无机材料学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 40 ›› Issue (10): 1129-1136.DOI: 10.15541/jim20240530 CSTR: 32189.14.jim20240530
收稿日期:2024-12-20
修回日期:2025-03-15
出版日期:2025-10-20
网络出版日期:2025-04-15
通讯作者:
牛德超, 教授. E-mail: dcniu@ecust.edu.cn作者简介:赵丽华(1999-), 女, 硕士研究生. E-mail: Lizzzzz233@outlook.com
基金资助:
ZHAO Lihua( ), WANG Yanshuai, YIN Xinwu, MAO Yeqiong, NIU Dechao(
), WANG Yanshuai, YIN Xinwu, MAO Yeqiong, NIU Dechao( )
)
Received:2024-12-20
Revised:2025-03-15
Published:2025-10-20
Online:2025-04-15
Contact:
NIU Dechao, professor. E-mail: dcniu@ecust.edu.cnAbout author:ZHAO Lihua (1999-), female, Master candidate. E-mail: Lizzzzz233@outlook.com
Supported by:摘要:
铋基纳米材料作为一种新型光热试剂, 具有毒性低、环境友好、原料廉价易得等优势, 在生物光热治疗方面展示出较大的应用潜力, 但其光热转换效率和抗菌性能仍然较低。本研究首先基于课题组前期报道的“限域凝胶化”方法, 以普朗尼克聚合物F127和3-巯基丙基-三甲氧硅烷为原料, 制备了有机硅氧骨架稳定胶束内核的硅基杂化胶束前驱体, 然后通过简便的“受限还原/硫化”方法, 即利用杂化胶束有机氧化硅网络内核中丰富的巯基基团作为受限吸附位点, 硼氢化钠作为还原剂, 硫化钠作为硫化剂, 制备了超小且具有无定形结构的硫化铋团簇负载的硅基杂化胶束体系。结果表明, 该功能杂化胶束体系具有优异的光热性能, 其光热转换效率高达86.93%, 这归因于具有缺陷结构的硫化铋团簇在硅氧骨架网络中的单分散稳定负载, 增强了硫化铋纳米材料在近红外光波段的光吸收能力。体外抗菌实验结果表明, 该体系在808 nm近红外光的辐照下展示出优异的光热抗菌性能且具有良好的生物相容性。
