
Journal of Inorganic Materials ›› 2012, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (4): 369-374.DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1077.2012.00369
• Orginal Article • Previous Articles Next Articles
LIU Xue-Zhen1, BAO Shan-Yong1, ZHANG Huan-Huan1, MA Chun-Yu1, XU Xiao-Ming2, ZHANG Qing-Yu1
Received:2011-05-12
Revised:2011-07-14
Published:2012-04-10
Online:2012-03-12
About author:LIU Xue-Zhen. E-mail: xzliu0130@yahoo.com.cn
Supported by:CLC Number:
LIU Xue-Zhen, BAO Shan-Yong, ZHANG Huan-Huan, MA Chun-Yu, XU Xiao-Ming, ZHANG Qing-Yu . Study on the Magnetism of Epitaxial ZnCoO Films Deposited by Pulsed Laser Deposition[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2012, 27(4): 369-374.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX

Fig. 1 (a) XRD patterns of Zn1-xCoxO films deposited at different oxygen pressures; inset is the rocking curves of (002) diffraction peaks; (b) Epitaxial relationship between Zn1-xCoxO film and sapphire substrate
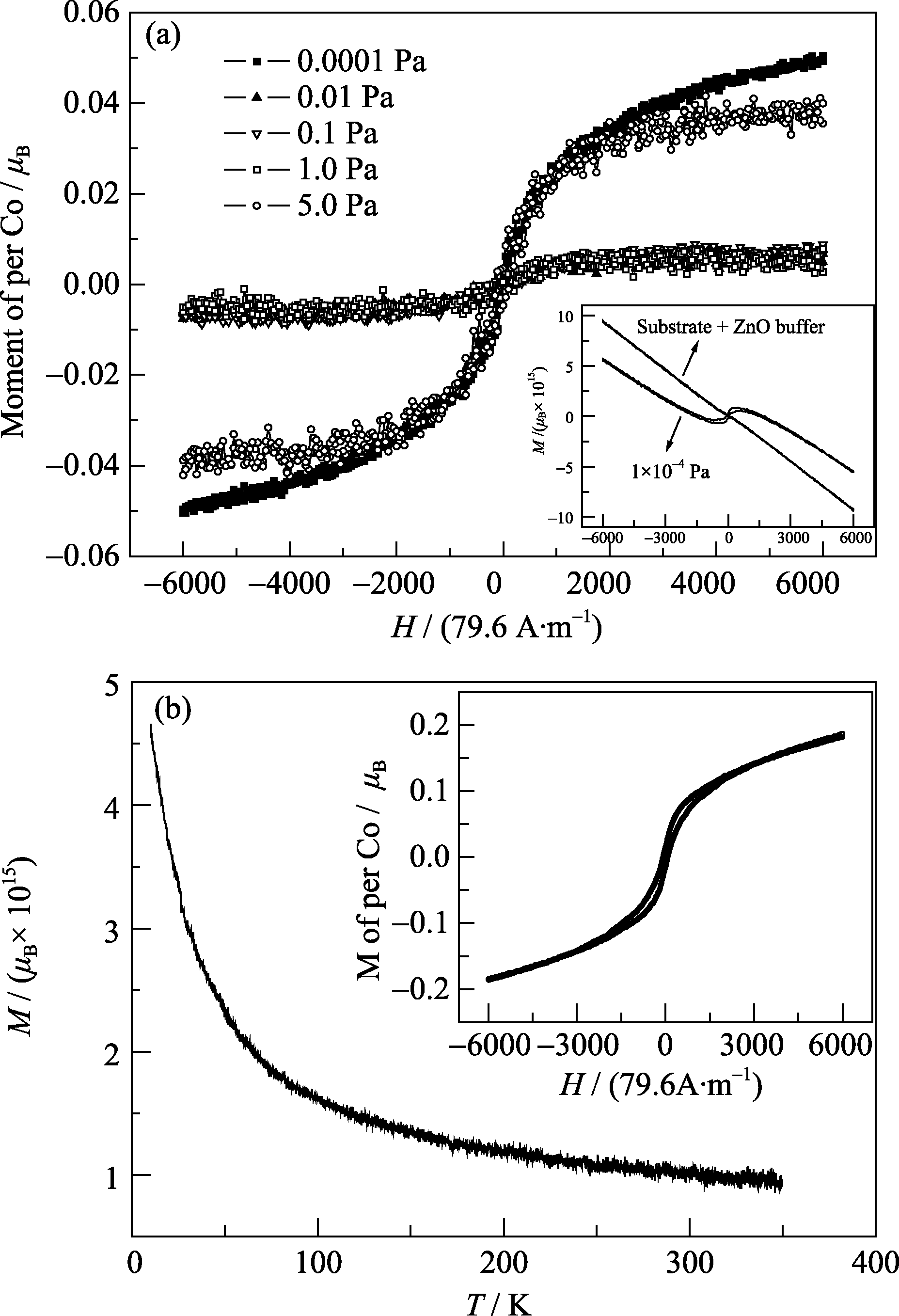
Fig. 2 (a) Magnetization curves of Zn1-xCoxO films, the inset is original magnetization curves of ZnO buffer and ZnCoO film deposited at 0.0001 Pa, (b) M-T curve of Co-doped ZnO film deposited at 0.0001 Pa, H=39800 A/m; the inset is magnetization curve of the film at 10 K

Fig. 4 (a) Absorption coefficients of Zn1-xCoxO films deposited at different oxygen pressures, (b) Absorption coefficients for Co2+ ions in the Zn1-xCoxO films
| [1] | Pearton S J, Norton D P, Ip K, et al. Recent progress in processing and properties of ZnO. Prog. Mater. Sci., 2005, 50(3): 293-340. |
| [2] | 谷建峰、付伟佳、刘 明, 等(GU Jian-Feng, et al). 电化学沉积高c轴取向ZnO薄膜及其光学性能分析. 物理学报(Acta Physica Sinica), 2007, 56(10): 5979-5985. |
| [3] | Dietl T, Ohno H, Matsukura F, et al. Zener model description of ferromagnetism in zinc-blende magnetic semiconductors. Science, 2000, 287(5455): 1019-1021. |
| [4] | Sato K, Yoshida H K. Material design for transparent ferromagnets with ZnO-based magnetic semiconductors. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys., 2001, 39(6B): L555-L558. |
| [5] | Ueda K, Tabata H, Kawai K. Magnetic and electric properties of transition-metal-doped ZnO films. Appl. Phys. Lett., 2001, 79(7): 988-990. |
| [6] | Kittilstved K R, Schwartz D A, Tuan A C, et al. Direct kinetic correlation of carriers and ferromagnetism in Co2+: ZnO. Phys. Rev. Lett. , 2006, 97(3): 037203-1-4. |
| [7] | Rode K, Anane A, Mattana R, et al. Magnetic semiconductors based on cobalt substituted ZnO. J. Appl. Phys., 2003. 93(10): 7676-7678. |
| [8] | Kobayashi M, Ishida Y, Hwang J I, et al. Antiferromagnetic interaction between paramagnetic Co ions in the diluted magnetic semiconductor Zn1-xCoxO. Phys. Rev. B, 2010, 81(7): 075204-1-7. |
| [9] | Park J H, Kim M G, Jang H M, et al. Co-metal clustering as the origin of ferromagnetism in Co-doped ZnO thin films. Appl. Phys. Lett., 2004, 84(08): 1338-1340. |
