|
|
Progress of Research on the Manganese Oxide Ion-sieve for Extracting Lithium
LI Li, LIU Fang, WU Feng, CHEN Ren-Jie
2012 Vol. 27 (10): 1009–1016
 Abstract
Abstract(
2233 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(586KB)(
1772
)
Metallic lithium plays an important role in the national economy and national defense construction. With the growing demand and exhausted lithium mineral resources, it is of great significance to extract lithium from abundant liquid lithium resources such as seawater and brines. Active exploration of lithium extraction methods and technologies have been carried out. Spinel-type manganese oxide has attracted much attention because of its remarkably high selectivity for lithium ions in the aqueous phase, and it is called ion-sieve adsorbent. Being environmentally friendly and efficient, the ion-sieve adsorption method is regarded as the most promising one for extracting lithium from seawater and brines. In this revieal, the structure of LiMn2O4 is presented, and the development of lithium-ion insertion/extraction mechanisms is introduced as well. The synthesis method and modification of the ion-sieve precursor are also summarized in details. Moreover, the granule/membrane formation and application of lithium ion-sieves are discussed. Finally, the existing problems and the prospects of the lithium ion-sieve are put forward.
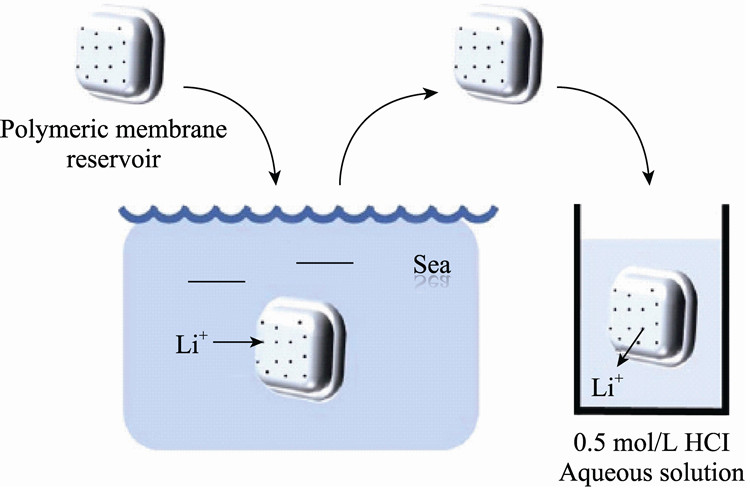
|
|
|
Sol-Gel Synthesis and Electrochemical Performance of Li3V2-2x/3Mnx(PO4)3 Cathode Material for Lithium-ion Batteries
LIU Guo-Cong, LIU You-Nian, LIU Su-Qing, DONG Hui
2012 Vol. 27 (10): 1017–1022
 Abstract
Abstract(
1519 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(533KB)(
1551
)
Novel cathode material Li3V2-2x/3Mnx(PO4)3/C was successfully synthesized by Sol-Gel method using CH3COOLi·2H2O, V2O5, Mn(CH3COO)2·4H2O, (NH4)2HPO4 and sucrose as raw materials. The as-prepared products were characterized by XRD, XPS, SEM.The results show that a small amount of Mn2+doping do not alter the structure of Li3V2(PO4)3 materials with a monoclinic structure (space group P21/n), and the valence states of V and Mn in Li3V1.94Mn0.09(PO4)3/C are +3 and +2, respectively. The Li3V1.94Mn0.09(PO4)3 particle with uniform shape of sphere and diameter less than 200 nm, shows the best cyclic stability and rate performance. Controlling the charge and discharge voltage range from 3.0 to 4.8 V at the rate of 0.1C, the first charge and discharge capacity of Li3V1.94Mn0.09(PO4)3 are up to 182.1 and 168.8 mAh/g, respectively, and its discharge efficiency is up to 92.69%. After 100 cycles, its discharge capacity can also retain 77.4% of the first one.
