|
|
Progress in Preparation of Patterned Sapphire Substrate for GaN-based Light Emitting Diodes
CUI Lin, WANG Gui-Gen, ZHANG Hua-Yu, ZHOU Fu-Qiang, HAN Jie-Cai
2012 Vol. 27 (9): 897–905
 Abstract
Abstract(
3907 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(717KB)(
2571
)
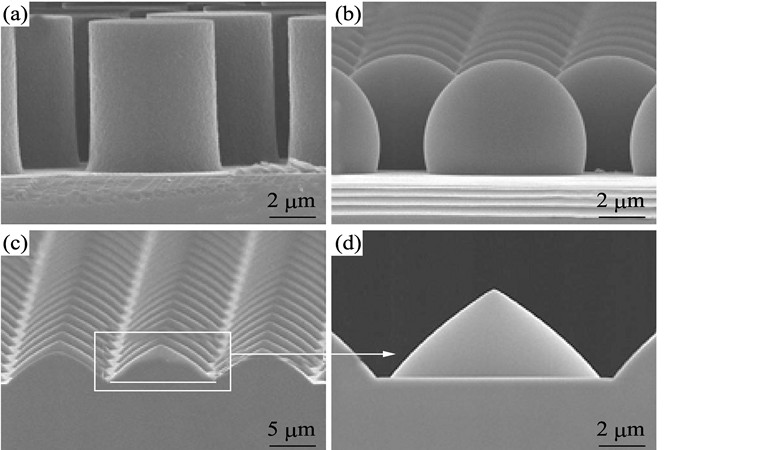
GaN-based light emitting diodes are extensively used for light emitting diodes in the green to ultraviolet (UV) wavelength region and have already been widely used in traffic signals, outdoor displays, full-color displays and back lighting in liquid-crystal displays. Although GaN-based light emitting diodes are commercially available, it is still difficult to manufacture highly efficient GaN-based light emitting diodes due to the high dislocation density and the low light extraction efficiency. Patterned sapphire substrates for GaN-based light-emitting diodes have attracted much interest in recent years because it can not only reduce the threading dislocation density of epitaxial GaN films, but also improve the light extraction efficiency of GaN-based light-emitting diodes. A comprehensive review is presented on the mechanisms responding for performance enhancement of GaN-based light emitting diodes on patterned sapphire substrates, methods of preparing patterned sapphire substrates and pattern-size of patterned sapphire substrates. What is more, improved performance of GaN-based light-emitting diodes on patterned sapphire substrates prepared by different methods and pattern-size are further discussed in detail. In view of the existing problems, the prospects for future development of patterned sapphire substrates are also proposed.
|
|
|
Manufacturing and Characterization of Buried Optical Waveguide Stack in Glass Substrate
ZHENG Bin, HAO Yin-Lei, LI Yu-Bo, YANG Jian-Yi, JIANG Xiao-Qing, ZHOU Qiang, WANG Ming-Hua
2012 Vol. 27 (9): 906–910
 Abstract
Abstract(
1965 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(386KB)(
1116
)
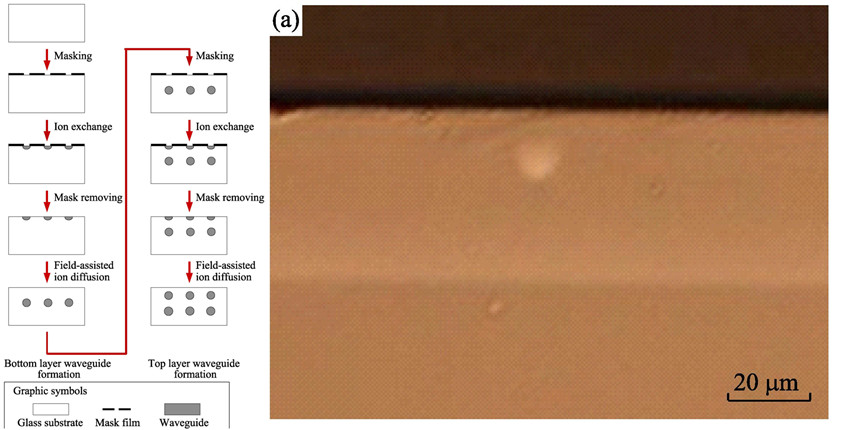
On silicate optical glass substrate, buried optical waveguide stacks were obtained. The stacks were composed of two layers of buried optical channel waveguide at different depth beneath the glass substrate surface, and each layer was manufactured by thermal Ag+/Na+ ion-exchange and field-assisted ion-diffusion. Microstructure of the optical waveguide chips was observed with optical microscope, and insertion loss of each layer in waveguide stacks is measured. Results show that the buried waveguide stack is composed of two layers of buried waveguide with their core center located at 14 μm and 35 μm, respectively. Beneath the glass surface, core dimension of top layer and bottom layer waveguide are 12 μm×7 μm and 9 μm×8 μm, respectively. Waveguides in both layers are single mode at operating wavelength of 1.55 μm. There is no directional coupling observed between waveguides at different layers. Insertion loss characterization indicates that propagation loss of both layers in the stack is 0.12 dB/cm, and coupling losses with single mode fiber are 0.78 dB/facet and 0.73 dB/facet, for top and bottom layer waveguides, respectively. The analysis suggests that this kind of optical waveguide stack is promising in application of high density integration of glass-based optical chip.
