|
|
High-speed Homoepitaxial Growth of 4H-SiC
ZHU Ming-Xing, SHI Biao, CHEN Yi, LIU Xue-Chao, SHI Er-Wei
2012 Vol. 27 (8): 785–789
 Abstract
Abstract(
3146 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(435KB)(
2345
)
Homoepitaxial growth of 4H-SiC at 1400℃ was explored. The growth rate, surface morphology and defects of the epi-layers were studied. Raman characterization combined with KOH etching indicated that the epi-layers were 4H-SiC single crystal without 3C-SiC polycrystalline. In addition, low growth rate and high C/Si ratio were beneficial to convert the basal plane dislocations (BPDs) in substrate surface to threading edge dislocations (TEDs) at the sub-epi interface. Furthermore, the low growth rate was also favorable to reduce the defects generated during the growth process. With the growth rate increasing, the surface triangle defects and dislocations of the epilayers significantly increased. Most of these defects and dislocations were considered to be generated at the sub-epi interface at the beginning of the growth. By optimizing the interface layer at initial stage, a smooth transition from surface etching to epi-layer deposition can be achieved and the surface morphological defects and crystal defects were greatly reduced at high growth rate.
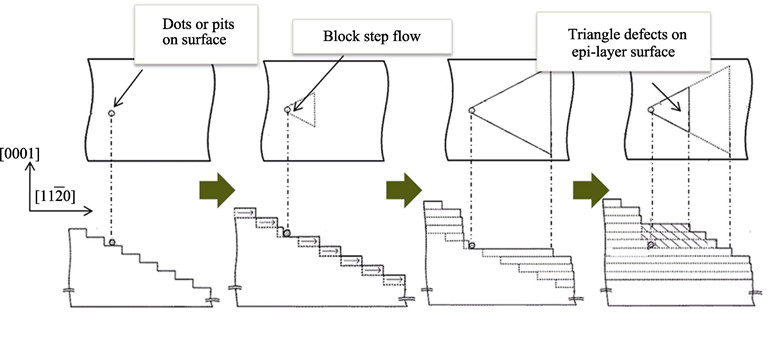
|
|
|
Influence of Free-space Volume in Ampoule on Defects of CdZnTe Crystal Grown by Bridgman Method
LI Hui, MIN Jia-Hua, WANG Lin-Jun, XIA Yi-Ben, ZHANG Ji-Jun, YE Bang-Jiao
2012 Vol. 27 (8): 790–794
 Abstract
Abstract(
2297 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(338KB)(
1875
)
CdZnTe crystal was grown by Bridgman method. The relationship between the free-space volume in the ampoule and the defects in CZT, such as Te inclusion and Cd vacancy, was studied by IR transmission microscopy and positron annihilation technique (PAT). With the decrease of the free-space volume in the ampoule, the density reduced from 6.67×104/cm2 to 2.36×103/cm2 with the reduction of Te inclusions. The average positron lifetime decreased from 325.4 ps to 323.4 ps with the decrease of the free-space volume, indicating a reduction of Cd vacancies. The improvement of IR transmittance and resistivity of CZT further demonstrates that lowing the free-space volume in the ampoule can effectively depress the defects in CZT crystal.
|
|
|
Preparation and Characterization of Cu Coated SiC Composite Powders by in-situ Chemical Deposition
SHI Jin-Gang, YAO Hui, CHEN Ming-Hai, LIU Ning, LI Qing-Wen
2012 Vol. 27 (8): 795–799
 Abstract
Abstract(
2586 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(558KB)(
1813
)
A facile one-step in-situ chemical deposition method was introduced to synthesize Cu-Coated SiC composite powders, using [Cu(NH3)4]2+ ions as copper source and N2H4·H2O as reductant, respectively. Scanning electronic microscope (SEM), X-Ray diffraction (XRD), Fourier transform infrared spectroscope (FT-IR) and Zeta potential were used to investigate the structure, morphology and composition of the prepared core/shell composite powders. The corresponding formation mechanism was proposed based on the comparative study. It is revealed that the SiO2 film on the surfaces of pre-oxidated SiC particles can effectively enhance the adsorption of [Cu(NH3)4]2+ ions toward the negatively charged surface, which is favorable to the following in-situ reduction by N2H4·H2O around SiC particles. Nearly continuous Cu coating can be formed by changing the reaction process. The concentration of [Cu (NH3)4]2+ ions and reaction temperature affect the reaction rate and coating structure. The process parameters are optimized to obtain the best coating structure with [Cu(NH3)4]2+ ions concentration of 0.2 mol/L and reaction temperature of 70℃, respectively.
