
Journal of Inorganic Materials ›› 2020, Vol. 35 ›› Issue (1): 131-138.DOI: 10.15541/jim20190139
Special Issue: MAX相和MXene材料; 副主编黄庆研究员专辑; MXene材料专辑(2020~2021); 【虚拟专辑】层状MAX,MXene及其他二维材料
• RESEARCH LETTERS • Previous Articles Next Articles
MA Bao-Kai1,2,3,LI Mian3,CHEONG Ling-Zhi2( ),WENG Xin-Chu1,SHEN Cai3,HUANG Qing3
),WENG Xin-Chu1,SHEN Cai3,HUANG Qing3
Received:2019-03-28
Published:2020-01-20
Online:2019-05-29
About author:MA Bao-Kai (1992-), male, Master candidate. E-mail: mabaokai@nimte.ac.cn
Supported by:CLC Number:
MA Bao-Kai, LI Mian, CHEONG Ling-Zhi, WENG Xin-Chu, SHEN Cai, HUANG Qing. Enzyme-MXene Nanosheets: Fabrication and Application in Electrochemical Detection of H2O2[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2020, 35(1): 131-138.
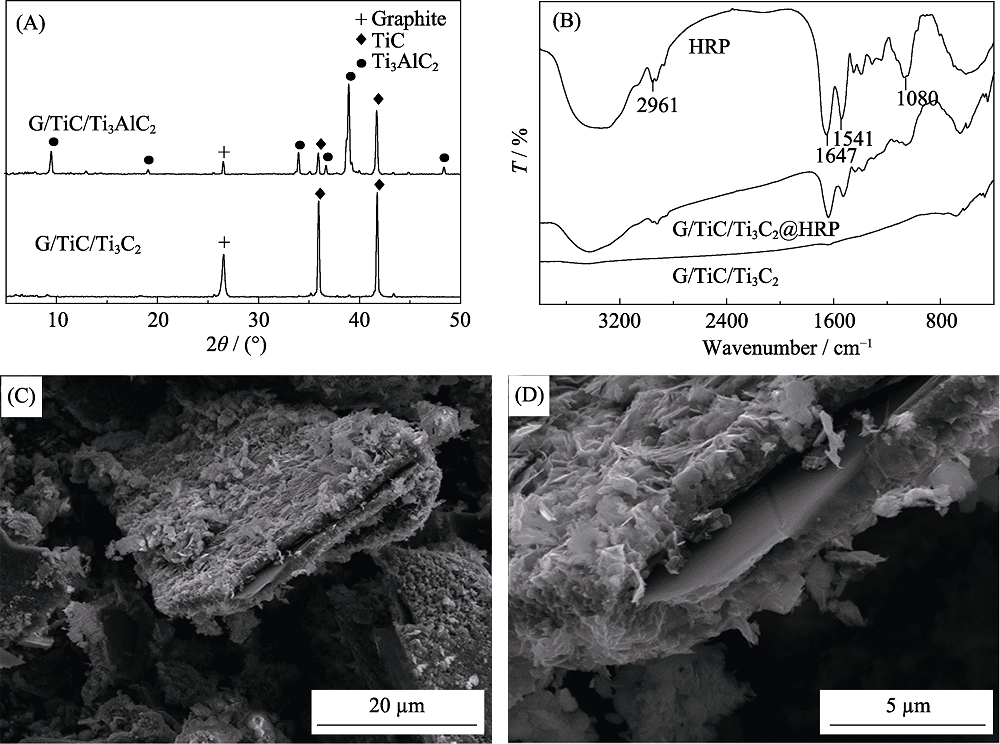
Fig. 2 XRD patterns of G/TiC/Ti3AlC2 and G/TiC/Ti3C2 (A); FT-IR spectra of the MXene, HRP and HRP@MXene (B); SEM images of the MXene G/TiC (C) and Ti3C2 (D)

Fig. S1 EIS of various electrodes in 0.1 mol?L-1 KCL aqueous solution containing 5 mmol?L-1 [Fe(CN)6]3-/4-: Chit (pH 5.0)/GCE (curve b, red line), Chit (pH 6.0)/GCE (curve c, blue line) , Chit (pH 6.5)/GCE (curve d, green line), Chit (pH 7.0)/GCE (curve e, pink line) (A); CV curves of Chit (pH 5.0)/GCE (curve b, red line), Chit (pH 6.0)/GCE (curve c, blue line) , Chit (pH 6.5)/GCE (curve d, green line) , Chit (pH 7.0)/GCE (curve e, pink line) electrodes cycled in 0.1 mol?L-1 KCL aqueous solution containing 5 mmol?L-1 [Fe(CN)6]3-/4-: (potential window: -0.1-0.5 V vs. SCE) (B)
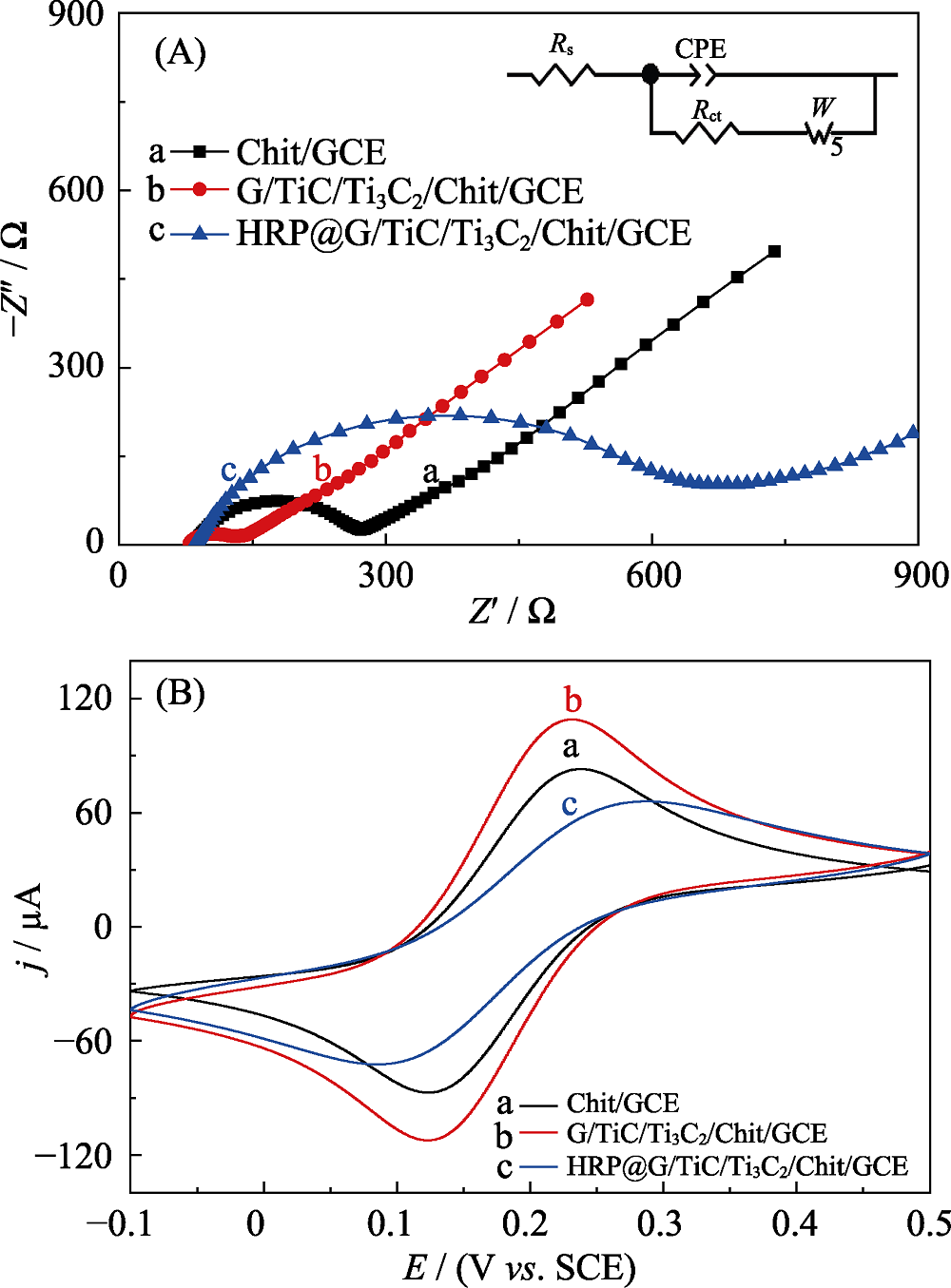
