无机材料学报 ›› 2024, Vol. 39 ›› Issue (12): 1357-1366.DOI: 10.15541/jim20240249 CSTR: 32189.14.10.15541/jim20240249
所属专题: 【结构材料】热障与环境障涂层(202506)
收稿日期:2024-05-17
修回日期:2024-07-13
出版日期:2024-07-16
网络出版日期:2024-07-16
通讯作者:
姜 岩, 讲师. E-mail: na_jiangyan@sina.com作者简介:郭晓阳(1999-), 男, 硕士研究生. E-mail: guoxiaoyang707722@163.com
基金资助:
GUO Xiaoyang1( ), ZHANG Xiaolin1, JIANG Yan1(
), ZHANG Xiaolin1, JIANG Yan1( ), TIAN Yuan1, GENG Zhi2
), TIAN Yuan1, GENG Zhi2
Received:2024-05-17
Revised:2024-07-13
Published:2024-07-16
Online:2024-07-16
Contact:
JIANG Yan, lecturer. E-mail: na_jiangyan@sina.comAbout author:GUO Xiaoyang (1999-), male, Master candidate. E-mail: guoxiaoyang707722@163.com
Supported by:摘要:
为了提高碳基材料在高温含氧环境下的抗烧蚀性能, 以石墨为基体, 采用浆料法和反应熔渗相结合的方式在其表面制备了Ti掺杂HfB2-SiC、ZrB2-SiC复合涂层。研究了涂层的物相组成、微观形貌和元素分布, 考察了涂层在2300 ℃的抗烧蚀能力。结果表明:渗硅后的Ti掺杂Hf(Zr)B2-SiC复合涂层结构十分致密, HfTiB2、ZrTiB2陶瓷相镶嵌于涂层中, 残余硅连续分布在Hf(Zr)B2、SiC颗粒周围, 涂层与基体结合良好且无缺陷; 在2300 ℃烧蚀480 s后, HfTiB2-SiC、ZrTiB2-SiC复合涂层试样的质量烧蚀率分别为-2.71×10-3和-4.20×10-1 mg/s(略微增重), 线烧蚀率分别为1.88×10-4和3.70×10-4 μm/s。HfTiB2-SiC复合涂层烧蚀后表面形成了以HfTiO4-HfO2为骨架、TiO2和SiO2为填充相的Hf-Ti-Si-O复相氧化层, 而ZrTiB2-SiC复合涂层烧蚀后表面形成了以ZrTiO4和ZrO2为镶嵌相、SiO2玻璃为半连续相, 且带有微孔的Zr-Ti-Si-O复相氧化层。其中, HfTiO4、HfO2、ZrTiO4、ZrO2等高熔点相可以有效抵抗高温火焰的冲刷, 高温下具有流动性的TiO2、SiO2可以填充烧蚀产生的孔隙缺陷并阻塞氧扩散通道, 防止氧向涂层内部和基体扩散, 二者共同作用实现了陶瓷涂层优异的抗烧蚀防护效果。
中图分类号:
郭晓阳, 张小琳, 姜岩, 田原, 耿志. Ti掺杂Hf(Zr)B2-SiC抗烧蚀涂层的制备及其抗烧蚀机理[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(12): 1357-1366.
GUO Xiaoyang, ZHANG Xiaolin, JIANG Yan, TIAN Yuan, GENG Zhi. Ti-doped Hf(Zr)B2-SiC Anti-ablation Coatings: Preparation and Ablation Resistance Mechanism[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(12): 1357-1366.