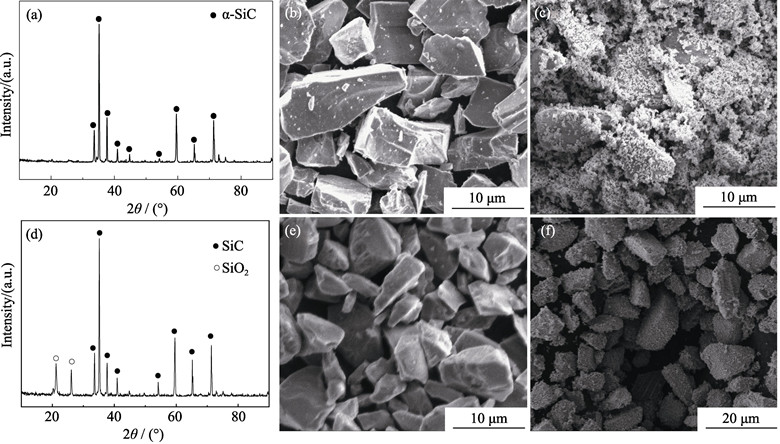
|
|
|
Structure Control of V2O5/CNFs/Cordierite Monolith Catalyst and Its Catalytic Performance on NO Removal from Flue Gas
WANG Yan-Li, WANG Xu-Jian, ZHAN Liang, QIAO Wen-Ming, LIANG Xiao-Yi, LING Li-Cheng
2012 Vol. 27 (8): 800–806
 Abstract
Abstract(
2313 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(641KB)(
1605
)
Carbon nanofibers (CNFs) were grown on Al2O3-coated cordierite monolith by chemical vapor deposition. The microstructure of V2O5 catalyst supported on cordierite monolith with CNFs layer was investigated by using scanning electron microscope (SEM), transmission electron microscope (TEM), X-ray powder diffraction (XRD) and X-ray photoelectron spectroscope (XPS) techniques, as well as its activity for the selective catalytic reduction (SCR) of NO by NH3. The compressive strength of prepared CNFs/cordierite monolith composite was 34.46 MPa and the thickness of CNFs layer was 0.74 μm. The V2O5/CNFs/cordierite monolith catalysts had high NO removal activity in the temperature range of 150-250℃. When the CNFs yield and V2O5 loading were 12.5% and 1%, respectively, the NO conversion of the catalyst could reach 95% at 250℃.
|
|
|
Microstructure and Mechanical Performance of Silicon Nitride Ceramics with Seeds Addition
ZHANG Ying-Wei, YU Jian-Bo, XIA Yong-Feng, ZUO Kai-Hui, YAO Dong-Xu, ZENG Yu-Ping, REN Zhong-Ming
2012 Vol. 27 (8): 807–812
 Abstract
Abstract(
2651 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(671KB)(
1555
)
With Y2O3:Al2O3 of different weight ratios as sintering additives and 3wt% β-Si3N4 seeds addition, silicon nitride ceramics were prepared by gas pressure sintering. The phase composition, density, microstructure, room temperature as well as elevated temperature mechanical properties were investigated. The experimental results indicated that the α→β phase transformation of silicon nitride would be finished at 1800℃ for 2 h, and the densities of all specimens were over 97% of theoretical density. Compared with the specimen without seeds addition, the room temperature bending strength, the elevated temperature flexural strength at 1200℃ and the fracture toughness of the specimen with 6wt%Y2O3-4.5wt%Al2O3 and 3wt% β-Si3N4 seeds addition can be improved by 20%, 16% and 8%, respectively.
|
|
|
Microwave Absorbing Property of Pre-oxidized PAN Fibers Carbonized in BCl3
YAN Jia, CHU Zeng-Yong, CHENG Hai-Feng, ZHANG Dong-Jiu
2012 Vol. 27 (8): 813–816
 Abstract
Abstract(
2470 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(465KB)(
1024
)
Pre-oxidized polyacrylonitrile fibers were carbonized in BCl3. Effect of processing temperature and time on B element content in the PAN-based carbon fibers was studied. A series of techniques including XPS, FTIR and SEM, were employed to characterize the composition and structure of the sample. The microwave absorbing properties of the resultant PAN-based carbon fibers were studied by voten network analyzer. The results indicate that the pre-oxidized polyacrylonitrile fibers are converted to carbon fibers by carbonization in BCl3 and BCN attachments are formed. The resultant fiber forms B–N bonds at the same time. The permittivity of carbon fibers/paraffin is lower in comparison of that of fibers carbonized in N2, especially the imaginary part of the permittivity of carbon fibers paraffin reduces fastly. The carbonization in BCl3 is beneficial to improve the microwave absorbing property.
