|
|
Research Progress on the Preparation of Ceramic Hollow Fiber Membranes by Nonsolvent Induced Phase Separation
LIU Peng-Chao, MA Jing-Hong, YANG Shu-Guang, GONG Jing-Hua, XU Jian
2012 Vol. 27 (7): 673–679
 Abstract
Abstract(
3282 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(519KB)(
1435
)
Ceramic hollow fiber membranes (CHFM) with an asymmetric structure can be fabricated by the method nonsolvent induced phase separation (NIPS). The paper reviews the progress and tendency of the ceramic hollow fiber membranes using NIPS technic, especially on the influence of factors on the structure of hollow membranes. The discussion on the mechanism of phase inversion in the systems containing much ceramic powders, with the balance between porous structure and mechanical strength, are two important issues of requiring concern. Through structure’s controlled effectively and mechanical strength preserved, hollow fiber membranes can be widely applied in the fields of separation and purification, solid oxide fuel cell (SOFC), membrane contactors and reactors.
|
|
|
Progress of Research on the Failure Mechanism of Thermal Barrier Coatings
HUA Jia-Jie, ZHANG Li-PENG, LIU Zi-Wei, WANG Yong-Zhe, LIN Chu-Cheng, ZENG Yi, ZHENG Xue-Bing
2012 Vol. 27 (7): 680–686
 Abstract
Abstract(
3655 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(584KB)(
2905
)
Thermal barrier coatings (TBCs) is one of the important materials of turbines for propulsion and power generation with excellent thermal insulation properties. At high temperature, the failure of TBCs will lead to serious problems, so the failure mechanisms is the hotspot of TBCs research. The microcracks caused by thermal stress and the TGO formation and growth will cause the failure of TBCs. The whole failure progress, such as the oxidation of the BC, the TGO growth process, initiation and propagation of the microcracks are reviewed in this paper. The factors led to the final failure are discussed, and the recent research progress on improving the lifetime of TBCs is summarized. In addition, the trend of the failure mechanism of thermal barrier coatings is described.
|
|
|
Preparation and Photocatalytic Properties of γ-Bi2O3/TiO2 Composite Fibers
LI Yue-Jun, CAO Tie-Ping, SHAO Chang-Lu, WANG Chang-Hua
2012 Vol. 27 (7): 687–692
 Abstract
Abstract(
2842 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(549KB)(
1552
)
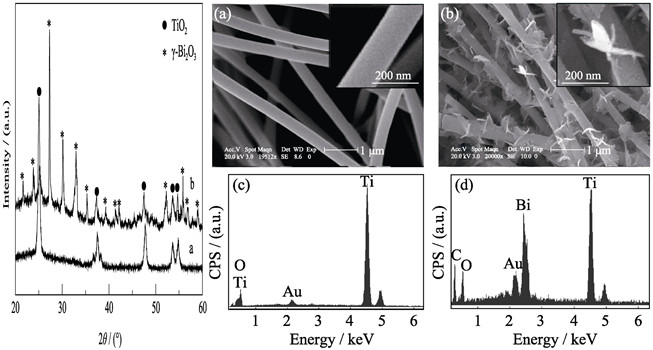
Heterostructured γ-Bi2O3/TiO2 composite fibers were prepared via combination of solvothermal method and electrospinning technique. X-ray diffraction (XRD), scanning electron microscope (SEM), energy dispersive spectroscope (EDS), transmission electron microscope (TEM), high-resolution transmission electron microscope (HRTEM) and UV-Vis absorption spectra were used to characterize heterostructured γ-Bi2O3/TiO2 composite fibers. The photocatalytic properties of the heterostructured samples were evaluated by degrading rhodamine B (RB) under visible light irradiation. The results showed that γ-Bi2O3 nanosheets could evenly grow on the TiO2 fibers surface and thus heterostructured γ-Bi2O3/TiO2 composite fibers were successfully obtained. The absorption range of the as-obtained heterostructured samples were extended to the visible light region. Moreover, the presence of γ-Bi2O3 nanostructures/TiO2 fibers heterostructures was beneficial to separation of photo-generated electrons and holes which enhanced the system’s quantum efficiency. In comparison with that of pure TiO2 nanofibers, the γ-Bi2O3/TiO2 heterostructures have enhanced photocatalytic efficiency under visible light irradiation, and the decolorizing efficiency of RB solution can reach 87.8%.
