无机材料学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 40 ›› Issue (6): 656-666.DOI: 10.15541/jim20240529 CSTR: 32189.14.jim20240529
唐莹1( ), 李洁1(
), 李洁1( ), 相怀成1, 方维双1,2, 林慧兴2, 杨俊峰3, 方亮1(
), 相怀成1, 方维双1,2, 林慧兴2, 杨俊峰3, 方亮1( )
)
收稿日期:2024-12-18
修回日期:2025-02-07
出版日期:2025-06-20
网络出版日期:2025-02-13
通讯作者:
李 洁, 副教授. E-mail: jielee@glut.edu.cn;作者简介:唐 莹(1988-), 女, 教授. E-mail: tangyinggl001@aliyun.com
基金资助:
TANG Ying1( ), LI Jie1(
), LI Jie1( ), XIANG Huaicheng1, FANG Weishuang1,2, LIN Huixing2, YANG Junfeng3, FANG Liang1(
), XIANG Huaicheng1, FANG Weishuang1,2, LIN Huixing2, YANG Junfeng3, FANG Liang1( )
)
Received:2024-12-18
Revised:2025-02-07
Published:2025-06-20
Online:2025-02-13
Contact:
LI Jie, associate professor. E-mail: jielee@glut.edu.cn;About author:TANG Ying (1988-), female, professor. E-mail: tangyinggl001@aliyun.com
Supported by:摘要:
微波介质陶瓷是5G/6G通信技术中关键的基础材料, 具有高品质因数(Q×f)、低介电常数(εr)以及近零谐振频率温度系数(τf)的材料逐渐成为研究与开发的重点。然而, 绝大多数低εr材料往往具有较负的τf。本研究首先系统概述了影响τf的经典机制, 包括离子极化率稀释机制、相变机制、晶胞体积机制、氧多面体畸变度、键能与键性以及键价等结构因素。随后, 详细介绍了本团队近期在无相变立方正反石榴石体系中观察到的τf异常变化现象, 提出“Rattling”效应是一种影响微波介质陶瓷τf的新机制。具有高配位数且弱化学键合的“Rattling”阳离子是影响材料整体微波介电极化和损耗的主要因素, 它不仅增大离子极化率和εr, 还导致τf正向偏移, 同时降低Q×f。该机制在不同材料体系中得到验证与应用。本研究引入了总离子极化偏差的加权函数新概念, 用于评估整个分子“Rattling”和“Compressed”效应对εr的影响, 并提出了离子极化率温度系数(ταm)新概念, 通过定量化计算从而将影响介电常数温度系数(τε)正负和大小的因素简化为εr、ταm和线膨胀系数αL之间的关系。