|
|
|
Dielectric and Microwave-absorbing Properties of the Carbon/Alumina/Silica Coating
LIU Bao-Rong, HUANG Zhi-Bin, LUO Fa, QIAN Qi-Hu
2012 Vol. 27 (8): 817–821
 Abstract
Abstract(
3028 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(512KB)(
2075
)
The permittivity and microwave-absorbing properties of carbon black or carbon fiber filled alumina/ silica coating were investigated in X-band. The results indicate that both the real and imaginary part of the complex permittivity increase with the increasing content of carbon absorber. With the same content of carbon absorber, the coatings filled with carbon fiber shows higher complex permittivity than the coatings filled with carbon black. As the absorber contents increase to 2wt%, the complex permittivity of the coatings decrease with the increase of frequency, which is so-called frequency-dependence dielectric response. The minimum reflection loss of the coatings shifts to low frequency region as their thickness increasing. The results of the microwave absorbing properties show that good microwave absorption ability (below -10 dB) can be obtained in the frequency range from 9.2 GHz to 12.4 GHz for the coating with 2wt% carbon black and 2 mm in thickness.
|
|
|
Preparation and Thermoelectric Properties of (Mg2Si1-xSbx)0.4-(Mg2Sn)0.6 Alloys
HAN Zhi-Ming, ZHANG Xin, LU Qing-Mei, ZHANG Jiu-Xing, ZHANG Fei-Peng
2012 Vol. 27 (8): 822–826
 Abstract
Abstract(
2767 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(410KB)(
1363
)
n-type (Mg2Si1-xSbx)0.4-(Mg2Sn)0.6 (0≤x≤0.0625) alloys were prepared by an induction melting and spark plasma sintering method using bulks of Mn, Si, Sn, Sb as raw materials. The analyzing results of the structure and thermoelectric properties show that the single-phase (Mg2Si1-xSbx)0.4-(Mg2Sn)0.6 alloys can be obtained at 8wt% excess of Mg addition. The lattice constant increases linearly with the amount of Sb, the electrical resistivity ρ firstly increases and then decreases. The electrical resistivity ρ of samples (x≤0.025) shows semi-conductor behavior, while that of the samples (x>0.025) shows the metallic behavior. The Seebeck coefficient a firstly increases and then decreases with the increase of x value. Compared with the non-doped sample, the thermal conductivity k for samples (x≤0.025) decreases and that of the other samples (x>0.025) increases. The ZT value for (Mg2Si0.95Sb0.05)0.4-(Mg2Sn)0.6 sample reaches its highest value of 1.22 at 773 K, which is much higher than that of the non-doped sample.
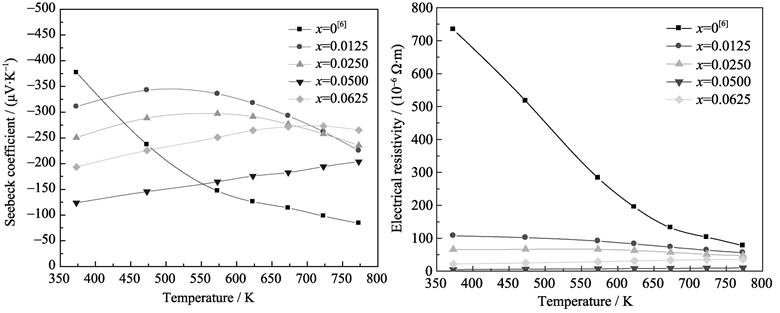
|
|
|
Piezoelectric Properties of Mn-modified Na0.5Bi2.5Nb2O9 for High Temperature Applications
JIANG Xiang-Ping, WEN Jia-Xin, CHEN-Chao, TU-Na, LI Xiao-Hong
2012 Vol. 27 (8): 827–832
 Abstract
Abstract(
2745 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(606KB)(
1139
)
Bismuth layer-structured ferroelectric ceramics Na0.5Bi2.5Nb2O9(NBN+xmol% MnCO3, 0≤x≤10.0) were synthesized by traditional solid state reaction. The effects of Mn addition on the microstructure and electrical properties of ceramics were investigated in detail. The results showed that all the ceramic samples were single-phase ferroelectrics with high Curie points (Tc≥700℃). With the addition of MnCO3, the mechanical quality factor, piezoelectric activity and electromechanical properties of Na0.5Bi2.5Nb2O9-based ceramics are enhanced significantly. Besides, the NBN+8.0mol% MnCO3 ceramic exhibits the optimum electrical properties: tanδ=0.749%, d33=20 pC/N, Qm=3120, kp=12.37%, kt=21.09%, Pr=7.01 μC/cm2. After annealing at 700℃, the d33 value of NBN+8.0mol% MnCO3 ceramic remains 75%(~15 pC/N), which indicates that this ceramic is a promising material for high temperature applications.
