无机材料学报 ›› 2018, Vol. 33 ›› Issue (6): 609-616.DOI: 10.15541/jim20170355 CSTR: 32189.14.10.15541/jim20170355
所属专题: 陶瓷基复合材料
黄喜鹏1, 王波2, 杨成鹏1, 潘文革1, 刘小瀛3
收稿日期:2017-08-07
修回日期:2017-11-09
出版日期:2018-06-20
网络出版日期:2018-05-24
作者简介:黄喜鹏(1994-), 男, 硕士研究生. E-mail: huangxp_nwpu@163.com
基金资助:HUANG Xi-Peng1, WANG Bo2, YANG Cheng-Peng1, PAN Wen-Ge1, LIU Xiao-Ying3
Received:2017-08-07
Revised:2017-11-09
Published:2018-06-20
Online:2018-05-24
About author:HUANG Xi-Peng. E-mail: huangxp_nwpu@163.com
Supported by:摘要:
本研究对三维针刺C/SiC(3-dimension needled C/SiC, 3D-N C/SiC)复合材料进行室温单调拉伸和拉伸加载-卸载试验, 利用声发射技术对试样损伤演化进行动态监测。采用K-均值聚类分析方法对小波降噪后的声发射信号进行了损伤模式识别, 结合试样断口扫描电镜观测, 发现3D-N C/SiC复合材料在拉伸载荷作用下主要存在五类损伤模式: 基体开裂、界面脱粘、界面滑移、纤维断裂和纤维束断裂。通过快速傅里叶变换(FFT)方法对小波降噪后的信号进行频谱分析得出: 3D-N C/SiC复合材料在拉伸载荷作用下主要存在240、370和455 kHz三种频率的损伤信号, 分别对应于界面损伤、基体损伤和纤维损伤。结合单调拉伸试验过程声发射信号能量柱分布和加卸载过程累积能量曲线特征, 分析了试样损伤演化机理。
中图分类号:
黄喜鹏, 王波, 杨成鹏, 潘文革, 刘小瀛. 基于声发射信号的三维针刺C/SiC复合材料拉伸损伤演化研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2018, 33(6): 609-616.
HUANG Xi-Peng, WANG Bo, YANG Cheng-Peng, PAN Wen-Ge, LIU Xiao-Ying. Evaluating Damage Evolution of Three-dimension Needled C/SiC Composite Based on Acoustic Emission Signal Analysis[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2018, 33(6): 609-616.
| Modulus/ GPa | Strength/ MPa | Failure strain/% | Elastic limit/MPa | Poisson’s ratio |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 104.29 | 115.06 | 0.3061 | 37.67 | 0.08 |
表1 3D-N C/SiC复合材料拉伸基本力学性能
Table 1 Tensile mechanical properties of 3D-N C/SiC
| Modulus/ GPa | Strength/ MPa | Failure strain/% | Elastic limit/MPa | Poisson’s ratio |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 104.29 | 115.06 | 0.3061 | 37.67 | 0.08 |
| Cluster | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Amplitude/mV | 226.4 | 1147.5 | 496.2 | 64.4 | 122.5 |
| Energy/(mV×ms) | 34.2 | 78.4 | 49.0 | 12.5 | 22.0 |
表2 聚类中心坐标值
Table 2 Numerical value of the clustering center
| Cluster | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Amplitude/mV | 226.4 | 1147.5 | 496.2 | 64.4 | 122.5 |
| Energy/(mV×ms) | 34.2 | 78.4 | 49.0 | 12.5 | 22.0 |
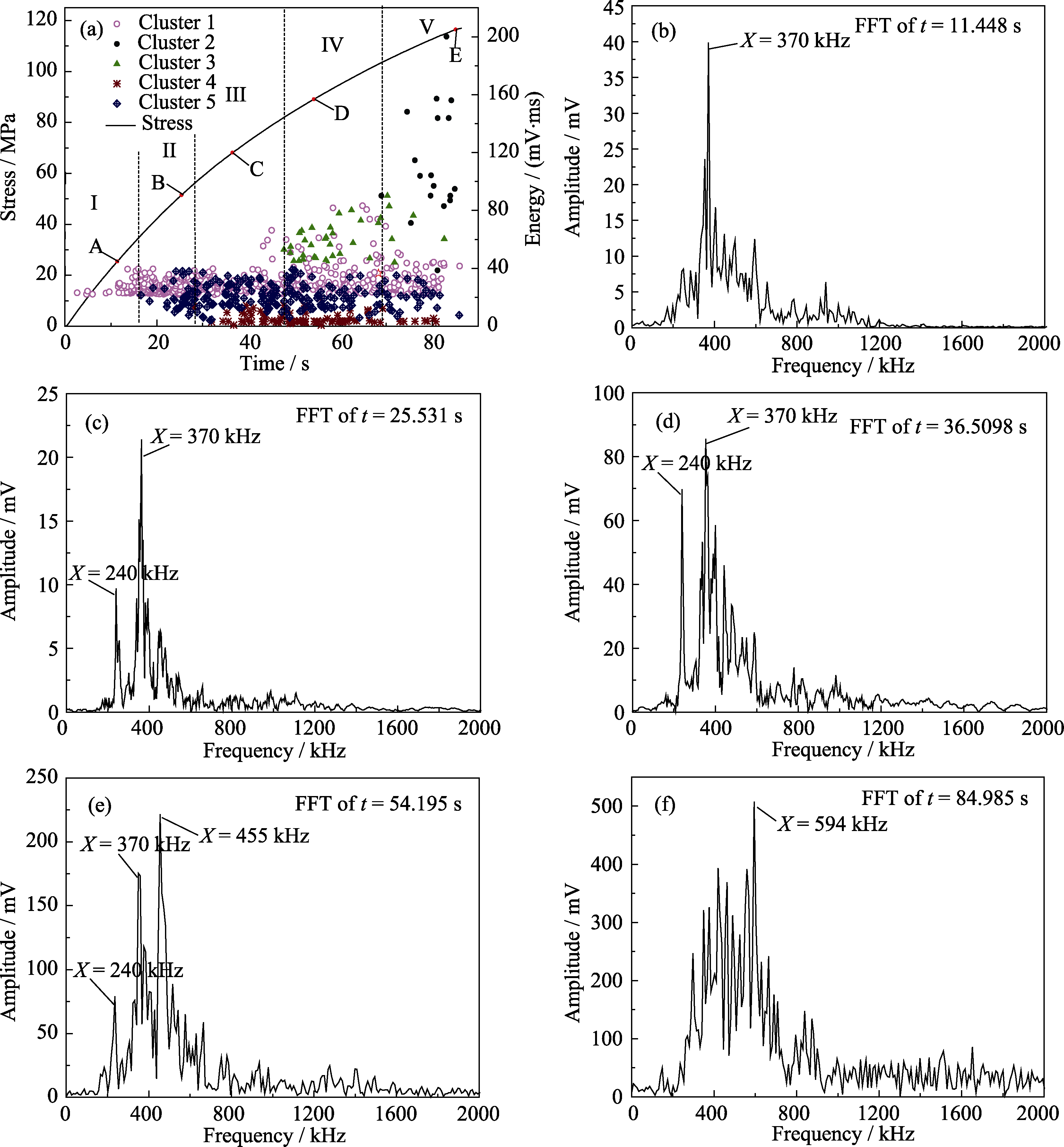
图8 3D-N C/SiC声发射事件随应力分布及特征点信号波频谱特征
Fig. 8 Characteristics of acoustic emission events with stress distribution in 3D-N C/SiC (a) and spectral characteristics of the signal wave at point A (b), B (c), C (d), D (e) and E (f) in (a)