图2 HfTiB2-SiC涂层XRD图谱, 表面、截面微观结构及EDS元素分析
Fig. 2 XRD pattern, surface and cross-sectional microstructures, and EDS element analysis of HfTiB2-SiC coating (a) XRD pattern; (b) Surface morphology; (c) Enlarged view of Fig. (b); (d) EDS element mappings of Fig. (c); (e) EDS element point-analysis of Fig. (c); (f) Cross-sectional morphology; (g) Enlarged view of Fig. (f); (h) EDS element mappings of Fig. (g); (i) EDS element point-analysis of Fig. (g)

图3 ZrTiB2-SiC涂层XRD图谱, 表面、截面微观结构及EDS元素分析
Fig. 3 XRD pattern, surface and cross-sectional microstructures, and EDS element analysis of ZrTiB2-SiC coating (a) XRD pattern; (b) Surface morphology; (c) Enlarged view of Fig. (b); (d) EDS element mappings of Fig. (c); (e) EDS element point-analysis of Fig. (c); (f) Cross-sectional morphology; (g) Enlarged view of Fig. (f); (h) EDS element mappings of Fig. (g); (i) EDS element point-analysis of Fig. (g)
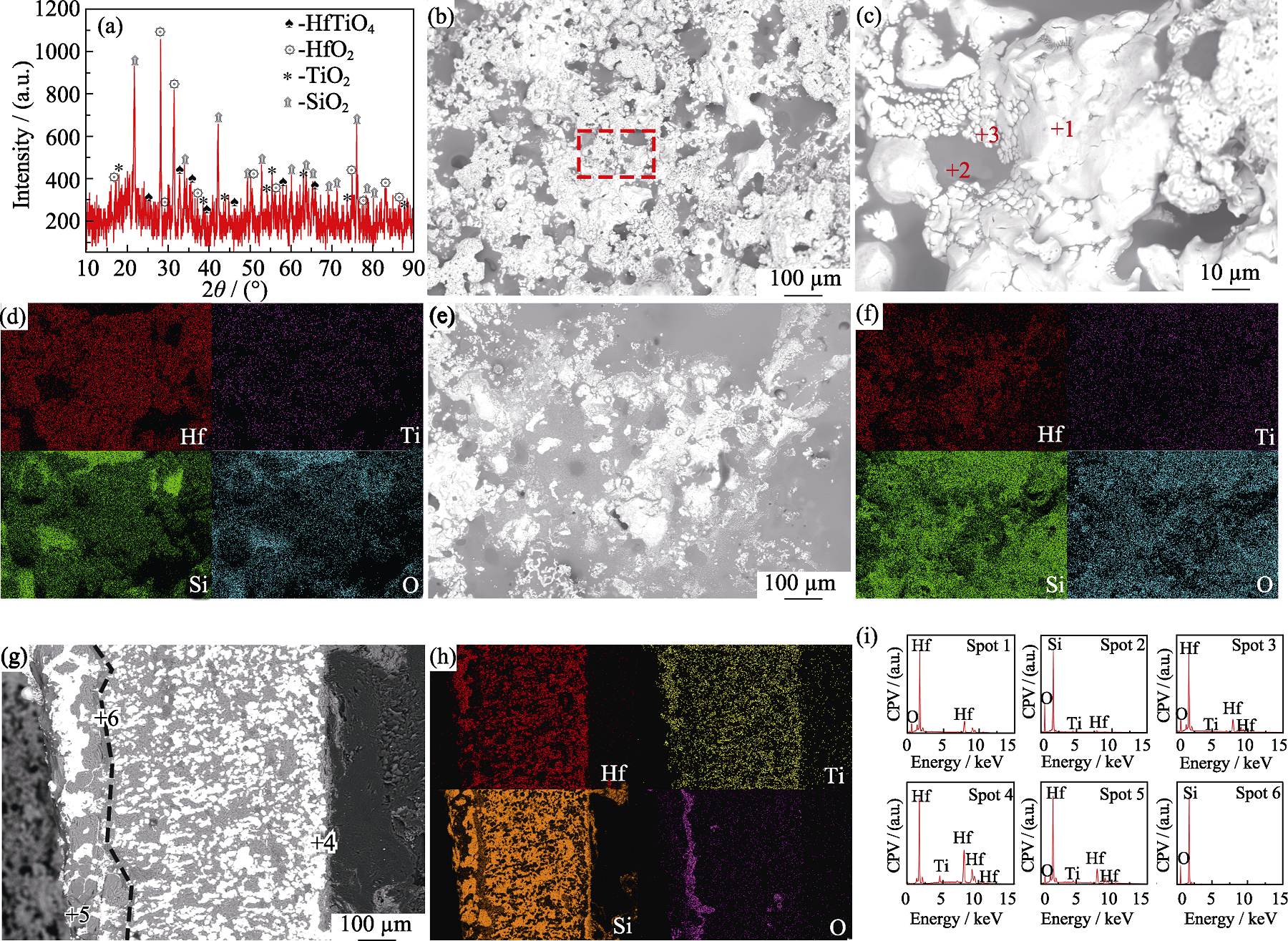
图4 HfTiB2-SiC涂层试样烧蚀480 s后表面XRD图谱、表面和截面微观形貌及元素分布
Fig. 4 XRD pattern, surface and cross-sectional microstructures, and element distribution of HfTiB2-SiC coating sample after ablation for 480 s (a) XRD pattern; (b) Surface microscopic morphology of the ablation center; (c) Enlarged view of Fig. (b); (d) EDS element mappings of Fig. (c); (e) Microscopic morphology of the transition zone; (f) Surface element analysis of Fig. (e); (g) Cross-sectional morphology of the ablation center; (h) EDS element mappings of Fig. (g); (i) EDS element point-analysis of Fig. (c, g)
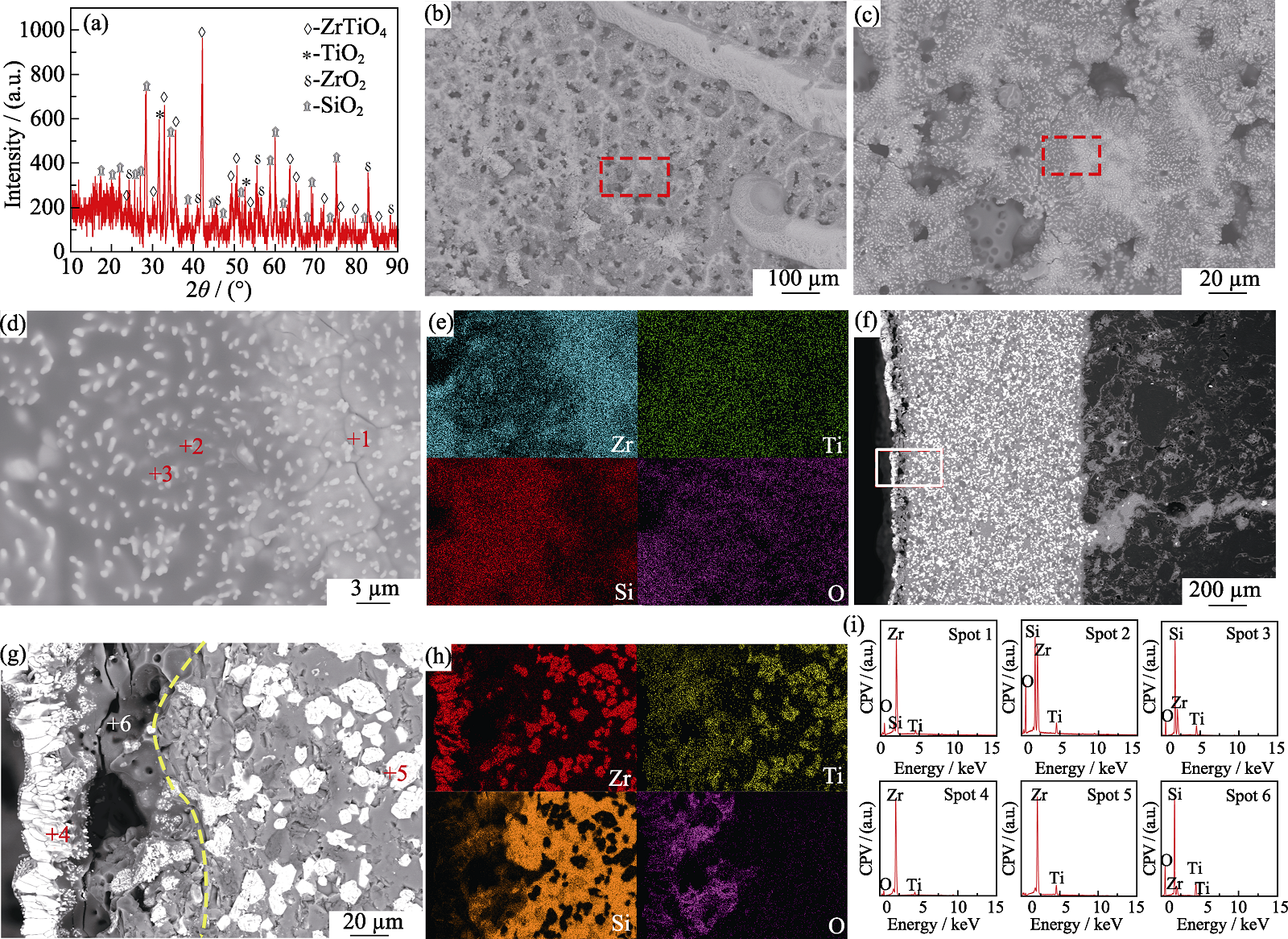
图5 ZrTiB2-SiC涂层试样烧蚀480 s后表面XRD图谱、烧蚀中心表面和截面微观形貌及元素分布
Fig. 5 XRD pattern, microstructures and element distributions of the ablation center surface and cross-sectional of ZrTiB2-SiC coating sample after ablation for 480 s (a) XRD pattern; (b) Surface microstructure; (c) Enlarged view of Fig. (b); (d) Enlarged view of Fig. (c); (e) EDS element mappings of Fig. (d); (f) Cross-sectional microscopic morphology; (g) Enlarged view of Fig. (f); (h) EDS element mappings of Fig. (g); (i) EDS element point-analysis of Fig. (d, g)

图7 涂层烧蚀过程中氧化产物蒸气压(a)和分解压(b)随温度的变化曲线
Fig. 7 Temperature dependent curves of vapor pressure (a) and decomposition pressure (b) for the oxidation products during coating ablation process

图S1 等离子火焰烧蚀150 s后HfTiB2-SiC涂层表面XRD图谱, 表面、截面微观形貌及EDS元素分析