|
|
|
Influence of ZnO Nanorods Morphology on the Photovoltaic Properties of ZnO/Cu2O Heterostructural Solar Cells
WEI Hao-Ming, CHEN Ling, GONG Hai-Bo, CAO Bing-Qiang
2012 Vol. 27 (8): 833–837
 Abstract
Abstract(
3809 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(426KB)(
1753
)
ZnO nanorods were prepared by electrochemical deposition (ECD). The influence of ECD parameters on the morphologies of ZnO nanorods was studied and optical properties of the ZnO nanorods were measured with optical absorption and specular reflection spectra. It is found that deposition time has significant influence on the length and diameter of ZnO nanorods which is also proved by the optical measurements. ZnO/Cu2O heterostructural solar cells were constructed by ECD with n-type ZnO nanowires and p-type Cu2O films and their photovoltaic characteristics such as open-circuit voltage, short-circuit current density and efficiency were measured. With the increase of nanorods’ length, the photovoltaic properties of ZnO/Cu2O solar cells are enhanced. Finally, the relation between the solar cell performance and the morphologies of ZnO nanorods are discussed. It is indicates that, by increasing the length of nanorods, the light scattering is enhanced, which improves the electronic collection efficiency and photon utilization rate, and accordingly, the performance of solar cells.
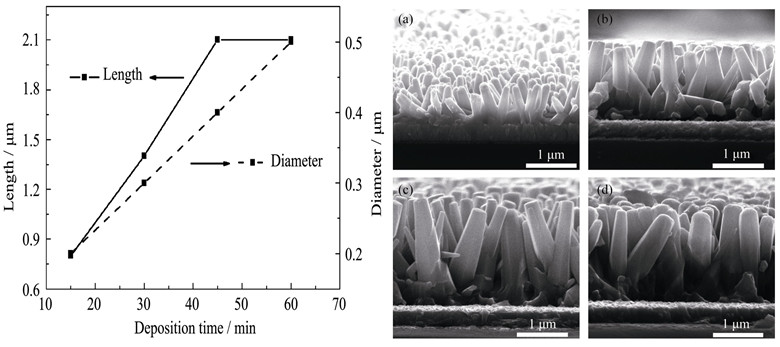
|
|
|
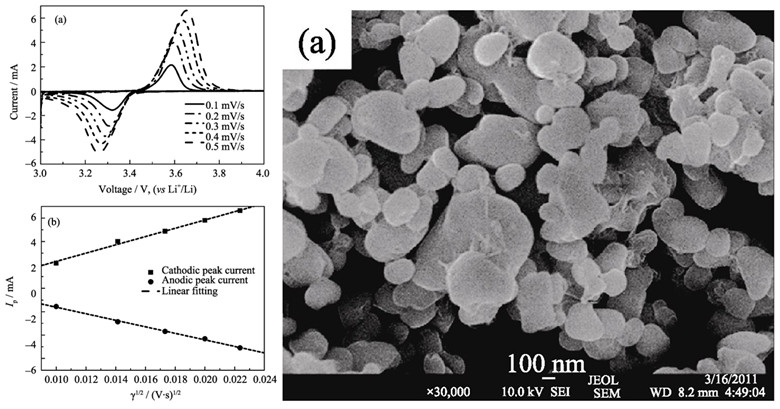
Effect of Sintering-method on Electrochemical Performance of LiFePO4/C Cathode Material
MOU Fei, YANG Xue-Lin, DAI Zhong-Xu, ZHANG Lu-Lu, WEN Zhao-Yin
2012 Vol. 27 (8): 838–842
 Abstract
Abstract(
3070 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(561KB)(
2041
)
Static nitrogen atmospheres (SA), dynamic nitrogen atmosphere (DA) and static vacuum (SV) sintering methods were adopted to synthesize LiFePO4/C cathode material. The crystalline structure, morphology and electrochemical performances of the products were characterized by X-ray diffraction (XRD), scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and galvanostatic charge/discharge test. Effects of sintering method on crystallinity, particle size, carbon content, reaction temperature and electrochemical performance of the as-obtained LiFePO4/C cathode material are remarkable. SV-sintered LiFePO4/C have better crystalline, but DA-sintering is helpful to obtain LiFePO4/C particles with smaller particle size and narrower particle size distribution, kinetics of Li+ diffusion is also improved. For the DA-sintered sample, sintering temperature can be reduced to 500℃ with excellent electrochemical performance. Specific discharge capacity for the first cycle reaches 163.4 mAh/g at 0.5C rate, and up to 99.02% of discharge capacity can be kept after 50 cycles.