图9 3D-N C/SiC试样(a)拉伸断口显微照片和(b)拉伸断口的微观形貌
Fig. 9 Micrograph (50×) of fractured surface and (b) micrograph (2000×) of fractured surface of 3N-C/SiC composite material after tensile stress
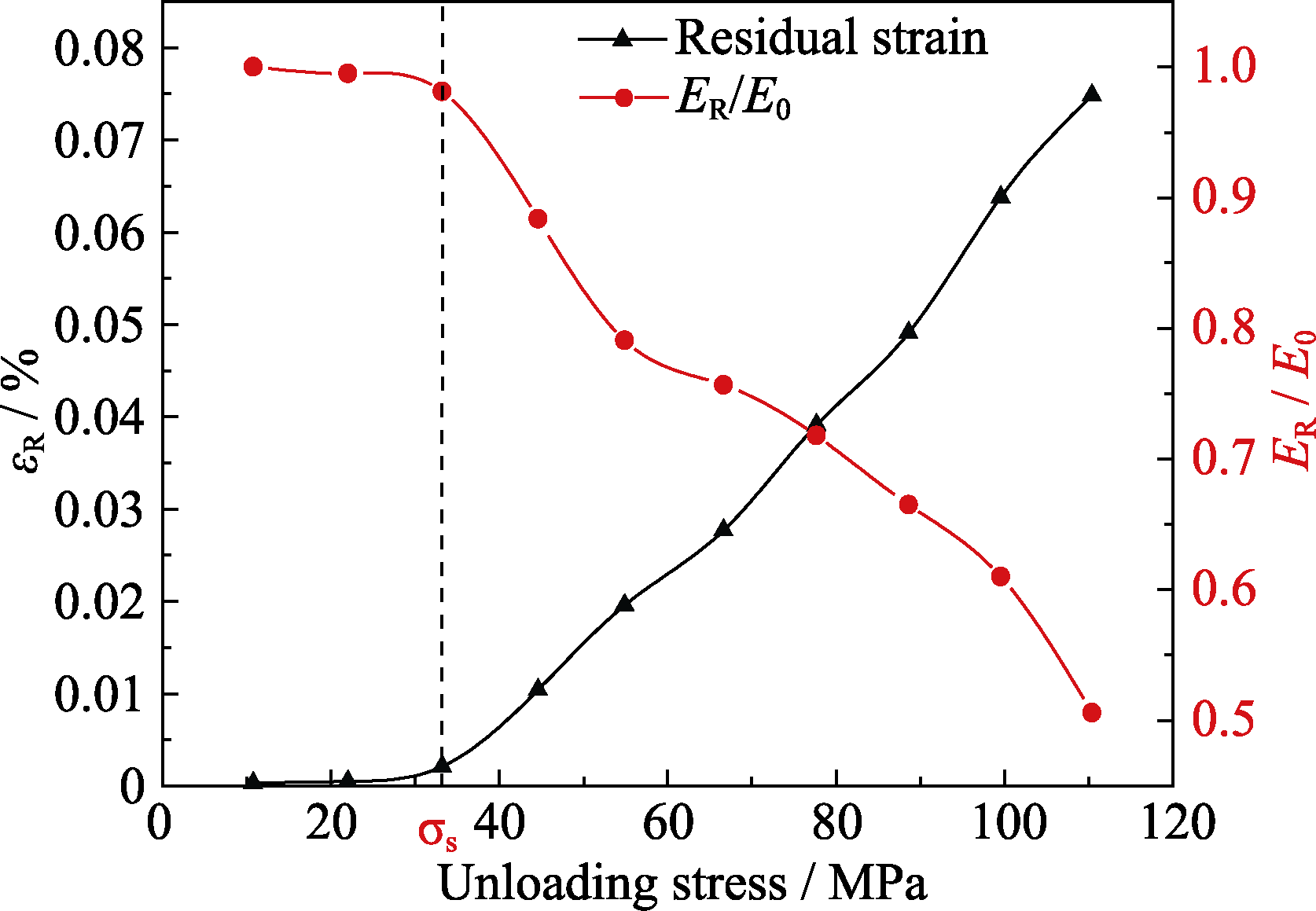
图11 卸载模量和残余应变随卸载应力的变化
Fig. 11 ER/E0 and residual strain vs. stressER: Unloading modulus; E0: Elastic modulus; εR: Residual strain; σR: Unloading stress
| Damage modes | Cluster | Energy/(mV·ms) | Frequency/kHz | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Matrix cracking | 1 | 20-80 | 370 | When the load exceeds the proportional limit (37 MPa), crack begins to form and spreads until the sample fails. |
| Interface debonding | 5 | 10-40 | 240 | When crack extends to the fiber, it deflects and expands along the interface. |
| Interfacial slipping | 4 | 0-20 | ||
| Fiber breakage | 3 | 40-80 | 455 | As cracks become saturated, the fibers begin to break. |
| Fiber cluster failure | 2 | 70-260 | 594 | That cracks in the material expand rapidly to form macro-cracks attributes to fiber bundle breakage. |
表3 损伤模式的声发射参数特征及演化过程描述
Table 3 Characterization of acoustic emission signals and description of the damage modes
| Damage modes | Cluster | Energy/(mV·ms) | Frequency/kHz | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Matrix cracking | 1 | 20-80 | 370 | When the load exceeds the proportional limit (37 MPa), crack begins to form and spreads until the sample fails. |
| Interface debonding | 5 | 10-40 | 240 | When crack extends to the fiber, it deflects and expands along the interface. |
| Interfacial slipping | 4 | 0-20 | ||
| Fiber breakage | 3 | 40-80 | 455 | As cracks become saturated, the fibers begin to break. |
| Fiber cluster failure | 2 | 70-260 | 594 | That cracks in the material expand rapidly to form macro-cracks attributes to fiber bundle breakage. |
| [1] | CHEN XIAO-MING, CHEN LI, ZHANG CHUN-YAN,et al. Three-dimensional needle-punching for composites - a review. Composites Part A: Applied Science and Manufacturing, 2016, 85: 12-30. |
| [2] | KADIR BILISIK.Three-dimensional braiding for composites: a review.Textile Research Journal, 2012, 83(13): 1414-1436. |
| [3] | NIE JING-JIANG, XU YONG-DONG, ZHANG LI-TONG,et al. Microstructure and tensile behavior of multiply needled C/SiC composite fabricated by chemical vapor infiltration. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 2009, 209(1): 572-576. |