|
|
|
Synthesis of Li2FeSiO4/C Composite as Cathode Materials for Lithium Ion Battery by Microwave Assisted Solid Reaction Method
CAO Yan-Bing, DUAN Jian-Guo, HU Guo-Rong, JIANG Feng, PENG Zhong-Dong, DU Ke
2012 Vol. 27 (10): 1023–1029
 Abstract
Abstract(
1510 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(1038KB)(
1351
)
The homogeneous distribution of FeOOH/SiO2 precursor material was prepared from FeCl2•4H2O and Na2SiO3•9H2O by low-heating solid-state reaction. Then Li2FeSiO4/C composites were prepared by microwave assisted solid reaction method, with prepared precursor FeOOH/SiO2 and Li2CO3 as the starting materials, PVA and super-P carbon as carbon sources. The prepared samples were characterized by X-ray diffractometry, SEM, TEM, and galvanostatic charge-discharge test. Highly pure Li2FeSiO4/C material with uniform and fine particle size was obtained at 650℃ in 12 min. Under the selective microwave synthesis system, super-P carbon powder and pyrolyzed amorphous carbon not only effectively provided the high temperature to induce the complete reaction but also formed the conductive network to enhance the electronic conductivity. The optimum Li2FeSiO4/C composite displayed discharge capacity of 129.6 mAh/g at 0.05C rate and 107.5 mAh/g at 0.5C rate at 60℃. After 15 cycles the discharge capacity maintained 104.8 mAh/g at 0.5C, indicating good electrochemical capacity and cycling stability. Consequently, the results show that microwave assisted solid synthesis process is a promising method for preparing Li2FeSiO4/C composite.
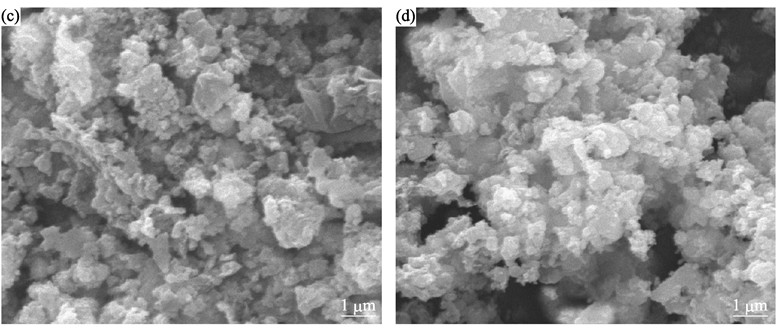
|
|
|
Synthesis and Characterization of LiFePO4/Al/C Composite Cathode Material
CHEN Wei, PENG Wen-Jie, WANG Zhi-Xing
2012 Vol. 27 (10): 1030–1034
 Abstract
Abstract(
1385 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(495KB)(
1183
)
LiFePO4/Al/C composite cathode materials were synthesized by two-step solid-state method. The crystalline structure, morphology, the particle size and the coated state of the samples were characterized by XRD, SEM and TEM. The effect of the amounts of Al powder on the electrochemical properties of the composite was investigated. The results show that the interface reaction occurs between metal Al and LiFePO4, resulting in the formation of several by-products and the passive film on the surface of LiFePO4. The surface of LiFePO4 particles are coated by the irregularly shaped metal Al and a thin carbon layer of 1-2 nm. The LiFePO4/Al/C containing 3wt% Al shows the best electrochemical performances, with discharge specific capacity of 117.8 mAh/g at 25℃ and 10C rate, and discharge specific capacity of 105.6 mAh/g at -20℃ and 0.1C rate, and discharge capacity of samples at -20℃ is 73.8% of that of samples at 25℃.
|
|
|
Preparation and Electrochemical Performance of Carbon nanotubes/Micro-expanded?Graphite Composite Anodes for Lithium-ion Batteries
GUO De-Chao, ZENG Xie-Rong, DENG Fei, ZOU Ji-Zhao, SHENG Hong-Chao
2012 Vol. 27 (10): 1035–1041
 Abstract
Abstract(
1618 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(685KB)(
2032
)
Micro-expanded?flake?graphite (MEFG) and micro-expanded?spherical?graphite (MESG) were prepared from two kinds of natural graphite by intercalation reaction and rapid heating processes. Then carbon nanotubes/ micro-expanded?graphite (CNTs/MEG) composites were prepared by chemical vapor deposition (CVD) process, for which CNTs were grown in the pores of micro-expanded?graphite. Electrochemical test results?show that first discharge/ charge capacities of CNTs/MEFG and CNTs/MESG could respectively accommodate up to 443 and 477 mAh/g. Both of the prepared CNTs/MEG composites keep more than 95% capacities after 30 cycles at the rate of 0.2C and their capacities are stable at?259 and 195 mAh/g after 50 cycles at 1C rate, respectively. The nanoporous structure and the CNTs network can improve the discharge capacities and effectively?buffer the volumetric change of the composite electrode materials in the charge/discharge process. The diffusion path of Li+ can be reduced because of the electrolyte solution that filled in the nanopores, which significantly improves the rate capability of the electrodes. In addition, the growing ivy-like CNTs could improve the electric conductive property of the composites in the charge/discharge process.