中图分类号:
赵丽华, 王言帅, 尹昕妩, 毛叶琼, 牛德超. 负载硫化铋纳米簇的硅基杂化胶束的制备及其光热抗菌性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(10): 1129-1136.
ZHAO Lihua, WANG Yanshuai, YIN Xinwu, MAO Yeqiong, NIU Dechao. Bismuth Sulfide Nanoclusters-loaded Silica-based Hybrid Micelles: Preparation and Photothermal Antibacterial Property[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(10): 1129-1136.
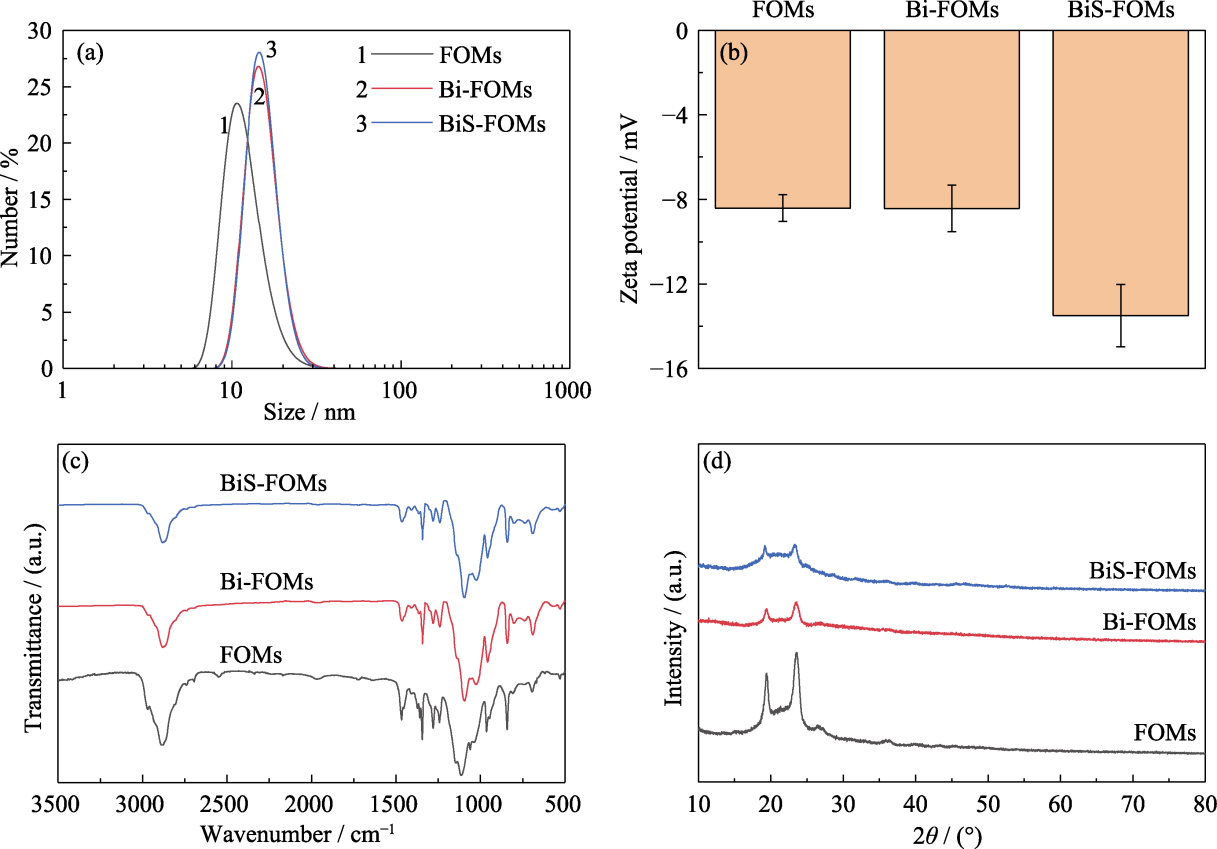
图3 FOMs、Bi-FOMs、BiS-FOMs的(a)粒径分布、(b) Zeta电位、(c) FT-IR光谱图和(d) XRD图谱
Fig. 3 (a) Size distributions, (b) Zeta potentials, (c) FT-IR spectra and (d) XRD patterns of FOMs, Bi-FOMs, and BiS-FOMs
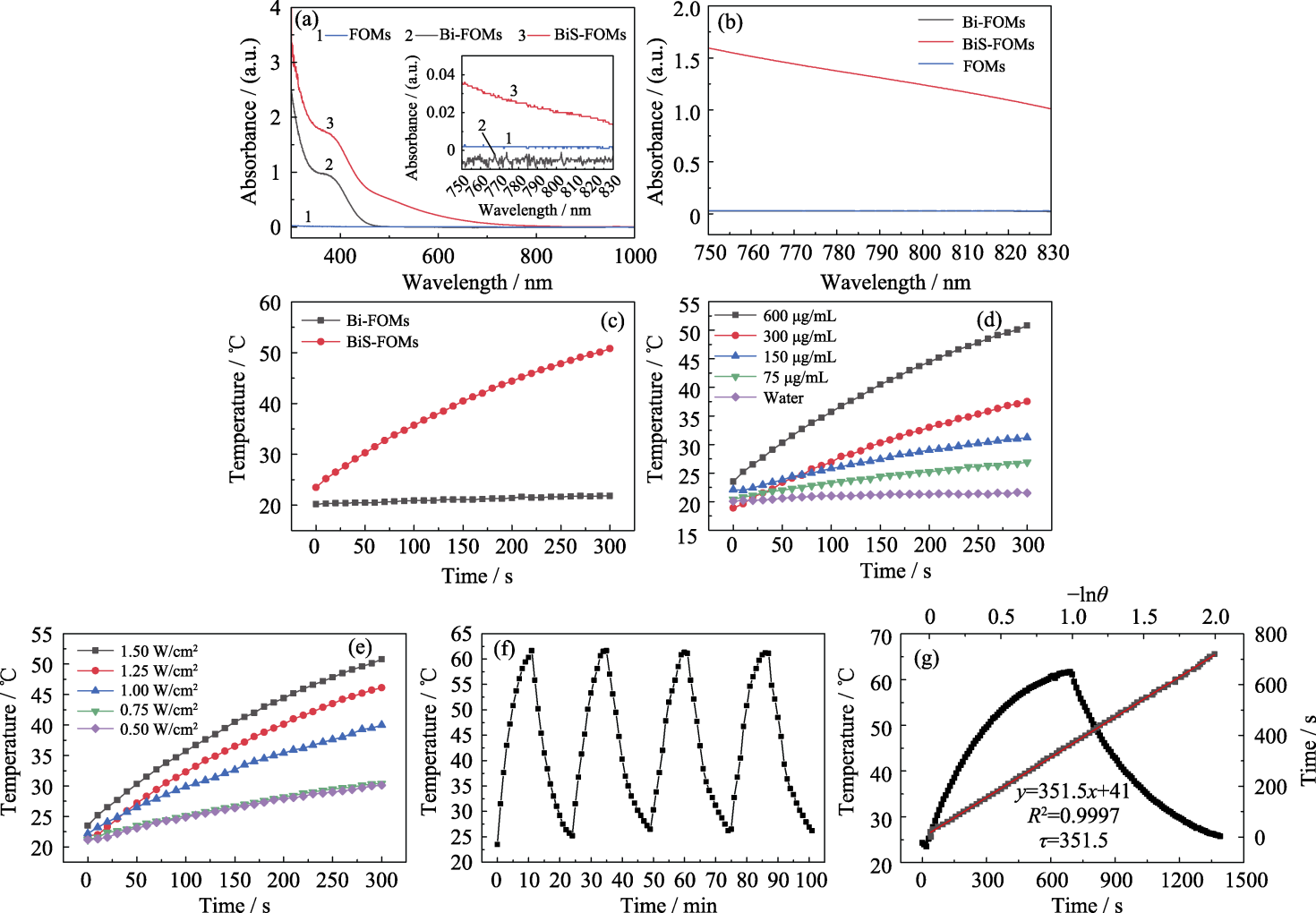
图7 FOMs、Bi-FOMs和BiS-FOMs的体外光热性能
Fig. 7 Photothermal performance of FOMs, Bi-FOMs and BiS-FOMs (a, b) UV-Vis absorption spectra of samples with Bi concentration of 60 (a) and 600 mg/L (b); (c) Temperature-time curves of samples under 808 nm laser radiation for 5 min (power density of 1.5 W/cm2, Bi concentration of 600 mg/L ); (d) Temperature-time relationship of BiS-FOMs with different Bi concentrations under 808 nm laser irradiation