中图分类号:
唐莹, 李洁, 相怀成, 方维双, 林慧兴, 杨俊峰, 方亮. Rattling效应: 一种影响微波介质陶瓷谐振频率温度系数的新机制[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(6): 656-666.
TANG Ying, LI Jie, XIANG Huaicheng, FANG Weishuang, LIN Huixing, YANG Junfeng, FANG Liang. Rattling Effect: A New Mechanism Affecting the Resonant Frequency Temperature Coefficient of Microwave Dielectric Ceramics[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(6): 656-666.
| Sample | Bond type of A site | Bond valence parameter | Bond valence | Measured εr | Theoretical εth | Q×f/GHz | τf/(×10-6, ℃-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ca3Y2Ge3O12 | Ca-O | 1.967 | 1.88 | 10.8 | 9.33 | 97126 | -40.6 |
| Mg3Y2Ge3O12 | Y-O Mg-O | 2.014 1.693 | 2.97 1.25 | 14.1 | 9.79 | 12600 | +120.5 |
表1 Ca3Y2Ge3O12和Mg3Y2Ge3O12陶瓷的键长、键价和微波介电性能
Table 1 Bond lengths, bond valences and microwave dielectric properties of Ca3Y2Ge3O12 and Mg3Y2Ge3O12 ceramics
