
Journal of Inorganic Materials ›› 2017, Vol. 32 ›› Issue (8): 863-869.DOI: 10.15541/jim20160625
• Orginal Article • Previous Articles Next Articles
LIN Jing-Cheng1, TANG Xiao1, CHU Wan-Yi2
Received:2016-11-15
Revised:2016-01-02
Published:2017-08-10
Online:2017-07-19
About author:LIN Jing-Cheng. E-mail: 1015958900@qq.com
Supported by:CLC Number:
LIN Jing-Cheng, TANG Xiao, CHU Wan-Yi. Synthesis and Photocatalysis Property of Ultra-small TiO2 Nanoclusters in Aqueous Media[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2017, 32(8): 863-869.
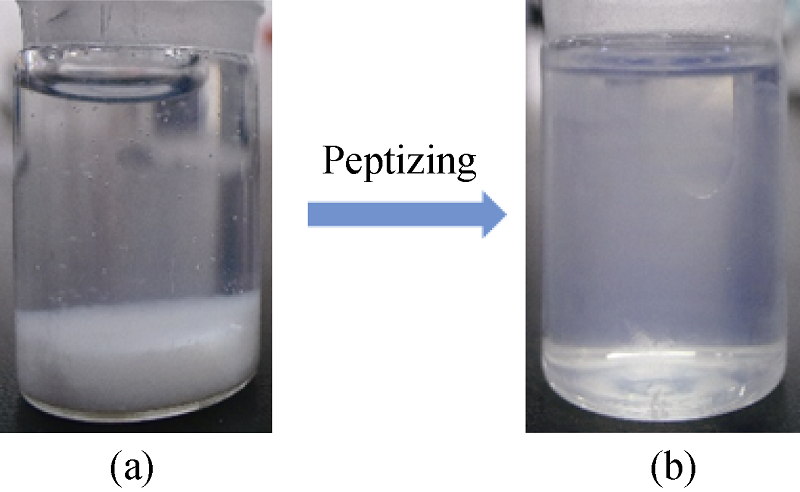
Fig. 2 Process of synthesizing ultra-small TiO2 nanoclusters(a) Tetrabutyl titanate (TPT) added into water to produce white precipitation hydrolysis products, and then (b) the hydrolysate peptized into transparent sol
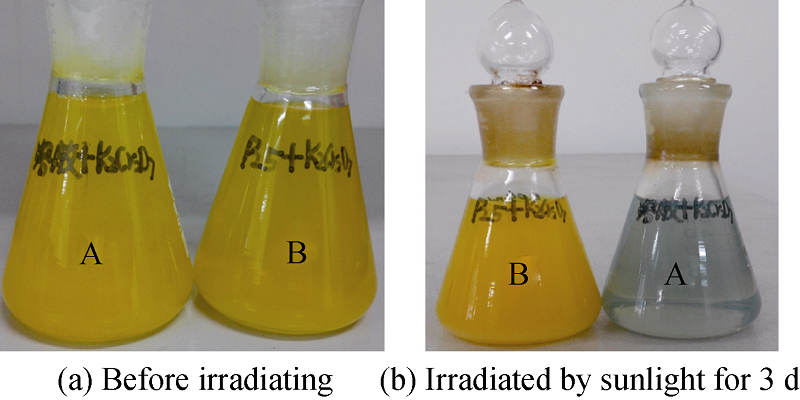
Fig. 9 (a) Mixtures of K2Cr2O7 solution with the sol of ultra- small TiO2 nanocluster (A) and that of the TiO2 nanocrystal (B) before sunlight irradiating; (b) after sunlight irradiating for 3 d
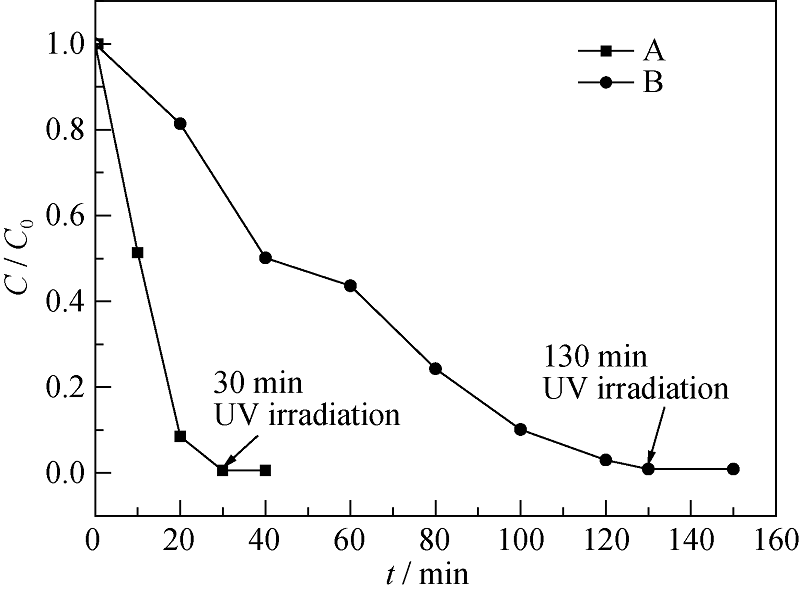
Fig. 10 Change of Cr6+ concentration with irradiating time for the ultra-small TiO2 nanocluster system (A) and TiO2 nanocrystal system (B) under UV irradiation
| [1] | TYO ERIC C, VAJDA S.Catalysis by clusters with precise numbers of atoms.Nature Nanotechnology, 2015, 10(7): 577-588. |
| [2] | CHIODO L, SALAZAR M, ROMERO A H, et al. Structure, electronic,optical properties of TiO2 atomic clusters: an ab initio study. The Journal of Chemical Physics, 2011, 135(24): 244704-1-9. |
| [3] | LINDQVIST M J, NILSINGM, PERRSSON P, et al.DFT study of bare and dye-sensitized TiO2 clusters and nanocrystals.International Journal of Quantum Chemistry, 2006, 106(7): 3214-3234. |
| [4] | SáNCHEZ-DE-ARMAS R, OVIEDO L, MIGUEL J F, et al. Direct vs indirect mechanisms for electron injection in dye-sensitized solar cells.J. Phys. Chem. C, 2011, 115(5): 11293-11301. |
| [5] | GALYńSKA M, PERSSON P. Emerging polymorphism in nanostructured TiO2: quantum chemical comparison of anatase, rutile, and brookite clusters.International Journal of Quantum Chemistry, 2013, 113(24): 2611-2622. |
| [6] | WANG L, LIU B, LI H, et al.Long-range ordered carbon clusters: a crystalline material with amorphous building blocks.Science, 2012, 337(2): 825-828. |
| [7] | PEARMAIN D, PARK S J, ABDELA A.The size-dependent morphology of Pd nanoclusters formed by gas condensation.Nanoscale, 2015, 7(46): 19647-19652. |
| [8] | JIN R.Atomically precise metal nanoclusters: stable sizes and optical properties.Nanoscale, 2015, 7(5): 1549-1565. |