for 5 min (power density of 1.5 W/cm2); (e) Temperature-time relationship of BiS-FOMs with Bi concentration at 600 mg/L under 808 nm laser irradiation with different power densities for 5 min; (f) Four ramp-up/down cycle curves of BiS-FOMs with or without laser radiation (1.5 W/cm2, 808 nm, 600 mg/L for Bi); (g) Photothermal conversion efficiency of BiS-FOMs (1.5 W/cm2, 808 nm, 600 mg/L for Bi); Colorful figures are available on website
| Material | Photothermal conversion efficiency, η | Concentration/ (mg·L-1) | Power density/ (W·cm-2) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bi2S3 | 33.58% | 100 | 0.75 | [ |
| Bi2S3-Au NRs | 51.06% | 100 | 0.75 | [ |
| Au/Bi2S3NFs | 58.3% | 180 | 2 | [ |
| Fe3O4@PDA@BSA-Bi2S3NPs | 47.6% | 900 | 1 | [ |
| Cu1.94S-Bi2S3@PSIOAm NCs | 31% | 300 | 1 | [ |
| Au-Bi2S3 HNSCs | ~15% | 50 | 1 | [ |
| Au@Bi2S3 | 35.30% | 125 | 2 | [ |
| Bi2S3/Cu2S/Cu3BiS3 | 43.8% | 200 | 0.75 | [ |
| BiS-FOMs | 86.93% | 600 | 1.5 | This work |
表1 已报道的Bi基光热材料在波长808 nm激光照射下的光热转化效率
Table 1 Photothermal conversion efficiency of reported Bi-based materials under 808 nm wavelength laser irradiation