Fig. S1 XRD pattern, surface and cross-sectional microstructures and EDS element analysis of HfTiB2-SiC coating after plasma flame ablation for 150 s (a) XRD pattern; (b) Surface microstructure; (c) Enlarged view of Fig. (b); (d) Enlarged view of the ablation center; (e) Surface element analysis of Fig. (d); (f) Cross-sectional morphology; (g) Enlarged view of Fig. (f); (h) Surface element analysis of Fig. (g); (i) Element point analysis of Fig. (d, g)
| Element | Spot 1/% |
|---|---|
| B | 30.42 |
| C | 59.20 |
| Si | 0.66 |
| Ti | 2.00 |
| Hf | 7.72 |
表S1 图2(c)中点1元素原子分数
Table S1 Element atomic fraction of Spot 1 in Fig. 2(c)
| Element | Spot 1/% |
|---|---|
| B | 30.42 |
| C | 59.20 |
| Si | 0.66 |
| Ti | 2.00 |
| Hf | 7.72 |
| Element | Spot 1/% |
|---|---|
| B | 57.66 |
| C | 30.13 |
| Si | 0 |
| Ti | 2.87 |
| Zr | 9.35 |
表S2 图3(c)中点1元素原子分数
Table S2 Element atomic fraction of Spot 1 in Fig. 3(c)
| Element | Spot 1/% |
|---|---|
| B | 57.66 |
| C | 30.13 |
| Si | 0 |
| Ti | 2.87 |
| Zr | 9.35 |
| Element | Spot 1/% | Spot 2/% | Spot 3/% |
|---|---|---|---|
| O | 64.15 | 64.42 | 60.46 |
| Si | 3.70 | 33.04 | 16.30 |
| Ti | 0.24 | 0.55 | 0.37 |
| Hf | 31.91 | 1.99 | 22.87 |
表S3 图4(c)中点1-3元素原子分数
Table S3 Eelement atomic fraction of Spots 1-3 in Fig. 4(c)
| Element | Spot 1/% | Spot 2/% | Spot 3/% |
|---|---|---|---|
| O | 64.15 | 64.42 | 60.46 |
| Si | 3.70 | 33.04 | 16.30 |
| Ti | 0.24 | 0.55 | 0.37 |
| Hf | 31.91 | 1.99 | 22.87 |
| Element | Spot 1/% | Spot 2/% | Spot 3/% |
|---|---|---|---|
| O | 64.20 | 72.86 | 57.10 |
| Si | 1.75 | 13.14 | 29.01 |
| Ti | 2.69 | 2.56 | 5.31 |
| Zr | 31.36 | 11.44 | 8.58 |
表S4 图5(d)中点1-3元素原子分数
Table S4 Element atomic fraction of Spots 1-3 in Fig. 5(d)
| Element | Spot 1/% | Spot 2/% | Spot 3/% |
|---|---|---|---|
| O | 64.20 | 72.86 | 57.10 |
| Si | 1.75 | 13.14 | 29.01 |
| Ti | 2.69 | 2.56 | 5.31 |
| Zr | 31.36 | 11.44 | 8.58 |
| Element | Spot 4/% | Spot 6/% |
|---|---|---|
| C | 17.38 | 12.51 |
| O | 42.38 | 59.93 |
| Si | 0.59 | 20.94 |
| Ti | 2.38 | 4.75 |
| Zr | 37.27 | 1.86 |
表S5 图5(g)中点4和点6元素原子分数
Table S5 Element atomic fraction of Spots 4 and 6 in Fig. 5(g)
| Element | Spot 4/% | Spot 6/% |
|---|---|---|
| C | 17.38 | 12.51 |
| O | 42.38 | 59.93 |
| Si | 0.59 | 20.94 |
| Ti | 2.38 | 4.75 |