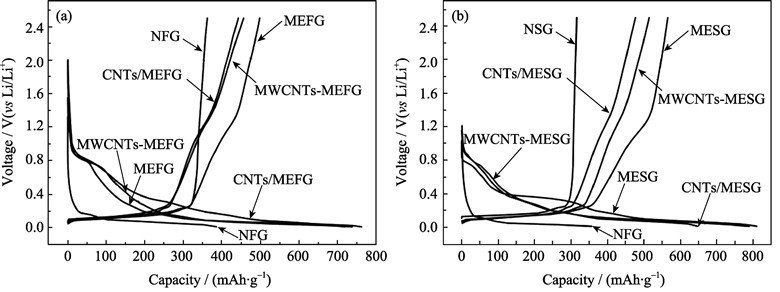
|
|
|
Fabrication and Properties of the Potassium Sodium Niobate/Cobalt Copper Ferritemultiferroic Magnetoelectric Composites
XUAN Min-Jie, LIU Xin-Yu, YUAN Chang-Lai, XU Ji-Wen, MA Jia-Feng
2012 Vol. 27 (10): 1042–1046
 Abstract
Abstract(
1235 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(510KB)(
2179
)
(1–x)(0.9462K0.5Na0.5NbO3-0.0498LiSbO3-0.004BiFeO3)-xCo0.85Cu0.15Fe2O4((1–x)(KNN-LS-BFO)-xCCFO) (x=0.1, 0.2, 0.3, 0.4, 0.5) multiferroic magnetoelectric ceramics were prepared by solid phase method. The presence of perovskite and spinel in the sintered composites were proved by XRD patterns and no impurity phase existed. SEM images show that particle size of KNN-LS-BFO is big and complete, while the particle size of CCFO is small. When x increases from 0.1 to 0.5, the piezoelectric coefficient of the composites decreases from 120 pC/N to 33 pC/N, While saturation magnetization and remanent magnetization increase and saturation magnetostriction constant increases from 18×10–6 to 52×10–6 approximately. When the applied magnetic field increases, the magnetoelectric properties of the composites increase to the maximum and then decrease. When the alternating magnetic field frequency is 1 kHz and x=0.3, the magnetoelectric voltage coefficient attains maximum value 20.6 mV/A.
|
|
|
Fatigue Life Investigation of PZT Ceramics by MSP Method
DENG Qi-Huang, WANG Lian-Jun, XU Hong-Jie, WANG Hong-Zhi, JIANG Wan
2012 Vol. 27 (10): 1047–1052
 Abstract
Abstract(
1316 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(463KB)(
1311
)
The cycle fatigue of PZT ceramic under different stress was investigated by modified small punch (MSP) tests. The research results show that residual strength and piezoelectric constant decrease with increasing cycle stress, which is attributed to crack propagation during cyclic stress process. The value of fatigue crack propagation (n) is calculated to be 395 according to the relationship between maximum stress and fatigue life. The fatigue life under series cycle maximum stress can be induce by fatigue crack propagation. Below the maximum strength of 79.1 MPa, the PZT ceramics can be used over 5 years.
|
|
|
Preparation and Characterization of Multiferroics BiFeO3
SONG Wei, WANG Xuan, ZHANG Dong, SUN Zhi, HAN Bai, HE Li-Juan, LEI Qing-Quan
2012 Vol. 27 (10): 1053–1057
 Abstract
Abstract(
1485 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(496KB)(
1656
)
The multiferroic materials BiFeO3 nanopowders of dispersion uniformity were synthesized by the citric acid Sol-Gel method, using the iron(Ⅲ) nitrate and bismuth nitrate as the reactants and dilute nitric acid as the catalyst. The physical and chemical characteristics, such as structure, morphology and purity of BiFeO3 nanopowders were investigated by TG-DSC, XRD, FT-IR, SEM and AFM, respectively. The results indicate that the preparation and purity of BiFeO3 nanopowders have a profound influence on the precursor solution pH value of sol process and the calcined temperature of the xerogel. The optimum reaction conditions are the precursor solution pH=7–8 and calcined temperature of 600℃. It is found that BiFeO3 nanopowders with 100 nm in size, good dispersion and without Bi25FeO40 and Bi2Fe4O9 impurity phase are synthesized under the optimum reaction conditions. The saturation magnetization (Ms), the remanent magnetization (Mr) and the coercivity (Hc) of BiFeO3 nanopowders under the optimum reaction conditions are 1.08 A·m2/kg, 0.13 A·m2/kg and 15.76 kA/m, respectively.