| [4] | CHEN ZHEN, FANG GUO-DONG, XIE JUN-BO,et al. Experimental study of high-temperature tensile mechanical properties of 3D needled C/C-SiC composites. Materials Science & Engineering A, 2016, 654(10): 271-277. |
| [5] | XU HUA-JIE, ZHANG LI-TONG, CHENG LAI-FEI.The yarn size dependence of tensile and in-plane shear properties of three- dimensional needled textile reinforced ceramic matrix composites.Materials & Design, 2015, 67: 428-435. |
| [6] | XIE JUN-BO, FANG GUO-DONG, CHEN ZHEN, et al. An anisotropic elastoplastic damage constitutive model for 3D needled C/C-SiC composites. Composite Structures, 2017, 176: 164-177. |
| [7] | ZARIF KARIMI N, MINAK G, KIANFAR P.Analysis of damage mechanisms in drilling of composite materials by acoustic emission.Composite Structures, 2015, 131: 107-114. |
| [8] | MEI HUI, SUN YU-YAO, ZHANG LI-TONG,et al. Acoustic emission characterization of fracture toughness for fiber reinforced ceramic matrix composites. Materials Science and Engineering: A, 2013, 560: 372-376. |
| [9] | MAILLET E, BAKER C, MORSCHER G N,et al. Feasibility and limitations of damage identification in composite materials using acoustic emission. Composites Part A: Applied Science and Manufacturing, 2015, 75: 77-83. |
| [10] | CHANG YAN-JUN, JIAO GUI-QIONG, ZHANG KE-SHI,et al. Investigation on tensile properties for 3D C/SiC composites by acoustic emission. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica, 2010, 27(6): 82-87. |
| [11] | MOMON S, GODIN N, REYNAUD P,et al. Unsupervised and supervised classification of AE data collected during fatigue test on CMC at high temperature. Composites Part A: Applied Science and Manufacturing, 2012, 43(2): 254-260. |
| [12] | TONG XIAO-YAN, ZHANG JIA-LI, YAO LEI-JIANG, et al. Cluster analysis of acoustic emission signals of 2D-C/SiC under tensile loading. Chinese Journal of Solid Mechanics, 2014, 35(2): 109-114. |
| [13] | YAN LIAN-SHENG, CUI HONG, LI KE-ZHI, et al. Preparation and properties of carbon fiber needling preform reinforced silicon carbide composite. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2008, 23(2): 223-228. |
| [14] | JEONG H.Analysis of plate wave propagation in anisotropic laminates using a wavelet transform.NDT & E International, 2001, 34(3): 185-190. |