|
|
|
Fabrication of Dense La0.7Ca0.3Cr0.97O3−δ Interconnect Membrane on Novel SOFC Composite Support by Co-firing
WANG Song-Lin, FENG Yi, WANG Dong-Sheng, MENG Guang-Yao
2012 Vol. 27 (9): 911–916
 Abstract
Abstract(
2210 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(589KB)(
1460
)
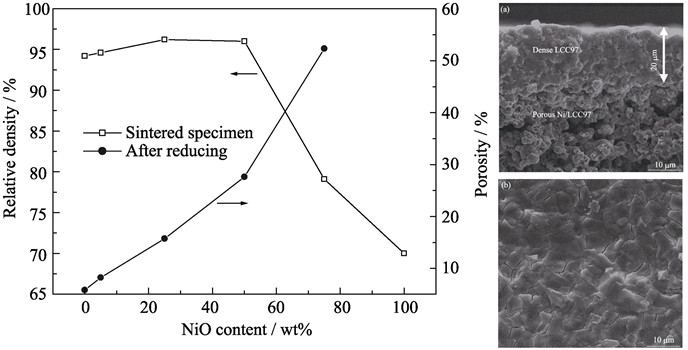
Developing cost-effective methods to prepare dense ceramic interconnect membrane for tubular solid oxide fuel cell (SOFC) stacks is currently considered as a major technical obstacle. In order to improve the co-firing compatibility of SOFC support with both LaCrO3-based interconnects and Ni-based anodes, double-phase composite NiO/La0.7Ca0.3Cr0.97O3−δ (LCC97) was designed and then examined as novel SOFC support. Sintering character, microstructure, porosity, electrical conductivity and thermal expansion coefficient of the NiO/LCC97 composites were investigated in detail as a function of NiO content (5wt%, 25wt%, 50wt% and 75wt%). Results indicate that the interconnect material LCC97has desirable chemical and sintering compatibility with NiO. The NiO/LCC97 composite with weight ratio of 1:1 has excellent overall performance which can sufficiently meet the requirements for tubular SOFC support. By using a simple and cost-effective drop-coating/co-firing process, dense LCC97 interconnect thin membrane is successfully prepared on the novel NiO/LCC97(1:1) composite support. This work provides a simple technical solution for dense LaCrO3-based interconnect fabrication for tubular SOFC stacks.