|
|
|
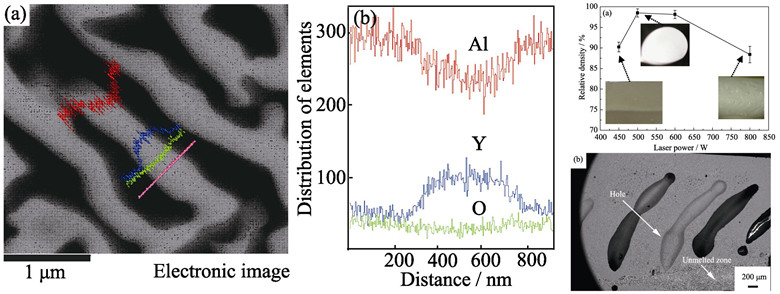
Fabrication and Characterization of Al2O3/Y3Al5O12 Eutectic in situ Composite Ceramics by Double Side Laser Zone Remelting Method
YU Jian-Zheng, ZHANG Jun, SU Hai-Jun, SONG Kan, LIU Lin, FU Heng-Zhi
2012 Vol. 27 (8): 843–848
 Abstract
Abstract(
2588 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(629KB)(
1476
)
Al2O3/YAG eutectic in situ composite ceramics were prepared by double side laser zone remelting (DSLZR) with aiming at investigate the melting and solidification rules of oxide eutectic ceramics with large size under DSLZR condition. The solidification microstructures were characterized by SEM, XRD and EDS. The results show that solidified layer thickness of eutectic ceramics is enhanced by DSLZR. The eutectic ceramic plates with density up to 98.5%±1% are obtained, in which the thickness is 8.2 mm, and the length is 65.0 mm. The thickness of solidified layer is increased with decreasing laser scanning rate and increasing laser power. The density is initially increased and then decreased with the increase of laser scanning rate. The eutectic ceramic obtained by DSLZR is only consisted of uniform and interweaved Al2O3 and YAG phases. The relation between the eutectic spacing (λ; only 1.0~3.5 μm) and solidification rate (v) agrees with the Jackson-Hunt formula. With the increase of laser scanning rate, the eutectic spacing reduces. Furthermore, the growth of eutectic at double side remelting interface is continuous, so the binded interface is very well. The eutectic ceramic obtained has high Vickers hardness ((18.6±1.0) GPa) due to the fine solidification microstructure.
|
|
|
Fabrication and Characterization of Mono-sized Spherical Fe-based Metallic Glass Micro-particles
LI Ying, DONG Wei, MIURA Ayako, TAN Yi, KAWASAKI Akira
2012 Vol. 27 (8): 849–854
 Abstract
Abstract(
2314 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(550KB)(
1133
)
[(Fe0.5Co0.5)0.75B0.2Si0.05]96Nb4 metallic glass alloy particles with narrow size distribution and high sphericity were prepared in a Helium atmosphere by pulsated orifice ejection method (POEM). The analysis of these obtained particles was carried out by X-ray diffraction (XRD), differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) and transmission electron microscope (TEM). The results show that the phase transitions of particles from the mixed phase consisting of the glassy phase and the crystalline phase to the fully glassy phase occur as the particle diameter is decreased. The particles obtained in the fully glassy phase have a diameter of less than 645 μm. The critical cooling rate for fully glassy phase is estimated to be in the range of 800-1100 K/s. No changes of the critical cooling rate occur in Ar or He atmosphere. Critical cooling rate measured in this method is definitely lower than that measured by time-temperature transformation diagram of bulk metallic alloy.