Fig. 3 EIS of Chit(chitosan)/GCE(a), MXene/Chit/GCE(b), HRP@MXene/Chit/GCE (c) electrodes cycled in 0.1 mol?L-1 KCL aqueous solution containing 5 mmol?L-1 [Fe(CN)6]3-/4- (A); CV curves of Chit/GCE (a), MXene/Chit/GCE (b), HRP@MXene/Chit/GCE (c) electrodes cycled in 0.1 mol?L-1 KCL aqueous solution containing 5 mmol?L-1 [Fe(CN)6]3-/4-: (potential window: -0.1-0.5 V vs. SCE) (B)
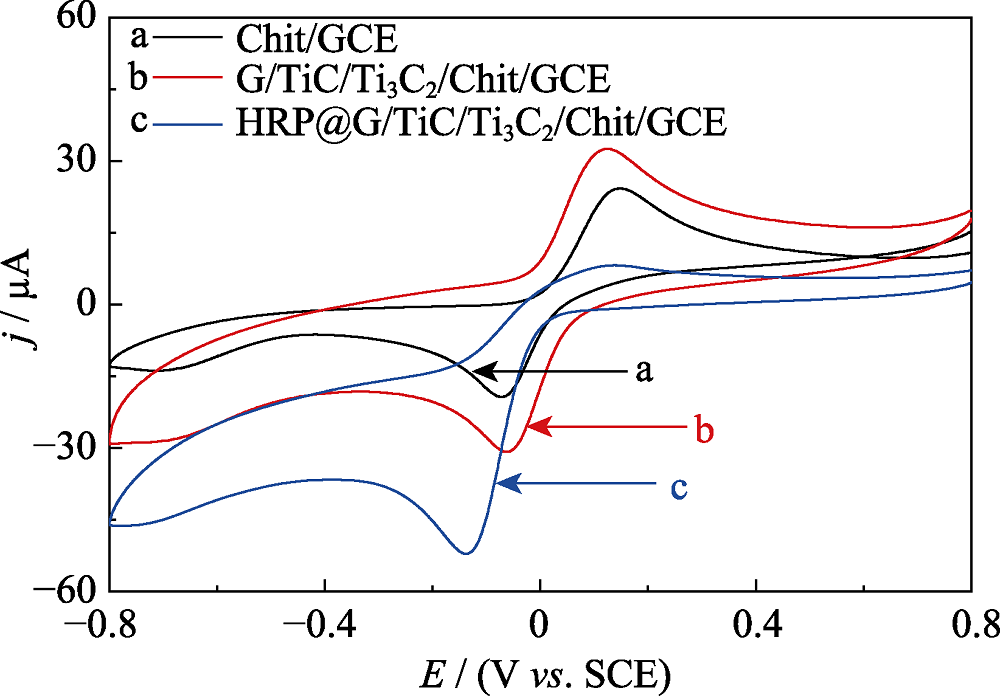
Fig. 4 CV curves of Chit/GCE (curve a, black line), MXene/ Chit/GCE (curve b, red line), HRP/Chit/GCE (curve c, pink line), HRP@MXene/Chit/GCE (curve d, blue line) electrodes cycled in N2-saturated 0.1 mol?L-1 PBS (pH 7.5) containing 1.0 mmol?L-1 HQ and 2.0 mmol?L-1 H2O2 at a scanning rate of 50 mV?s-1 (potential window: -0.8-0.8 V vs. SCE).