| [9] | PRASENJIT M, SONGHAI X, MIHO Y.Stabilized gold clusters: from isolation toward controlled synthesis.Nanoscale, 2012, 4(14): 4027-4037. |
| [10] | LAN W, LING Z, JINCAI Z.Green synthesis of shape-defined anatase TiO2 nanocrystals wholly exposed with {001} and {100} facets.Chemical Communications, 2012, 48(96): 11736-11738. |
| [11] | JIANWEI M, BIN L.Anatase TiO2 microspheres with reactive {001} facets for improved photocatalytic activity.RSC Advances, 2012, 3(4): 1222-1226. |
| [12] | SHIEN G, HONGYAN N, MINGXIA L.The fabrication and the characterization of a TiO2/titanate nanohybrid for efficient hydrogen evolution.RSC Advances, 2015, 5(17):13011-13015. |
| [13] | XIAOFEI Q, LIXIN C, FANGLIN D.Fabrication of ordered arrays of CNT/TiO2 nanotubes and their photocatalytic properties.RSC Advances, 2015, 5(27): 20976-20980. |
| [14] | CESANO F, AGOSTINI G, SCARANO D.Nanocrystalline TiO2 micropillar arrays grafted on conductive glass supports: microscopic and spectroscopic studies.Thin Solid Films, 2015, 590(9): 200-206. |
| [15] | LLANSOLA-PORTOLES M J, BERGKAMP J J, FINKELSTEIN- SHAPIRO D. Controlling surface defects and photophysics in TiO2 nanoparticles.J. Phys. Chem. A, 2014, 118(8): 10631-10638. |
| [16] | CHEN C, JUANG K, LEE D.Effects of liming on Cr(VI) reduction and Cr phytotoxicity in Cr(VI)-contaminated soils.Soil Science and Plant Nutrition, 2012, 58(11): 135-143. |
| [17] | YANG J K, LEE S M, FARROKHI M.Photocatalytic removal of Cr(VI) with illuminated TiO2.Desalination and Water Treatment, 2012, 46(4): 375-380. |
| [1] | FAN Xiaoxuan, ZHENG Yonggui, XU Lirong, YAO Zimin, CAO Shuo, WANG Kexin, WANG Jiwei. Organic Pollutant Fenton Degradation Driven by Self-activated Afterglow from Oxygen-vacancy-rich LiYScGeO4: Bi3+ Long Afterglow Phosphor [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(5): 481-488. |
| [2] | JIA Xianghua, ZHANG Huixia, LIU Yanfeng, ZUO Guihong. Cu2O/Cu Hollow Spherical Heterojunction Photocatalysts Prepared by Wet Chemical Approach [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(4): 397-404. |
| [3] | MA Binbin, ZHONG Wanling, HAN Jian, CHEN Liangyu, SUN Jingjing, LEI Caixia. ZIF-8/TiO2 Composite Mesocrystals: Preparation and Photocatalytic Activity [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(8): 937-944. |
| [4] | CAO Qingqing, CHEN Xiangyu, WU Jianhao, WANG Xiaozhuo, WANG Yixuan, WANG Yuhan, LI Chunyan, RU Fei, LI Lan, CHEN Zhi. Visible-light Photodegradation of Tetracycline Hydrochloride on Self-sensitive Carbon-nitride Microspheres Enhanced by SiO2 [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(7): 787-792. |