|
|
|
Effect of Crystalline State of Anodized Porous Al2O3/Al as Supports by Hydration
ZHANG Qi, JIANG Zhong-Rui, SUN Dong-Mei, HAN Da-Ying, ZHU Zi-Bin
2012 Vol. 27 (7): 693–698
 Abstract
Abstract(
2512 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(758KB)(
1889
)
The porous alumina as a plate catalytic support was prepared by anodization. Effects of hydration condition on the property of alumina supports were studied. The samples were characterized by XRD, SEM, BET and etc. to illustrate the Al2O3/Al forming mechanism. The results show that the best hydration temperature is 80℃, at which the amorphous alumina can be transformed into AlOOH, and become γ-Al2O3 after 500℃ calcination. Meanwhile, the monoliths catalytic carriers have a superior stability for crystalline structures in the steam atmosphere at high temperature.
|
|
|
Synthesis of Vanadium-mesoporous Hollow Spheres
SHI Xiao-Bo, CHEN Yu, KONG Yan, WU Cheng, WANG Jun
2012 Vol. 27 (7): 699–705
 Abstract
Abstract(
2540 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(695KB)(
1556
)
Vanadium-containing mesoporous silica with hollow spherical morphology was successfully synthesized by using CTAB, SDS and P123 as co-template. The influences of vanadium content and reaction conditions on the formation of the materials were also studied. Results indicated that the hollow spheres could not be shaped as molar ratio of V to Si was lower than 0.05 while excess vanadium content led large amount of vanadium oxides existed in the materials. The adequate molar ratio of V to Si was 0.1. The optimal synthesis conditions were reacted at 45℃ for 2 h under pH value of 5. The products with regular structure and morphology exhibited high catalytic activity on the selective oxidation of styrene by hydrogen peroxide.
|
|
|
Hydrothermal Method Synthesis and Characterization of YVO4:Eu3+@YPO4 Core-shell Phosphor
WU Ke, WANG Le, XU Guo-Tang, ZOU Shi-Bi, HUANG Jie, GU Pei-Fu, LIANG Pei
2012 Vol. 27 (7): 706–710
 Abstract
Abstract(
3124 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(597KB)(
1657
)
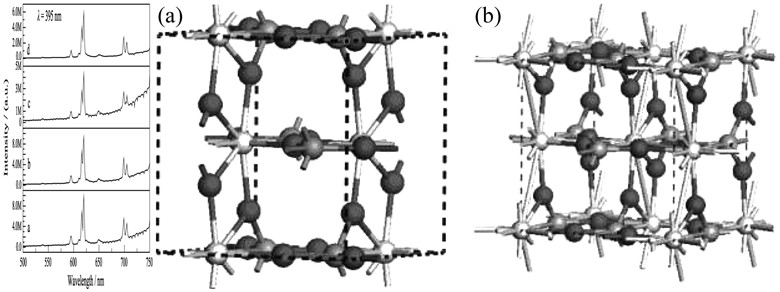
In order to improve the stability and luminous efficiency of YVO4:Eu3+ phosphor, YVO4:Eu3+@YPO4 nano core-shell phosphor was prepared by using hydrothermal method. X-ray diffraction (XRD), transmission electron microscope (TEM), and photoluminescence spectra were used to characterize the feature of YVO4:Eu3+@YPO4 core-shell phosphor. The XRD and TEM results indicate that the synthetic products are composed of the YVO4:Eu3+ core and YPO4 shell. The core-shell phosphor with diameter of 10–30 nm and shell thickness of 5–10 nm, regular crystalline morphologies, highly uniform in size and distribution, high degree of crystallinity. The photoluminescence spectra show that the luminous efficiency of YVO4:Eu3+@YPO4 core-shell phosphor is 66.75% higher than that of YVO4:Eu3+ phosphor, which also has high color purity. Furthermore, the first principle calculation is used to calculate the band-structure of the YVO4 and YPO4 crystals. On base of the calculated result, the relationship between the electron transition and the luminance is illustrated.