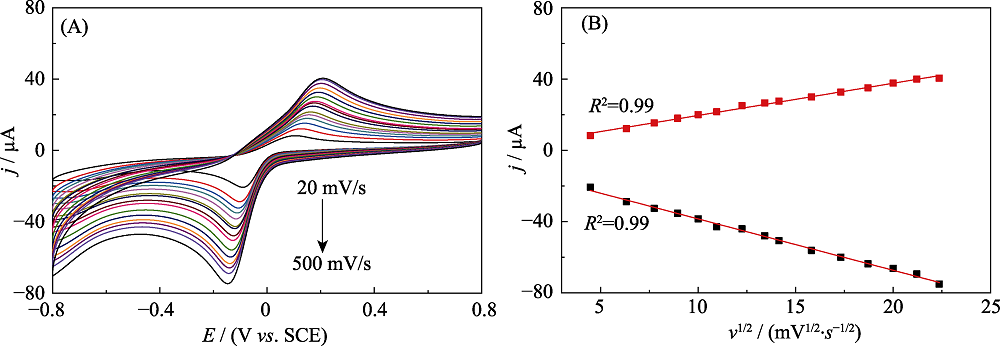
Fig. S2 CV curves of HRP@MXene/Chit/GCE electrodes cycled in N2-saturated 0.1 mol?L-1 PBS (pH 7.5) containing 1.0 mmol?L-1 HQ and 2.0 mmol?L-1 H2O2 at a different scanning rates (20-500 mV?s-1) (A); Plot of cathodic and anodic peak current for HRP@MXene/Chit/GCE versus scanning rate (B); Inset: Plots of anodic peak potential and cathodic peak potential for HRP@MXene/Chit/GCE electrode versus the logarithm of scan rate
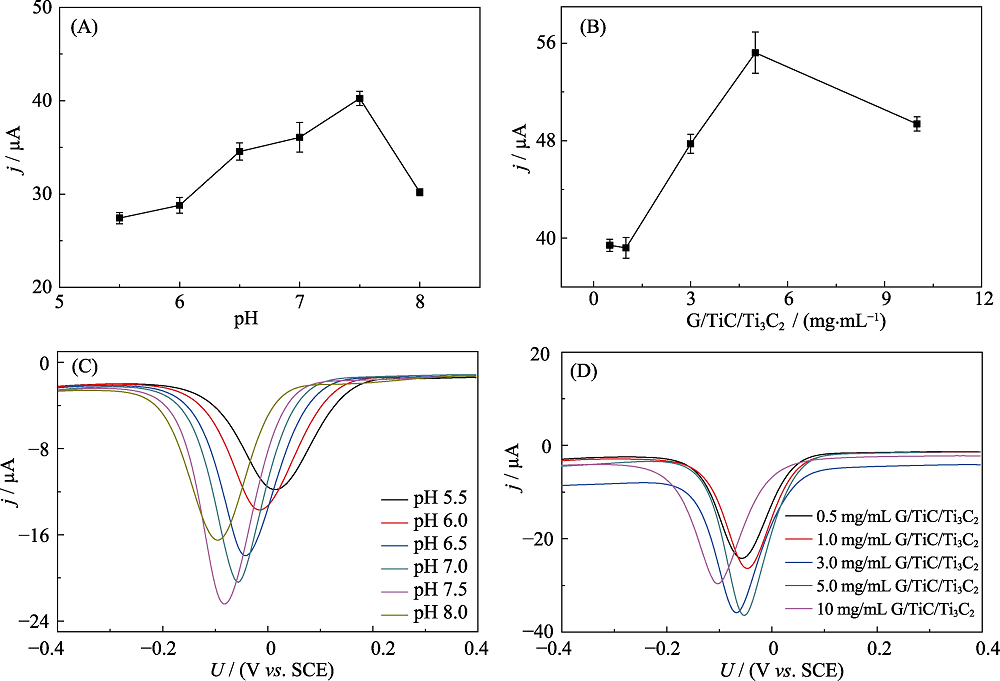
Fig.S3 Effects of PBS buffer’s pH (A) and concentration of MXene (B) on the cathodic peak current of enzyme biosensor cycled in N2-saturated 0.1 mol?L-1 PBS ( pH 7.5) containing 1.0 mmol?L-1 HQ and 2.0 mmol?L-1 H2O2; Effects of PBS buffer’s pH (C) and concentration of MXene (D) on the DPV response of enzyme biosensor cycledin N2-saturated 0.1 mol?L-1 PBS (pH 7.5) containing 1.0 mmol?L-1 HQ and 2.0 mmol?L-1 H2O2
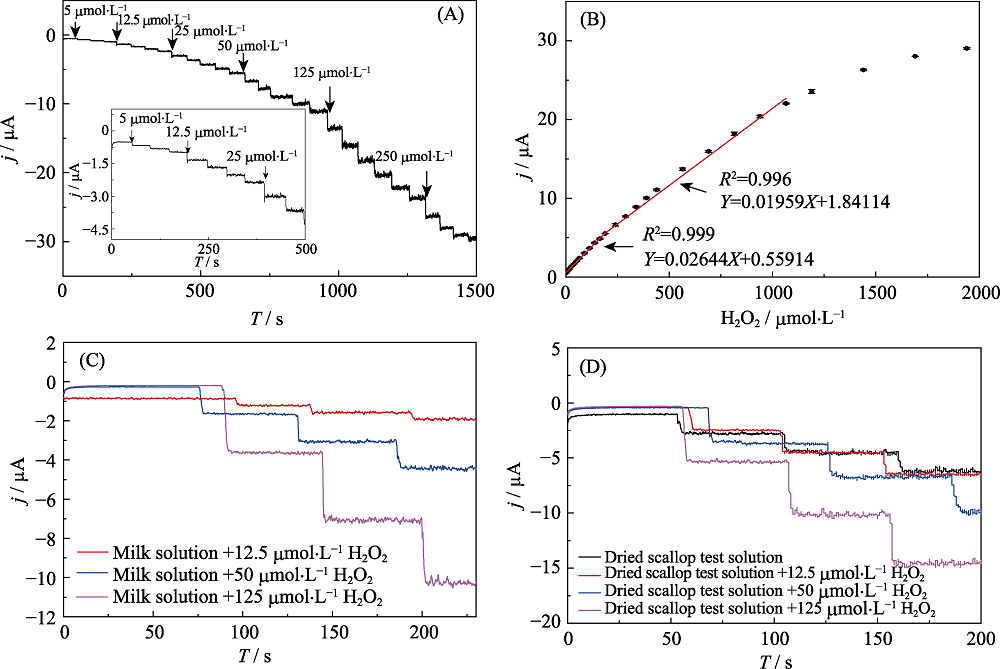
Fig. 5 Amperometric responses of HRP@MXene/Chit/ GCE at -0.1 V upon successive additions of H2O2 in astirred 0.1 mol?L-1 PBS (pH 7.5) (A); Calibration curve of amperometric responses at different H2O2 concentrations (B); Amperometric responses of HRP@MXene/Chit/ GCE at -0.1 V upon successive additions of solutions extracted from milk sample (C) and dried scallop (D) spiked with different H2O2 under stirred 0.1 mol?L-1 PBS (pH 7.5)
| Electrode | Linear range/(mmol?L-1) | LOD/(mmol?L-1) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|
| HRP-CTAB-Au/GCE | 0.50-105 | 0.23 | [1] |
| HRP/GO/GCE | 0.002-0.5 | 1.6 | [2] |
| HRP/TB/CCB | 0.429-455 | 0.17 | [3] |
| HRP-BMIM·BF4/SWCNTs | 0.49 to 10.2 | 0.13 | [4] |
| HRP/PGN/GCE | 2.77-835 | 2.67 ×10-4 | [5] |
| Hb-MXene-GO/Au foil | 2-1×103 | 1.95 | [6] |
| MXene/GCE | - | 0.7×10-3 | [7] |