| Sample | Bond type of A site | Bond valence parameter | Bond valence | Measured εr | Theoretical εth | Q×f/GHz | τf/(×10-6, ℃-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ca3Y2Ge3O12 | Ca-O | 1.967 | 1.88 | 10.8 | 9.33 | 97126 | -40.6 |
| Mg3Y2Ge3O12 | Y-O Mg-O | 2.014 1.693 | 2.97 1.25 | 14.1 | 9.79 | 12600 | +120.5 |
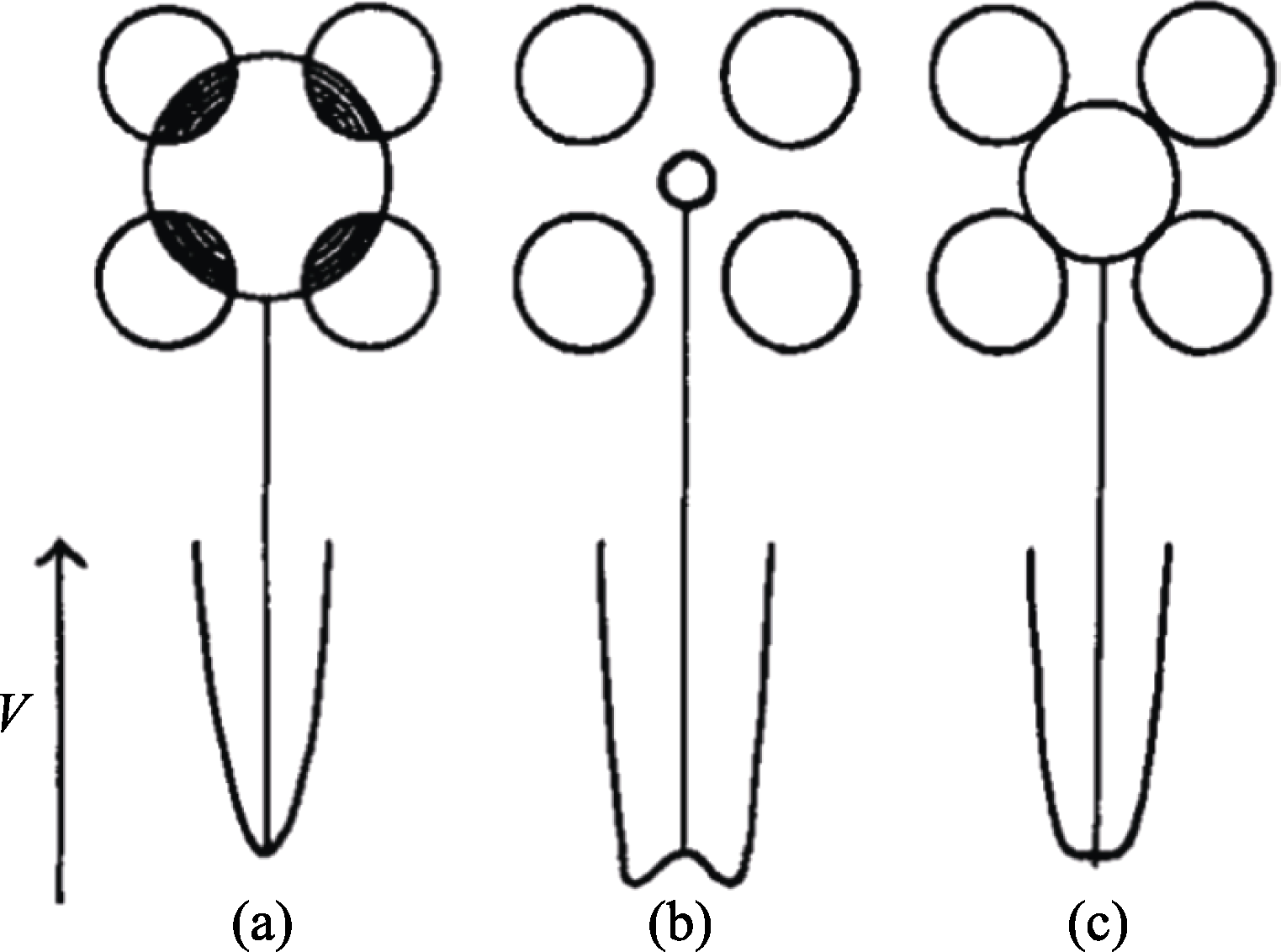
图1 势能随八面体中心金属离子的尺寸变化(为清晰起见, 用二维表示)[6]
Fig. 1 Variation of potential energy with displacement of a metal ion from the center of a fixed oxide octahedron (shown in two dimensions for clarity)[6] (a) Large ion; (b) Small ion; (c) Ion of intermediate size
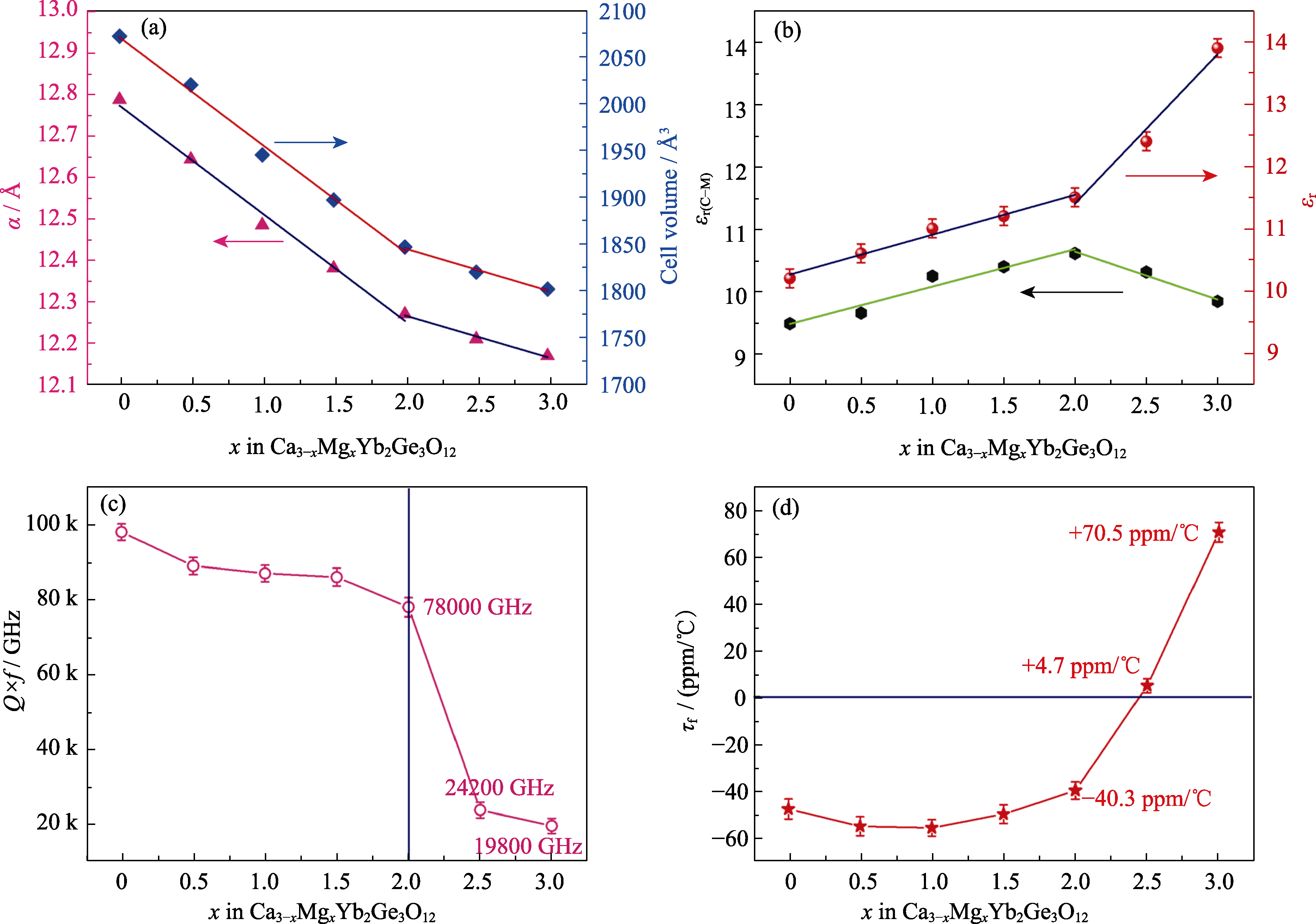
图2 Ca3-xMgxYb2Ge3O12(0≤x≤3)陶瓷的微波介电性能[57]
Fig. 2 Microwave dielectric properties of Ca3-xMgxYb2Ge3O12 (0≤x≤3) ceramics[57] (a) Unit cell parameters and volumes; (b) Theoretical and measured permittivity; (c) Q×f; (d) τf. 1 ppm/℃=1×10-6 ℃-1
| x | Ceramic | ST/℃ | εr | Q×f/GHz | τf/(×10-6, ℃-1) | ταm/(×10-6, ℃-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | Ca3Yb2Ge3O12 | 1360 | 10.3 | 98000 | -48.2 | +50.64 |
| 0.5 | Ca2.5Mg0.5Yb2Ge3O12 | 1380 | 10.6 | 89000 | -55.6 | +53.97 |
| 1.0 | Ca2MgYb2Ge3O12 | 1400 | 11.0 | 87000 | -56.3 | +53.49 |
| 1.5 | Ca1.5Mg1.5Yb2Ge3O12 | 1400 | 11.2 | 86000 | -50.4 | +50.16 |