| Zr | 37.27 | 1.86 |
| [1] |
田原, 姜岩, 付琬璐. 石墨表面Si-SiC-TaB2抗烧蚀复合涂层的制备及性能研究. 耐火材料, 2023, 57(1):35.
DOI |
| [2] | 任岩. 石墨材料表面ZrB2-SiC基抗高温/超高温氧化防护涂层的制备与性能研究. 合肥: 中国科学技术大学博士学位论文, 2021. |
| [3] |
JU Y C, LIU X Y, WANG Q, et al. Ablation behavior of ultra-high temperature composite ceramic matrix composites. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(1):86.
DOI |
| [4] | XU B, HE R, HONG C, et al. Ablation behavior and mechanism of double-layer ZrB2-based ceramic coating for lightweight carbon- bonded carbon fiber composites under oxyacetylene flame at elevate temperature. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2017, 702: 551. |
| [5] | SUN W, HAO Z, XIONG X, et al. Microstructure and cyclic ablation behaviour of a Si-Mo-Ti protected C/C composites by a two- step method. Materials at High Temperatures, 2021, 38(2):114. |
| [6] | XU Y, SUN W, XIONG X, et al. Microstructure and ablation resistance of ZrCxNy-modified ZrC-SiC composite coating for carbon/carbon composites. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2018, 38(13):4363. |
| [7] | WANG Y, GUO L, ZHANG Y, et al. Ablation behaviors and mechanism of ZrC-SiC-Si/SiC-Si double-layered coatings on C/C composite under plasma flame at 3000 ℃. Corrosion Science, 2023, 218: 111200. |
| [8] | DENG N, SUN W, XIONG X, et al. ZrC, HfC, and ZrC/ZrxSiy coatings prepared via molten salt solid-liquid two-phase diffusion method and ablation properties. Journal of Materials Research and Technology, 2022, 20: 572. |
| [9] | TORABI S, VALEFI Z, EHSANI N. Ablation behavior of SiC/ZrB2 ultra-high temperature ceramic coatings by solid shielding shrouded plasma spray for high-temperature applications (temperature above 2000 ℃). Surface and Coatings Technology, 2020, 403: 126271. |
| [10] | CAI F Y, NI D W, DONG S M. Research progress of high-entropy carbide ultra-high temperature ceramics. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(6):591. |
| [11] | ZHANG X H, WANG Y M, CHENG Y, et al. Research progress on ultra-high temperature ceramic composites. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(6):571. |
| [12] | 张瑞涛, 杨鑫, 王秀飞, 等. HfC-SiC复合涂层的制备及高温耐烧蚀性能研究. 碳素技术, 2021, 40(6):38. |