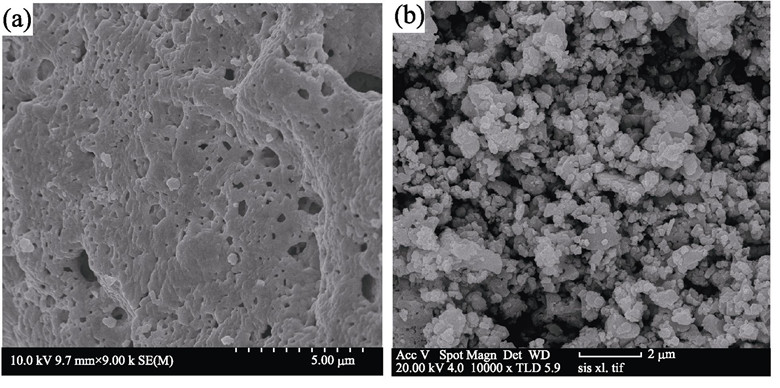
|
|
|
Preparation and Properties of Lateral Contact Structure SiC Photoconductive Semiconductor Switches
CHANG Shao-Hui, LIU Xue-Chao, HUANG Wei, ZHOU Tian-Yu, YANG Jian-Hua, SHI Er-Wei
2012 Vol. 27 (10): 1058–1062
 Abstract
Abstract(
1608 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(390KB)(
1882
)
A series of lateral structural photoconductive semiconductor switches (PCSS) were fabricated on V-doped semi-insulating 6H-SiC substrate with the Ni/Au contacts. These PCSS were measured with different bias voltages, excitation energies and excitation wavelengths. The photoelectric absorption effect and photoelectric response of SiC PCSS were investigated. It is found that the absorption coefficient is between 0.601 and 0.692 mm–1 for semi-insulating 6H-SiC substrate when it is excited by 532 nm laser, and the corresponding pulse signal is much smaller than that excited by 1064 nm laser. Nanosecond-pulse signal is obtained for 6H-SiC PCSS excited by 532 nm laser. The peak current flowing through the switch is increased with increasing the bias voltage and excitation energy, while it is decreased with the increase in substrate thickness.
|
|
|
Effects of Annealing Temperatures on Resistive Switching Characteristics of TiO2 Based ReRAM
LI Hong-Xia, JI Zhen-Guo, XI Jun-Hua
2012 Vol. 27 (10): 1063–1067
 Abstract
Abstract(
1597 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(391KB)(
1308
)
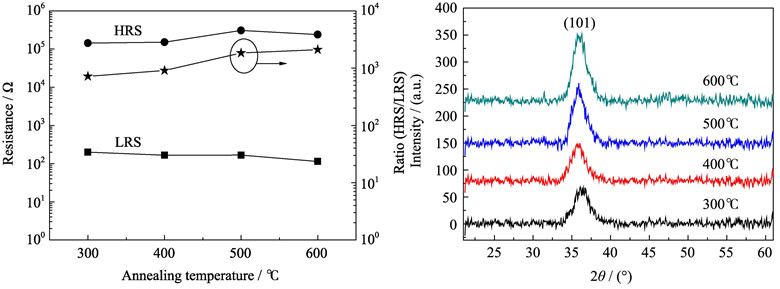
TiO2 thin films were deposited on heavily doped silicon wafer by DC magnetron sputtering and the Au electrodes were evaporated on TiO2/n+-Si by electric beam evaporation to get Au/TiO2/n+-Si structured resistive random access memory (ReRAM). The effects of annealing temperatures on the crystalline structure of the TiO2 thin films and the resistive switching characteristics of the fabricated device were investigated. Au/TiO2/n+-Si structured device exhibits reversible and steady unipolar resistive switching behaviors. The values of set voltage, reset voltage, reset current and reset power vary with the annealing temperatures. The resistive switching mechanism is discussed based on the filamentary model. The results reveal that the fabricated device annealed at 500℃ has good nonvolatile property. The average ratio of resistances between high resistance state (HRS) and low resistance state (LRS) is larger than 103 and the devices could maintain a sufficient margin of memory for more than 10 years. The resistive switching characteristic is remained after 100 switching cycling tests.