|
|
|
Effect of Refinement Process Condition and Sintering Property on the Low Melting Point Glass Powder by High-pressure Homogenization Technology
ZHANG Nian-Chun, XIONG Jun-Jun, DING En-Yong
2012 Vol. 27 (8): 855–859
 Abstract
Abstract(
2500 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(554KB)(
1891
)
Using carboxymethyl cellulose (CMC) as an anti-settling agent of low melting point glass powder aqueous dispersion, the high-pressure homogenizer can refine glass powder particle to reduce their size. Different high-pressure homogenized time affected on glass powder’s particle size and the sintering property. Under the same pressure (50 MPa) a longer high-homogeneous time gets smaller particle size and narrows particle size distribution. And the softening temperature and sintering temperature are also lower. The results show that the high-pressure homogenizer techniques can be used to reduce the particle size of the glass powder, so that the softening temperature and sintering temperature will be lowered.
|
|
|
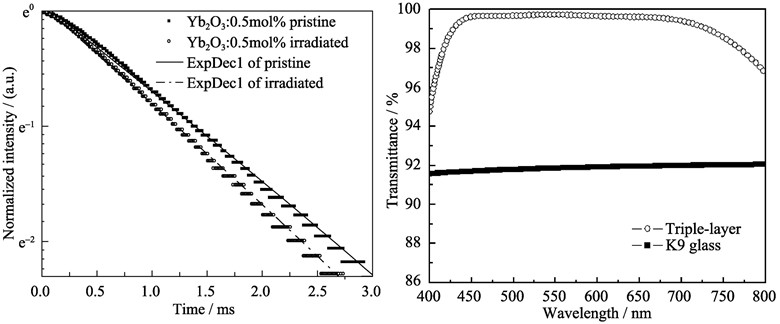
Gamma Radiation Effects on the Optical Properties of Yb-doped Silicate Glasses
SHENG Yu-Bang, XING Rui-Xian, LUAN Huai-Xun, LIU Zi-Jun, LI Jin-Yan, DAI Neng-Li
2012 Vol. 27 (8): 860–864
 Abstract
Abstract(
2357 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(400KB)(
2033
)
A series of Yb-doped silicate glasses were prepared by a conventional melting method under normal processing conditions. The effects of gamma-ray (from a 60Co γ source) radiation on the absorption and emission properties of all glass samples were investigated. The radiation exposure leaded to the formation of color centers in glass samples. Such radiation-induced photodarkening caused a strong broad optical absorption band, which had a maximum wavelength centered at around 400 nm and the tail extended into the near infrared region. In addition, a minor part of the Yb3+ ions were converted into Yb2+ by trapping free electrons during irradiation based on the radiation induced absorption (RIA) spectra. The excitation energy could be transfered from Yb3+ ions to radiation-induced defects through cooperative upconversion or multiphoton absorption processes under 960 nm LD pumping. Such energy transfer processes resulted in a decrease of the upper state lifetime of Yb3+ ion which was accompanied by an increase in oxygen deficient center ODC(Ⅱ) defect fluorescence at around 476 nm. Photobleaching effect was observed in irradiated Yb-doped glasses during the fluorescence measurement at room temperature.