| Hb-naf-MXene/GCE | 0.1-260 | 0.02 | [8] |
| TiO2-Hb-naf-MXene/GCE | 0.1-380 | 1.4×10-2 | [9] |
| HRP@MXene/Chitosan/GCE | 5-1.65×103 | 0.74 | This work |
| Electrode | Linear range/(mmol?L-1) | LOD/(mmol?L-1) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|
| HRP-CTAB-Au/GCE | 0.50-105 | 0.23 | [1] |
| HRP/GO/GCE | 0.002-0.5 | 1.6 | [2] |
| HRP/TB/CCB | 0.429-455 | 0.17 | [3] |
| HRP-BMIM·BF4/SWCNTs | 0.49 to 10.2 | 0.13 | [4] |
| HRP/PGN/GCE | 2.77-835 | 2.67 ×10-4 | [5] |
| Hb-MXene-GO/Au foil | 2-1×103 | 1.95 | [6] |
| MXene/GCE | - | 0.7×10-3 | [7] |
| Hb-naf-MXene/GCE | 0.1-260 | 0.02 | [8] |
| TiO2-Hb-naf-MXene/GCE | 0.1-380 | 1.4×10-2 | [9] |
| HRP@MXene/Chitosan/GCE | 5-1.65×103 | 0.74 | This work |
| Sample | Added H2O2/ (mmol?L-1) | Found H2O2/ (mmol?L-1) | Recovery /% | RSD /% |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Milk | 12.5 | 13.037 | 104.30 | 5.88 |
| Milk | 50 | 52.57 | 105.14 | 1.12 |
| Milk | 125 | 136.5 | 109.20 | 3.33 |
| Dried scallop | 0 | 66.56 | - | - |
| Dried scallop | 12.5 | 77.84 | 90.24 | 6.97 |
| Dried scallop | 50 | 120.08 | 107.04 | 1.46 |
| Dried scallop | 125 | 189.11 | 98.04 | 8.39 |
| Sample | Added H2O2/ (mmol?L-1) | Found H2O2/ (mmol?L-1) | Recovery /% | RSD /% |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Milk | 12.5 | 13.037 | 104.30 | 5.88 |
| Milk | 50 | 52.57 | 105.14 | 1.12 |
| Milk | 125 | 136.5 | 109.20 | 3.33 |
| Dried scallop | 0 | 66.56 | - | - |
| Dried scallop | 12.5 | 77.84 | 90.24 | 6.97 |
| Dried scallop | 50 | 120.08 | 107.04 | 1.46 |
| Dried scallop | 125 | 189.11 | 98.04 | 8.39 |
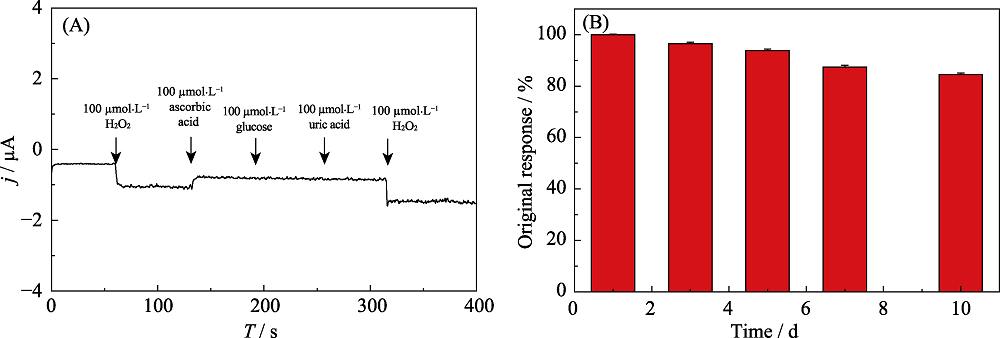
Fig.S4 Amperometric response of HRP@MXene/Chit/GCE in 0.1 mol?L-1 pH 7.5 PBS containing 100 mmol?L-1 of ascorbic acid, glucose, uric acid and H2O2 (Applied potential: -0.1 V) (A); Reduction peak currents of HRP@MXene/Chit/GCE stored in 50 mmol?L-1 PBS (pH 7.5) at 4 for 10 d (B)
