无机材料学报 ›› 2017, Vol. 32 ›› Issue (6): 581-586.DOI: 10.15541/jim20160488 CSTR: 32189.14.10.15541/jim20160488
鲍 艳, 康巧玲
收稿日期:2016-08-29
修回日期:2016-10-14
出版日期:2017-06-20
网络出版日期:2017-05-27
基金资助:BAO Yan, KANG Qiao-Ling
Received:2016-08-29
Revised:2016-10-14
Published:2017-06-20
Online:2017-05-27
Supported by:摘要:
以阳离子PS微球为模板, 钛酸四丁酯为钛源, 氨水为催化剂制备中空TiO2微球, 通过物理共混法将中空TiO2微球引入到聚丙烯酸酯薄膜中, 考察了中空TiO2微球的空心粒径及用量对复合薄膜光反射性、导热系数及力学性能的影响。结果表明: 中空TiO2微球的引入可显著提升聚丙烯酸酯薄膜的各项性能, 中空TiO2微球的空心粒径和用量对复合薄膜的性能有不同程度的影响, 随着中空TiO2微球空心粒径和用量的增加, 复合薄膜的性能基本呈现先提升后降低的趋势, 其中当中空TiO2微球空心粒径为300 nm、用量为1%时, 所制备的复合薄膜保温性能和力学性能最优。
中图分类号:
鲍 艳, 康巧玲. 中空TiO2微球的制备及其对聚丙烯酸酯薄膜保温性能的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2017, 32(6): 581-586.
BAO Yan, KANG Qiao-Ling. Fabrication of Hollow TiO2 Spheres and Their Effect on Thermal Insulation Property of Polyacrylate Film[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2017, 32(6): 581-586.

图3 中空TiO2微球空心粒径对聚丙烯酸酯薄膜导热系数的影响
Fig. 3 Effect of hollow cavity of hollow TiO2 spheres on thermal conductivity of polyacrylate film(a) Pure polyacrylate film; (b-f) Composite films containing hollow TiO2 spheres with hollow diameter of 150, 200, 300, 400, and 500 nm, respectively
| Sample | SBET/(m2·g-1) | Pore volume / (cm3·g-1) | Pore size / nm |
|---|---|---|---|
| 150 nm | 58.2790 | 0.005458 | 33.2 |
| 500 nm | 50.9239 | 0.002651 | 14.5 |
表1 中空TiO2微球的比表面积、孔体积及平均孔径
Table1 Specific surface area, pore volume, average pore size of hollow TiO2 spheres samples
| Sample | SBET/(m2·g-1) | Pore volume / (cm3·g-1) | Pore size / nm |
|---|---|---|---|
| 150 nm | 58.2790 | 0.005458 | 33.2 |
| 500 nm | 50.9239 | 0.002651 | 14.5 |
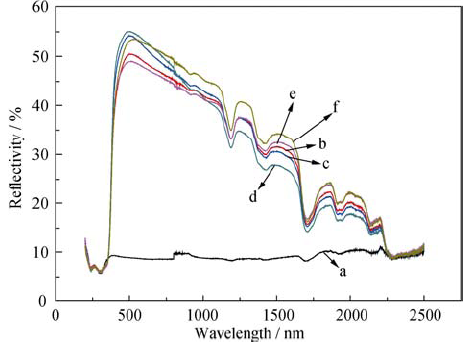
图5 中空TiO2微球空心粒径对聚丙烯酸酯薄膜光反射率的影响
Fig. 5 Effect of hollow cavity of hollow TiO2 spheres on light reflectivity of polyacrylate film(a) Pure polyacrylate film; (b-f) Composite films containing hollow TiO2 spheres with hollow diameter of 150, 200, 300, 400, and 500 nm, respectively

图6 中空TiO2微球空心粒径对聚丙烯酸酯薄膜力学性能的影响
Fig. 6 Effect of hollow cavity of hollow TiO2 spheres on tensile strength and elongation at break of polyacrylate film(a) Pure polyacrylate film; (b-f) Composite films containing hollow TiO2 spheres with hollow diameter of 150, 200, 300, 400, and 500 nm, respectively
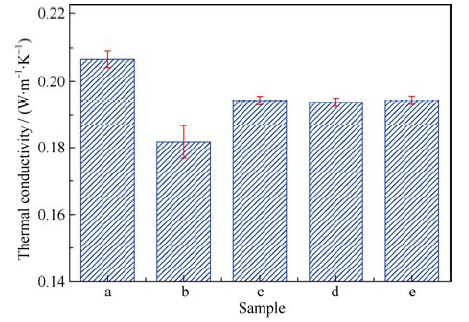
图7 中空TiO2微球用量对聚丙烯酸酯薄膜导热系数的影响
Fig. 7 Effect of hollow TiO2 spheres content on thermal conductivity of polyacrylate film(a) Pure polyacrylate film; (b-e) Composite films containing hollow TiO2 spheres of 1%, 2%, 3% and 4%, respectively

图8 中空TiO2微球用量对聚丙烯酸酯薄膜光反射率的影响
Fig. 8 Effect of hollow TiO2 spheres content on light reflectivity of polyacrylate film(a) Pure polyacrylate film; (b-e) Composite films containing hollow TiO2 spheres of 1%, 2%, 3% and 4%, respectively

图9 中空TiO2微球用量对聚丙烯酸酯薄膜抗张强度与断裂伸长率的影响
Fig. 9 Effect of hollow TiO2 spheres content on tensile strength and elongation at break of polyacrylate film(a) Pure polyacrylate film; (b-e) Composite films containing hollow TiO2 spheres of 1%, 2%, 3% and 4%, respectively
| [1] | YIN L W, BANDO Y, LI M S, et al.Growth of semiconducting GaN hollow spheres and nanotubes with very thin shells via a controllable liquid gallium-gas interface chemical reaction.Small, 2005, 1(11): 1094-1099. |