|
|
|
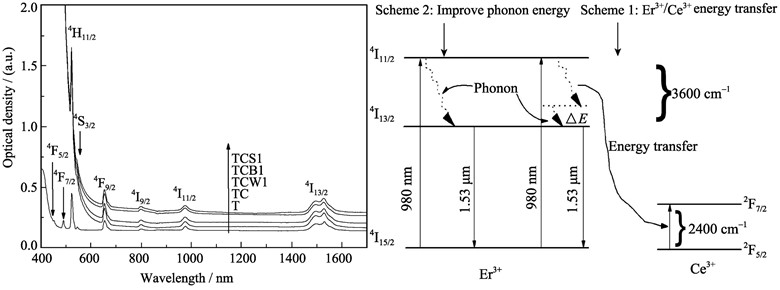
Influence of High Phonon Energy Oxide on Spectroscopic Properties of Er3+/Ce3+ Co-doped Tellurite Glasses
WANG Sen, ZHOU Ya-Xun, DAI Shi-Xun, WANG Xun-Si, SHEN Xiang, CHEN Fei-Fei
2012 Vol. 27 (8): 865–870
 Abstract
Abstract(
2368 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(554KB)(
1240
)
High phonon energy oxides of WO3, SiO2 and B2O3 were introduced into the Er3+/Ce3+ co-doped tellurite glass (TeO2-Bi2O3-TiO2) with low phonon energy, respectively. The absorption spectra in the wavelength region of 400–1700 nm, fluorescence spectra of 1.53 μm band, fluorescence lifetimes of Er3+ and Raman spectra of the glasses were measured. The spectral parameters of Er3+ were calculated with the help of McCumber theory. It is shown that the energy transfer process between Er3+ and Ce3+ becomes more effectively when introducing the high phonon energy oxide, and the 1.53 μm band fluorescence emission corresponding to Er3+:4I13/2→4I15/2 transition enhances accordingly due to the increased population of Er3+ in the 4I13/2 level. Meanwhile, the fluorescence width at half magnitude (FWHM) and bandwidth quality factor (σe×FWHM) can be improved with the introducing of high phonon energy oxide. The results provide practical significance to obtain the excellent spectroscopic glass host applied for the Er3+-doped fiber amplifier (EDFA).
|
|
|
Design and Preparation of SiO2/TiO2/SiO2-TiO2 Antireflective Coatings with Excellent Abrasion-resistance and Transmittance via Sol-Gel Process
YE Long-Qiang, ZHANG Qing-Hua, ZHANG Yu-Lu, ZHANG Xin-Xiang, JIANG Bo
2012 Vol. 27 (8): 871–875
 Abstract
Abstract(
2584 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(430KB)(
1739
)
Triple-layer broadband antireflective (AR) coatings with excellent abrasion-resistance and transmittance were designed using the theory of optical coating design. And the designed coatings were prepared on K9 glass via Sol-Gel process in this work. SiO2 and TiO2 sols were prepared using tetraethylorthosilicate (TEOS) and titanium tetraisopropoxide (TTIP) as precursors, respectively, and hydrochloric acid as catalyst. It is found that the average transmittance of the AR coatings over the entire visible region can reach 98.7%, which is 7.1% higher than that at the blank K9 glass. Moreover the transmittance of the AR coating does not obviously decrease after abrasion test, showing the excellent abrasion-resistance of the AR coatings. Hexamethyldisiloxane (HMDS) is further used to modify the surface of the AR coatings, which greatly improves the hydrophobicity of the coatings, and thus gives the AR coatings excellent environmental resistance.
|
|
|
Research on the Wear Behaviors of WC-8Co and Al2O3-TiC Conical Dies
YANG Xue-Feng, WANG Shou-Ren, YANG Li-Ying, WANG Yan-Jun, ZHANG Bing, SONG Pei-Long
2012 Vol. 27 (8): 876–882
 Abstract
Abstract(
3079 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(713KB)(
1069
)
Two types of conical dies, WC-8Co and Al2O3-TiC, were fabricated by way of cold and hot press sintering method, respectively. The wear and tear behaviors were investigated when the die samples were applied on the real 45 steel wire drawing process. After that, the friction mechanisms under the experimental phenomena were carefully studied. It is found that both of there two types of conical dies showed reasonable hardness and strength, indicating acceptable drawing ability. Further study reveals that the deformation zone and the invariable zone are the most worn area of the inner bore surface. Metal shedding, fallen-off granules from dies and leftover of lubrication grease are observed on the surface. Two different wear mechanisms for WC-8Co (adhesive and abrasive wear) and Al2O3-TiC (adhesive and abrasive wear) are then concluded. By comparison, conical die made from Al2O3-TiC is more suitable for 45 steel wire drawing process.