| 2.0 | CaMg2Yb2Ge3O12 | 1400 | 11.8 | 78000 | -40.3 | +44.40 |
| 2.5 | Ca0.5Mg2.5Yb2Ge3O12 | 1420 | 12.4 | 24000 | +4.7 | +23.34 |
| 3.0 | Mg3Yb2Ge3O12 | 1440 | 13.5 | 19800 | +70.5 | -3.66 |
表2 Ca3-xMgxYb2Ge3O12 (0≤x≤3)陶瓷的最佳烧结温度(ST)、微波介电性能以及ταm
Table 2 Optimum sintering temperature (ST), microwave dielectric properties and ταm of Ca3-xMgxYb2Ge3O12 (0≤x≤3) ceramics
| x | Ceramic | ST/℃ | εr | Q×f/GHz | τf/(×10-6, ℃-1) | ταm/(×10-6, ℃-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | Ca3Yb2Ge3O12 | 1360 | 10.3 | 98000 | -48.2 | +50.64 |
| 0.5 | Ca2.5Mg0.5Yb2Ge3O12 | 1380 | 10.6 | 89000 | -55.6 | +53.97 |
| 1.0 | Ca2MgYb2Ge3O12 | 1400 | 11.0 | 87000 | -56.3 | +53.49 |
| 1.5 | Ca1.5Mg1.5Yb2Ge3O12 | 1400 | 11.2 | 86000 | -50.4 | +50.16 |
| 2.0 | CaMg2Yb2Ge3O12 | 1400 | 11.8 | 78000 | -40.3 | +44.40 |
| 2.5 | Ca0.5Mg2.5Yb2Ge3O12 | 1420 | 12.4 | 24000 | +4.7 | +23.34 |
| 3.0 | Mg3Yb2Ge3O12 | 1440 | 13.5 | 19800 | +70.5 | -3.66 |
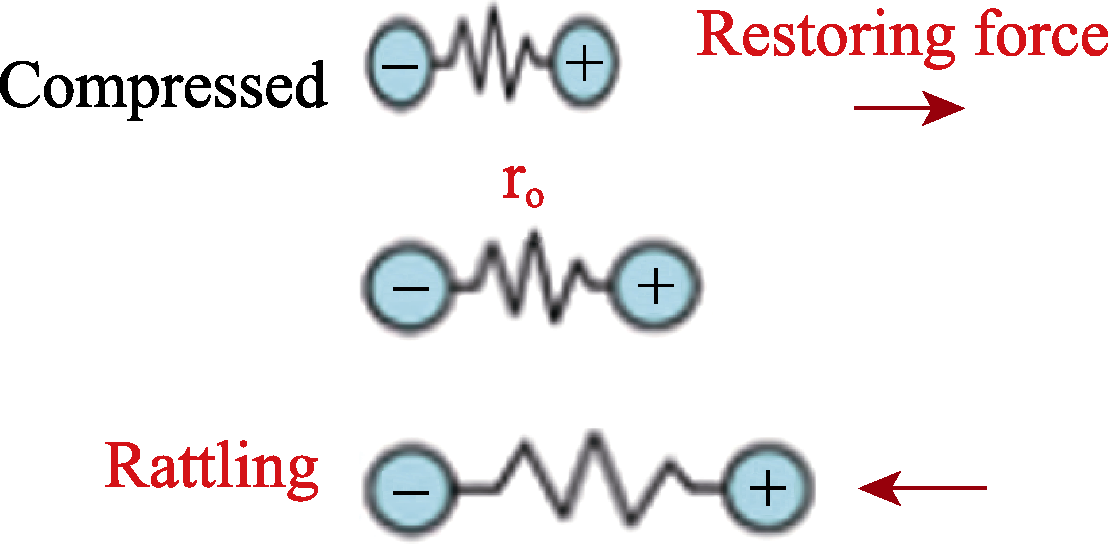
图3 简谐振子模型分别在“Compressed”、平衡位置和“Rattling”状态下的回复力
Fig. 3 Restoring force of the simple harmonic oscillator model in “Compressed”, equilibrium position and “Rattling” states, respectively