| Material | Photothermal conversion efficiency, η | Concentration/ (mg·L-1) | Power density/ (W·cm-2) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bi2S3 | 33.58% | 100 | 0.75 | [ |
| Bi2S3-Au NRs | 51.06% | 100 | 0.75 | [ |
| Au/Bi2S3NFs | 58.3% | 180 | 2 | [ |
| Fe3O4@PDA@BSA-Bi2S3NPs | 47.6% | 900 | 1 | [ |
| Cu1.94S-Bi2S3@PSIOAm NCs | 31% | 300 | 1 | [ |
| Au-Bi2S3 HNSCs | ~15% | 50 | 1 | [ |
| Au@Bi2S3 | 35.30% | 125 | 2 | [ |
| Bi2S3/Cu2S/Cu3BiS3 | 43.8% | 200 | 0.75 | [ |
| BiS-FOMs | 86.93% | 600 | 1.5 | This work |
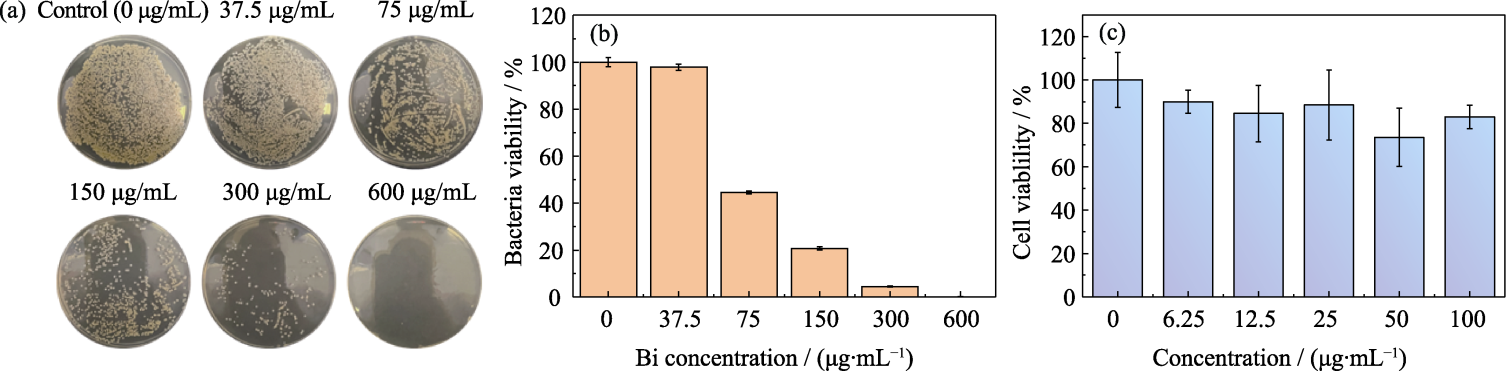
图8 BiS-FOMs的抗菌性和细胞相容性
Fig. 8 Antibacterial effect and cytocompatibility of BiS-FOMs (a) Digital photos and (b) quantitetive colonies of Staphylococcus aureus treated with BiS-FOMs at different Bi concentrations under 808 nm laser (1.5 W/cm2) rediation for 10 min; (c) In vitro cell survival rates of HUVECs treated with BiS-FOMs at different Bi concentrations for 48 h
| [1] |
ZHI D F, YANG T, O’HAGAN J, et al. Photothermal therapy. Journal of Controlled Release, 2020, 325: 52.