| [1] |
ZHANG R, CHEN W . Recent advances in graphene-based nanomaterials for fabricating electrochemical hydrogen peroxide sensors. Biosensors & bioelectronics, 2017,89(Pt1):249-268.
DOI URL PMID |
| [2] | ADMINISTRATION F D . Code of Federal Regulations, 21CFR184.1366 2018. |
| [3] |
DAI H, LU W, ZUO X ,et al. A novel biosensor based on boronic acid functionalized metal-organic frameworks for the determination of hydrogen peroxide released from living cells. Biosensors & Bioelectronics, 2017,95:131-137.
DOI URL PMID |
| [4] | WANG Y, ZHAO K J, ZHANG Z Q ,et al. Simple approach to fabricate a highly sensitive H2O2 biosensor by one-step of graphene oxide and horseradish peroxidase co-immobilized glassy carbon electrode. International Journal of Electrochemical Science, 2018,13(3):2921-2933. |
| [5] |
CHANG M C Y, PRALLE A, ISACOFF E Y ,et al. A selective, cell-permeable optical probe for hydrogen peroxide in living cells. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2004,126(47):15392-15393.
DOI URL PMID |
| [6] |
SHARMA M, KOTHARI C, SHERIKAR O ,et al. Concurrent estimation of amlodipine besylate, hydrochlorothiazide and valsartan by RP-HPLC, HPTLC and UV-Spectrophotometry. Journal of Chromatographic Science, 2014,52(1):27-35.
DOI URL |
| [7] |
MATSUBARA C, KAWAMOTO N, TAKAMURA K . Oxo[5, 10, 15, 20-tetra(4-pyridyl)porphyrinato]titanium(IV): an ultra-high sensitivity spectrophotometric reagent for hydrogen peroxide. Analyst, 1992,117(11):1781-1784.
DOI URL |
| [8] |
ZHOU K, ZHU Y, YANG X ,et al. A novel hydrogen peroxide biosensor based on Au-graphene-HRP-chitosan biocomposites. Electrochimica Acta, 2010,55(9):3055-3060.