|
|
|
Effect of Silk Fibroin Content on the Bionic Mineralization and In Vitro Cellular Compatibility of Silk Fibroin/Hydroxyapaptite Nanocomposites
ZHU Yun-Rong, CHEN Yu-Yun, XU Guo-Hua, YE Xiao-Jian, ZHONG Jian, HE Dan-Nong
2012 Vol. 27 (8): 883–886
 Abstract
Abstract(
2597 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(500KB)(
1542
)
Silk fibroin and hydroxyapatite nanocomposites (SF/HA) with various SF content were prepared. Effect of Silk fibroin content on the bionic mineralization and cellular compatibility in vitro of HA nanocrystals (n-HA) was investigated. The results show that SF content has an obvious effect on the nucleation and growth of n-HA. However, though SF content does not show obvious difference on the nucleation and growth of n-HA, it has obvious effect on the n-HA aggregation. When SF content is less than 20wt%, n-HA orderly disperses in SF matrix. While the SF content is more than 20wt%, the n-HA aggregation becomes disordered. The in vitro cellular compatibility experiments demonstrate that the SF/HA composites exhibit better cell affinity than pure n-HA. However, SF content has no obvious effect on the cell affinity of n-SF/HA 20wt% SF/HA and 30wt% SF/HA show better osteoblast proliferation.
|
|
|
Investigation on Oxygen Resistance Properties of RBaCo2O5+δ Ceramics
SONG Hong-Zhang, QIN Zhen, GAO Feng, JIA Jian-Feng, YANG De-Lin, HU Xing
2012 Vol. 27 (8): 887–890
 Abstract
Abstract(
4279 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(373KB)(
1461
)
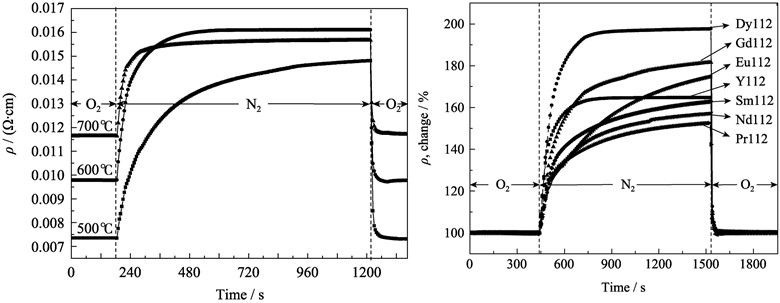
RBaCo2O5+δ (R=Y, Dy, Gd, Pr, Nd, Sm, and Eu) ceramics were synthesized by the solid-state reaction method. Their resistivities depending on temperature were investigated by the standard four-probe method from room temperature to 600℃. At low temperature, all the resistivities decrease with the rising temperature, and exhibit semiconducting behavior. After the resistivities reach minimum values at certain temperatures, they increase slowly with temperature, and exhibit semimetal conducting behavior. Especially, the resistivity variations of RBaCo2O5+δ samples with the change of atmosphere at constant temperatures are studied. The results show that RBaCo2O5+δ could be potential oxygen resistance sensor materials, and that the responding rates of RBaCo2O5+δ are YBaCo2O5+δ > DyBaCo2O5+δ > GdBaCo2O5+δ > PrBaCo2O5+δ > NdBaCo2O5+δ > SmBaCo2O5+δ > EuBaCo2O5+δ. For YBaCo2O5+δ, the resistivity rises quickly due to the oxygen desorption when the atmosphere is switched from oxygen to nitrogen at 700℃, and reaches its maximum equilibrium value within 90 s. In addition, the resistivity drops drastically due to the oxygen adsorption when the nitrogen atmosphere is switched to oxygen, and reaches its minimum equilibrium value within 30 s.
|
|
|
Study on Phase Transition Property of Tungsten-doped Vanadium Dioxide Thin Film at Terahertz Range
MAO Mao, HUANG Wan-Xia, ZHANG Ya-Xin, YAN Jia-Zhen, LUO Yi, SHI Qi-Wu, CAI Jing-Han
2012 Vol. 27 (8): 891–896
 Abstract
Abstract(
5036 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(452KB)(
1972
)
Vanadium dioxide and tungsten-doped (W-doped) vanadium dioxide thin films deposited by aqueous Sol-Gel method were characterized with several different techniques (i.e. X-ray photoelectron spectroscope, atomic force microscope, X-ray diffraction), to determine their morphology and microstructure. Their metal-to-insulator (MIT) phase transition behavior in infrared spectral region (λ=4 μm) and terahertz (THz) spectral region (0.3–1.0 THz) were observed respectivele. The results demonstrate that the transmittance of W-doped VO2 film at room temperature is visibly lower than that of undoped VO2 film in both infrared and terahertz spectral region. The transition temperature of W-doped VO2 film is also lower than that of undoped VO2 film in the THz range. The MIT and structural phase transition (SPT) are observed during the phase transition of VO2 and W-doped VO2, and an obvious change of peak position occurs in W-doped VO2 film.
|
|