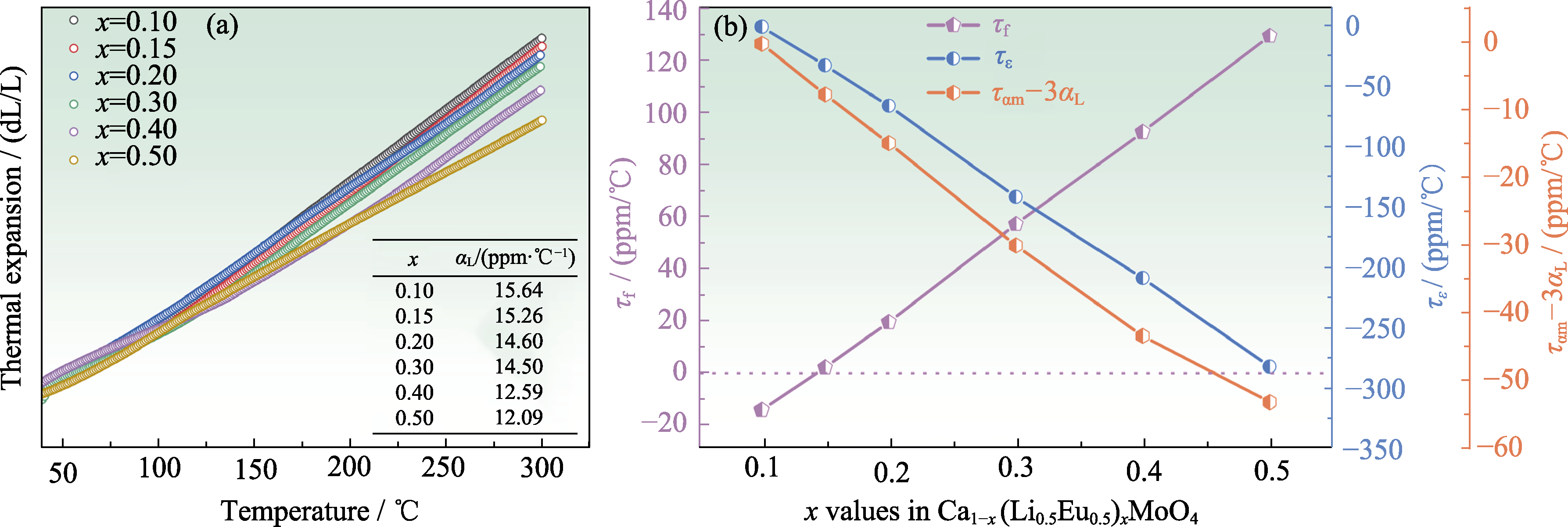
图4 Ca1-x(Li0.5Eu0.5)xMoO4陶瓷的(a)热膨胀系数(50~300 ℃)和(b) τε、τf与ταm-3αL[62]
Fig. 4 (a) Thermal expansion data (50-300 ℃)and (b) τε, τf and ταm-3αL for Ca1-x(Li0.5Eu0.5)xMoO4 ceramics[62] Colorful figures are available on website; 1 ppm/℃=1×10-6 ℃-1
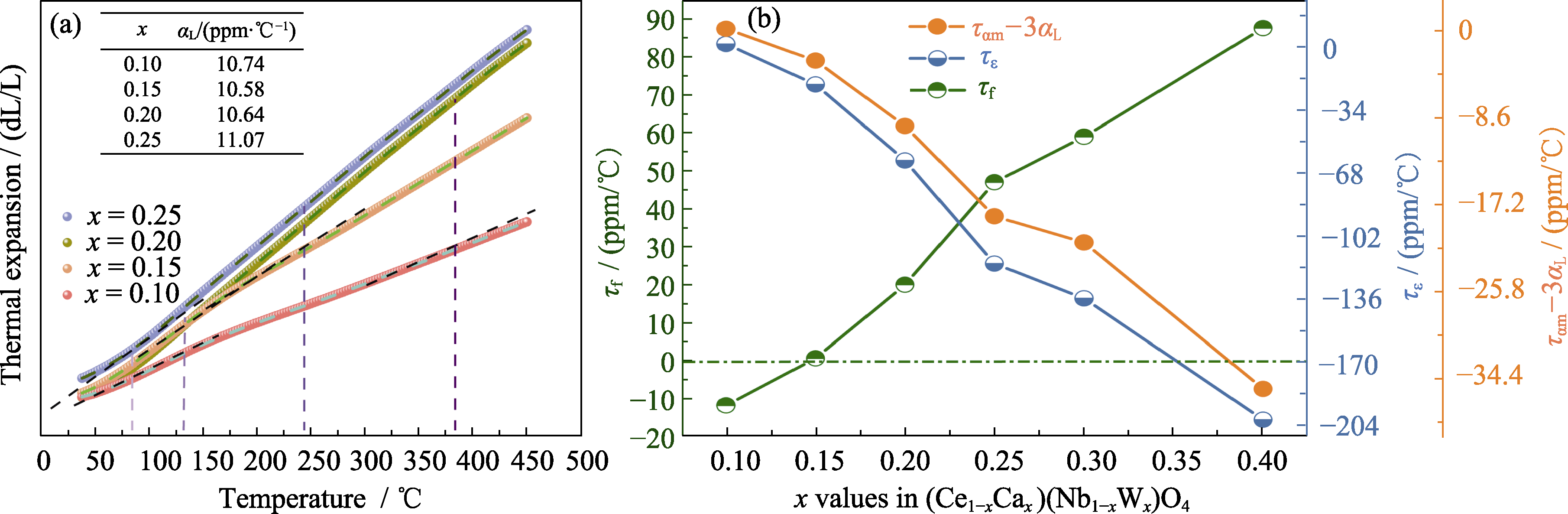
图5 (Ce1-xCax)(Nb1-xWx)O4陶瓷的(a)热膨胀系数(40~100 ℃)和(b) τε、τf与ταm-3αL[63]
Fig. 5 (a) Thermal expansion data (40-100 ℃) and (b) τε, τf and ταm-3αL for (Ce1-xCax)(Nb1-xWx)O4 ceramics[63] Colorful figures are available on website; 1 ppm/℃=1×10-6 ℃-1
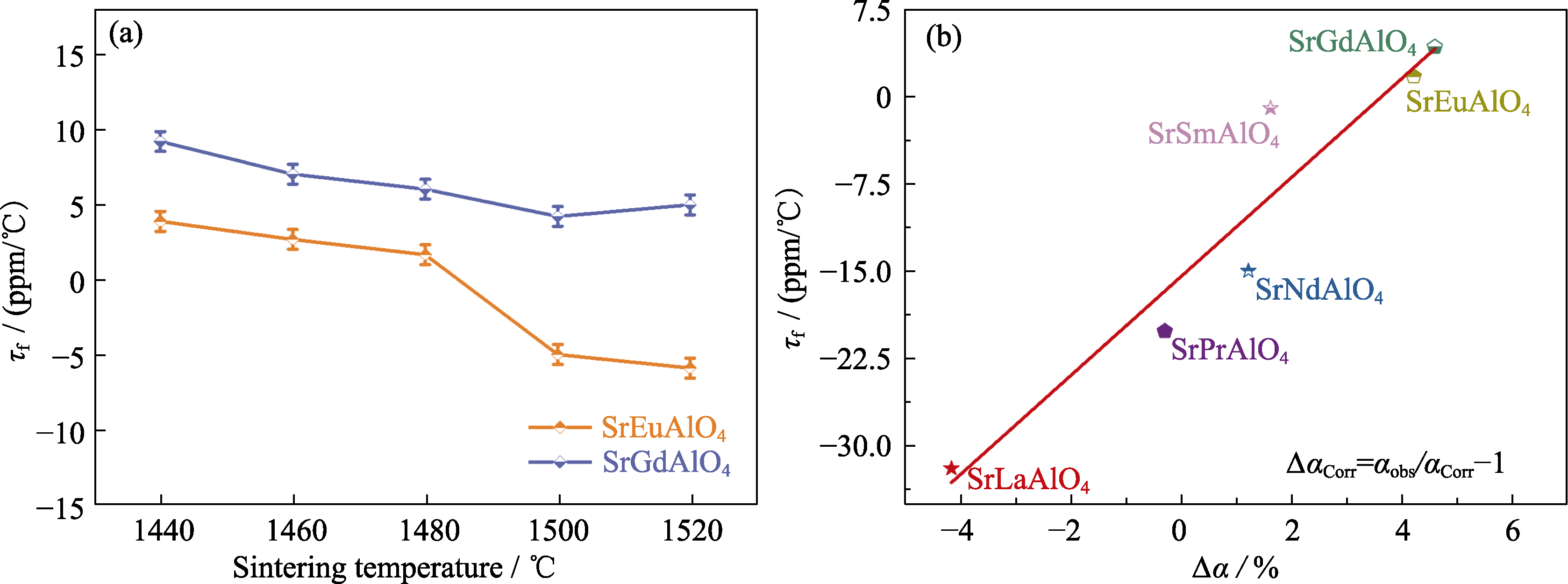
图6 (a) SrEuAlO4和SrGdAlO4陶瓷的τf; (b) SrLnAlO4(Ln=La, Pr, Nd, Sm, Eu, Gd)陶瓷的τf和Δα[64]
Fig. 6 (a) τf of SrEuAlO4 and SrGdAlO4 ceramics; (b) τf and Δα in SrLnAlO4 (Ln= La, Pr, Nd, Sm, Eu, and Gd) ceramics[64] Colorful figures are available on website; 1 ppm/℃=1×10-6 ℃-1
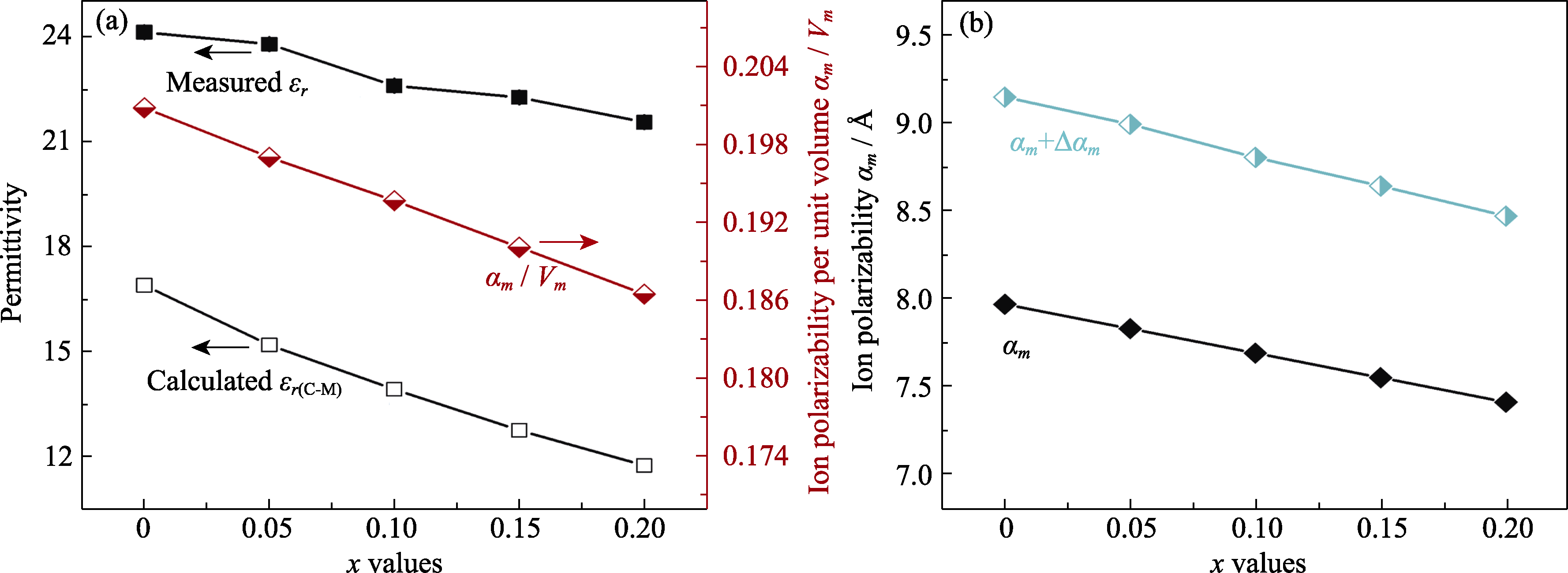
图7 Ce1-xCaxO2-x(x=0~0.20)陶瓷的(a)介电常数和(b)离子极化率与x的函数关系[68]
Fig. 7 (a) Permittivity and (b) ion polarizability of Ce1-xCaxO2-x (x=0−0.20) ceramics as a function of x[68]
| [1] |
周济, 李龙土, 熊小雨. 我国电子陶瓷技术发展的战略思考. 中国工程科学, 2020, 22(5): 20.