|
|
|
Fabrication of Au/SnO2 Nanocomposites Based on 3D Structures of Butterfly Wing Scales and Research on Its SERS Effects
LIU Bo-Yang, ZHANG Wang, HE Zhao-Wen, ZHANG Di
2012 Vol. 27 (9): 917–922
 Abstract
Abstract(
2838 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(507KB)(
1362
)
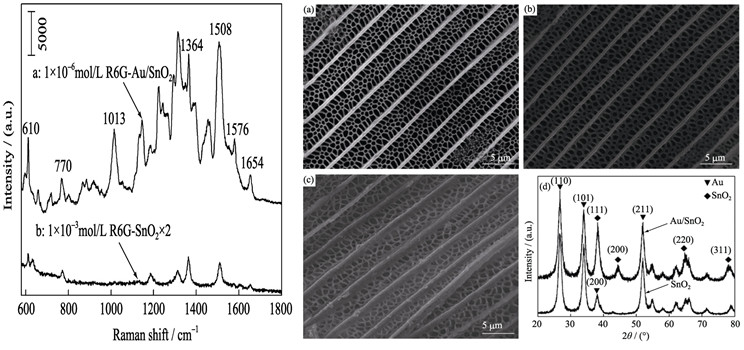
Scales from fore wings ofPapilio paris was used as templates, by ringing the original fore wings in the precursor and treatment by calcinations, SnO2 (rutile) which inherited the 3D quasi-periodic structures of original wing scale was fabricated. After that, Au nanoparticles were incorporated in the system of as-prepared SnO2 to form the Au/SnO2 nanocomposites. XRD, SEM and TEM were carried out to investigate the morphologies, structures and elemental composition. For measuring Surface-enhanced Raman Scattering (SERS) effects of the Au/SnO2 substrate, R6G was used as analyte molecules. By analyzing morphologies of this nanocomposites and UV-Vis DRS spectra of different substrates, mechanisms of SERS effects for this Au/SnO2 nanocomposites substrate were analyzed. The three-dimensional nanostructures of the substrate provide large quantities of Raman ‘hot spots’, meanwhile, the SnO2 and Au make synergetic contribution to the enhancement effects. The satisfying SERS properties combined with low synthesis costs show the prospective application possibilities of this novel SERS substrate.
|
|
|
Preparation and Gas Separation Properties of Carbon/Carbon Nanotubes Hybrid Membranes Derived from PMDA-ODA Polyimide
SONG Cheng-Wen, JIANG Da-Wei, LI Lin, SUN Mei-Yue, WANG Tong-Hua
2012 Vol. 27 (9): 923–927
 Abstract
Abstract(
2601 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(582KB)(
1261
)
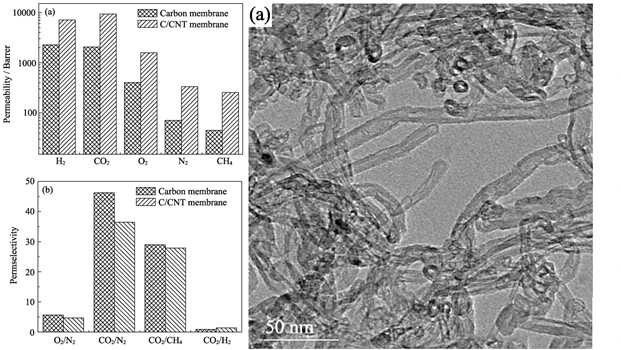
A convenient and effective strategy was used to develop a novel carbon/carbon nanotubes (C/CNT) hybrid membrane by incorporating multi-walled carbon nanotubes (MWNT) into PMDA-ODA polyimide precursor through controlled pyrolysis process at 600℃. Transmission electron microscope, X-ray diffraction and gas permeation experiments were employed to investigate the microstructural characteristics and gas separation performance of hybrid carbon membrane. Results show that the as-prepared C/CNT hybrid membrane has excellent gas (H2, CO2, O2, N2 and CH4) separation properties as compared with pure carbon membrane, and the O2 permeability of hybrid carbon membrane increases by nearly 4 times reaching 1576 Barrer, while the O2/N2 permselectivity decreasing by only 17%. It is believed that carbon membrane doped by MWNT can make effective use of the interfacial gaps formed between MWNT and carbon matrix to reconstruct the pore structure of hybrid carbon membrane, which helps to increase the gas diffusion ability and further improve the gas permeability of hybrid carbon membrane.
|
|
|
Influence of Surface States on Gas Response Properties of Pt/TiO2
ZHANG Mao-Lin, YUAN Zhan-Heng, SONG Jian-Ping, ZHENG Che
2012 Vol. 27 (9): 928–932
 Abstract
Abstract(
1897 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(579KB)(
1285
)
Pt/TiO2 thick film gas sensors were modified by dipping method in H2PtCl6 contained solution. In order to get different Pt/TiO2 surface states, the thick films were treated with different process. Microstructural and morphological characteristics were investigated by XRD and SEM. The resistance-oxygen partial pressure relationship was used to calculate activation energy (E) of this film. Steady-state resistance and dynamic response of the sensor exposed to H2/O2 were tested, separately. The results indicated that the steady-state resistance which affected by “spill-over” effect arose from the Pt distribution states. However, the response time was associated with the activation energy (E). Sensors with lower activation energy exhibited a faster rate of response when the magnitude of response was approximately uniform.
