无机材料学报 ›› 2024, Vol. 39 ›› Issue (10): 1100-1106.DOI: 10.15541/jim20240215 CSTR: 32189.14.10.15541/jim20240215
所属专题: 【信息功能】介电、铁电、压电材料(202506)
收稿日期:2024-04-24
修回日期:2024-05-10
出版日期:2024-10-20
网络出版日期:2024-05-16
作者简介:彭 萍(1991-), 女, 博士, 副教授. E-mail: xgpengping@163.com
基金资助:Received:2024-04-24
Revised:2024-05-10
Published:2024-10-20
Online:2024-05-16
About author:PENG Ping (1991-), female, PhD, associate professor. E-mail: xgpengping@163.com
Supported by:摘要:
(Ba,Ca)(Ti,Sn)O3 (BCTS)压电陶瓷具有优异的压电性能, 在压电传感器、换能器领域表现出巨大的应用潜力。其烧结温度非常高(通常在1450 ℃以上), 导致其在实际应用中受到限制。为了降低烧结温度, 本研究以(Ba0.95Ca0.05)(Ti0.90Sn0.10)O3为基体, 选择CuO作为烧结助剂, 通过传统固相烧结法制备BCTS-xCuO压电陶瓷, 系统研究CuO含量对BCTS陶瓷的烧结温度、结构及介电、压电性能的影响规律。研究发现, 加入CuO后, 陶瓷主相为钙钛矿结构, 存在少量杂相, 可能是Ba2TiO4和Ba2Cu3O5.9。CuO掺杂能有效将陶瓷的烧结温度从1480 ℃降低至1360 ℃, 提高压电陶瓷的相对致密度, 增大陶瓷的平均晶粒尺寸。当x=0.03时, 陶瓷获得最高相对致密度(98.7%)和最大平均晶粒尺寸(22.5 μm), 同时获得最优异的电学性能: 压电系数d33=573 pC/N, 机电耦合系数kp=36%, 相对介电常数εr=9467, 介电损耗tanδ=0.021。与其他低温烧结的BaTiO3基陶瓷相比, x=0.03陶瓷组分在低烧结温度下具有更高的d33, 表现出优异的综合性能。本研究结果表明, CuO掺杂可有效降低BCTS陶瓷的烧结温度, 提高压电性能, 为其在压电器件领域的应用提供指导。
中图分类号:
彭萍, 谭礼涛. CuO掺杂(Ba,Ca)(Ti,Sn)O3陶瓷的结构与压电性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(10): 1100-1106.
PENG Ping, TAN Litao. Structure and Piezoelectric Properties of CuO-doped (Ba,Ca)(Ti,Sn)O3 Ceramics[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(10): 1100-1106.

图1 不同温度烧结BCTS-0.03CuO的SEM照片
Fig. 1 SEM images of BCTS-0.03CuO ceramics sintered at different temperatures (a) 1360 ℃; (b) 1370 ℃; (c) 1380 ℃; (d) 1390 ℃; (e) 1400 ℃

图2 BCTS-xCuO的SEM照片
Fig. 2 SEM images of BCTS-xCuO ceramics (a) x=0, Ts=1480 ℃; (b) x=0.01, Ts=1380 ℃; (c) x=0.03, Ts=1380 ℃; (d) x=0.05, Ts=1360 ℃; (e) x=0.07, Ts=1360 ℃

图6 BCTS-xCuO的变温介电性能
Fig. 6 Temperature-dependent dielectric properties of BCTS-xCuO samples (a) Relative permittivity εr; (b) TC as a function of CuO content; Colorful figures are available on website
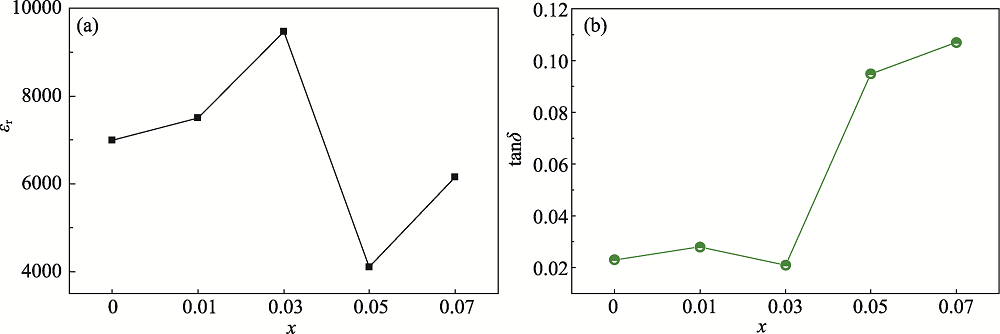
图7 室温、10 kHz下BCTS-xCuO的介电性能变化图
Fig. 7 Dielectric properties of BCTS-xCuO ceramics measured at 10 kHz and room temperature (a) εr as a function of CuO content; (b) tanδ as a function of CuO content

图8 BCTS-xCuO的压电性能
Fig. 8 Piezoelectric properties of BCTS-xCuO (a) d33 as a function of CuO content; (b) Impedance and phase angle for the x=0.03 component ceramics; (c) kp as a function of CuO content; (d) Dependence of d33 on sintering temperature for the x=0.03 component ceramics

图9 文献报道BaTiO3基压电陶瓷的压电系数d33与烧结温度Ts对比[22⇓⇓-25,29⇓⇓⇓⇓⇓⇓⇓ -37]
Fig. 9 Comprehensive comparison of d33 and Ts of BaTiO3- based piezoelectric ceramics in literature[22⇓⇓-25,29⇓⇓⇓⇓⇓⇓⇓ -37]
| [1] | BOULOS M, GUILLEMET-FRITSCH S, MATHIEU F, et al. Hydrothermal synthesis of nanosized BaTiO3 powders and dielectric properties of corresponding ceramics. Solid State Ionics, 2005, 176(13/14): 1301. |
| [2] | TINA G A, PUNETHA P, ADHIKARY G D, et al. Simultaneous increase in piezoelectric response and Curie point in BaTiO3 based Pb-free piezoceramic. Scripta Materialia, 2024, 243: 115994. |
| [3] | KARAKI T, YAN K, MIYAMOTO T, et al. Lead-free piezoelectric ceramics with large dielectric and piezoelectric constants manufactured from BaTiO3 nano-powder. Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, 2007, 46: L97. |