| [10] | Ramachandran S, Tiwari A, Narayan J. Zn0.9Co0.1O-based diluted magnetic semiconducting thin films. Appl. Phys. Lett., 2004, 84(25): 5255-5257. |
| [11] | Belghazi Y, Schmerber G, Colis S, et al. Extrinsic origin of ferromagnetism in ZnO and Zn0.9Co0.1O magnetic semiconductor films prepared by Sol-Gel technique. Appl. Phys. Lett. , 2006, 89(12): 122504-1-3. |
| [12] | Tietze T, Gacic M, Schütz G, et al. XMCD studies on Co and Li doped ZnO magnetic semiconductors. New J. Phys. , 2008, 10: 055009-1-17. |
| [13] | Opel M, Nielsen K W, Bauer S, et al. Nanosized superparamagnetic precipitates in cobalt-doped ZnO. Eur. Phys. J. B, 2008, 63(4): 437-444. |
| [14] | Rode K, Mattana R, Anane A, et al. Magnetism of (Zn, Co)O thin films probed by X-ray absorption spectroscopies. Appl. Phys. Lett. , 2008, 92(1): 012509-1-3. |
| [15] | Kaspar T C, Droubay T, Heald S M, et al. Lack of ferromagnetism in n-type cobalt-doped ZnO epitaxial thin films. New J. Phys. , 2008, 10: 055010-1-18. |
| [16] | Kim J H, Kim H, Kim D, et al. Magnetic properties of epitaxially grown semiconducting Zn1-xCoxO thin films by pulsed laser deposition. J. Appl. Phys., 2002, 92(10): 6066-6071. |
| [17] | Prater J T, Ramachandran S, Tiwari A, et al. Co-doped ZnO dilute magnetic semiconductor. J. Electro. Mater., 2006, 35(5): 852-856. |
| [18] | Rozale H, Lakdja A, Lazreg A, et al. Electronic and magnetic properties of Co-doped ZnO:first principles study. Phys. Status Solidi B, 2010, 247(7): 1641-1644. |
| [19] | Kuo Y K, Huang M F, Bimbaum M. Tunable Cr4+:YSO Q-switched Cr:LiCAF laser. IEEE J. Quantum Electr., 1995. 31(4): 657-663. |
| [20] | Denisov I A, Volk Y V, Malyarenvich A M, et al. Linear and nonlinear optical properties of cobalt-doped zinc aluminum glass ceramics. J. Appl. Phys., 2003, 93(7): 3827-3831. |
| [21] | 梁敬魁,编著. 粉末衍射法测定晶体结构. 北京: 科学出版社, 2003: 344. |
| [22] | Kolesnik S, Dabrowski B, Mais J. Structural and magnetic properties of transition metal substituted ZnO. J. Appl. Phys., 2004, 95(5): 2582-2586. |
| [23] | Lawes G, Risbud A S, Ramirez A P, et al. Absence of ferromagnetism in Co and Mn substituted polycrystalline ZnO. Phys. Rev. B, 2005, 71(4): 045201-1-5. |
| [24] | 冯 端,翟宏如,著. 金属物理学, 第四卷 超导电性和磁性. 北京: 科学出版社, 1998: 578. |
| [1] | ZHANG Xiao, LI Youbing, CHEN Ke, DING Haoming, CHEN Lu, LI Mian, SHI Rongrong, CHAI Zhifang, HUANG Qing. Tailoring MAX Phase Magnetic Property Based on M-site and A-site Double Solid Solution [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(12): 1247-1255. |
| [2] | BAI Jiawei, YANG Jing, LÜ Zhenfei, TANG Xiaodong. Magnetic and Dielectric Properties of Ti 4+-doped M-type Hexaferrite BaFe12-xTixO19 Ceramics [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(1): 43-48. |
| [3] | CHEN Chun-Xia, LI Hao-Ran, ZHENG Ren-Kui. Properties of Multiferroic PrBi4Fe0.5Co0.5Ti3O15 Ceramics [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2015, 30(5): 511-515. |