|
|
|
2.00 μm Emission Properties of Tm3+/Ho3+ Co-doped Chalcohalide Glasses
WEI Shu-Lin, XU Yin-Sheng, ZHANG Pei-Qing, CHEN Fei-Fei, NIE Qiu-Hua, XU Tie-Feng, DAI Shi-Xun
2012 Vol. 27 (7): 711–715
 Abstract
Abstract(
2638 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(445KB)(
1676
)
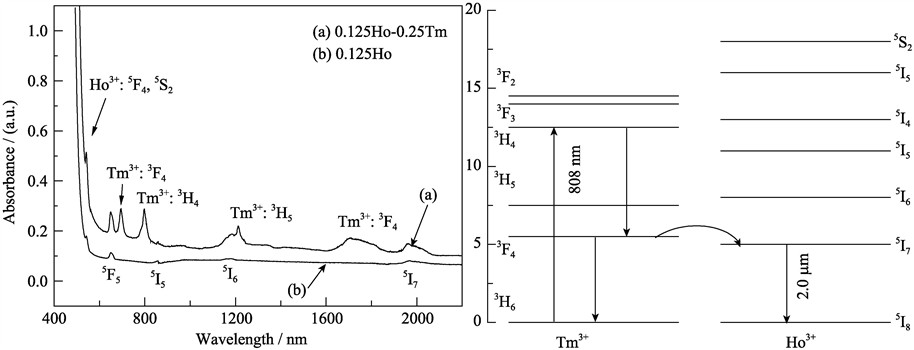
2 μm laser has many potential applications on the medical surgery, laser radar, and pollution monitoring etc. Tm3+ and Ho3+ ions co-doped 70GeS2-20In2S3-10CsI chalcohalide glasses were synthesized by vacuumed melting- quenching technique. The DSC curves and Raman spectra showed that these glasses had good thermal stability and low phonon energy, respectively. The absorption and emission characteristics were evaluated with an emphasis on the 2.00 μm fluorescence from Ho3+: 5I7→5I8 transition. Under 808 nm excitation, the infrared emission bands extending from 1.80 μm to 2.10 μm can be seen on the emission spectra of the Tm3+ and Ho3+ ions co-doped glasses. This broad emission was consisted of two emission bands centered at 1.86 and 2.00 μm, corresponding to the optical transitions Tm3+:3F4→3F5 and Ho3+:5I7→5I8, respectively. At fixed Tm3+ ions concentration, the intensity of 2.00 μm emission increased with Ho3+ ions concentration increasing from 0.05mol% to 0.125mol%. The enhanced emission of Ho3+ ions gives another route to obtain the 2.00 μm infrared laser.
|
|
|
ZnO Nano-arrays on High Power Blue LED Chip for Enhanced Light Extraction Efficiency
XU Bing, ZHAO Jun-Liang, ZHANG Jian-Ming, SUN Xiao-Wei, ZHUGE Fu-Wei, LI Xiao-Min
2012 Vol. 27 (7): 716–720
 Abstract
Abstract(
2836 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(664KB)(
1391
)
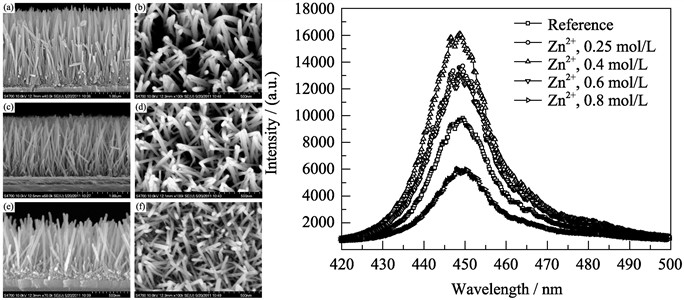
ZnO nano-arrays were grown on high power GaN blue LED chip by low-cost chemical solution methods, which aimed to enhance the light extraction efficiency of LED chip. Various morphology was achieved by adjusting the concentration of ammonia and Zn2+ in the growth solution. With different growth solution, ZnO nano-arrays exhibited different morphologies and densities. The effect of nano-array morphology on the light extraction performance of the ZnO nano-array coated LED chip were studied. The mechanism of light extraction efficiency enhancement by nano-arrays was also discussed based on the experimental results. The result shows that ZnO nano-arrays with higher density and cone-shaped morphology are favorable for the improvement of light extraction in LED chip. ZnO nano-arrays grown at the optimum conditions can enhance the light extraction of LED chip by more than 60%. Meanwhile, ZnO nano-arrays have no significant effect on the electrical properties and electroluminescence stability of LED chip.