DOI PMID |
| [2] | LI C W, CHENG Y, LI D W, et al. Antitumor applications of photothermal agents and photothermal synergistic therapies. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 2022, 23(14): 7909. |
| [3] | HE Z Y, BU P Z, XU K, et al. Remodeling of the pro-inflammatory microenvironment in osteoarthritis via hydrogel-based photothermal therapy. Advanced Composites and Hybrid Materials, 2024, 7(2): 36. |
| [4] | LV H W, ZHOU X M, YANG G, et al. Bismuth@bismuth sulfide core@shell structure for near infrared II light triggered photothermal therapy. ChemistrySelect, 2024, 9(12): e202304834. |
| [5] | YE M L, SHI F, SHEN M, et al. Composite soft-template method synthesis and biosensing application of hedgehog-like bismuth sulfide micro-nanostructures. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 2021, 613: 126094. |
| [6] | SUN B, FENG T T, DONG J, et al. Green synthesis of bismuth sulfide nanostructures with tunable morphologies and robust photoelectrochemical performance. CrystEngComm, 2019, 21(9): 1474. |
| [7] | ANASANE N, AMETA R. Morphologies of nanostructured bismuth sulphide and Mn (II) doped bismuth sulphide nanoparticles: characterization and application. Materials Science-Poland, 2017, 35(1): 6. |
| [8] | SHAHBAZI M A, FAGHFOURI L, FERREIRA M P A, et al. The versatile biomedical applications of bismuth-based nanoparticles and composites: therapeutic, diagnostic, biosensing, and regenerative properties. Chemical Society Reviews, 2020, 49(4): 1253. |
| [9] | NIKODIMOS Y, HUANG C J, TAKLU B W, et al. Chemical stability of sulfide solid-state electrolytes: stability toward humid air and compatibility with solvents and binders. Energy & Environmental Science, 2022, 15(3): 991. |
| [10] | LI Y H, TAN X X, WANG H, et al. Spectral computed tomography-guided photothermal therapy of osteosarcoma by bismuth sulfide nanorods. Nano Research, 2023, 16(7): 9885. |
| [11] | FANG Q L, XU Y, LUO L J, et al. Controllable synthesis of layered black bismuth oxidechloride nanosheets and their applications in internal tumor ablation. Regenerative Biomaterials, 2022, 9: rbac036. |
| [12] | SONG S L, LIAO L, LEI H, et al. Purification of iodine from high-temperature argon environment by bismuth sulfide-modified zeolite. Atomic Energy Science and Technology, 2025, 59(1): 57. |
| [13] | DING F C, WANG Q J, ZHOU S F, et al. Synthesis of Bi2S3 thin films based on pulse-plating bismuth nanocrystallines and its photoelectrochemical properties. Royal Society Open Science, 2020, 7(8): 200479. |
| [14] | CHENG J H, FENG W L, YANG X Z, et al. High-performance Bi2S3 photodetector based on oxygen-mediated defect engineering and its wafer-scale fast fabrication. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2025, 679: 373. |
| [15] | ZHAO Z W, CHI Z R, SUN Q Q, et al. Preparation and performance of palladium clusters-loaded silica-based hybrid micelles. Journal of East China University of Science and Technology, 2023, 49(4): 498. |
| [16] |
ZHANG X, QIAO X F, SHI W, et al. Phonon and Raman scattering of two-dimensional transition metal dichalcogenides from monolayer, multilayer to bulk material. Chemical Society Reviews, 2015, 44(9): 2757.