DOI URL |
| [9] |
THENMOZHI K, NARAYANAN S S . Horseradish peroxidase and toluidine blue covalently immobilized leak-free Sol-Gel composite biosensor for hydrogen peroxide. Materials Science & Engineering C,Materials for Biological Applications, 2017,70(Pt1):223-230.
DOI URL PMID |
| [10] |
MA B K, CHEONG L Z, WENG X C ,et al. Lipase@ZIF-8 nanoparticles-based biosensor for direct and sensitive detection of methyl parathion. Electrochimica Acta, 2018,283:509-516.
DOI URL |
| [11] |
JOS´E I, REYES-DE-CORCUERA H E O, GARC´ıA-TORRES A R . Stability and Stabilization of Enzyme Biosensors: The Key to Successful Application and Commercialization. 2018.
DOI URL PMID |
| [12] |
LIU Y, LIU X, GUO Z ,et al. Horseradish peroxidase supported on porous graphene as a novel sensing platform for detection of hydrogen peroxide in living cells sensitively.Biosensors & Bioelectronics, 2017,87:101-107.
DOI URL PMID |
| [13] |
ZHENG J, DIAO J, JIN Y ,et al. An inkjet printed Ti3C2-GO electrode for the electrochemical sensing of hydrogen peroxide. Journal of The Electrochemical Society, 2018,165(5):B227-B231.
DOI URL PMID |
| [14] |
ZHAO M Q, XIE X, REN C E ,et al. Hollow mxene spheres and 3D macroporous mxene frameworks for Na-ion storage. Advanced Materials, 2017,29(37):1702410.
DOI URL PMID |
| [15] |
ZHOU J, ZHA X, ZHOU X ,et al. Synthesis and electrochemical properties of two-dimensional hafnium carbide. ACS Nano, 2017,11(4):3841-3850.
DOI URL PMID |
| [16] |
XU B, ZHU M, ZHANG W ,et al. Ultrathin MXene-micropattern- based field-effect transistor for probing neural activity. Advanced Materials, 2016,28(17):3333-3339.
DOI URL PMID |
| [17] |
LORENCOVA L, BERTOK T, DOSEKOVA E ,et al. Electrochemical performance of Ti3C2Tx MXene in aqueous media: towards ultrasensitive H2O2 sensing. Electrochimica Acta, 2017,235:471-479.
DOI URL PMID |
| [18] |
LORENCOVA L, BERTOK T, FILIP J ,et al. Highly stable Ti3C2Tx(MXene)/Pt nanoparticles-modified glassy carbon electrode for H2O2 and small molecules sensing applications. Sensors and Actuators B: Chemical, 2018,263:360-368.
DOI URL |
| [19] |
WANG F, YANG C, DUAN M ,et al. TiO2 nanoparticle modified organ-like Ti3C2 MXene nanocomposite encapsulating hemoglobin for a mediator-free biosensor with excellent performances. Biosensors and Bioelectronics, 2015,74:1022-1028.
DOI URL PMID |
| [20] |
LIU H, DUAN C, YANG C ,et al. A novel nitrite biosensor based on the direct electrochemistry of hemoglobin immobilized on MXene-Ti3C2. Sensors and Actuators B: Chemical, 2015,218:60-66.
DOI URL PMID |
| [21] |
RAKHI R B, NAYAK P, XIA C ,et al. Novel amperometric glucose biosensor based on MXene nanocomposite. Scientific Reports, 2016,6:36422.
DOI URL PMID |
| [22] |
VEITCH N C . Horseradish peroxidase: a modern view of a classic enzyme. Phytochemistry, 2004,65(3):249-259.
DOI URL PMID |
| [23] |
REN Q Q, WU J, ZHANG W C ,et al. Real-time in vitro detection of cellular H2O2 under camptothecin stress using horseradish peroxidase, ionic liquid, and carbon nanotube-modified carbon fiber ultramicroelectrode. Sensors and Actuators B: Chemical, 2017,245:615-621.
DOI URL |
| [24] |
LI M, HAN M, ZHOU J ,et al. Novel scale-like structures of graphite/TiC/Ti3/C2 hybrids for electromagnetic absorption.Advanced Electronic Materials, 2018,4(5):1700617.
DOI URL |
| [25] |
SHAN C, YANG H, HAN D ,et al. Graphene/AuNPs/chitosan nanocomposites film for glucose biosensing. Biosensors & bioElectronics, 2010,25(5):1070-1074.