|
|
|
Preparation and Characterization of Flower-like TiO2 Induced by Rod-like Nanocrystalline Cellulose
PENG Xin-Yan, DING En-Yong
2012 Vol. 27 (10): 1068–1072
 Abstract
Abstract(
1417 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(524KB)(
1288
)
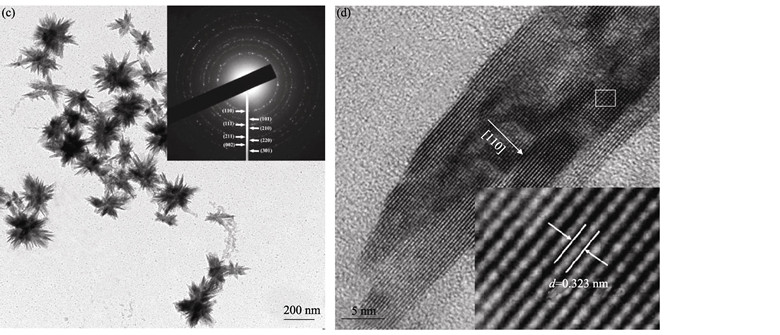
Flower-like titania nanocrystals were synthesized by hydrolysis of titanium (IV) chloride at a low temperature of 70℃ in 4–6 h, employing nanocrystal cellulose (NCC) as a morphology controlling agent. The obtained nanocrystals were characterized by transmission electron microscope (TEM), high-resolution transmission electron microscope (HRTEM), X-ray diffraction (XRD) and FTIR. TEM and HRTEM investigations reveal that the morphologies of the nancrystals are flower-like, and each flower is composed of several nanoneedles with a diameter of 15–20 nm and a length of 100–200 nm. The XRD results show that the crystalline phase of the nanocrystals have a strong dependence on the mole ratio of TiCl4 to H2O and the reaction time. FTIR result shows that a chemical bond is formed between NCC and TiO2. A possible growth mechanism is proposed based on the characteristic results. The NCC whose surface is full of hydrophilic groups can establish hydrogen bonding with TiO2 to promote the nucleation and crystal growth of TiO2 at low temperature. Moreover, the selective adsorption of NCC molecules on the crystal face of TiO2 varies the growth rate of different crystal planes, and the anisotropic crystal growth leads to the formation of nanoneedles. Then these nanoneedles aggregate together to assemble into a flower-like secondary structure. TiO2 prepared at low temperature exhibites high activity in the photocatalytic degradation of methyl orange in aqueous solution under metal halide lamp.
|
|
|
Preparation of Co-BiVO4 Photocatalyst and Its Application in the Photocatalytic Oxidative Thiophene
GAO Xiao-Ming, FU Feng, WU Yu-Fei, ZHANG Li-Ping, LI Wen-Hong
2012 Vol. 27 (10): 1073–1078
 Abstract
Abstract(
1606 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(509KB)(
1472
)
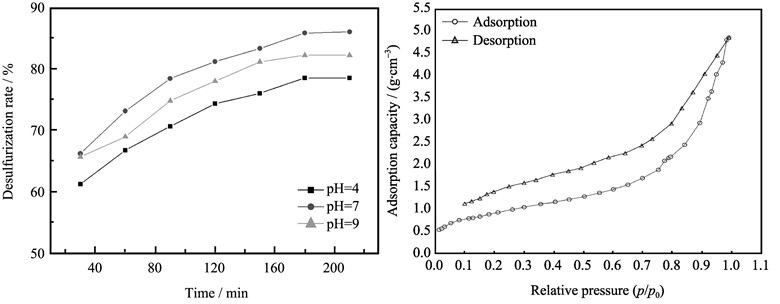
The Co-BiVO4 photocatalyst was prepared by hydrothermal method and characterized by X-ray diffraction, scanning electron microscope, UV-Vis absorption spectroscope, and low-temperature N2 adsorption. The characterized results indicate that highly crystalline monoclinic scheelite structure of Co-BiVO4 is obtained at pH=7 and the Co dopant does not change the crystal phase of BiVO4. The Co-BiVO4 has a significant red-shift in the absorption band in the visible region, and its absorption intensity increases greatly for the doped catalyst compared with pure BiVO4. Low-temperature N2 adsorption result reveals that the pore size of the Cu-BiVO4(pH=7) mostly distributes at 2.67 nm. The desulfurization ability of Co-BiVO4 was researched by photocatalytic oxidation of thiophene in visible light. The results show that the Co-BiVO4 photocatalysts exhibit higher photocatalytic activities for degradation of thiophene under visible light irradiation. When pH value is 7.0 and the hydrothermal synthesize time is 8 h, the photocatalytic activities reach the maximum. Under the conditions of 150 mL/min air flow, 1.0 mg/L catalyst amount, and visible light irradiation for 3 h in 400 W xenon lamp light, the desulfurization rate by Co-BiVO4 at 600 mg/L initial concentration increases to 86%.