| [2] | WANG W S, ZHEN L, XU C Y, et al.Aqueous solution synthesis of Cd(OH)2 hollow microspheres via Ostwald ripening and their conversion to CdO hollow microspheres.The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2008, 112(37): 14360-14366. |
| [3] | ZHOU L, ZHAO D, LOU X W.Double-shelled CoMn2O4 hollow microcubes as high-capacity anodes for lithium-ion batteries.Advanced Materials, 2012, 24(6): 745-748. |
| [4] | JOO J B, ZHANG Q, LEE I, et al.Mesoporous anatase titania hollow nanostructures though silica-protected calcination.Advanced Functional Materials, 2012, 22(1): 166-174. |
| [5] | GAO T, JELLE B P, SANDBERG L I C, et al. Monodisperse hollow silica nanospheres for nano insulation materials: synthesis, characterization, and life cycle assessment.ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2013, 5(3): 761-767. |
| [6] | HAN L, LIU R, LI C, et al.Controlled synthesis of double-shelled CeO2 hollow spheres and enzyme-free electrochemical bio-sensing properties for uric acid. Journal of Materials Chemistry, 2012, 22(33): 17079-17085. |
| [7] | ZENG Y, WANG X, WANG H, et al.Multi-shelled titania hollow spheres fabricated by a hard template strategy: enhanced photocatalytic activity.Chemical Communications, 2010, 46(24): 4312-4314. |
| [8] | ZHANG H, DU G, LU W, et al.Porous TiO2 hollow nanospheres: synthesis, characterization and enhanced photocatalytic properties.CrystEngComm, 2012, 14(10): 3793-3801. |
| [9] | XI G, YAN Y, MA Q, et al.Synthesis of multiple-shell WO3 hollow spheres by a binary carbonaceous template route and their applications in visible-light photocatalysis.Chemistry-A European Journal, 2012, 18(44): 13949-13953. |
| [10] | WANG B, CHEN J S, WU H B, et al.Quasiemulsion-templated formation of α-Fe2O3 hollow spheres with enhanced lithium storage properties.Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2011, 133(43): 17146-17148. |
| [11] | YAO Y, MCDOWELL M T, RYU I, et al.Interconnected silicon hollow nanospheres for lithium-ion battery anodes with long cycle life.Nano letters, 2011, 11(7): 2949-2954. |
| [12] | JIN L, XU L, MOREIN C, et al.Titanium containing γ-MnO2 (TM) hollow spheres: one-step synthesis and catalytic activities in Li/air batteries and oxidative chemical reactions.Advanced Functional Materials, 2010, 20(19): 3373-3382. |
| [13] | ZHOUJ K, LV L, YU J, et al.Synthesis of self-organized polycrystalline F-doped TiO2 hollow microspheres and their photocatalytic activity under visible light.The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2008, 112(14): 5316-5321. |
| [14] | CHEN J S, LOU X W D. SnO2-based nanomaterials: synthesis and application in lithium-ion batteries.small, 2013, 9(11): 1877-1893. |
| [15] | CHEN Y, CHEN H R, SHI J L.Construction of homogenous/heterogeneous hollow mesoporous silica nanostructures by silica-etching chemistry: principles, synthesis, and applications.Accounts of Chemical Research, 2013, 47(1): 125-137. |
| [16] | WU D, ZHU F, LI J, et al.Monodisperse TiO2 hierarchical hollow spheres assembled by nanospindles for dye-sensitized solar cells.Journal of Materials Chemistry, 2012, 22(23): 11665-11671. |
| [17] | AGRAWAL M, PICH A, ZAFEIROPOULOS N E, et al.Fabrication of hollow titania microspheres with tailored shell thickness.Colloid and Polymer Science, 2008, 286(5): 593-601. |