DOI |
| [2] | DING Y H, LIU L, YANG Z J, et al. Structure and microwave dielectric characteristics of Hf1-xTixO2 ceramics. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2022, 105(2): 1127. |
| [3] | 闻立群, 王亦菲, 李晖, 等. 主要国家和地区5G发展战略举措及对我国的启示. 通信世界, 2021, 8: 28. |
| [4] | HILL M D, CRUICKSHANK D B, MACFARLANE I A. Perspective on ceramic materials for 5G wireless communication systems. Applied Physics Letters, 2021, 118(12): 120501. |
| [5] | ZURMÜHLEN R, PETZELT J, KAMBA S, et al. Dielectric- spectroscopy of Ba(B'1/2B''1/2)O3 complex perovskite ceramics- correlations between ionic parameters and microwave dielectric properties. I. Infrared reflectivity study (1012-1014 Hz). Journal of Applied Physics, 1995, 77(10): 5341. |
| [6] | BOSMAN A J, HAVINGA E E. Temperature dependence of dielectric constants of cubic ionic compounds. Physical Review, 1963, 129(4): 1593. |
| [7] | REANEY I M, IDDLES D. Microwave dielectric ceramics for resonators and filters in mobile phone networks. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2006, 89(7): 2063. |
| [8] | HARROP P J. Temperature coefficients of capacitance of solids. Journal of Materials Science, 1969, 4: 370. |
| [9] | COCKBAIN A G, HARROP P J. The temperature coefficient of capacitance. Journal of Physics D Applied Physics, 1968, 1(9): 1109. |
| [10] | WISE P L, REANEY I M, LEE W E, et al. Tunability of τf in perovskites and related compounds. Journal of Materials Research, 2002, 17(8): 2033. |
| [11] | XIAO Y, CHEN X M, LIU X Q. Microstructures and microwave dielectric characteristics of CaRAlO4 (R = Nd, Sm, Y) ceramics with tetragonal K2NiF4 structure. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2004, 87(11): 2143. |
| [12] | FAN X C, CHEN X M, LIU X Q. Structural dependence of microwave dielectric properties of SrRAlO4 (R = Sm, Nd, La) ceramics: crystal structure refinement and infrared reflectivity study. Chemistry of Materials, 2008, 20(12): 4092. |
| [13] | LIU B, LI L, LIU X Q, et al. Structural evolution of SrLaAl1-x(Zn0.5Ti0.5)xO4 ceramics and effects on their microwave dielectric properties. Journal of Materials Chemistry C, 2016, 4(21): 4684. |
| [14] | COLLA E L, REANEY I M, SETTER N. Effect of structural changes in complex perovskites on the temperature coefficient of the relative permittivity. Journal of Applied Physics, 1993, 74(5): 3414. |
| [15] | REANEY I M, COLLA E L, SETTER N. Dielectric and structural characteristics of Ba-and Sr-based complex perovskites as a function of tolerance factor. Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, 1994, 33(7R): 3984. |
| [16] | REANEY I M, WISE P L, UBIC R, et al. On the temperature coefficient of resonant frequency in microwave dielectrics. Philosophical Magazine A, 2001, 81(2): 501. |
| [17] | WISE P L, REANEY I M, LEE W E, et al. Structure-microwave property relations in (SrxCa1-x)n+1TinO3n+1. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2001, 21(10/11): 1723. |
| [18] | ZHOU D, RANDALL C A, WANG H, et al. Ultra-low firing high-k scheelite structures based on [(Li0.5Bi0.5)xBi1-x][MoxV1-x]O4 microwave dielectric ceramics. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2010, 93(8): 2147. |
| [19] | DU K, YIN C Z, GUO Y B, et al. Phase transition and permittivity stability against temperature of CaSn1-xTixGeO5 ceramics. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2022, 42(1): 147. |
| [20] | WU F F, ZHOU D, DU C, et al. Design of a sub-6 GHz dielectric resonator antenna with novel temperature-stabilized (Sm1-xBix) NbO4 (x = 0-0.15) microwave dielectric ceramics. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2022, 14(5): 7030. |
| [21] | CHENG K, LI C C, YIN C Z, et al. Effects of Sr2+ substitution on the crystal structure, Raman spectra, bond valence and microwave dielectric properties of Ba3-xSrx(VO4)2 solid solutions. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2019, 39(13): 3738. |
| [22] | YIN C Z, YIN Y H, DU K, et al. Fabrication of high-efficiency dielectric patch antennas from temperature-stable Sr3-xCaxV2O8 microwave dielectric ceramic. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2023, 43(4): 1492. |
| [23] | LEE H J, HONG K S, KIM S J, et al. Dielectric properties of MNb2O6 compounds (where M = Ca, Mn, Co, Ni, OR Zn). Materials Research Bulletin, 1997, 32(7): 847. |
| [24] | LEI W, ZOU Z Y, CHEN Z H, et al. Controllable τf value of barium silicate microwave dielectric ceramics with different Ba/Si ratios. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2018, 101(1): 25. |
| [25] | KIM E S, CHOI W. Effect of phase transition on the microwave dielectric properties of BiNbO4. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2006, 26(10/11): 1761. |
| [26] | JO H J, KIM J S, KIM E S. Microwave dielectric properties of MgTiO3-based ceramics. Ceramics International, 2015, 41: S530. |
| [27] | CHEN J Q, FANG W S, AO L Y, et al. Structure and chemical bond characteristics of two low-εr microwave dielectric ceramics LiBO2 (B = Ga, In) with opposite τf. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2021, 41(6): 3452. |
| [28] | ZHANG J Y, LI J, SUN Y H, et al. Densification, microwave dielectric properties and rattling effect of LiYbO2 ceramics with low εr and anomalous positive τf. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2022, 42(16): 7455. |
| [29] | KANG D H, KIM E S. Microwave dielectric properties of rutile (Zn1/3Nb2/3)0.40(Ti1-xSnx)0.60O2 (0.15≤x≤0.30) ceramics. Ceramics International, 2008, 34(4): 889. |