|
|
|
Effects of Heat Treatment Temperature on Photocatalytic Activity of TiO2/SiO2 Composite Aerogels
LIU Zhao-Hui, HOU Gen-Liang, SU Xun-Jia, GUO Feng, XIAO Zhou, JIA Hai-Peng
2012 Vol. 27 (10): 1079–1083
 Abstract
Abstract(
1294 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(414KB)(
1203
)
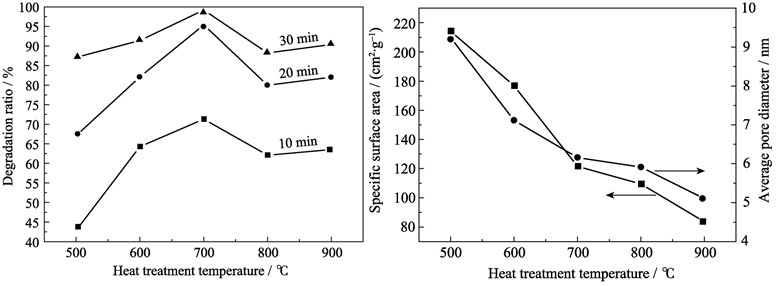
TiO2/SiO2 composite aerogels were prepared by Sol-Gel method at ambient pressure and heat-treated at different temperatures. The microstructure of TiO2/SiO2 composite aerogels was characterized by X-ray diffraction (XRD), thermo gravimetric analyzer (TGA) and N2 adsorption-desorption. The photocatalytic activity was evaluated by means of photocatalytic degradation of methyl orange under UV irradiation. The effects of heat treatment temperatures on microstructure and photocatalytic activity were investigated. With the increase of heat treatment temperature, the crystallization of anatase and the anatase grain size increase, however, the specific surface area decreases. As a result, the photocatalytic activity of TiO2/SiO2 composite aerogels is enhanced initially, then decreases with the increase of heat treatment temperature. When the heat treatment temperature is set at about 700℃, the degradation ratio of methyl orange on the TiO2/SiO2 composite aerogels reaches 95.4% after irradiated by ultraviolet light for 20 min.
|
|
|
Lead Evaporation from CRT Glass and Nanocrystallization Mechanism in the High-temperature Self-propagating Process
WANG Yu, XIE Yi-Jun, GAO Ya, ZHU Jian-Xin
2012 Vol. 27 (10): 1084–1088
 Abstract
Abstract(
1529 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(416KB)(
1130
)
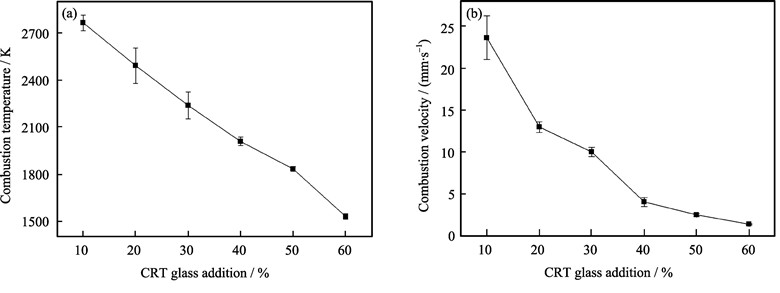
Lead evaporation and recovery of nanoparticle materials from waste cathode-ray tube (CRT) glass using the self-propagating high-temperature synthesis (SHS) method was investigated. The reaction temperature and combustion velocity of the mixture of Fe2O3-Mg-CRT in the SHS process were studied in detail. Then the lead extraction ratio, phase compositions as well as the micromorphology of extracted PbO nanoparticles were examined. The thermodynamics of lead evaporation and nanocrystallization mechanism were also analyzed. It can be found that the SHS reaction temperature and combustion velocity decrease with increasing CRT glass content, and the addition of CRT glass as a diluent can be used to control the SHS lead extraction behavior to obtain PbO nanoparticles with good desperation and morphology. With 40wt% CRT glass addition, about 93% of lead can be recovered from CRT glass as nano-sized PbO with high purity. The collected PbO nanoparticles are almost spherical in shape with particle sizes ranging from 40 nm to 50 nm, which are mainly from the volatilization and rapid condensation during the SHS process. The study indicates a novel method to recycle and reuse waste CRT glass.
|
|
|
Preparation and Gas-sensing Properties of Cu2+-doped ZnO Nanorods
CHEN Tong-Yun, ZHU Xiao-Hua, CHU Xiang-Feng, GE Xiu-Tao, DONG Yong-Ping, YE Ming-Fu
2012 Vol. 27 (10): 1089–1094
 Abstract
Abstract(
1351 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(535KB)(
1390
)
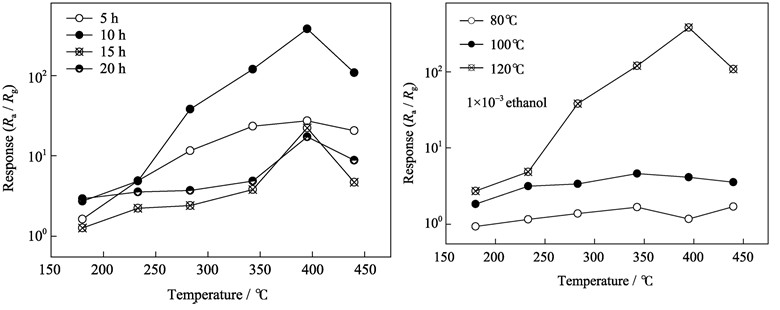
Cu2+-doped ZnO nano-rod powders (0–6mol%) were prepared via solvothermal method. The crystal and micro-morphology of the doped ZnO nano-rods were characterized by X-ray diffraction (XRD) and scanning electron microscope (SEM). The effects of Cu2+ dopant and the thermal condition (reaction temperature and duration) on the gas sensitivities of ZnO nano-rods were studied. The gas sensing properties of pure ZnO nanorod sensor and 3mol% Cu2+-doped ZnO nano-rod sensors to formaldehyde, acetic acid, toluene, ethanol, acetone and trimethylamine were also studied. The results show that the micro-morphology of ZnO powders are nano-rods, the lengths and diameters of ZnO nanorods change with the variation of the Cu2+ concentration. The sensor based on 3mol% Cu2+-doped ZnO nano-rods exhibits high response and good selectivity to dilute ethanol, the responses to 1×10-3 ethanol and 1×10–6 ethanol reach 380.5 and 4.2 when it works at 395℃, respectively, and its response time and recovery time are 16 s and 40 s, respectively.