|
|
|
Synthesis of PbS Intercalated K4Nb6O17 Composite and Its Photocatalytic Activity for Hydrogen Production
CUI Wen-Quan, LIU Yan-Fei, HU Jin-Shan, LIU Li, LIANG Ying-Hua
2012 Vol. 27 (9): 933–938
 Abstract
Abstract(
2145 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(456KB)(
1438
)
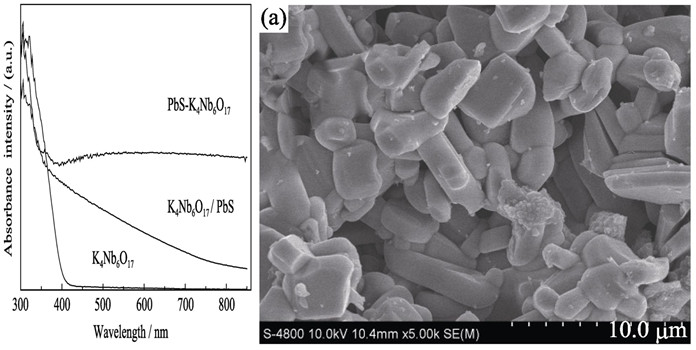
Thelayered compound K4Nb6O17 was prepared via high temperature solid reaction, and PbS intercalated K4Nb6O17 (designated as K4Nb6O17/PbS) photocatalyst was synthesized via direct ion exchange, alkylamines intercalation and sulfurization procedures. The as-prepared samples were characterized by X-ray diffraction (XRD), scanning electron microscope (SEM), ultraviolet-visible diffuse reflection spectra (UV-Vis) and photoluminescence measurement (PL), energy dispersive X-ray detector (EDS) and X-ray fluorescence spectrometer (XRF). The photocatalytic performance of these catalysts for hydrogen production was also investigated in the presence of Na2S and Na2SO3 sacrificial reagents. The absorption edge of K4Nb6O17 shifted to visible light region after the intercalation of PbS. K4Nb6O17/PbS photocatalysts exhibit higher activities for photocatalytic hydrogen production under both UV light and visible light irradiation, and the amounts of hydrogen produced are 123.94 mmol/(g cat) and 0.66 mmol/(g cat) after 3 h irradiation, respectively. The mechanism of charge separation is also discussed.
|
|
|
Surface Structure and Electrochemical Properties of MoO3/CeO2 Composite Catalysts by Hydrothermal Method
HUANG Hui, GUO Zhong-Cheng
2012 Vol. 27 (9): 939–944
 Abstract
Abstract(
2448 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(478KB)(
1820
)
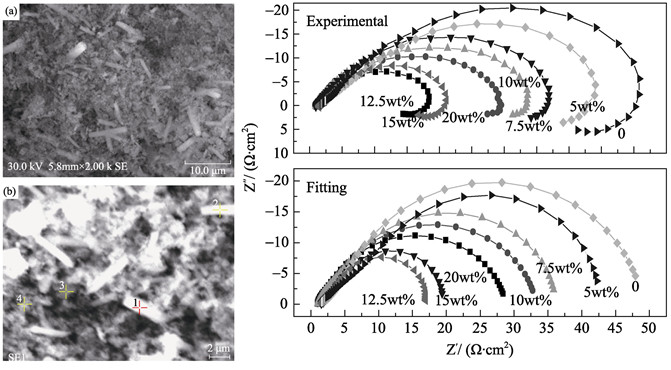
A series of molybdic oxide/ceria (MoO3/CeO2) composite catalysts with different MoO3 concentrations (0, 5wt%, 7.5wt%, 10wt%, 12.5wt%, 15wt% and 20wt%) were prepared by hydrolysis of ammonium molybdate and the supports of CeO2 at 70℃. The crystal structure, the morphology and interaction between MoO3 and CeO2 on the surface of the prepared MoO3/CeO2 composite catalysts were characterized by X-ray diffraction (XRD), Fourier transform infrared spectroscope (FT-IR), X-ray photoelectron spectrometer (XPS), scanning electron microscope (SEM) and energy dispersive spectrometer (EDS), respectively. The catalytic activities of the prepared catalysts were evaluated by the electrolysis sulfuric acid solution. Results show that the catalytic activity of MoO3/CeO2 composite catalysts are superior compared with that of pure CeO2, and the optimal concentration of MoO3 is12.5wt%. The MoO3 content threshold value of composite catalysts is between 12.5wt% and 15wt%, and it is identified that the Mo-O-Ce bond forms at the interface of MoO3 and CeO2 in the composite catalysts. Moreover, more surface Mo-O-Ce bond over the MoO3/CeO2 composite catalysts will further benefit the improvement of the catalytic activity.