| [15] | MORIZET N, GODIN N, TAMG J, et al. Classification of acoustic emission signals using wavelets and random forests: application to localized corrosion. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, 2016, 70-71: 1026-1037. |
| [16] | SAIDANE E H, SCIDA D, ASSARAR M,et al. Damage mechanisms assessment of hybrid flax-glass fiber composites using acoustic emission. Composite Structures, 2017, 174(Supplement C): 1-11. |
| [17] | MORSCHER G, SINGH M, KISER J,et al. Modeling stress- dependent matrix cracking and stress-strain behavior in 2D woven SiC fiber reinforced CVI SiC composites. Composites Science and Technology, 2007, 67(6): 1009-1017. |
| [18] | BREEDE F, KOCH D, MAILLET E,et al. Modal acoustic emission of damage accumulation in C/C-SiC composites with different fiber architectures. Ceramic International, 2015, 41(9, Part B): 12087-12098. |
| [19] | LI PAN, WANG BO, ZHEN WEN-QIANG.Tensile constitutive model of 2D-SiC/SiC ceramic matrix composites.China Ceramic Industry, 2013, 20(5): 10-14. |
| [20] | LI LI, LOMOV S V, YAN X,et al. Cluster analysis of acoustic emission signals for 2D and 3D woven glass/epoxy composites. Composite Structures, 2014, 116(1): 286-299. |
| [21] | ECH-CHOUDARY Y, ASSARAR M, SCIDA D,et al. Unsupervised clustering for building a learning database of acoustic emission signals to identify damage mechanisms in unidirectional laminates. Applied Acoustics, 2017, 123: 123-132. |
| [22] | XU YONG-DONG, CHENG LAI-FEI, ZHANG LI-TONG.Carbon/ silicon carbide composites prepared by chemical vapor infiltration combined with silicon melt infiltration. Carbon, 1999, 37(8): 1179-1187. |
| [23] | SINGH Y P, MANSOUR R, MORSCHER G N.Combined acoustic emission and multiple lead potential drop measurements in detailed examination of crack initiation and growth during inter-laminar testing of ceramic matrix composites.Composites Part A: Applied Science and Manufacturing, 2017, 97: 93-99. |
| [24] | SUN ZHI-GANG, SHAO HONG-YAN, NIU XU-MING,et al. Failure simulation of unidirectional fiber-reinforced ceramic matrix composites based on evolving compliant interfacial debonding model. Materials Science and Engineering: A, 2016, 663: 78-85. |