| [18] | ZHANG K, ZHANG X, CHEN H, et al.Hollow titania spheres with movable silica spheres inside.Langmuir, 2004, 20(26): 11312-11314. |
| [19] | LI Y, KUNITAKE T, FUJIKAWA S.Efficient fabrication and enhanced photocatalytic activities of 3D-ordered films of titania hollow spheres.The Journal of Physical Chemistry B, 2006, 110(26): 13000-13004. |
| [20] | LI H, HA C S, KIM I.Facile fabrication of hollow silica and titania microspheres using plasma-treated polystyrene spheres as sacrificial templates.Langmuir, 2008, 24(19): 10552-10556. |
| [21] | LI X, XIONG Y, LI Z, et al.Large-scale fabrication of TiO2 hierarchical hollow spheres.Inorganic Chemistry, 2006, 45(9): 3493-3495. |
| [22] | NAKASHIMA T, KIMIZUKA N.Interfacial synthesis of hollow TiO2 microspheres in ionic liquids.Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2003, 125(21): 6386-6387. |
| [23] | BALA H, YU Y, ZHANG Y.Synthesis and photocatalytic oxidation properties of titania hollow spheres.Materials Letters, 2008, 62(14): 2070-2073. |
| [24] | SHANG S, JOAO X, CHEN D.Template-free fabrication of TiO2 hollow spheres and their photocatalytic properties.ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2012, 4(2): 860-865. |
| [25] | REN L, LI Y, HOU J, et al.Preparation and enhanced photocatalytic activity of TiO2 nanocrystals with internal pores.ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2014, 6(3): 1608-1615. |
| [26] | LI D, QIN Q, DUAN X, et al.General one-pot template-free hydrothermal method to metal oxide hollow spheres and their photocatalytic activities and lithium storage properties.ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2013, 5(18): 9095-9100. |
| [27] | ZHUANG Y, SUN J, GUAN M.Template free preparation of TiO2/C core-shell hollow sphere for high performance photocatalysis.Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2016, 662: 84-88. |
| [28] | VAZ F A S, DE CASTRO P M, MOLINA C, et al. External polyacrylate-coating as alternative material for preparation of photopolymerized Sol-Gel monolithic column.Talanta, 2008, 76(1): 226-229. |
| [29] | BAO Y, SHI C, YANG Y, et al.Effect of hollow silica spheres on water vapor permeability of polyacrylate film.RSC Advances, 2015, 5(15): 11485-11493. |
| [30] | BAO Y, YANG Y, MA J.Fabrication of monodisperse hollow silica spheres and effect on water vapor permeability of polyacrylate membrane.Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2013, 407: 155-163. |
| [31] | YUE Q, LI Y, KONG M, et al.Ultralow density, hollow silica foams produced through interfacial reaction and their exceptional properties for environmental and energy applications.Journal of Materials Chemistry, 2011, 21(32): 12041-12046. |
| [32] | LI B, YUANG J, AN Z, et al.Effect of microstructure and physical parameters of hollow glass microsphere on insulation performance. Materials Letters, 2011, 65(12): 1992-1994. |
| [33] | QIAN BO ZHANG, ZHU JIAN FANG.Technology progress of thermal insulation materials of building energy efficiency.Journal of Building Energy Efficiency, 2009, 37(2): 56-60. |
| [34] | TACHIBANA Y, HARA K, SAYAMA K, et al.Quantitative analysis of light-harvesting efficiency and electron-transfer yield in ruthenium-dye-sensitized nanocrystalline TiO2 solar cells.Chemistry of Materials, 2002, 14(6): 2527-2535. |