| [30] | KIM E S, KANG D H. Relationships between crystal structure and microwave dielectric properties of (Zn1/3B2/35+)xTi1-xO2 (B5+ = Nb, Ta) ceramics. Ceramics International, 2008, 34(4): 883. |
| [31] | KIM E S, KANG D H. Microwave dielectric properties of (A2+1/3B5+2/3)0.5Ti0.5O2 (A2+ = Zn, Mg, B5+= Nb, Ta) ceramics. IEEE Transactions on Ultrasonics, Ferroelectrics, and Frequency Control, 2008, 55(5): 1069. |
| [32] | CHOI J W, VAN DOVER R B. Correlation between temperature coefficient of resonant frequency and tetragonality ratio. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2006, 89(3): 1144. |
| [33] | LIAO Q W, LI L X, REN X, et al. New low-loss microwave dielectric material ZnTiNbTaO8. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2011, 94(10): 3237. |
| [34] | RAMARAO S D, MURTHY V R K. Crystal structure refinement and microwave dielectric properties of new low dielectric loss AZrNb2O8 (A: Mn, Zn, Mg and Co) ceramics. Scripta Materialia, 2013, 69(3): 274. |
| [35] | LIAO Q W, LI L X. Structural dependence of microwave dielectric properties of ixiolite structured ZnTiNb2O8 materials: crystal structure refinement and Raman spectra study. Dalton Transactions, 2012, 41(23): 6963. |
| [36] | XIA W S, LI L X, NING P F, et al. Relationship between bond ionicity, lattice energy, and microwave dielectric properties of Zn(Ta1-xNbx)2O6 ceramics. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2012, 95(8): 2587. |
| [37] | MA X M, ZHOU X, TIAN H R, et al. Effect of (Zn1/3Nb2/3)4+ co-substitution on the microwave dielectric properties of Ce2Zr3(MoO4)9 ceramics. Ceramics International, 2022, 48(6): 7441. |
| [38] | LI H, CHEN X Q, XIANG Q Y, et al. Structure, bond characteristics and Raman spectra of CaMg1-xMnxSi2O6 microwave dielectric ceramics. Ceramics International, 2019, 45(11): 14160. |
| [39] | PASCHOAL C W A, MOREIRA R L, SURENDRAN K P, et al. Infrared reflectivity and intrinsic dielectric behavior of RETiTaO6 (RE = Y, Ce, Pr, Nd, Sm, Eu, Gd, Tb, Dy, Ho, Er, and Yb) microwave ceramics. Journal of Materials Research, 2005, 20(5): 1164. |
| [40] | PARK H S, YOON K H, KIM E S. Relationship between the bond valence and the temperature coefficient of the resonant frequency in the complex perovskite (Pb1-xCax)[Fe0.5(Nb1-yTay)0.5]O3. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2001, 84(1): 99. |
| [41] | YOON K H, KIM W S, KIM E S. Dependence of the octahedral bond valence on microwave dielectric properties of Ca1-xSm2x/3TiO3 ceramics. Materials Science and Engineering B, 2003, (1/2/3): 112. |
| [42] | PARK H S, YOON K H, KIM E S. Effect of bond valence on microwave dielectric properties of complex perovskite ceramics. Materials Chemistry and Physics, 2003, 79(2/3): 181. |
| [43] | CHO Y S, YOON K H, LEE B D, et al. Understanding microwave dielectric properties of Pb-based complex perovskite ceramics via bond valence. Ceramics International, 2004, 30(8): 2247. |
| [44] | LUFASO M W. Crystal structures, modeling, and dielectric property relationships of 2 : 1 ordered Ba3MM'2O9 (M = Mg, Ni, Zn; M' = Nb, Ta) perovskites. Chemistry of Materials, 2004, 16(11): 2148. |
| [45] | ZHANG H, FANG L, DRONSKOWSKI R, et al. Some A6B5O18 cation-deficient perovskites in the BaO-La2O3-TiO2-Nb2O5 system. Journal of Solid State Chemistry, 2004, 177(11): 4007. |
| [46] | ZHANG H, FANG L, ELSEBROCK R, et al. Crystal structure and microwave dielectric properties of a new A6B5O18-type cation-deficient perovskite Ba3La3Ti4NbO18. Materials Chemistry and Physics, 2005, 93(2/3): 450. |
| [47] | KIM E S, CHUN B S, FREER R, et al. Effects of packing fraction and bond valence on microwave dielectric properties of A2+B6+O4 (A2+: Ca, Pb, Ba; B6+: Mo, W) ceramics. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2010, 30(7): 1731. |
| [48] | KIM E S, JEON C J, CLEM P G. Effects of crystal structure on the microwave dielectric properties of ABO4 (A=Ni, Mg, Zn and B= Mo, W) ceramic. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2012, 95(9): 2934. |
| [49] | YOON S H, KIM D W, CHO S Y, et al. Investigation of the relations between structure and microwave dielectric properties of divalent metal tungstate compounds. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2006, 26(10/11): 2051. |
| [50] | CHOI G K, KIM J R, YOON S H, et al. Microwave dielectric properties of scheelite (A=Ca, Sr, Ba) and wolframite (A=Mg, Zn, Mn) AMoO4 compounds. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2007, 27(8/9): 3063. |
| [51] | 严康, 高兆芬, 卞建江. 钨酸盐类陶瓷微波介电性能. 硅酸盐学报, 2006, 34(2): 251. |
| [52] | NEELAKANTAN U A, KALATHIL S E, RATHEESH R. Structure and microwave dielectric properties of ultralow-temperature cofirable BaV2O6 ceramics. European Journal of Inorganic Chemistry, 2015, 2015(2): 305. |
| [53] | TANG Y, ZHANG Z W, LI J, et al. A3Y2Ge3O12 (A=Ca, Mg): two novel microwave dielectric ceramics with contrasting τf and Q×f. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2020, 40(12): 3989. |
| [54] | DUNITZ J D, ORGEL L E. Stereochemistry of ionic solids. Advances in Inorganic Chemistry and Radiochemistry, 1960, 2: 1. |
| [55] | SHANNON R D. Dielectric polarizabilities of ions in oxides and fluorides. Journal of Applied Physics, 1993, 73(1): 348. |
| [56] | 唐莹. 石榴石型低介电常数微波介质陶瓷制备与性能. 北京: 北京科技大学博士学位论文, 2021. |
| [57] | 唐莹, 相怀成, 李洁, 等. Ca3-xMgxYb2Ge3O12(0≤x≤3)石榴石的A位Rattling效应与微波介电性能. 硅酸盐学报, 2023, 51(4): 872. |