DOI PMID |
| [17] | YU N, LIU X L, LU Z W, et al. Polymorph control, phase transitions and photocatalytic activity of bismuth oxide with emphasis on sodium-impurity effects. Ceramics International, 2025, 51(18): 24960. |
| [18] | CHENG D Y, CHANG Y, FENG Y L, et al. Deep-level defect enhanced photothermal performance of bismuth sulfide-gold heterojunction nanorods for photothermal therapy of cancer guided by computed tomography imaging. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2018, 57(1): 246. |
| [19] | ZHAO X S, LI S W, HUANG T D, et al. Synthesis of Au/Bi2S3 nanoflowers for efficient photothermal therapy. New Journal of Chemistry, 2020, 44(43): 18724. |
| [20] | LUO K Y, ZHAO J L, JIA C Z, et al. Integration of Fe3O4 with Bi2S3 for multi-modality tumor theranostics. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2020, 12(20): 22650. |
| [21] | LU X, LI Y, BAI X, et al. Multifunctional Cu1.94S-Bi2S3@polymer nanocomposites for computed tomography imaging guided photothermal ablation. Science China Materials, 2017, 60(8): 777. |
| [22] | WANG X, ZHANG C Y, DU J F, et al. Enhanced generation of non-oxygen dependent free radicals by Schottky-type heterostructures of Au-Bi2S3 nanoparticles via X-ray-induced catalytic reaction for radiosensitization. ACS Nano, 2019, 13(5): 5947. |
| [23] | WANG W N, PEI P, CHU Z Y, et al. Bi2S3 coated Au nanorods for enhanced photodynamic and photothermal antibacterial activities under NIR light. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2020, 397: 125488. |
| [24] | YU G D, LIU A L, JIN H L, et al. Urchin-shaped Bi2S3/Cu2S/Cu3BiS3 composites with enhanced photothermal and CT imaging performance. The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2018, 122(7): 3794. |
| [1] | 王月月, 黄佳慧, 孔红星, 李怀珠, 姚晓红. 载银放射状介孔二氧化硅的制备及其在牙科树脂中的应用[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(1): 77-83. |
| [2] | 曹青青, 陈翔宇, 吴健豪, 王筱卓, 王乙炫, 王禹涵, 李春颜, 茹菲, 李兰, 陈智. SiO2增强自敏性氮化碳微球可见光降解盐酸四环素的研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(7): 787-792. |
| [3] | 吴锐, 张敏慧, 金成韵, 林健, 王德平. 光热核壳TiN@硼硅酸盐生物玻璃纳米颗粒的降解和矿化性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(6): 708-716. |
| [4] | 王红宁, 黄丽, 清江, 马腾洲, 黄维秋, 陈若愚. 有机-无机氧化硅空心球的合成及VOCs吸附应用[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(9): 991-1000. |
| [5] | 池哲人, 张辽, 郭志前, 李永生, 牛德超. 氧化硅基杂化胶束负载Flav7光热剂的合成与性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(11): 1236-1244. |
| [6] | 李雪渊,王宏刚,田柱,朱建辉,刘影,贾兰,尤东江,李向明,康利涛. 一种用于长寿命水系锌锰电池的海藻酸钠/二氧化硅准凝胶复合电解质[J]. 无机材料学报, 2020, 35(8): 909-915. |
| [7] | 方美蓉,秦利梅,贾晓博,李永生,牛德超,胡泽岚. 聚乙烯亚胺改性的双介孔氧化硅基因载体构建[J]. 无机材料学报, 2020, 35(2): 187-192. |
| [8] | 李远洋,江波. 具有超亲水光催化性能的λ/4-λ/2型两层宽频增透膜的制备和性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2019, 34(2): 159-163. |
| [9] | 李鑫,牛书鑫,姚建省,唐定中,曹春晓,闫军浩. 金属Al粉对氧化硅基陶瓷型芯的性能及组织的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2019, 34(2): 207-212. |
| [10] | 何前军, 陈丹阳, 范明俭. 精准纳米气体治疗研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2018, 33(8): 811-824. |
| [11] | 宋晶晶, 陈波, 林开利. 核壳结构羟基磷灰石/介孔二氧化硅纳米颗粒的制备及其药物释放研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2018, 33(6): 623-628. |
| [12] | 王亚斌, 刘忠, 史时辉, 呼科科, 张琰图, 郭敏. 树枝状纤维形二氧化硅纳米粒子的研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2018, 33(12): 1274-1288. |
| [13] | 陈孟秋, 陈云, 舒杼, 王钰, 邬红娟, 郭利民. 埃洛石原料无模板法制备高比表面积介孔氧化硅及其在亚甲基蓝吸附中的应用[J]. 无机材料学报, 2018, 33(12): 1365-1370. |
| [14] | 白家峰, 王希庆, 陈义昌, 邓勇辉, 李志华, 刘 鸿, 刘绍华. 聚多巴胺修饰的介孔二氧化硅微球的合成及其用于负载左旋薄荷醇凉味剂[J]. 无机材料学报, 2017, 32(8): 845-850. |
| [15] | 罗 维, 魏 晶, 邓勇辉, 李宇慧, 王连军, 赵 涛, 江 莞. 新型两亲性嵌段共聚物导向合成有序大孔径介孔材料的研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2017, 32(1): 1-10. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||