|
|
|
Synthesis and Properties of Visible-light Photocatalytic Bi2WO6 via Microemulsion- assisted Hydrothermal Method
LAI Shu-Ting, ZHANG Peng, ZHOU Wu-Yi, XIE Zhen-Hua, YANG Zhuo-Hong
2012 Vol. 27 (9): 945–950
 Abstract
Abstract(
2605 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(491KB)(
2297
)
The novel Bi2WO6 and Fe3+/Bi2WO6 photocatalysts were fabricated separately via a reverse microemulsion method. The effect factors including synthesis temperature, pH value, molar ratio of water to surfactant (ω) and Fe3+ doping on the structure, morphologies and photocatalysis performance of photocatalysts were studied in detail. These results show that Bi2WO6 possesses a high degree of crystallinity of nano-spherical structure with the size of 15–25 nm. The photodegradation rate of methylene blue (MB) is 93.8% as the Bi2WO6 photocatalyst was synthesized at 150℃. The results reveal that the photodegradation rate of MB reaches 97.8% as ω is 27. It’s found that the photodegradation rate of MB for 1.03% Fe-doped Bi2WO6 sample has increased to 90.2%, which is two times higher than that of pure Bi2WO6.
|
|
|
Simulation of Oxygen Permeability of Dual-phase Hollow Fiber Membrane
YANG Chun-Li, XU Qi-Ming, GONG Ming, LIU Wei
2012 Vol. 27 (9): 951–955
 Abstract
Abstract(
2061 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(458KB)(
1260
)
Dense Bi1.5Y0.3Sm0.2O3 (BYS)-La0.8Sr0.2MnO3–d(LSM) hollow fiber membrane was fabricated by the combined phase inversion/sintering technique. The hollow fiber possesses an asymmetric structure: a finger-like porous structure near the inner surface and a dense layer near the outer surface. The outlet oxygen content is related to the oxygen partial pressure on the core and shell side and the length of the hollow fiber. Because the oxygen partial pressure on the permeated side increases along the axis, the hollow fiber is evenly divided into n segments. The oxygen permeation process is simulated by a plug flow model in combination with the Wagner theory. The simulation results are consistent with the measured results, which is a good guide for estimating oxygen production capacity of membrane components.
|
|
|
Studies on H2O-based Atomic Layer Deposition of Al2O3 Dielectric on Pristine Graphene
ZHANG You-Wei, WAN Li, CHENG Xin-Hong, WANG Zhong-Jian, XIA Chao, CAO Duo, JIA Ting-Ting, YU Yue-Hui
2012 Vol. 27 (9): 956–960
 Abstract
Abstract(
3060 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(487KB)(
2277
)
Al2O3 films were deposited directly onto the surface of graphene by H2O-based atomic layer deposition (ALD) method, where physically absorbed water molecules acted as oxidant and the growing temperature changed from 60℃ to 260℃. The morphology of Al2O3 films was characterized by atomic force microscope (AFM). AFM images revealed that the distribution of physically adsorbed H2O molecules on the surface of graphene decided the morphology of Al2O3 film, and conformal and uniform Al2O3 film was achieved with the root mean square (RMS) roughness of 0.26 nm when the growing temperature was around 100-130℃. X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) analysis showed that the O/Al ratio was close to stoichiometric condition of 1.5. Raman spectroscopy analysis revealed that H2O-based ALD process did not destroy the structure of graphene. The growing temperature in the H2O-based ALD process had significant impact on the initial nucleation and the growth of Al2O3 films.