|
|
|
Effect of Ho Doping on Structure and Ferroelectric Property of Bi4-xHoxTi3O12 Ceramics
WANG Chuan-Bin, FU Li, SHEN Qiang, ZHANG Lian-Meng
2012 Vol. 27 (7): 721–725
 Abstract
Abstract(
2577 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(526KB)(
1622
)
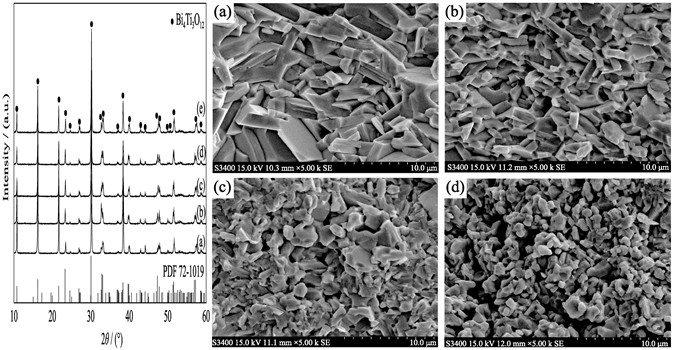
Ho-doped bismuth titanate (Bi4-xHoxTi3O12) ceramics were prepared by hot-press sintering. The effects of Ho doping on the crystalline phase, density, microstructure and ferroelectric property of the ceramics were investigated. At first, Bi4-xHoxTi3O12(x=0-0.8) powders in the main phase of Bi4Ti3O12 were synthesized from Bi2O3, TiO2 and Ho2O3 micro-powders by solid-state reaction at 900℃. The as-synthesized powders were then sintered by hot-press at 850℃ and 30 MPa to prepare Bi4-xHoxTi3O12 ceramics. With the appropriate Ho doping content of x=0-0.4, single-phased and dense (relative density >99%) Bi4-xHoxTi3O12 ceramics were obtained. The remanent polarization (Pr) of the ceramics increased with Ho doping increasing but decreased at x>0.4, mainly due to the oxygen vacancy concentration and different doping sites. The Bi4-xHoxTi3O12 ceramics have the highest value of 2Pr=13.92 μC/cm2 at x=0.4, which is higher that that of the undoped Bi4Ti3O12 ceramics. The result indicates that appropriate Ho doping can improve the ferroelectric property of Bi4Ti3O12 ceramics.