| [4] | HAO J, LI W, ZHAI J, et al. Progress in high-strain perovskite piezoelectric ceramics. Materials Science & Engineering R: Reports, 2019, 135: 1. |
| [5] | ACOSTA M, NOVAK N, ROJAS V, et al. BaTiO3-based piezoelectrics: fundamentals, current status, and perspectives. Applied Physics Reviews, 2017, 4(4): 041305. |
| [6] | WANG L, LIU L, XUE D, et al. Wet routes of high purity BaTiO3 nanopowders. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2007, 440(1/2): 78. |
| [7] | SHEN Z, LI J. Enhancement of piezoelectric constant d33 in BaTiO3 ceramics due to nano-domain structure. Journal of the Ceramic Society of Japan, 2010, 118(1382): 940. |
| [8] | WANG X, ZHU Y, ZHANG P, et al. Phase structure and piezoelectric property of (Ba0.85Ca0.15)(Ti0.9Zr0.1-xSnx)O3 lead-free piezoceramics. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(5): 513. |
| [9] | BOWEN C R, GITTINGS J, TURNER I G, et al. Dielectric and piezoelectric properties of hydroxyapatite-BaTiO3 composites. Applied Physics Letters, 2006, 89(13): 132906. |
| [10] | HU J, FAN H, WU S, et al. Characterization of temperature dependence of dielectric, elastic and piezoelectric properties of BaTiO3 ceramics. Ceramics International, 2022, 48(18): 25741. |
| [11] | CHEN M, XU Z, CHU R, et al. Polymorphic phase transition and enhanced piezoelectric properties in (Ba0.9Ca0.1)(Ti1-xSnx)O3 lead- free ceramics. Materials Letters, 2013, 97: 86. |
| [12] | ZHAO Q, XIAO H, GENG H F, et al. Highly-efficient piezocatalytic performance of nanocrystalline BaTi0.89Sn0.11O3 catalyst with Tc near room temperature. Nano Energy, 2021, 85: 106028. |
| [13] | PETZELT J, BOVTUN V, NUZHNYY D, et al. Broadband dielectric, terahertz, and infrared spectroscopy of BaTiO3-BaZrO3 solid solution: from proper ferroelectric over diffuse and relaxor ferroelectrics and dipolar glass to normal dielectric. Physica Status Solidi (b), 2021, 258(10): 2100259. |
| [14] | KATHAIT G S, MAINI S. Dielectric, Dielectric, piezoelectric and energy storage properties of Ca, Zr and Sn doped (Ba1-xCax)(Ti0.85+xZr0.02Sn0.13-x)O3 lead-free ceramics at MPB for 0.05≤x≤0.09. Materials Science and Engineering: B, 2024, 301: 117139. |
| [15] | LIU W, REN X. Large piezoelectric effect in Pb-free ceramics. Physical Review Letters, 2009, 103(25): 257602. |
| [16] | XUE D, ZHOU Y, BAO H, et al. Large piezoelectric effect in Pb-free Ba(Ti,Sn)O3-x(Ba,Ca)TiO3 ceramics. Applied Physics Letters, 2011, 99(12): 122901. |
| [17] | ZHU L F, ZHANG B P, ZHAO X K, et al. Enhanced piezoelectric properties of (Ba1-xCax)(Ti0.92Sn0.08)O3 lead-free ceramics. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2013, 96(1): 241. |
| [18] | FU J, XIE A, LI T, et al. Ultrahigh piezoelectricity in (Ba,Ca)(Ti,Sn)O3 lead-free compounds with enormous domain wall contribution. Acta Materialia, 2022, 230: 117862. |
| [19] | KUMAR N, KURCHANIA R, BALL R J, et al. Enhanced dielectric, ferroelectric and piezoelectric properties of lead-free (Ba,Ca)(Sn,Ti)O3 ceramics by optimisation of sintering temperature. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2024, 989: 174358. |