| [13] | HUANG K, XIA Y, WANG A. High temperature oxidation and oxyacetylene ablation properties of ZrB2-ZrC-SiC ultra-high temperature composite ceramic coatings deposited on C/C composites by laser cladding. Coatings, 2023, 13(1):173. |
| [14] | LIU H, YANG X, FANG C, et al. Ablation resistance and mechanism of SiC-LaB6 and SiC-LaB6-ZrB2 ceramics under plasma flame. Ceramics International, 2020, 46(10):16249. |
| [15] | JIANG Y, HU C, LIANG B, et al. Cyclic ablation resistance at 2300 ℃ of (Hf0.4Zr0.4Ta0.2)B2-SiC-Si coating for C/SiC composites prepared by SiC-assisted reactive infiltration of silicon. Surface and Coatings Technology, 2022, 451: 129072. |
| [16] | ZHANG P, CHENG C, XU M, et al. High-entropy (Hf0.25Zr0.25- Ti0.25Cr0.25)B2 ceramic incorporated SiC-Si composite coating to protect C/C composites against ablation above 2400 K. Ceramics International, 2022, 48(18):27106. |
| [17] | YAN N, ZHANG J, LIU T, et al. One-step preparation and ablation behavior of ZrC-SiC-Si coating for nose-shaped ZrC/C composites with gradient pore structure by vapor silicon infiltration. Corrosion Science, 2022, 206: 110505. |
| [18] | ZHANG J, ZHANG Y, ZHU X, et al. A novel Hf0.75Zr0.25N solid solution coating with high mechanical strength: ablation protection application above 2200 ℃. Ceramics International, 2023, 49(15):26022. |
| [19] | ZHANG J, ZHANG Y, CHEN R, et al. Effect of microstructure on the ablation behavior and mechanical properties of CVD-HfC coating. Corrosion Science, 2021, 192: 109815. |
| [20] | 李新星, 韩伯群, 王红侠, 等. 熔渗反应合成铝基表面Al3Ti/Al复合涂层. 轻金属, 2019(3): 40. |
| [21] | SHALMANI S A A, SOBHANI M, MIRZAEE O, et al. Effect of HfB2 and WC additives on the ablation resistance of ZrB2-SiC composite coating manufactured by SPS. Ceramics International, 2020, 46(16):25106. |
| [22] | 汪宏兵. 浆料法制备Mo2FeB2金属陶瓷-钢覆层材料及其性能研究. 武汉: 武汉科技大学硕士学位论文, 2008. |
| [23] | ALIASGRIAN R, NADERI M, MIRSALEHI S E, et al. The ablation behavior of ZrB2-SiC coating prepared by shrouded plasma spray on SiC-coated graphite. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2018, 742: 797. |
| [24] | HU D, FU Q, ZHOU L, et al. Grain growth limitation in the monolayer ZrB2-SiC coating above 1700 °C. Ceramics International, 2022, 48(10):14767. |
| [25] | BAI Y, WANG Q, MA Z, et al. Characterization and ablation resistance of ZrB2-xSiC gradient coatings deposited with HPPS. Ceramics International, 2020, 46(10):14756. |