|
|
|
Study on A-site Cation Doping of CaBi2Nb2O9 with Bismuth Layered Structure
ZONG Li-Chao, ZENG Jiang-Tao, ZHAO Su-Chuan, RUAN Wei,LI Guo-Rong
2012 Vol. 27 (7): 726–730
 Abstract
Abstract(
2537 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(511KB)(
2093
)
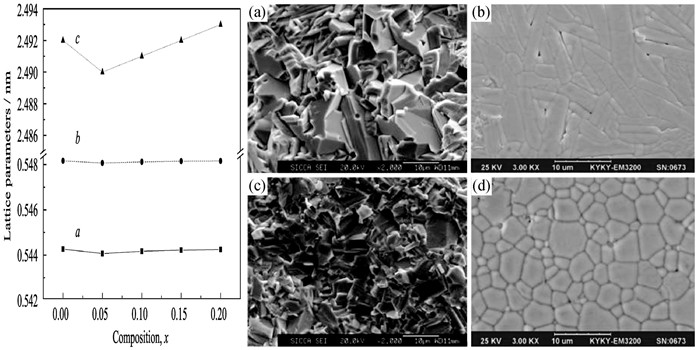
High curie temperature piezoelectric ceramics based on KLa-doped Ca1-x(KLa)x/2Bi2Nb2O9(x=0–0.20) were prepared by a conventional solid state reaction method. Crystal structure and microstructures of Ca1-x(KLa)x/2Bi2Nb2O9 ceramics were characterized by XRD and SEM. XRD patterns show that the crystal structures are a single phase of bismuth oxide layer structure having general formula (Bi2O2)2+(Am-1BmO3m+1)2- with m = 2. The grains of polished and thermally etched surfaces revealled a plate-liked morphology. The Curie point (Tc) decreases obviously whereas the piezoelectric activity of CBNO ceramics is significantly improved by the doping of potassium and lanthanum. The KLa-doped CBNO materials have an electrical conductivity value 1–2 orders of magnitude lower than undoped samples. The thermal depoling behavior of Ca1-x(KLa)x/2Bi2Nb2O9 ceramics shows that all of them have a high Curie point (Tc≥850℃) and show good resistance to thermal depoling up to temperatures close to their Curie points. The results showed that the excellent properties is obtained in the ceramics with composition of x=0.1, i.e. d33=15.8 pC/N, Tc=870℃ and the DC conductivity is one order of magnitude smaller than that of undoped CBNO. All the results suggest that the doped CaBi2Nb2O9 is a potential material for high temperature sensor.
|
|
|
Preparation and Properties of Sm2O3 Doped (Ba0.7Ca0.3)TiO3-Ba(Zr0.2Ti0.8)O3 Lead-free Piezoelectric Ceramics
CUI Ye-Rang, LIU Xin-Yu, YUAN Chang-Lai, ZHAI Xia, HU Yao-Bin, LI Ruo-Wen
2012 Vol. 27 (7): 731–734
 Abstract
Abstract(
2734 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(484KB)(
1549
)
Sm2O3 doped (Ba0.7Ca0.3)TiO3-Ba(Zr0.2Ti0.8)O3 (BCZT) lead-free piezoelectric ceramics were prepared by solid state synthesis method. The microstructure and electrical properties of prepared ceramics were investigated by XRD, SEM and other techniques. The results demonstrate that Sm2O3 doping reduces sintering temperature of BCZT lead-free piezoelectric ceramics and increases the Curie temperature Tc from 85℃ to 95℃. BCZT ceramics doped with 0.02wt%-0.1wt% Sm2O3 possess a typical ABO3 type perovskite structure.With the doping of 0.02wt% Sm2O3, the BCZT ceramics show the optimum electrical properties, and its piezoelectric constant d33, electromechanical coupling factor kp, mechanical quality factor Qm, dielecteic loss tanδ and relative dielectric constant εr reach 590 pC/N, 0.52, 43, 1.3% and 3372, respectively.