DOI URL PMID |
| [26] |
WANG F, YANG C, DUAN C ,et al. An organ-like titanium carbide material (MXene) with multilayer structure encapsulating hemoglobin for a mediator-free biosensor. Journal of The Electrochemical Society, 2014,162(1):B16-B21.
DOI URL |
| [27] |
KANG X B, PANG G C, LIANG X Y ,et al. Study on a hydrogen peroxide biosensor based on horseradish peroxidase/GNPs-thionine/ chitosan. Electrochimica Acta, 2012,62:327-334.
DOI URL |
| [28] |
KOPOSOVA E, LIU X, KISNER A ,et al. Bioelectrochemical systems with oleylamine-stabilized gold nanostructures and horseradish peroxidase for hydrogen peroxide sensor. Biosensors & Bioelectronics, 2014,57:54-58.
DOI URL PMID |
| [29] |
YANG S, DING S, LI L ,et al. One-step preparation of direct electrochemistry HRP biosensor via electrodeposition. Journal of The Electrochemical Society, 2017,164(13):B710-B714.
DOI URL |
| [30] |
CHEN W, YANG W, LU Y ,et al. Encapsulation of enzyme into mesoporous cages of metal-organic frameworks for the development of highly stable electrochemical biosensors. Analytical Methods, 2017,9(21):3213-3220.
DOI URL |
| [31] |
BARD A J, FAULKNER L R, LEDDY J , et al. Electrochemical methods: Fundamentals and Applications. Wiley New York, 1980.
DOI URL PMID |
| [32] |
SONG H, NI Y, KOKOT S . Investigations of an electrochemical platform based on the layered MoS2-graphene and horseradish peroxidase nanocomposite for direct electrochemistry and electrocatalysis. Biosensors & Bioelectronics, 2014,56:137-143.
DOI URL PMID |
| [33] |
MART N M, SALAZAR P, VILLALONGA R ,et al. Preparation of core-shell Fe3O4@poly(dopamine) magnetic nanoparticles for biosensor construction. J. Mater. Chem. B, 2014,2(6):739-746.
DOI URL |
| [1] | HE Qian, TANG Wanlan, HAN Bingkun, WEI Jiayuan, LÜ Wenxuan, TANG Zhaomin. pH Responsive Copper-Doped Mesoporous Silica Nanocatalyst for Enhanced Chemo-Chemodynamic Tumor Therapy [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(1): 90-98. |
| [2] | LIU Yao, YOU Xunhai, ZHAO Bing, LUO Xiaoying, CHEN Xing. Functional Nanomaterials for Electrochemical SRAS-CoV-2 Biosensors: a Review [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(1): 32-42. |
| [3] | LI Yanyan, PENG Yusi, LIN Chenglong, LUO Xiaoying, TENG Zheng, ZHANG Xi, HUANG Zhengren, YANG Yong. Nanomaterials and Biosensing Technology for the SARS-CoV-2 Detection [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(1): 3-31. |
| [4] | ZHANG Xiao-Feng,ZHANG Guan-Hua,MENG Yue,XUE Ji-Long,XIA Sheng-Jie,NI Zhe-Ming. Photocatalytic Degradation of Methylene Blue by Schiff-base Cobalt Modified CoCr Layered Double Hydroxides [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2019, 34(9): 974-982. |
| [5] | GUO Ling-Xia, SHI Yu-Chen, ZHAO Zhen-Jie, LI Xin. Fabrication and Fluorescence Biodetection of ZnO Nanorods Using Microfluidic Technology [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2018, 33(10): 1103-1109. |
| [6] | SUN Li-Mei, SHI Le-Le, ZHANG Shuai-Shuai, ZHANG Yi-Jia, LI Zeng-Hui, HE Wurigamula. Cathode Performance of Mg-H2O2 Semi-fuel Cell with Pdn-Fe Alloy as Cathode [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2018, 33(1): 81-86. |
| [7] | ZHAO De-Rui, ZHAI Ying-Jiao, LI Jin-Hua, CHU Xue-Ying, XU Ming-Ze, LI Xue, FANG Xuan, WEI Zhi-Peng, WANG Xiao-Hua. Preparation and Properties of Glucose Biosensor Based on Flower-like MoS2 Micrometer Material [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2016, 31(2): 153-158. |
| [8] | WANG Yan, WANG Hong-Ning, CHEN Ruo-Yu. Structure of Antireflective Films with Si-O-P Bonds and Impact Factors on Its Performance [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2014, 29(6): 639-644. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||