|
|
|
Photoluminescence Properties of Eu2+, Dy3+, Li+ Co-doped CaSi2O2N2 Phosphors
LU Ya-Jun, WANG Hong-Zhi, LI Yao-Gang, ZHANG Qing-Hong
2012 Vol. 27 (10): 1095–1098
 Abstract
Abstract(
1159 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(400KB)(
1399
)
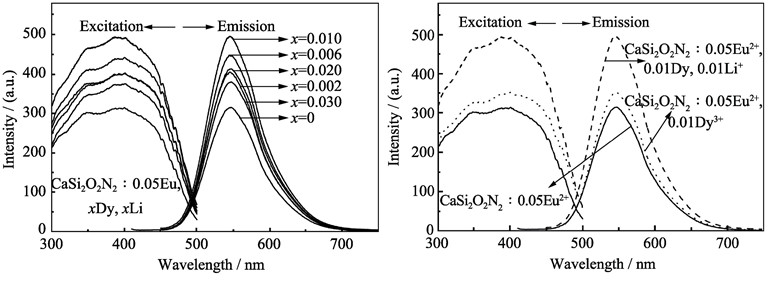
A series of CaSi2O2N2: 0.05Eu2+, xDy3+, xLi+ (0≤x≤0.03) phosphors were prepared through high-temperature solid-state reaction method. The phosphors were characterized by X-ray diffraciton (XRD) and fluorescence spectrophotometer (PL). XRD patterns revealed that the samples maintained CaSi2O2N2 single phase after doping Dy3+ or Li+ ions. The PL results showed that the excitation spectra of samples were all located in the UV to blue spectral region. The emission spectra for 400 nm excitation showed the typical broad band of Eu2+ peaking at about 545 nm (5d-4f). In addition, the emission intensity could be greatly enhanced through doping Dy3+ in CaSi2O2N2:Eu2+ phosphors. Furthermore, the effect of the Li+ doping was studied. Li+ ions could be used as charge compensation in CaSi2O2N2:Eu2+, Dy3+ phosphors. Thus the doping of Li+ ions could further improve the emission intensity of CaSi2O2N2:Eu2+, Dy3+ phosphor. When the doping concentrations of Dy3+ and Li+ were 1mol%, the emission intensity reached a maximum, which was about 157% of that of the sample without doping Dy3+ or Li+.
|
|
|
Reaction Mechanism of Ti3SiC2 Formed on the Diamond
MU Yun-Chao, LIANG Bao-Yan, GUO Ji-Feng
2012 Vol. 27 (10): 1099–1104
 Abstract
Abstract(
1300 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(509KB)(
1423
)
Ti3SiC2 bonded diamond materials were fabricated by spark plasma sintering using Ti/Si/TiC/diamond abrasive as the raw materials. The result showed that displace, dispalce rate and vaccum degree of Ti-Si-2TiC sample sintered by SPS were obviously changed. The Ti/Si/TiC powders were obviously sintered and transformed to TiC and Ti3SiC2 at 1200℃ during the sintering process. With increasing sintering temperature, Ti3SiC2 content in the samples increased. Ti3SiC2 content in the samples were 65.9%, 79.97%, 87.5% and 90.1%, respectively. Addition of (5% and 10%) appropriate amounts of diamond did not inhibit the reaction synthesis of Ti3SiC2. SEM observation showed that diamond had one close combination with the matris, and Ti3SiC2 grains grew on the surface of diamond. One formation mechanism of Ti3SiC2 on the surface of diamond was proposed, C on the surface of diamond reacted with Ti and formed TiC firstly, then TiC reacted with Ti-Si phase and formed Ti3SiC2.