| [26] | WANG P, ZHOU S, HU P, et al. Ablation resistance of ZrB2- SiC/SiC coating prepared by pack cementation for graphite. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2016, 682: 203. |
| [27] | WANG P, LI H, JIA Y, et al. Ablation resistance of HfB2-SiC coating prepared by in-situ reaction method for SiC coated C/C composites. Ceramics International, 2017, 43(15):12005. |
| [28] | WANG P, LI S, WEI C, et al. Microstructure and ablation properties of SiC/ZrB2-SiC/ZrB2/SiC multilayer coating on graphite. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2019, 781: 26. |
| [29] | JIANG Y, LIU T, RU H, et al. Ultra-high-temperature ceramic TaB2-SiC-Si coating by impregnation and in-situ reaction method to prevent graphite materials from oxidation and ablation. Ceramics International, 2019, 45(5):6541. |
| [30] | SHI A, YANG X, FANG C, et al. Microstructure and ablation behavior of Zr-Ti-Si-C multiphase coating fabricated by solid solution and in-situ reaction. Corrosion Science, 2021, 192: 109852. |
| [31] | LIU C, CAO L, CHEN J, et al. Microstructure and ablation behavior of SiC coated C/C-SiC-ZrC composites prepared by a hybrid infiltration process. Carbon, 2013, 65: 196. |
| [32] | FANG C, YANG X, HE K, et al. Microstructure and ablation properties of La2O3 modified C/C-SiC composites prepared via precursor infiltration pyrolysis. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2019, 39(4):762. |
| [33] | XUE L, SU Z, YANG X, et al. Microstructure and ablation behavior of C/C-HfC composites prepared by precursor infiltration and pyrolysis. Corrosion Science, 2015, 94: 165. |
| [34] | JIANG Y, LIU T, RU H, et al. Oxidation and ablation protection of multiphase Hf0.5Ta0.5B2-SiC-Si coating for graphite prepared by dipping-pyrolysis and reactive infiltration of gaseous silicon. Applied Surface Science, 2018, 459: 527. |
| [35] | ZHOU L, ZHANG J, HU D, et al. Investigation on the oxidation and ablation behaviors of HfB2-SiC-Si/SiC-Si coatings for carbon/carbon composites. Corrosion Science, 2021, 190: 109638. |
| [36] | ZHOU L, ZHANG J, HU D, et al. High temperature oxidation and ablation behaviors of HfB2-SiC/SiC coatings for carbon/carbon composites fabricated by dipping-carbonization assisted pack cementation. Journal of Materials Science & Technology, 2022, 111: 88. |