|
|
|
Fabrication of TiB2/TiC Composites by Spark Plasma Sintering
MA Zhi-Qiang, JI Ying-Hu, WANG Lian-Jun
2012 Vol. 27 (9): 961–964
 Abstract
Abstract(
2373 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(536KB)(
1605
)
TiB2/TiC composites were in situ fabricated through spark plasma sintering (SPS) technique using Ti and B4C powders as starting materials. The phase constituent of the samples was analyzed by X-ray diffraction techniques and microstructures were observed by scanning electron microscope. The Vickers hardness, fracture toughness and MSP strength at room temperature was measured by indentation method and Modified Small Punch (MSP) test. The results showed that the TiB2/TiC composite fabricated by one-step sintering (sintering at 1550℃ for 6 min) has an average grain size greater than 1 μm with MSP strength of 844 MPa. While the TiB2/TiC composite with an average grain size of about 200 nm could be fabricated by two-step sintering (at higher sintering temperature of 1550℃ and lower holding temperature of 1450℃) and its MSP strength reached as high as 1095 MPa.
|
|
|
Effects of Vickers Cracks on the Mechanical Properties of Solid-phase-sintered Silicon Carbide Ceramics
YANG Xiao, LIU Xue-Jian, HUANG Zheng-Ren, LIU Gui-Ling, YAO Xiu-Min
2012 Vol. 27 (9): 965–969
 Abstract
Abstract(
2284 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(434KB)(
1638
)
In order to study the effects of Vickers cracks on the mechanical properties of solid-phase-sintered silicon carbide (SSiC for short) ceramics, the indentation cracks and the crack profiles were observed after loading 0.1–100 N loads on the SSiC samples by SEM. The critical indentation load for Vickers crack initiation in SSiC ceramics lies between 0.1 N and 0.2 N. Indentations by loads lower than 0.5 N have limited influence on bending strength. And if the indentation loads is higher than 10 N, the obtained hardness floats around 24.2 GPa and the cracks are half-coin type. The proper Vickers indentation load range for SSiC ceramic hardness and toughness tests are determined to be 10 N or above.
|
|
|
Microstructure and Tribological Properties of Ti5Si3 Coating In-situ Synthesized on Titanium Substrate by Laser Cladding
GUO Chun, ZHOU Jian-Song, CHEN Jian-Min
2012 Vol. 27 (9): 970–976
 Abstract
Abstract(
2098 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(768KB)(
1955
)
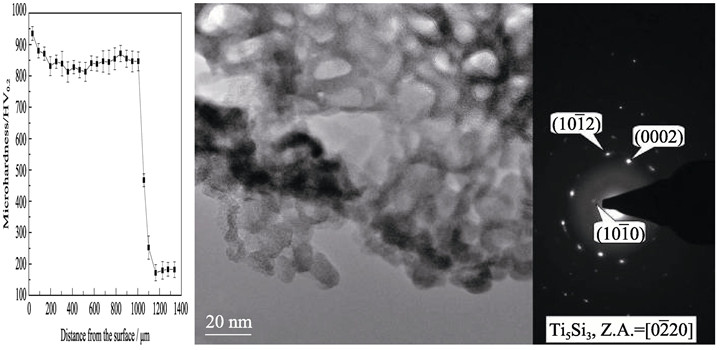
Using silicon powder as the precursor to improve the wear resistance of Ti5Si3 coating was in situ successfully synthesized on Ti substrate by laser cladding. Friction and wear behavior of Ti5Si3 coatings under different normal loads and sliding speeds wear test conditions were evaluated using a UMT-2MT friction and wear tester. It is found that the prepared coating is mainly composed of Ti5Si3 and Ti phases. The high resolution transmission electron microscopy results confirm further the existence of Ti5Si3 compound in the prepared coating. Ti5Si3 coating has spherical and block-like microstructure. The Ti5Si3 coating shows a high average hardness of approximately 840 HV0.2, which is about 4.4 times as that of Ti substrate. Tribological properties of the prepared Ti5Si3 coating were systematically evaluated. It is found that the Ti5Si3 coating can improve the wear resistance of Ti. The wear mechanism of Ti5Si3 coating is abrasive and adhesive wear when sliding against GCr15 steel ball under all wear conditions.