| [4] | TANG Ying-Mao, MIAO Qing-Qing, XIAO Li-Ren, QIAN Qing-Rong, CHEN Qing-Hua. Preparation and Characterization of Electrospun Magnetic Carbon Composite Nanofibres [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2014, 29(8): 827-834. |
| [5] | HU Dong-Li, XING Juan-Juan, ZHENG Qiang, GU Hui, NI De-Wei, ZHANG Guo-Jun. Comparative Study on Quantitation of Phase Component and Phase Composition of HfB2-SiC-HfC Ceramics [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2014, 29(10): 1105-1109. |
| [6] | LI Hai-Feng, GONG Rong-Zhou, LU Xiu-Fang, YU Wei, WANG Xian, FAN Li-Ren1, He Gang. Molten Salt Synthesis and Magnetic Properties of BaFe12O19 Hexaferrite [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2011, 26(8): 792-796. |
| [7] | YAO Chun-Fa, LI Cai-Fu, LIU Zhi-Quan, SHANG Jian-Ku. Structural Ordering and Magnetic Property of Complex Perovskite Solid Solution (1-x)Pb(Fe2/3W1/3)O3-xPb(Mg1/2W1/2)O3 [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2011, 26(6): 649-654. |
| [8] | LIU Gu, WANG Liu-Ying, CHEN Gui-Ming, WEI Wan-Ning, HUA Shao-Chun, ZHU Er-Lei. Preparation and Properties of SiC-CNTs/Al2O3-TiO2 Coating [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2011, 26(11): 1187-1192. |
| [9] | WANG Wei-Qing,FENG Qi-Ming,DONG Fa-Qin,LI Hu-Jie,ZHAO Xiao-Dong. Preparation and Properties of Fe3O4/Clinoptilolite Magnetic Composite [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2010, 25(4): 401-405. |
| [10] | LAI Wen-Zhong,DONG Xiao-Jie,HUANG Jing,LENG Yong-Hua,LI Xing-Guo. Preparation and Characterization of Co/Co9S8/ZnO Coreshell Nanoshperes [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2010, 25(3): 265-271. |
| [11] | ZHANG Li, ZHU Zi-Wei, KUANG Ren-Xiong, DENG Long-Jiang. Microstructural and Microwave Electromagnetic Properties of FeCoB-SiO2 Film on PET Substrate [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2010, 25(11): 1150-1154. |
| [12] | GAI Zhen-Tao, YU Li-Ming, ZHOU Yun, ZHAO Xin-Luo, ZHANG Jin-Cang. Magnetic Dielectric and Magnetoelectric Properties of Magnetoelectric Nano-composites xCoAl0.2Fe1.8O4+(1-x)BaTiO3 [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2010, 25(11): 1155-1158. |
| [13] | JIANG Xiao-Na,LAN Zhong-Wen,YU Zhong,Zhuang Ya-Ming,LIU Pei-Yuan. Effects of Mn3O4 on Magnetic Property, Microstructure and Resistivity of LiZn Ferrites [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2010, 25(1): 77-82. |
| [14] | LIU Ming-Quan,SHEN Xiang-Qian,MENG Xian-Feng,SONG Fu-Zhan,XIANG Jun. Fabrication and Magnetic Property of M-type Strontium Ferrite Nanofibers by Electrospinning [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2010, 25(1): 68-72. |
| [15] | WEI Ping,ZHAO Wen-Yu,WU Xiao-Yan,ZHANG Qing-Jie. M-type Barium Hexaferrite with Excessive Divalent Iron Synthesized by Spark Plasma Sintering Method [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2009, 24(3): 586-590. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||