|
|
|
Properties and Phase-transition Temperature of (1–x)Bi(Mg2/3Nb1/3)O3-xPbTiO3 Piezoelectric Ceramics Near the Morphotropic Phase Boundary
HONG Lin, ZHAO Li-Yan, ZHU Xing-Wen, ZHENG Liao-Ying, ZENG Jiang-Tao, LI Guo-Rong
2012 Vol. 27 (7): 735–740
 Abstract
Abstract(
2713 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(546KB)(
1382
)
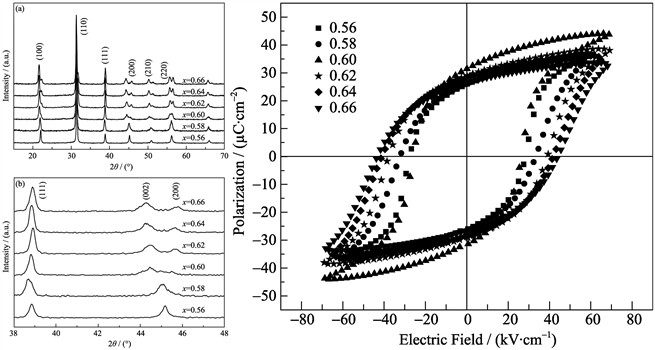
The (1–x)Bi(Mg2/3Nb1/3)O3-xPbTiO3 (BMN-PT) piezoelectric ceramics were fabricated by a traditional solid-reaction method. The crystal structures, the piezoelectric, dielectric and ferroelectric behaviors of BMN-PT ceramics were investigated as a function of the content of PbTiO3. XRD results showed that a single perovskite structure was obtained in all ceramic samples. XRD patterns of the samples with PbTiO3 content x≥0.60 had two obvious divided peaks, which verified that the rhombohedral and tetragonal phase were coexisted. The morphotropic phase boundary (MPB) of BMN-PT material was located at x=0.60. The largest piezoelectric coefficient d33 (170 pC/N), remnant polarization Pr (31.4 μC/cm2), planar electromechanical coupling factor kp (0.35) and the smallest coercive field Ec were obtained on 0.4BMN-0.6PT. The measurements of dielectric constant εr(T) dependencies showed that the maximum εr(T) temperature (Tm) increased with the increase of PbTiO3 content, and Tm was about 276℃ for the MPB composition.
|
|
|
Analysis on Equilibrium Shape of Nano-precipitations at Grain Boundaries in Bismuth Doped Strontium Titanate Ceramics
XING Juan-Juan, GU Hui
2012 Vol. 27 (7): 741–745
 Abstract
Abstract(
2552 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(574KB)(
1464
)
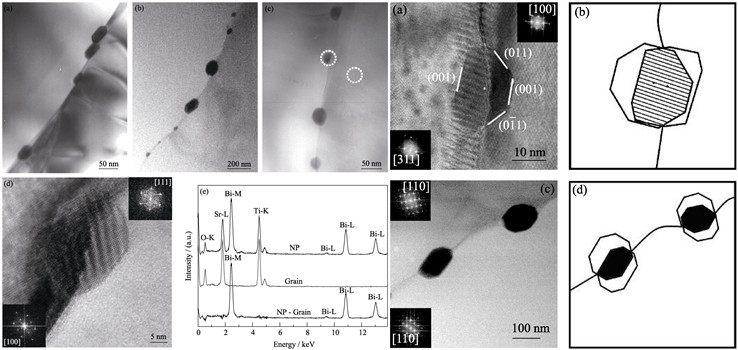
Grain boundary structures in Bi-doped strontium titanate ceramics were characterized by transmission electron microscope (TEM). Discontinuous nano-precipitations (NPs), whose sizes ranged from ten to over one hundred nanometers, were observed aligning along some grain boundaries. The composition of NP was detected as pure bismuth by spatial difference energy dispersive X-ray spectra (EDXS) method. Different shapes with facets were possessed by the NPs, indicating the anisotropy of NPs. The Cahn-Hoffman ξ-vector construction based on anisotropic surfaces was successfully applied to qualitatively describe the equilibrium shape of NP, which can be regarded as the intersection of two Wulff shapes at the grain boundaries. The distance between the two Wulff shapes centers is equal to the grain boundary energy. The Wulff shape itself, orientation of neighboring grains, grain boundary energy and grain boundary twist are considered as the important factors to affect the equilibrium shape of NP. Besides these, the size of NP will also influence the faceting of NP. This work is helpful to deepen the understanding of the microstructure evolvement during the sintering.
|
|
|
Characteristics of Sb Film Electrode Prepared by Vacuum Depositing
LI Yan-Hong, QIU Xin-Ping, LIU Yuan
2012 Vol. 27 (7): 746–750
 Abstract
Abstract(
2701 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(579KB)(
1537
)
Vacuum depositing was employed to prepare antimony (Sb) film electrode as anode for lithium-ion batteries. The crystal structure, surface morphology, electrochemical properties and lithium insertion/ extraction characteristics of the so-obtained film electrode were investigated by XRD, SEM, constant current charge-discharge testing and CV. The results show that Sb film is obtained with a hexagonal structure and (003) preferred orientation. The morphology of Sb film is similar to that of Cu foil and Sb metal possesses a platelet shape. It can be observed that Li3Sb alloy appears and Sb phase disappears during the first lithium insertion process, and Sb phase appeares and Li3Sb alloy disappears reversibly during the lithium extraction process. The initial lithium insertion/ extraction specific capacity of Sb film can reach 652 and 454 mAh/g, respectively. And insertion specific capacity is 300 mAh/g after 16 cycles, which is larger than that of Sb powder electrode.