|
|
|
Seeded Secondary Growth Synthesis of ZIF-8 Membranes Supported on α-Al2O3 Ceramic Tubes
DU Shu-Hui, LIU Ya-Guang, KONG Ling-Yin, ZHANG Jian, LIU Hai-Ou, ZHANG Xiong-Fu
2012 Vol. 27 (10): 1105–1111
 Abstract
Abstract(
1806 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(962KB)(
1998
)
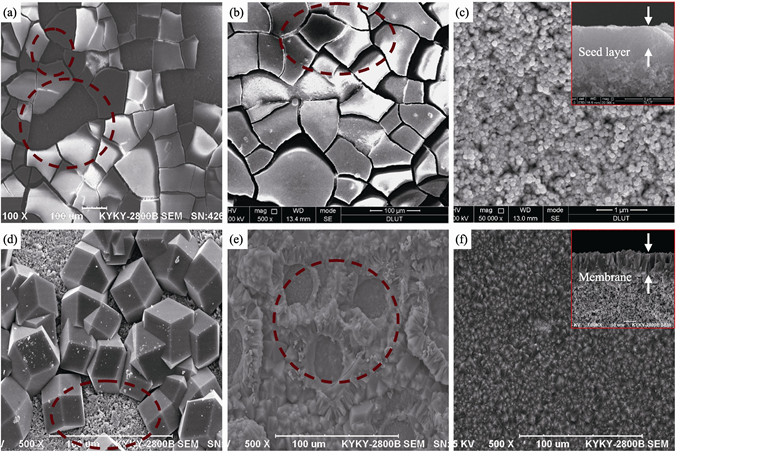
A seeded growth procedure was used to successfully prepare continuous and well inter-grown zeolitic imidazolate framework-8 (ZIF-8) membranes on porous α-alumina tubes. The effects of some parameters including the content of seeds and PEI in seeding solution, the concentration of sodium formate in synthesis solution and synthesis temperature on the formation of ZIF-8 membranes were investigated in detail. The characterization of SEM, XRD and single gas permeation showed that PEI added in the seeding solution can improve the adhesion between the seed crystals and the support surface. Moreover, sodium formate used in synthesis solution could prevent the seed layer from peeling off during the membrane growing process. The as-synthesized ZIF-8 membrane is well inter-grown and continuous. Single gas permeation shows that the separation factors of H2/CO2 and H2/CH4 are 5.4 and 2.56, respectively, indicating that Knudsen diffusion plays a controlling role in the gas permeation through the ZIF-8 membrane.
|
|
|
Effect of Sputtering Pressure on Al-doped ZnO Films by DC Magnetron Sputtering
SUN Ke-Wei, ZHOU Wan-Cheng, HUANG Shan-Shan, TANG Xiu-Feng
2012 Vol. 27 (10): 1112–1116
 Abstract
Abstract(
4529 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(628KB)(
1615
)
Al-doped ZnO (AZO) films were deposited on the glass substrates by direct current magnetron sputtering using different sputtering pressures ranging from 0.2 Pa to 2.2 Pa. Microstructure, phase, electrical and optical properties of AZO films were characterized by X-ray diffraction (XRD), scanning electron microscope (SEM), four-point probe and UV-Vis spectrophotometer, respectively. The results revealed that the deposition rate decreased with the increasing sputtering pressure according to Keller-Simmons model; the crystalline phase of all films was hexagonal wurtzite and the preferred orientation changed with the sputtering pressure; the surface morphology greatly depended on the sputtering pressure and the film deposited at 1.4 Pa showed low resistivity (8.4×10-4 Ω·cm), high average transmission and the highest Q, a criterion factor as the film figure of merit, which was the ratio between the normalized average transmission and the normalized resistivity.
|
|
|
Preparation and Thermal Insulating Properties of Antimony Doped Nano-SnO2/Waterborne Polyurethane Composite Coatings
LU Kou-Liu, JI Zhen-Guo, KONG Ze, LI Hong-Xia, ZHANG Jun
2012 Vol. 27 (10): 1117–1120
 Abstract
Abstract(
3183 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(387KB)(
1551
)
Transparent and thermal insulation coatings were prepared from antimony doped nano-SnO2/waterborne polyurethane composite emulsion. It’s found that thermal insulation is resulted from the absorbance of the infrared light by antimony doped nano-SnO2 particles in the composite coatings. Thermal insulation measurement results show that under illumination of sunlight, the temperature of the coated glass surface increases, while the temperature inside the measurement box decrease as much as 17.5℃. Therefore, antimony doped nano-SnO2/waterborne polyurethane composite coatings are cost effective thermal insulating coating due to many advantages such as low cost, chemically stable, and easy in process.
|
|