WEN Y, QU Y, et al. Pillar[5]arene based glyco-targeting nitric oxide nanogenerator for hyperthermia-induced triple-mode cancer therapy. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2022, 615: 386.
DOI PMID |
| [31] | ZHANG Z Q, WU J Y, SHANG Z H, et al. Photocalibrated NO release from N-nitrosated napthalimides upon one-photon or two- photon irradiation. Analytical Chemistry, 2016, 88(14): 7274. |
| [32] |
DUAN Y T, WANG Y, LI X H, et al. Light-triggered nitric oxide (NO) release from photoresponsive polymersomes for corneal wound healing. Chemical Science, 2020, 11(1): 186.
DOI PMID |
| [33] | GAO L, CHENG J, SHEN Z Q, et al. Orchestrating nitric oxide and carbon monoxide signaling molecules for synergistic treatment of MRSA infections. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2022, 61(3): 9. |
| [34] | NGUYEN T K, SELVANAYAGAM R, HO K K K, et al. Co-delivery of nitric oxide and antibiotic using polymeric nanoparticles. Chemical Science, 2016, 7(2): 1016. |
| [35] | SUN J, SONG L J, FAN Y, et al. Synergistic photodynamic and photothermal antibacterial nanocomposite membrane triggered by single NIR light source. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2019, 11(30): 26581. |
| [36] | SUN Y, XU W Z, JIANG C, et al. Gold nanoparticle decoration potentiate the antibacterial enhancement of TiO2 nanotubes via sonodynamic therapy against peri-implant infections. Frontiers in Bioengineering and Biotechnology, 2022, 10: 12. |
| [37] | WU M Q, ZHANG Z Y, LIU Z R, et al. Piezoelectric nanocomposites for sonodynamic bacterial elimination and wound healing. Nano Today, 2021, 37: 12. |
| [1] | 赵丽华, 王言帅, 尹昕妩, 毛叶琼, 牛德超. 负载硫化铋纳米簇的硅基杂化胶束的制备及其光热抗菌性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(10): 1129-1136. |
| [2] | 王月月, 黄佳慧, 孔红星, 李怀珠, 姚晓红. 载银放射状介孔二氧化硅的制备及其在牙科树脂中的应用[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(1): 77-83. |
| [3] | 李承瑜, 丁自友, 韩颖超. 锰掺杂纳米羟基磷灰石的体外抗菌-促成骨性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(3): 313-320. |
| [4] | 张志民, 葛敏, 林翰, 施剑林. 新型磁电催化纳米粒子的活性氮释放与抗菌性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(10): 1114-1124. |
| [5] | 张淑敏, 奚晓雯, 孙磊, 孙平, 王德强, 魏杰. 基于声动力和类酶活性的铌基涂层: 抗菌及促进细胞增殖与分化[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(10): 1125-1134. |
| [6] | 谢家晔, 李力文, 朱强. 三种临床盖髓剂的抗菌性及生物相容性对比研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(12): 1449-1456. |
| [7] | 杜佳恒, 范鑫丽, 肖东琴, 尹一然, 李忠, 贺葵, 段可. 电泳沉积制备微弧氧化钛表面氧化镁涂层及其生物学性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(12): 1441-1448. |
| [8] | 吴雪彤, 张若飞, 阎锡蕴, 范克龙. 纳米酶: 一种抗微生物感染新方法[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(1): 43-54. |
| [9] | 盛丽丽, 常江. 光/磁热Fe2SiO4/Fe3O4双相生物陶瓷及其复合电纺丝膜制备及抗菌性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(9): 983-990. |
| [10] | 王恩典, 常江. 钼掺杂铜硅钙石的制备及其抗菌性能和细胞相容性研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2021, 36(7): 738-744. |
| [11] | 傅佳骏, 沈涛, 吴佳, 王成. 纳米酶: 对抗细菌的新策略[J]. 无机材料学报, 2021, 36(3): 257-268. |
| [12] | 郭小炜, 李玉妍, 陈南春, 王秀丽, 解庆林. 负载二甲酸钾缓释抗菌微球的构建[J]. 无机材料学报, 2021, 36(2): 181-187. |
| [13] | 伍凡, 赵梓俨, 黎邦鑫, 董帆, 周莹. Bi2O2CO3/PPy界面氧空位构建及其可见光下NO氧化机理研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2020, 35(5): 541-548. |
| [14] | 李昆强,乔玉琴,刘宣勇. 钛表面铜离子注入对细菌和细胞行为的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2020, 35(2): 158-164. |
| [15] | 郑倩, 曹玥晗, 黄南建, 董帆, 周莹. BiOBr-BN光催化氧化NO及其抑制毒副产物的机理研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2020, 35(11): 1255-1262. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||