| [20] | ZHAO C, WANG H, XIONG J, et al. Composition-driven phase boundary and electrical properties in (Ba0.94Ca0.06)(Ti1-xMx)O3 (M= Sn, Hf, Zr) lead-free ceramics. Dalton Transactions, 2016, 45(15): 6466. |
| [21] | LIU Q F, MA J J, SHARMA M, et al. Photocatalytic, piezocatalytic, and piezo‐photocatalytic effects in ferroelectric (Ba0.875Ca0.125)(Ti0.95Sn0.05)O3 ceramics. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2019, 102(10): 5807. |
| [22] | CHITRA, LAISHRAM R, VASHISHTHA A, et al. Effect of holmium doping on structural, electrical and piezoelectric properties of lead-free (Ba,Ca)(Ti,Sn)O3 ceramics. Journal of Materials Science: Materials in Electronics, 2019, 30: 3965. |
| [23] | WU B, XIAO D, WU J, et al. Microstructure and electrical properties of (Ba0.98Ca0.02)(Ti0.94Sn0.06)O3-xwt% ZnO lead-free piezoelectric ceramics sintered at lower temperature. Journal of Materials Science: Materials in Electronics, 2015, 26(4): 2323. |
| [24] | SONG H, PENG C, HUANG R, et al. Effect of MnO2 addition on the structure and electric properties of (Ba0.94Ca0.06)(Ti0.9Sn0.1)O3 ceramics. Ceramics International, 2018, 44(7): 7877. |
| [25] | SUN Y, CHANG Y, WU J, et al. Domain structures and piezoelectric properties of low-temperature sintered (Ba0.95Ca0.05)- (Ti0.94Sn0.06)O3 ceramics with CuO additive. Materials Letters, 2016, 177: 128. |
| [26] | ZHANG J L, JI P F, WU Y Q, et al. Strong piezoelectricity exhibited by large-grained BaTiO3 ceramics. Applied Physics Letters, 2014, 104(22): 222909. |
| [27] | YAN S, CAO Z, LIU Q, et al. Enhanced piezoelectric activity around orthorhombic-tetragonal phase boundary in multielement codoping BaTiO3. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2022, 923: 166398. |
| [28] | LENG H, YAN Y, LIU H, et al. Design and development of high- power piezoelectric ceramics through integration of crystallographic texturing and acceptor-doping. Acta Materialia, 2021, 206: 116610. |
| [29] | MUHSEN K N D K, OSMAN R A M, IDRIS M S, et al. Effect of sintering temperature on (Ba0.85Ca0.15)(SnxZr0.1-xTi0.9)O3 for piezoelectric energy harvesting applications. Ceramics International, 2021, 47(9): 13107. |
| [30] | SHARMA S, SHARMA H, KUMAR S, et al. Analysis of sintering temperature effects on structural, dielectric, ferroelectric, and piezoelectric properties of BaZr0.2Ti0.8O3 ceramics prepared by Sol-Gel method. Journal of Materials Science: Materials in Electronics, 2020, 31: 19168. |
| [31] | DU J, QIU L, YANG C, et al. Structure and electrical properties in CuO-modified BCZT lead-free piezoelectric ceramics. Journal of Electroceramics, 2022, 49(3): 125. |
| [32] | TSAI C, LIAO W, CHU S, et al. Investigation of the piezoelectric and anti-reduction properties of (Ba,Ca)(Ti,Sn,Hf) textured ceramics prepared under low oxygen partial pressure conditions at low sintering temperatures. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2021, 41(4): 2472. |