|
|
|
Bio-filler from Mussel Shell: Preparation and Its Effects on Polypropylene Composites Properties
LI Hai-Yan, TAN Ye-Qiang, ZHANG Lu, CHEN Tao, SONG Yi-Hu, YE Ying, XIA Mei-Sheng
2012 Vol. 27 (9): 977–983
 Abstract
Abstract(
2234 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(662KB)(
1952
)
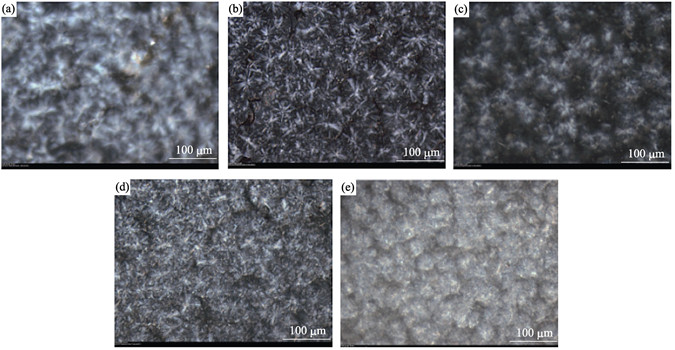
Waste mussel shell stacking with a significant odor and toxicity which are hazardous to human constitutes a serious environmental hazard. For utilization of waste mussel shell resource, granule of mussel shell (YBCC) was prepared from waste mussel shell by removing cuticle, crushing, grinding and shearing emulsification and was introduced as a filler to reinforce polypropylene (PP). The characterization results of YBCC show that the mainly composition of YBCC is aragonite (CaCO3) platelets and the particle size distribution range of YBCC powder is from 40 nm to 500 nm, the proportion of organic components of YBCC is about 2.04wt% and YBCC has a good thermal stability. The mechanical behavior of PP/YBCC composite shows a higher yield strain, yield strength, tensile strength and elongation at break than traditional commercial calcium carbonate (CMCC) filled PP. Yield strength of PP/YBCC composite with 3wt% YBCC is improved by about 11.1%. A small content (about 1wt%) of YBCC can promote the heterogeneous nucleation for PP crystallization and the formation β-crystalline PP. Using mussel shell for producing bio-filler is valuable for industrial production and practical application as fillers for reinforcing polymers.
|
|
|
Synthesis and Characterization of Pr-ZrSiO4 Pigment by a Two-step Method
CAO Kun-Wu, GUO Xu-Hong, GAO Yan-Feng, LUO Hong-Jie
2012 Vol. 27 (9): 984–990
 Abstract
Abstract(
2477 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(559KB)(
1590
)
Nanoscale praseodymium-doped zircon yellowish pigment was prepared by a two-step new method using ZrOCl2•8H2O, Na2SiO3•9H2O and Pr6O11 as raw materials. Intermediate nanopowders were hydrothermally synthesized firstly, then these intermediate powders were calcined at high temperatures to produce nanoscale Pr-zircon yellowish pigment. The products were characterized by XRD, TEM, SEM, reflectance spectra and the CIE L*a*b* parameters. The pH of hydrothermal solution, the hydrothermal temperature and the heat treatment temperature are main factors that influenced the quality of pigment. Low pH is favorable for decreasing the calcination temperatures and producing the pigment with good dispersion and homogeneous sizes. The product with best pigment performance is obtained at the reaction conditions as follows, pH=3.5 of hydrothermal solution, hydrothermal temperature of 220℃ and heat treatment temperature of 900℃.