| [58] | TANG Y, LI H, LI J, et al. Relationship between Rattling Mg2+ ions and anomalous microwave dielectric behavior in Ca3-xMg1+xLiV3O12 ceramics with garnet structure. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2021, 41(15): 7697. |
| [59] | LIU M X, LI J, TANG Y, et al. Tunability of τf in garnet-structured Y3Ga5O12 microwave dielectric ceramics. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2021, 41(15): 7711. |
| [60] | YANG Y, ZHAI Y F, XIANG H C, et al. Rattling effects on microwave dielectric properties of Ca3TiBGe3O12 (B = Mg, Zn) garnets. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2022, 42(11): 4566. |
| [61] | YANG Y, TANG Y, LI J, et al. Effects of ionic coordination bonding on microwave dielectric properties of Y2CaBGa4O12 (B = Zr, Sn) garnets. ACS Applied Electronic Materials, 2022, 4(7): 3512. |
| [62] | GU X L, TANG Y, CHEN J Q, et al. Tuning microwave dielectric properties of low-temperature sintered Ca1-x(Li0.5Eu0.5)xMoO4 (0.1≤x≤0.5) ceramics by the strong rattling effect of Li+. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2025, 45(5): 117149. |
| [63] | XU L, FANG W S, TANG Y, et al. Crystal structure evolution, bond characteristics and tunable microwave dielectric properties of (Ce1-xCax)(Nb1-xWx)O4 ceramics. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2024, 44(7): 4657. |
| [64] | WANG S J, FANG W S, WU D F, et al. Two K20 microwave dielectric ceramics SrLnAlO4 (Ln=Eu, Gd) with near-zero τf and contrasting Q×f. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2024, 44(11): 6470. |
| [65] | MENG K Y, WU D F, WANG S J, et al. Tuning εr and τf by the combined effects of rattling RE3+ and compressed Ca2+ at the A-site in microwave dielectric ceramics CaREAlO4 (RE=Eu, Ho, Er, Yb). Ceramics International, 2024, 50(15): 26792. |
| [66] | LI F H, TANG Y, LI J, et al. Effect of A-site cation on crystal structure and microwave dielectric properties of AGe4O9 (A=Ba, Sr) ceramics. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2021, 41(7): 4153. |
| [67] | SUN Y, XIANG H C, TANG Y, et al. Constructing the cationic rattling effect to realize the adjustability of the temperature coefficient in Nd2-xSmxO3 microwave dielectric ceramics. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2024, 44(5): 2859. |
| [68] | SUN Y, WU J T, TANG Y, et al. Effects of ion polarizability and oxygen vacancy on microwave dielectric properties of fluorite- structured Ce1-xCaxO2-x. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2024, 107(2): 1148. |
| [69] | JIA Y Q, LUO W K, LI L, et al. MSO4 (M = Ca, Sr, Ba) microwave dielectric ceramics with low dielectric constant. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2023, 106(2): 1250. |
| [70] | WANG X, ZHU X L, LI L, et al. Structure evolution and adjustment of τf in (Ba, Sr)HfO3 and (Sr, Ca)HfO3 microwave dielectric ceramics. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2024, 107(1): 285. |
| [71] | JIANG Y, WU G F, MAO M M, et al. Deeper insights into dodecahedron distortion and microwave dielectric properties of Y3-xRxAl(Oct)2Al(Tet)3-xSixO12 (x = 0.1-0.5; R = Mg, Ca) garnet-type ceramics. Ceramics International, 2023, 49(14): 23334. |
| [1] | 何国强, 张恺恒, 王震涛, 包健, 席兆琛, 方振, 王昌昊, 王威, 王鑫, 姜佳沛, 李祥坤, 周迪. Ba(Nd1/2Nb1/2)O3: 一种被低估的K40微波介质陶瓷[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(6): 639-646. |
| [2] | 李文元, 徐佳楠, 邓瀚澳, 常爱民, 张博. 钒取代对LaTaO4陶瓷微观结构和微波介电性能的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(6): 697-703. |
| [3] | 胡智超, 杨鸿宇, 杨鸿程, 孙成礼, 杨俊, 李恩竹. P-V-L键理论在微波介质陶瓷性能调控中的应用[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(6): 609-626. |
| [4] | 杨燕, 张发强, 马名生, 王墉哲, 欧阳琪, 刘志甫. 基于CuO-TiO2-Nb2O5复合氧化物烧结助剂的ZnAl2O4陶瓷低温烧结研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(6): 711-718. |
| [5] | 李海涛, 李 谦, 闫焉服, 许荣辉. ZnO掺杂对Ca0.25(Li0.43Sm0.57)0.75TiO3陶瓷烧结性能和微波介电性能的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2015, 30(4): 369-373. |
| [6] | 刘 林, 方有维, 邓新峰, 庄文东, 唐 斌, 张树人. (Ba1-xSrx)La4Ti4O15(x=0.8~0.95)陶瓷的微结构及微波介电性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2012, 27(3): 281-284. |
| [7] | 姚晓刚, 林慧兴, 姜少虎, 陈 玮, 罗 澜. Al2O3掺杂对Ba4Sm9.33Ti18O54陶瓷显微结构和介电性能的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2012, 27(12): 1266-1270. |
| [8] | 刘 昊, 沈春英, 卢正东, 丘 泰. (1-x)(Mg0.9Co0.1)TiO3-x(Ca0.61La0.26)TiO3陶瓷的微波介电性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2011, 26(6): 664-668. |
| [9] | 赵 莉, 沈春英, 丘 泰. (1- x)(Mg0.7Zn0.3)TiO3– xCa0.61La0.26TiO3系陶瓷的微波介电性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2011, 26(2): 219-224. |
| [10] | 卢正东,沈春英,李 亮,杨 建,丘 泰. (1-x)(Mg0.7Zn0.3)TiO3-x(Ca0.61Nd0.26)TiO3系微波介质陶瓷介电性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2010, 25(3): 332-336. |
| [11] | 李月明1,宋婷婷1,尤源2,胡元云2,刘维良1,唐春宝1. Ca0.3(Li1/2Sm1/2)0.7TiO3微波介质陶瓷的低温烧结研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2008, 23(6): 1293-1297. |
| [12] | 姚国光,刘鹏. V5+取代对 Mg4(SbNb1-xVx)O9陶瓷介电性能的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2008, 23(5): 877-880. |
| [13] | 周东祥,余晓华,王鹤,赵俊. BaO-CeO2-TiO2微波介质陶瓷的烧结特性及物相组成[J]. 无机材料学报, 2007, 22(6): 1197-1200. |
| [14] | 杨秋红,金应秀,徐军. Nd3+A位置换对(Pb0.5Ca0.5)(Fe0.5Nb0.5)O3陶瓷微波介电性能的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2003, 18(5): 1051-1056. |
| [15] | 沈强,张联盟,涂溶. Mo添加对Ni3Al-TiC润湿特性的影响机制研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2002, 17(6): 1306-1310. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||