| [33] | SHI S, HASHIMOTO H, SEKINO T. Optimizing the piezoelectric properties of Ba0.85Ca0.15Zr0.10Ti0.90O3 lead-free ceramics via two-step sintering. Ceramics International, 2023, 49(8): 12293. |
| [34] | LIU C, ZOU J, WANG X, et al. Processing, microstructure and piezoelectric properties of Li-doped BCZT ceramics. Ceramics International, 2023, 49(3): 4119. |
| [35] | MEKONNEN M A, TADESSE M Z. Low temperature sintering of (Ba0.85Ca0.15)(Ti0.90Zr0.10)O3 lead-free piezoceramic with the additive of MnO2. Journal of Electroceramics, 2021, 46(3): 115. |
| [36] | ZHAO L, ZHANG B, ZHOU P, et al. Effect of Li2O addition on sintering and piezoelectric properties of (Ba,Ca)(Ti,Sn)O3 lead-free piezoceramics. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2015, 35(2): 533. |
| [37] | YU M C, TSAI C C, HONG C S, et al. Effects of LiF on the properties of (Ba,Ca)(Ti,Sn,Hf)O3-based multilayer ceramics co-fired with Ni at reduced atmosphere. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2023, 106(2): 1037. |
| [1] | 陈相杰, 李玲, 雷添福, 王佳佳, 汪尧进. 相界工程和畴工程调控(1-x)(0.8PZT-0.2PZN)-xBZT陶瓷的压电性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(6): 729-734. |
| [2] | 杨燕, 张发强, 马名生, 王墉哲, 欧阳琪, 刘志甫. 基于CuO-TiO2-Nb2O5复合氧化物烧结助剂的ZnAl2O4陶瓷低温烧结研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(6): 711-718. |
| [3] | 姜昆, 李乐天, 郑木鹏, 胡永明, 潘勤学, 吴超峰, 王轲. PZT陶瓷的低温烧结研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(6): 627-638. |
| [4] | 高天宇, 刘东, 赵思雪, 邓伟, 张波萍, 朱立峰. 温度稳定性优异的K0.5Na0.5NbO3基压电陶瓷及其1-3型换能器[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(3): 297-304. |
| [5] | 黄建锋, 梁瑞虹, 周志勇. W/Cr共掺杂对CaBi2Nb2O9陶瓷晶体结构及电学性能的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(8): 887-894. |
| [6] | 江强, 施立志, 陈政燃, 周志勇, 梁瑞虹. 高于居里温度极化的硬性PZT压电陶瓷的制备及叠层驱动器性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(10): 1091-1099. |
| [7] | 柯鑫, 谢炳卿, 王忠, 张敬国, 王建伟, 李占荣, 贺会军, 汪礼敏. 第三代半导体互连材料与低温烧结纳米铜材的研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(1): 17-31. |
| [8] | 南博, 臧佳栋, 陆文龙, 杨廷旺, 张升伟, 张海波. 增材制造压电陶瓷研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(6): 585-595. |
| [9] | 王新健, 朱逸璇, 张鹏, 杨文龙, 王挺, 郇宇. (Ba0.85Ca0.15)(Ti0.9Zr0.1-xSnx)O3无铅压电陶瓷的相结构与压电性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(5): 513-519. |
| [10] | 刘鼎伟, 曾江涛, 郑嘹赢, 满振勇, 阮学政, 时雪, 李国荣. BiAlO3掺杂PZT陶瓷的高压电性能和低电场应变滞后[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(12): 1365-1370. |
| [11] | 郭霖, 乔显集, 李修芝, 龙西法, 何超. 三元陶瓷Pb(In1/2Nb1/2)O3-Pb(Ni1/3Nb2/3)O3-PbTiO3准同型相界附近组分的介电、铁电和压电性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2020, 35(12): 1380-1384. |
| [12] | 张晓晨, 王雪梅, 王春雷. 烧结方式对(K,Na,Li)(Nb,Sb,Ta)O3压电陶瓷的微观结构和物理性能的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2019, 34(7): 721-726. |
| [13] | 吴盾, 秦帅, 刘春林, 方必军, 曹峥, 成骏峰. 硬脂酸表面改性对PLZT压电陶瓷粉末注射成型性能的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2019, 34(5): 535-540. |
| [14] | 夏标军, 周志勇, 董显林. 过量Nb2O5对偏铌酸铅压电陶瓷烧结性能和电学性能的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2018, 33(11): 1248-1252. |
| [15] | 赵林, 马健, 张俊, 吴波, 肖定全. (1-x)K0.48Na0.52NbO3-xBi0.45Nd0.05(Na0.92Li0.08)0.5ZrO3无铅压电陶瓷相结构及压电性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2018, 33(1): 87-92. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