| [25] | MORSCHER G N, GORDON N A.Acoustic emission and electrical resistance in SiC-based laminate ceramic composites tested under tensile loading.Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2017, 37(13): 3861-3872. |
| [26] | GUTKIN R, GREEN C J, VANGRATTANACHAI S,et al. On acoustic emission for failure investigation in CFRP: pattern recognition and peak frequency analyses. Mechanical Systems & Signal Processing, 2011, 25(4): 1393-1407. |
| [1] | 陈义, 邱海鹏, 陈明伟, 徐昊, 崔恒. SiC/SiC复合材料基体硼改性方法及其力学性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(5): 504-510. |
| [2] | 穆爽, 马沁, 张禹, 沈旭, 杨金山, 董绍明. Yb2Si2O7改性SiC/SiC复合材料的氧化行为研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(3): 323-328. |
| [3] | 全文心, 余艺平, 方冰, 李伟, 王松. 管状C/SiC复合材料高温空气氧化行为与宏细观建模研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(8): 920-928. |
| [4] | 吴晓晨, 郑瑞晓, 李露, 马浩林, 赵培航, 马朝利. SiCf/SiC陶瓷基复合材料高温环境损伤原位监测研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(6): 609-622. |
| [5] | 沈轩逸, 马沁, 薛玉冬, 廖春景, 朱敏, 张翔宇, 杨金山, 董绍明. 复合界面层对SiCf/SiC复合材料力学损伤行为的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(8): 917-922. |
| [6] | 王洪达, 冯倩, 游潇, 周海军, 胡建宝, 阚艳梅, 陈小武, 董绍明. SiC/SiC-哈氏合金异质连接机制及其氟熔盐腐蚀特性分析[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(4): 452-458. |
| [7] | 张亚晨, 孟佳, 蔡坤, 盛晓晨, 乐军, 宋力昕. 基于声发射技术的Si-Cr-Ti高温抗氧化涂层弯曲失效机理研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2021, 36(11): 1185-1192. |
| [8] | 李陇彬, 薛玉冬, 胡建宝, 杨金山, 张翔宇, 董绍明. 碳化硅纳米线增韧碳化硅纤维/碳化硅基体损伤行为研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2021, 36(10): 1111-1117. |
| [9] | 马登浩, 侯振华, 李军平, 孙新, 金恩泽, 尹健. 界面相对3D-SiC/SiC复合材料静态力学性能及内耗特征的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2021, 36(1): 55-60. |
| [10] | 张冰玉,王岭,王晓猛,邱海鹏. 不同先驱体制备C/SiC复合材料及其浸渍行为[J]. 无机材料学报, 2020, 35(9): 1017-1022. |
| [11] | 张勇祯, 童小燕, 姚磊江, 李斌, 白国栋. 基于改进遗传算法的C/SiC拉伸损伤声发射模式识别[J]. 无机材料学报, 2020, 35(5): 593-600. |
| [12] | 何 飞, 李 亚, 骆 金, 方旻翰, 赫晓东. 具有气凝胶结构特征的C/SiO2和C/SiC复合材料研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2017, 32(5): 449-458. |
| [13] | 赵 爽, 杨自春, 周新贵. 不同界面SiC/SiC复合材料的断裂行为研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2016, 31(1): 58-62. |
| [14] | 王 浩, 周卿军, 简 科, 邵长伟, 朱旖华. C/SiC复合材料有序多孔陶瓷接头的制备及其连接技术研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2013, 28(7): 763-768. |
| [15] | 马青松, 刘海韬, 潘 余, 刘卫东, 陈朝辉. C/SiC复合材料在超燃冲压发动机中的应用研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2013, 28(3): 247-255. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||