| [5] | WANG Zhaoyang, QIN Peng, JIANG Yin, FENG Xiaobo, YANG Peizhi, HUANG Fuqiang. Sandwich Structured Ru@TiO2 Composite for Efficient Photocatalytic Tetracycline Degradation [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(4): 383-389. |
| [6] | WU Lin, HU Minglei, WANG Liping, HUANG Shaomeng, ZHOU Xiangyuan. Preparation of TiHAP@g-C3N4 Heterojunction and Photocatalytic Degradation of Methyl Orange [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(5): 503-510. |
| [7] | LING Jie, ZHOU Anning, WANG Wenzhen, JIA Xinyu, MA Mengdan. Effect of Cu/Mg Ratio on CO2 Adsorption Performance of Cu/Mg-MOF-74 [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(12): 1379-1386. |
| [8] | SUN Chen, ZHAO Kunfeng, YI Zhiguo. Research Progress in Catalytic Total Oxidation of Methane [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(11): 1245-1256. |
| [9] | MA Xinquan, LI Xibao, CHEN Zhi, FENG Zhijun, HUANG Juntong. BiOBr/ZnMoO4 Step-scheme Heterojunction: Construction and Photocatalytic Degradation Properties [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(1): 62-70. |
| [10] | CHEN Hanxiang, ZHOU Min, MO Zhao, YI Jianjian, LI Huaming, XU Hui. 0D/2D CoN/g-C3N4 Composites: Structure and Photocatalytic Performance for Hydrogen Production [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(9): 1001-1008. |
| [11] | XUE Hongyun, WANG Congyu, MAHMOOD Asad, YU Jiajun, WANG Yan, XIE Xiaofeng, SUN Jing. Two-dimensional g-C3N4 Compositing with Ag-TiO2 as Deactivation Resistant Photocatalyst for Degradation of Gaseous Acetaldehyde [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(8): 865-872. |
| [12] | CHI Congcong, QU Panpan, REN Chaonan, XU Xin, BAI Feifei, ZHANG Danjie. Preparation of SiO2@Ag@SiO2@TiO2 Core-shell Structure and Its Photocatalytic Degradation Property [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(7): 750-756. |
| [13] | WANG Xiaojun, XU Wen, LIU Runlu, PAN Hui, ZHU Shenmin. Preparation and Properties of Ag@C3N4 Photocatalyst Supported by Hydrogel [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(7): 731-740. |
| [14] | LIU Xuechen, ZENG Di, ZHOU Yuanyi, WANG Haipeng, ZHANG Ling, WANG Wenzhong. Selective Oxidation of Biomass over Modified Carbon Nitride Photocatalysts [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(1): 38-44. |
| [15] | ZHANG Xian, ZHANG Ce, JIANG Wenjun, FENG Deqiang, YAO Wei. Synthesis, Electronic Structure and Visible Light Photocatalytic Performance of Quaternary BiMnVO5 [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(1): 58-64. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||