|
|
|
Solid-state Reaction Preparation and Sintering Behavior of MgAl2O4 Nanopowders
SU Xing-Hua, LI Jian-Gong, ZHOU Zhen-Jun
2012 Vol. 27 (9): 991–996
 Abstract
Abstract(
2402 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(846KB)(
1683
)
Well-crystallized MgAl2O4 nanopowders were prepared by calcining a powder mixture of Al(OH)3 and MgSO4 at 800℃, and then washing with water. The effect of Mg/Al atomic ratios on the particle sizes and agglomeration degrees, and sintering behavior of MgAl2O4 nanopowders were studied by differential thermal and thermogravimetric analysis (DSC/TG), X-ray diffraction (XRD), scanning electron microscope (SEM) and transmission electron microscope (TEM). The obtained MgAl2O4 nanopowders have an average particle size of 12 nm, a narrow size distribution, and weak agglomeration. The formation of MgAl2O4 can be attributed to a solid-state reaction between γ-Al2O3 and MgSO4. Besides, these MgAl2O4 nanopowders own an excellent sinterability, e.g., a relative density of 95% can be achieved after sintered at 1450℃ for 1 h.
|
|
|
LiFePO4/C Nanocomposites Synthesized from Fe2O3 by a Hydrothermal Reaction-calcination Process and Their Electrochemical Performance
DENG Hong-Gui, JIN Shuang-Ling, HE Xing, ZHAN Liang, QIAO Wen-Ming, LING Li-Cheng
2012 Vol. 27 (9): 997–1002
 Abstract
Abstract(
4013 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(506KB)(
1402
)
LiFePO4 nanoparticles coated with a carbon layer were synthesized by a hydrothermal reaction-calcination process, using Fe2O3 as an iron source and ascorbic acid as carbon source. The amount of ascorbic acid have an effect on the structure, phase and carbon amount of the final product. With 1 g ascorbic acid used in the reaction, the particle sizes of synthesized LiFePO4/C nanocomposites are in a range of 220–280 nm. Using as the cathode materials for the lithium-ion batteries, the as-prepared material shows high capacity and good cycle stability (159 mAh/g at 0.1C over 500 cycles), as well as good rate capability.
|
|
|
One-step Self Assemble of Cu-TiO2 Heterogeneous Nanoparticles Using a Soft Template
ZHAO Peng-Jun, WU Rong, HOU Juan, CHANG Ai-Min, GUAN Fang, ZHANG Bo
2012 Vol. 27 (9): 1003–1008
 Abstract
Abstract(
4395 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(435KB)(
1713
)
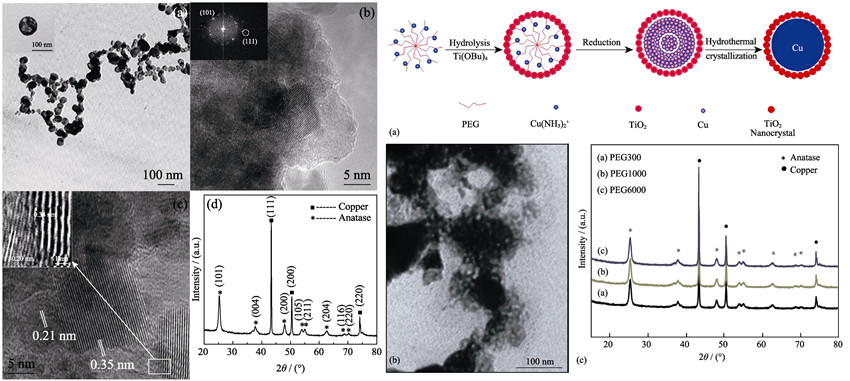
Cu-TiO2 heterostructure nanoparticles were successfully synthesized via a novel one-step self-assemble hydrothermal method using polyethylene glycol as the soft template. The nanospheres were characterized in light of the chemical composition and morphology using X-ray diffraction (XRD) and transmission electron microscope (TEM), respectively. The products are composed of cubic copper and anatase TiO2. Interfaces between Cu (101) and TiO2 (111) were observed by HRTEM. In addition, the nanoparticles size could be controlled by adjusting the polymerization degrees of PEG. The accommodations of the particle sizes were mainly caused by Cu nanospheres rather than TiO2. A possible synthetic mechanism which interprets the formation of Cu-TiO2 heterogeneous nanoparticles could be ascribed to the hydrogen bonds between Cu(NH3)2+ and PEG. UV-Vis absorption spectra indicated that the prepared product has strong absorbency in the visible region. Therefore, the unique interface nanomaterial could be used as a potential class of the materials platform as visible-light-driven photocatalyst and electrode on enhancing the photoelectric properties of solar cells.
|
|