| [35] | T LI H, BIAN Z, ZHU J, et al. Mesoporous titania spheres with tunable chamber stucture and enhanced photocatalytic activity. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2007, 129(27): 8406-8407. |
| [36] | LEE J, HWANG S H, YUN J, et al.Fabrication of SiO2/TiO2 double-shelled hollow nanospheres with controllable size via Sol-Gel reaction and sonication-mediated etching.ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2014, 6(17): 15420-15426. |
| [37] | BAO Y, LI MIAO, MA J.The effect of hollow SiO2 spheres on thermal insulation property of polyacrylate film.Journal of Functional Materials, 2016, 47(7): 7022-7027. |
| [38] | LEI ZHUO YAN, WANG ZHI, FAN HENG BING.Effect of B2O3 doping and phosphate impregnation on oxidation resistance and mechanical properties of mesocarbon microbead composites.Journal of Inorganic Materials. 2015, 30(7): 769-773. |
| [39] | ZHU PING, SUI SHU YING, LI JING.Study on performance of Nano-Far-Infrared PET Fiber.Nannoscience&Nanotechnology. 2007, 4(4): 17-21. |
| [40] | WANG F, LIANG J, TANG Q, et al.Preparation and performance of thermal insulation energy saving coating materials for exterior wall.Journal of Nanoscience and Nanotechnology, 2014, 14(5): 3861-3867. |
| [1] | 陈义, 邱海鹏, 陈明伟, 徐昊, 崔恒. SiC/SiC复合材料基体硼改性方法及其力学性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(5): 504-510. |
| [2] | 崔宁, 张玉新, 王鲁杰, 李彤阳, 于源, 汤华国, 乔竹辉. (TiVNbMoW)Cx高熵陶瓷的单相形成过程与碳空位调控[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(5): 511-520. |
| [3] | 李紫薇, 弓伟露, 崔海峰, 叶丽, 韩伟健, 赵彤. 前驱体法制备(Zr, Hf, Nb, Ta, W)C-SiC复相陶瓷及性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(3): 271-280. |
| [4] | 高晨光, 孙晓亮, 陈君, 李达鑫, 陈庆庆, 贾德昌, 周玉. 基于湿法纺丝技术的SiBCN-rGO陶瓷纤维的组织结构、力学和吸波性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(3): 290-296. |
| [5] | 穆浩洁, 张源江, 喻彬, 付秀梅, 周世斌, 李晓东. ZrO2掺杂Y2O3-MgO纳米复相陶瓷的制备及性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(3): 281-289. |
| [6] | 李伟, 许志明, 苟燕子, 尹森虎, 余艺平, 王松. SiC纤维烧结陶瓷的制备及其性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(2): 177-183. |
| [7] | 范武刚, 曹雄, 周响, 李玲, 赵冠楠, 张兆泉. 8YSZ陶瓷在模拟压水堆水环境中的耐腐蚀性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(7): 803-809. |
| [8] | 王伟明, 王为得, 粟毅, 马青松, 姚冬旭, 曾宇平. 以非氧化物为烧结助剂制备高导热氮化硅陶瓷的研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(6): 634-646. |
| [9] | 孙海洋, 季伟, 王为民, 傅正义. TiB-Ti周期序构复合材料设计、制备及性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(6): 662-670. |
| [10] | 蔡飞燕, 倪德伟, 董绍明. 高熵碳化物超高温陶瓷的研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(6): 591-608. |
| [11] | 刘国昂, 王海龙, 方成, 黄飞龙, 杨欢. B4C含量对(Ti0.25Zr0.25Hf0.25Ta0.25)B2-B4C陶瓷力学性能及抗氧化性能的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(6): 697-706. |
| [12] | 粟毅, 史扬帆, 贾成兰, 迟蓬涛, 高扬, 马青松, 陈思安. 浆料浸渍辅助PIP工艺制备C/HfC-SiC复合材料的微观结构及性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(6): 726-732. |
| [13] | 李雷, 程群峰. 高性能MXenes纳米复合材料研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(2): 153-161. |
| [14] | 刘艳艳, 谢曦, 刘增乾, 张哲峰. MAX相陶瓷增强金属基复合材料: 制备、性能与仿生设计[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(2): 145-152. |
| [15] | 王博, 蔡德龙, 朱启帅, 李达鑫, 杨治华, 段小明, 李雅楠, 王轩, 贾德昌, 周玉. SrAl2Si2O8增强BN陶瓷的力学性能及抗热震性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(10): 1182-1188. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||