| [37] | JIANG Y, LIU T, RU H, et al. Oxidation and ablation protection of double layer HfB2-SiC-Si/SiC-Si coating for graphite materials. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2019, 782: 761. |
| [38] | TANG P, HU C, JIANG Y, et al. Facile preparation of SiC/ZrB2- SiC-Si coatings on Cf/SiC composites for ultrahigh temperature ablation resistance. Corrosion Science, 2024, 232: 112051. |
| [39] | 张天助, 陈招科, 熊翔. C/C复合材料ZrB2-SiC基陶瓷涂层制备及烧蚀性能研究. 中国材料进展, 2013, 32(11):659. |
| [40] | ZHAO R D, TANG S F. Research progress of ceramic matrix composites prepared by improved reactive melt infiltration through ceramization of porous carbon matrix. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(6):623. |
| [1] | 谭敏, 陈小武, 杨金山, 张翔宇, 阚艳梅, 周海军, 薛玉冬, 董绍明. 流延成型结合反应熔渗制备ZrB2-SiC陶瓷及其微观结构与氧化行为研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(8): 955-964. |
| [2] | 赵日达, 汤素芳. 多孔碳陶瓷化改进反应熔渗法制备陶瓷基复合材料研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(6): 623-633. |
| [3] | 粟毅, 史扬帆, 贾成兰, 迟蓬涛, 高扬, 马青松, 陈思安. 浆料浸渍辅助PIP工艺制备C/HfC-SiC复合材料的微观结构及性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(6): 726-732. |
| [4] | 蔡飞燕, 倪德伟, 董绍明. 高熵碳化物超高温陶瓷的研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(6): 591-608. |
| [5] | 孙小凡, 陈小武, 靳喜海, 阚艳梅, 胡建宝, 董绍明. 低温反应熔渗工艺制备AlN-SiC复相陶瓷及其性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(10): 1223-1229. |
| [6] | 张俊敏, 陈小武, 廖春景, 郭斐宇, 杨金山, 张翔宇, 董绍明. SiCf/SiC复合材料的RMI制备方法以及微观结构和性能优化[J]. 无机材料学报, 2021, 36(10): 1103-1110. |
| [7] | 周海军, 张翔宇, 高 乐, 胡建宝, 吴 斌, 董绍明. ZrB2-SiC超高温陶瓷涂层的抗烧蚀性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2013, 28(3): 256-260. |
| [8] | 关永军,夏原. 铝合金表面等离子体电解氧化陶瓷涂层在NaCl溶液中的电化学阻抗谱研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2008, 23(4): 784-788. |
| [9] | 张小立,金志浩,冯耀荣,赵文轸,吕振林,霍春勇. 反应熔渗法制备纳米 MoSi2-SiC复合材料[J]. 无机材料学报, 2007, 22(4): 690-694. |
| [10] | 王建江,杜心康,刘宏伟,张龙,陆大勤. Al对反应火焰喷涂TiC-TiB2复相陶瓷涂层的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2007, 22(3): 550-554. |
| [11] | 辛世刚,宋力昕,赵荣根,胡行方. 微弧氧化 Al-Si-O陶瓷涂层的结构与结合强度[J]. 无机材料学报, 2006, 21(2): 493-498. |
| [12] | 王引真,孙永兴,鄢君辉,郑修麟,阎国超. 热障涂层热震失效寿命定量计算的研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 1999, 14(1): 138-142. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||