|
|
|
Synthesis and Characterization of GdBaCo2O5+δ Cathode Material by Glycine-nitrate Process
JIN Hong-Jian, WANG Huan, ZHANG Hua, JIN Jiang
2012 Vol. 27 (7): 751–756
 Abstract
Abstract(
2750 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(608KB)(
1264
)
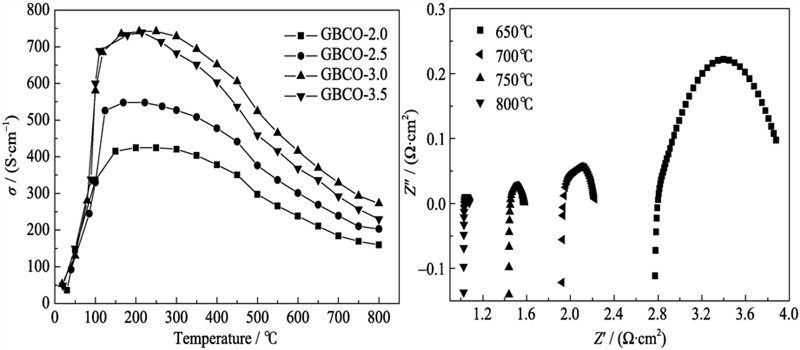
GdBaCo2O5+δ (GBCO) powders were synthesized by the glycine-nitrate process (GNP) with different glycine/metal ratios (G/M) and characterized as cathode material for intermediate temperature solid oxide fuel cell(IT-SOFC). The effects of G/M ratios on the performance and properties of GBCO electrodes including the morphology, crystal structure, electrical conductivity and electrochemical properties were evaluated. The GBCO powder synthesized at G/M ratio of 3.0 (GBCO-3.0) showed the highest specific surface area. XRD results proved that the precursor powders calcined at 1000℃ for 5 h formed GBCO single-phase when the ratio of glycine to metal was in the range of 2.5–3.5. There were no chemical reaction occurred between the GBCO cathode and the Sm0.2Ce0.8O1.9 (SDC) electrolyte after calcination at 1100℃. The electrical conductivities of all GBCO cathodes were over 100 S/cm at intermediate temperature (500–800℃). The GBCO-3.0 cathode calcined at 1050℃ exhibited the lowest polarization resistance (RP) of 0.125 Ω·cm2 at 750℃.
|
|
|
Synthesis and Electrochemical Performance of TiO2/C Nanocomposites
JIN Shuang-Ling, DENG Hong-Gui, ZHAN Liang, ZHAO Yue, QIAO Wen-Ming, LING Li-Cheng
2012 Vol. 27 (7): 757–763
 Abstract
Abstract(
3243 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(706KB)(
1477
)
TiO2/C nanocomposites with diameter of 300-400 nm were synthesized through hydrothermal reaction from titanium glycolate spheres with glucose as carbon precursor. The effects of the glucose concentration on the morphology, structure and carbon coating and electrochemical performance of the product were investigated. When the carbon content of TiO2/C nanocomposite was 7wt%, its average crystallite size, BET surface area and average pore size were 7.1 nm, 157 m2/g and 5.2 nm, respectively. When the TiO2/C nanocomposites is used as anode materials for lithium-ion battery, it delivered a capacity of 160 mAh/g after 80 charge/discharge cycles at a current rate of 0.2C with a good rate capability.
|
|
|
Grinding Characteristics of Reaction Bonded Silicon Carbide
YAO Wang, ZHANG Yu-Min, HAN Jie-Cai, ZHOU Yu-Feng
2012 Vol. 27 (7): 764–768
 Abstract
Abstract(
2700 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(477KB)(
2979
)
Surface topography, surface residual stress and bending strength of RBSiC ground using diamond wheel were studied. Grinding RBSiC is removed mainly by brittle fracture and lightly by ductile cutting. With the increase of down feed, surface roughness Ra increases. Burnishing with no down feed can improve the Ra in some way. With increasing down feed, the compressive residual stress decreases because of an inadequately cooling effect. Compare with the specimens grounded using 0.9 μm/s, those using down feed of 1.35 μm/s have worse surface quality. Considering both the processing efficiency and the surface quality, the optimum parameters are as follow: 0.9 μm/s down feed, 2.1 r/min work table rotational speed and 1 min burnishing.
|
|
|
Synthesis of Graphene with Microwave Irradiation in Liquid Phase
WANG Can, WANG Yan-Li, ZHAN Liang, YANG Guang-Zhi, YANG Jun-He, QIAO Wen-Ming, LING Li-Cheng
2012 Vol. 27 (7): 769–774
 Abstract
Abstract(
3849 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(537KB)(
2392
)
Graphite oxide was synthesized with Hummers method using natural flake graphite as carbon source, and then graphene was prepared through microwave irradiation in N-methyl-2-pyrrolidinone (NMP) solvent. NMP solvent was heated selectively during the microwave irradiation process, meantime, the oxygen containing groups of graphite oxide were decomposed into CO, CO2 and H2O gases, resulting in the exfoliation and reduction of graphite oxide. XRD, SEM, EDS, TEM, HRTEM, SAED, XPS and Raman were performed to characterize the synthesized graphene. The results indicate that the synthesized graphene is transparent with several microns in size, which consists of 2–5 graphitic layers with high crystalline structure. The synthesized graphene can disperse homogenously in the NMP solvent.
|
|
|
Effects of Hydrothermal Growth Conditions of ZnO Nanorods Arrays on Flexible Dye-sensitized Solar Cells
ZHU Xin-Bo, FANG Xiao-Dong, DENG Zan-Hong, DONG Wei-Wei, WANG Shi-Mao, SHAO Jing-Zhen, HU Lin-Hua, ZHU Jun
2012 Vol. 27 (7): 775–779
 Abstract
Abstract(
6441 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(510KB)(
1904
)
ZnO nanorod arrays (ZNRs) were prepared on the tin-doped indium oxide polyethylene terephthalate (ITO-PET) by hydrothermal method under different conditions. Morphology of ZNRs was characterized by some quantitative parameters such as the diameter and length of nanorod and the density of rods. All these parameters were adjusted by changing the reaction conditions. Two important reaction conditions including reaction time and precursor concentration are discussed separately. It is demonstrated that the precursor concentration has great influence on the aspect ratio of nanorod. Flexible substrates with ZNRs are used as the novel photoanode of flexible dye-sensitized solar cells (DSCs). The aspect ratio of nanorod has major influence on the performance of flexible DSCs. The performance of flexible DSCs is improved by controlling the reaction conditions.
|
|
|
Investigation on Intercalation Modification of Sodium-montmorillonite by Cationic Surfactant
LIU Hua-Bin, XIAO Han-Ning
2012 Vol. 27 (7): 780–784
 Abstract
Abstract(
7077 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(400KB)(
1810
)
Sodium-montmorillonite (Na+-MMT) was intercalation modified with octadecyl trimethyl ammonium chloride (OTAC) in aqueous suspension via an ion exchange mechanism. Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) study indicates that OTAC is successfully intercalated into Na+-MMT layers and/or adsorbed on the surface of Na+-MMT. X-ray diffraction (XRD) analysis revealed that the interlayer spacing of the Na+-MMT was extended with the content of OTAC increasing, and the maximum spacing can reach about 3.80 nm. Results of scanning electron microscopy (SEM) analysis reveals the morphologies change from soherical-like particles to high-aspect ratio flakes after modification. Different configurations of OTA+ chains within MMT interlayer are proposed based on the above analysis. The results of contact angle and the dispersion analysis show that the surface wettability of Na+-MMT is converted from hydrophilic to organophilic.
|
|